1. Two missions the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched in the five months since its success with Chandrayaan-3 have both been scientific in nature: the Aditya L-1 space probe to study the sun and the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) to study polarised X-rays emitted in astrophysical phenomena. ISRO launched the XPoSat, in a two-part mission, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on its C58 flight on January 1. The relative timing of these launches may be a coincidence but it is heartening because the ratio of scientific to technological missions ISRO has launched is skewed in favour of the latter, at the expense of research in the sense of discovery. Those science-oriented missions have all been exceptional in their own right. For example, XPoSat is only the second space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation, and at higher x-ray energies than the other, NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Its POLIX payload, realised by the Raman Research Institute, will track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range and observe emissions from around 50 sources in five years. The XSPECT payload, by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre, will study X-rays of energy 0.8-15 keV and changes in continuous X-ray emissions. Together, they are expected to shed light on intense X-ray sources such as pulsars and black holes.
Then again, the science-technology skew is a reminder that ISRO among the world’s spacefaring organisations has unique needs and priorities. This is exemplified by the second part of the C58 mission. After launching XPoSat in a 650-km circular orbit around the earth, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a 350-km-high orbit and unfurled solar panels, becoming a rudimentary satellite and orbital testbed for the 10 payloads it carried. These are a radio payload by the K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology and a device to measure ultraviolet radiation from L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women; a ‘green’ cubesat propulsion unit, a ‘green’ monopropellant thruster, a tantalum-based radiation shield, a heater-less hollow cathode, and a nanosatellite platform, all from private entities; and an interplanetary dust counter, a fuel-cell power system, and a high-energy cell from ISRO centres. This is only the third time ISRO has operated the PSLV fourth stage in this way. As such, the C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, aspiring students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector. This again is a vignette of the demands of ISRO itself as it navigates an era in which a permanent lunar station seems inevitable, drawing as much on technological capabilities as — based on scientific missions — humankind’s knowledge of the universe.
Find the synonym of the word ‘skew’ used in the passage.
A. distribute
B. distortion
C. aligned
D. different
E. harmonious
Solutions
The correct answer is “distortion“.
Key Points
- In this context, ‘skew’ is used to signify an imbalance or disproportion.
- Therefore, the word ‘distortion’ is a close synonym, as it signifies a deviation from the true representation or standard.
- Thus, distorting can also imply skewing, making option 2 the correct choice.
The correct answer is ‘option 2‘.
Additional Information
- Option 1 is the antonym of ‘skew’; an equal distribution would signify balance, not a skew.
- Option 3, ‘aligned’, indicates order or arrangement, which is opposite to skew.
- Option 4, ‘different’, does not necessarily imply a disproportion or a deviation from the truth.
- Option 5, ‘harmonious’, signifies balance and compatibility, an opposite concept to skewing.
2. Two missions the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched in the five months since its success with Chandrayaan-3 have both been scientific in nature: the Aditya L-1 space probe to study the sun and the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) to study polarised X-rays emitted in astrophysical phenomena. ISRO launched the XPoSat, in a two-part mission, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on its C58 flight on January 1. The relative timing of these launches may be a coincidence but it is heartening because the ratio of scientific to technological missions ISRO has launched is skewed in favour of the latter, at the expense of research in the sense of discovery. Those science-oriented missions have all been exceptional in their own right. For example, XPoSat is only the second space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation, and at higher x-ray energies than the other, NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Its POLIX payload, realised by the Raman Research Institute, will track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range and observe emissions from around 50 sources in five years. The XSPECT payload, by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre, will study X-rays of energy 0.8-15 keV and changes in continuous X-ray emissions. Together, they are expected to shed light on intense X-ray sources such as pulsars and black holes.
Then again, the science-technology skew is a reminder that ISRO among the world’s spacefaring organisations has unique needs and priorities. This is exemplified by the second part of the C58 mission. After launching XPoSat in a 650-km circular orbit around the earth, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a 350-km-high orbit and unfurled solar panels, becoming a rudimentary satellite and orbital testbed for the 10 payloads it carried. These are a radio payload by the K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology and a device to measure ultraviolet radiation from L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women; a ‘green’ cubesat propulsion unit, a ‘green’ monopropellant thruster, a tantalum-based radiation shield, a heater-less hollow cathode, and a nanosatellite platform, all from private entities; and an interplanetary dust counter, a fuel-cell power system, and a high-energy cell from ISRO centres. This is only the third time ISRO has operated the PSLV fourth stage in this way. As such, the C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, aspiring students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector. This again is a vignette of the demands of ISRO itself as it navigates an era in which a permanent lunar station seems inevitable, drawing as much on technological capabilities as — based on scientific missions — humankind’s knowledge of the universe.
Select the most suitable title for the passage from the following:
A. The highlights of ISRO’s XPoSat journey
B. ISRO – Redefining space exploration beyond technology
C. The unparalleled scientific prospects of Aditya L-1 and XPoSat
D. The future prospects of India’s private spaceflight sector
E. ISRO’s global contributions to X-ray studies
Solutions
The Correct answer is “ISRO – Redefining space exploration beyond technology”.
Key Points
- The passage provides an overview of ISRO’s missions, focusing on their scientific significance.
- It explores different aspects, including the nature of the missions, the balance between space technology and space science, and the involvement of different stakeholders.
- Therefore, the title should reflect this expansive discussion, making option 2 the most suitable title.
The Correct answer is ‘option 2‘.
Additional Information
- Option 1 is too specific, focusing only on XPoSat, whereas the passage covers broader topics.
- Option 3 similarly focuses only on the two missions, narrowing the broader deliberations of the passage.
- Option 4 is misaligned, as while the passage covers an aspect of the private spaceflight sector, it is not the central focus.
- Option 5 again limits the wider discussion to X-ray studies.
3. Two missions the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched in the five months since its success with Chandrayaan-3 have both been scientific in nature: the Aditya L-1 space probe to study the sun and the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) to study polarised X-rays emitted in astrophysical phenomena. ISRO launched the XPoSat, in a two-part mission, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on its C58 flight on January 1. The relative timing of these launches may be a coincidence but it is heartening because the ratio of scientific to technological missions ISRO has launched is skewed in favour of the latter, at the expense of research in the sense of discovery. Those science-oriented missions have all been exceptional in their own right. For example, XPoSat is only the second space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation, and at higher x-ray energies than the other, NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Its POLIX payload, realised by the Raman Research Institute, will track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range and observe emissions from around 50 sources in five years. The XSPECT payload, by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre, will study X-rays of energy 0.8-15 keV and changes in continuous X-ray emissions. Together, they are expected to shed light on intense X-ray sources such as pulsars and black holes.
Then again, the science-technology skew is a reminder that ISRO among the world’s spacefaring organisations has unique needs and priorities. This is exemplified by the second part of the C58 mission. After launching XPoSat in a 650-km circular orbit around the earth, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a 350-km-high orbit and unfurled solar panels, becoming a rudimentary satellite and orbital testbed for the 10 payloads it carried. These are a radio payload by the K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology and a device to measure ultraviolet radiation from L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women; a ‘green’ cubesat propulsion unit, a ‘green’ monopropellant thruster, a tantalum-based radiation shield, a heater-less hollow cathode, and a nanosatellite platform, all from private entities; and an interplanetary dust counter, a fuel-cell power system, and a high-energy cell from ISRO centres. This is only the third time ISRO has operated the PSLV fourth stage in this way. As such, the C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, aspiring students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector. This again is a vignette of the demands of ISRO itself as it navigates an era in which a permanent lunar station seems inevitable, drawing as much on technological capabilities as — based on scientific missions — humankind’s knowledge of the universe.
According to the passage, who realized the POLIX payload?
A. NASA
B. The K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology
C. ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre
D. The Raman Research Institute
E. L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women
Solutions
The correct answer is “The Raman Research Institute”.
Key Points
- According to the passage, the POLIX payload was realized by The Raman Research Institute.
- This payload is destined to track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range.
- The passage clearly states this, making option 4, The Raman Research Institute, the correct answer.
The correct answer is ‘option 4’.
Additional Information
Options 1, 2, 3, and 5 are incorrect, as they were not involved in realizing the POLIX payload according to the information in the passage
4. Two missions the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched in the five months since its success with Chandrayaan-3 have both been scientific in nature: the Aditya L-1 space probe to study the sun and the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) to study polarised X-rays emitted in astrophysical phenomena. ISRO launched the XPoSat, in a two-part mission, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on its C58 flight on January 1. The relative timing of these launches may be a coincidence but it is heartening because the ratio of scientific to technological missions ISRO has launched is skewed in favour of the latter, at the expense of research in the sense of discovery. Those science-oriented missions have all been exceptional in their own right. For example, XPoSat is only the second space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation, and at higher x-ray energies than the other, NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Its POLIX payload, realised by the Raman Research Institute, will track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range and observe emissions from around 50 sources in five years. The XSPECT payload, by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre, will study X-rays of energy 0.8-15 keV and changes in continuous X-ray emissions. Together, they are expected to shed light on intense X-ray sources such as pulsars and black holes.
Then again, the science-technology skew is a reminder that ISRO among the world’s spacefaring organisations has unique needs and priorities. This is exemplified by the second part of the C58 mission. After launching XPoSat in a 650-km circular orbit around the earth, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a 350-km-high orbit and unfurled solar panels, becoming a rudimentary satellite and orbital testbed for the 10 payloads it carried. These are a radio payload by the K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology and a device to measure ultraviolet radiation from L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women; a ‘green’ cubesat propulsion unit, a ‘green’ monopropellant thruster, a tantalum-based radiation shield, a heater-less hollow cathode, and a nanosatellite platform, all from private entities; and an interplanetary dust counter, a fuel-cell power system, and a high-energy cell from ISRO centres. This is only the third time ISRO has operated the PSLV fourth stage in this way. As such, the C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, aspiring students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector. This again is a vignette of the demands of ISRO itself as it navigates an era in which a permanent lunar station seems inevitable, drawing as much on technological capabilities as — based on scientific missions — humankind’s knowledge of the universe.
It can be inferred from the passage that:
A. ISRO’s scientific missions are viewed as less important than their technological ones
B. The scientific missions of ISRO carry potential for significant breakthroughs
C. The XPoSat mission solely focuses on studying X-ray polarization
D. ISRO plans to construct a permanent lunar station in the foreseeable future
E. The C58 mission was a failure due to lack of private participation
Solutions
The correct answer is “The scientific missions of ISRO carry potential for significant breakthroughs”.
Key Points
- The passage highlights the scientific missions, Aditya L-1 and XPoSat, launched by ISRO, detailing their contributions to understanding space phenomena.
- One can infer from the distinct roles of these missions and the expected insights they will provide that they carry great potential for significant scientific breakthroughs.
- Accordingly, as this is the only option that aligns with the passage, option 2 must be the correct answer.
The correct answer is ‘option 2’.
Additional Information
Option 1 misrepresents the passage’s description of ISRO’s balance of scientific and technological missions.
Option 3 is incorrect as XPoSat also includes studying continuous X-ray emissions besides X-ray polarization.
Option 4 provides a broader future speculation not directly supported by the passage.
Option 5 is incorrect; the passage states that there was participation from private entities in the C58 mission
5. Two missions the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched in the five months since its success with Chandrayaan-3 have both been scientific in nature: the Aditya L-1 space probe to study the sun and the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) to study polarised X-rays emitted in astrophysical phenomena. ISRO launched the XPoSat, in a two-part mission, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on its C58 flight on January 1. The relative timing of these launches may be a coincidence but it is heartening because the ratio of scientific to technological missions ISRO has launched is skewed in favour of the latter, at the expense of research in the sense of discovery. Those science-oriented missions have all been exceptional in their own right. For example, XPoSat is only the second space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation, and at higher x-ray energies than the other, NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Its POLIX payload, realised by the Raman Research Institute, will track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range and observe emissions from around 50 sources in five years. The XSPECT payload, by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre, will study X-rays of energy 0.8-15 keV and changes in continuous X-ray emissions. Together, they are expected to shed light on intense X-ray sources such as pulsars and black holes.
Then again, the science-technology skew is a reminder that ISRO among the world’s spacefaring organisations has unique needs and priorities. This is exemplified by the second part of the C58 mission. After launching XPoSat in a 650-km circular orbit around the earth, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a 350-km-high orbit and unfurled solar panels, becoming a rudimentary satellite and orbital testbed for the 10 payloads it carried. These are a radio payload by the K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology and a device to measure ultraviolet radiation from L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women; a ‘green’ cubesat propulsion unit, a ‘green’ monopropellant thruster, a tantalum-based radiation shield, a heater-less hollow cathode, and a nanosatellite platform, all from private entities; and an interplanetary dust counter, a fuel-cell power system, and a high-energy cell from ISRO centres. This is only the third time ISRO has operated the PSLV fourth stage in this way. As such, the C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, aspiring students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector. This again is a vignette of the demands of ISRO itself as it navigates an era in which a permanent lunar station seems inevitable, drawing as much on technological capabilities as — based on scientific missions — humankind’s knowledge of the universe.
According to the passage, which one of them must be true?
A. XPoSat is the first space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation
B. All scientific missions launched by ISRO have underperformed
C. The importance of scientific missions is belittled because of ISRO’s technological missions
D. The fourth stage of the rocket in the C58 mission transformed into a rudimentary satellite
E. ISRO centers did not contribute any payloads in the second part of the C58 mission
Solutions
The correct answer is “The fourth stage of the rocket in the C58 mission transformed into a rudimentary satellite.”
Key Points
- The passage explicitly states that after launching XPoSat, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a different orbit, unfolded solar panels, and became a rudimentary satellite.
- This event is directly mentioned, making option 4 the action that must be true based on the passage.
The correct answer is ‘option 4′.
Additional Information
Option 1 is incorrect as according to the passage, XPoSat is the second, not the first, space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation.
Option 2 is a negative assertion not directly supported by the passage.
Option 3 is not accurate; the passage explains that there is a skew, but does not belittle scientific missions.
Option 5 is incorrect. ISRO centers did contribute payloads in the second part of the C58 mission.
6. Two missions the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched in the five months since its success with Chandrayaan-3 have both been scientific in nature: the Aditya L-1 space probe to study the sun and the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) to study polarised X-rays emitted in astrophysical phenomena. ISRO launched the XPoSat, in a two-part mission, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on its C58 flight on January 1. The relative timing of these launches may be a coincidence but it is heartening because the ratio of scientific to technological missions ISRO has launched is skewed in favour of the latter, at the expense of research in the sense of discovery. Those science-oriented missions have all been exceptional in their own right. For example, XPoSat is only the second space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation, and at higher x-ray energies than the other, NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Its POLIX payload, realised by the Raman Research Institute, will track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range and observe emissions from around 50 sources in five years. The XSPECT payload, by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre, will study X-rays of energy 0.8-15 keV and changes in continuous X-ray emissions. Together, they are expected to shed light on intense X-ray sources such as pulsars and black holes.
Then again, the science-technology skew is a reminder that ISRO among the world’s spacefaring organisations has unique needs and priorities. This is exemplified by the second part of the C58 mission. After launching XPoSat in a 650-km circular orbit around the earth, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a 350-km-high orbit and unfurled solar panels, becoming a rudimentary satellite and orbital testbed for the 10 payloads it carried. These are a radio payload by the K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology and a device to measure ultraviolet radiation from L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women; a ‘green’ cubesat propulsion unit, a ‘green’ monopropellant thruster, a tantalum-based radiation shield, a heater-less hollow cathode, and a nanosatellite platform, all from private entities; and an interplanetary dust counter, a fuel-cell power system, and a high-energy cell from ISRO centres. This is only the third time ISRO has operated the PSLV fourth stage in this way. As such, the C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, aspiring students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector. This again is a vignette of the demands of ISRO itself as it navigates an era in which a permanent lunar station seems inevitable, drawing as much on technological capabilities as — based on scientific missions — humankind’s knowledge of the universe.
Fill in the blank with the most appropriate word:
The C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, _________ students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector.
A. discouraged
B. aspiring
C. disrespectful
D. hesitant
E. neglectful
Solutions
The correct answer is “option 2”.
Key Points
- The most suitable word to fit the context is looking for a word that describes students who have ambitions or goals relating to science.
- Based on this logic, only the word “aspiring” fits the context correctly.
The correct answer is ‘option 2’.
Additional Information
Options 1, 3, 4, and 5 impart a negative connotation that does not match the positive context of the sentence.
7. Two missions the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched in the five months since its success with Chandrayaan-3 have both been scientific in nature: the Aditya L-1 space probe to study the sun and the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) to study polarised X-rays emitted in astrophysical phenomena. ISRO launched the XPoSat, in a two-part mission, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on its C58 flight on January 1. The relative timing of these launches may be a coincidence but it is heartening because the ratio of scientific to technological missions ISRO has launched is skewed in favour of the latter, at the expense of research in the sense of discovery. Those science-oriented missions have all been exceptional in their own right. For example, XPoSat is only the second space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation, and at higher x-ray energies than the other, NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Its POLIX payload, realised by the Raman Research Institute, will track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range and observe emissions from around 50 sources in five years. The XSPECT payload, by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre, will study X-rays of energy 0.8-15 keV and changes in continuous X-ray emissions. Together, they are expected to shed light on intense X-ray sources such as pulsars and black holes.
Then again, the science-technology skew is a reminder that ISRO among the world’s spacefaring organisations has unique needs and priorities. This is exemplified by the second part of the C58 mission. After launching XPoSat in a 650-km circular orbit around the earth, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a 350-km-high orbit and unfurled solar panels, becoming a rudimentary satellite and orbital testbed for the 10 payloads it carried. These are a radio payload by the K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology and a device to measure ultraviolet radiation from L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women; a ‘green’ cubesat propulsion unit, a ‘green’ monopropellant thruster, a tantalum-based radiation shield, a heater-less hollow cathode, and a nanosatellite platform, all from private entities; and an interplanetary dust counter, a fuel-cell power system, and a high-energy cell from ISRO centres. This is only the third time ISRO has operated the PSLV fourth stage in this way. As such, the C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, aspiring students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector. This again is a vignette of the demands of ISRO itself as it navigates an era in which a permanent lunar station seems inevitable, drawing as much on technological capabilities as — based on scientific missions — humankind’s knowledge of the universe.
Find the antonym of the word ‘unfurled’ used in the passage.
A. Shrink
B. Steep
C. Hide
D. Scroll
E. Curl
Solutions
The correct answer is “Curl“.
Key Points
- ‘Unfurled’ means to unroll, unfold, or spread out from a rolled or folded state.
- Thus, the opposite of unfurling would be to roll or fold something. Hence, ‘curl’ is the antonym of ‘unfurled’.
- So the appropriate antonym in the provided options is ‘curl’, making option 5 the correct choice.
The correct answer is ‘option 5’.
Additional Information
Options 1, 2, 3, and 4 do not align with the opposite meaning of ‘unfurled’.
8. Two missions the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched in the five months since its success with Chandrayaan-3 have both been scientific in nature: the Aditya L-1 space probe to study the sun and the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) to study polarised X-rays emitted in astrophysical phenomena. ISRO launched the XPoSat, in a two-part mission, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on its C58 flight on January 1. The relative timing of these launches may be a coincidence but it is heartening because the ratio of scientific to technological missions ISRO has launched is skewed in favour of the latter, at the expense of research in the sense of discovery. Those science-oriented missions have all been exceptional in their own right. For example, XPoSat is only the second space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation, and at higher x-ray energies than the other, NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Its POLIX payload, realised by the Raman Research Institute, will track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range and observe emissions from around 50 sources in five years. The XSPECT payload, by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre, will study X-rays of energy 0.8-15 keV and changes in continuous X-ray emissions. Together, they are expected to shed light on intense X-ray sources such as pulsars and black holes.
Then again, the science-technology skew is a reminder that ISRO among the world’s spacefaring organisations has unique needs and priorities. This is exemplified by the second part of the C58 mission. After launching XPoSat in a 650-km circular orbit around the earth, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a 350-km-high orbit and unfurled solar panels, becoming a rudimentary satellite and orbital testbed for the 10 payloads it carried. These are a radio payload by the K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology and a device to measure ultraviolet radiation from L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women; a ‘green’ cubesat propulsion unit, a ‘green’ monopropellant thruster, a tantalum-based radiation shield, a heater-less hollow cathode, and a nanosatellite platform, all from private entities; and an interplanetary dust counter, a fuel-cell power system, and a high-energy cell from ISRO centres. This is only the third time ISRO has operated the PSLV fourth stage in this way. As such, the C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, aspiring students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector. This again is a vignette of the demands of ISRO itself as it navigates an era in which a permanent lunar station seems inevitable, drawing as much on technological capabilities as — based on scientific missions — humankind’s knowledge of the universe.
Which of the following idioms best describes the phrase ‘drawing as much on technological capabilities as scientific missions’ used in the passage?
A. To have one’s finger in every pie
B. To burn the midnight oil
C. A piece of cake
D. To bite off more than one can chew
E. To kill two birds with one stone
Solutions
The correct answer is “To kill two birds with one stone”.
Key Points
- The phrase describes ISRO’s ability to utilize both technological capabilities and scientific missions, indicating it addresses two objectives simultaneously.
- Therefore, the idiom ‘To kill two birds with one stone’, which signifies achieving two objectives with one action, best suits the phrase.
- Hence, option 5 is the idiom that best describes the given phrase.
The correct answer is ‘option 5’.
Additional Information
- The other idioms, options 1, 2, 3, and 4 do not correctly depict the idea of simultaneously achieving two goals as per the given context.
9. Two missions the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched in the five months since its success with Chandrayaan-3 have both been scientific in nature: the Aditya L-1 space probe to study the sun and the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) to study polarised X-rays emitted in astrophysical phenomena. ISRO launched the XPoSat, in a two-part mission, onboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on its C58 flight on January 1. The relative timing of these launches may be a coincidence but it is heartening because the ratio of scientific to technological missions ISRO has launched is skewed in favour of the latter, at the expense of research in the sense of discovery. Those science-oriented missions have all been exceptional in their own right. For example, XPoSat is only the second space-based experiment to study X-ray polarisation, and at higher x-ray energies than the other, NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Its POLIX payload, realised by the Raman Research Institute, will track X-rays in the 8-30 kilo-electron-volt (keV) energy range and observe emissions from around 50 sources in five years. The XSPECT payload, by ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre, will study X-rays of energy 0.8-15 keV and changes in continuous X-ray emissions. Together, they are expected to shed light on intense X-ray sources such as pulsars and black holes.
Then again, the science-technology skew is a reminder that ISRO among the world’s spacefaring organisations has unique needs and priorities. This is exemplified by the second part of the C58 mission. After launching XPoSat in a 650-km circular orbit around the earth, the fourth stage of the rocket lowered itself into a 350-km-high orbit and unfurled solar panels, becoming a rudimentary satellite and orbital testbed for the 10 payloads it carried. These are a radio payload by the K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology and a device to measure ultraviolet radiation from L.B.S. Institute of Technology for Women; a ‘green’ cubesat propulsion unit, a ‘green’ monopropellant thruster, a tantalum-based radiation shield, a heater-less hollow cathode, and a nanosatellite platform, all from private entities; and an interplanetary dust counter, a fuel-cell power system, and a high-energy cell from ISRO centres. This is only the third time ISRO has operated the PSLV fourth stage in this way. As such, the C58 mission represents a union of the aspirations of professional scientists, aspiring students of science, and India’s private spaceflight sector. This again is a vignette of the demands of ISRO itself as it navigates an era in which a permanent lunar station seems inevitable, drawing as much on technological capabilities as — based on scientific missions — humankind’s knowledge of the universe.
Which of the following most accurately states the main idea of the passage?
A. The impact of ISRO’s recent launches on India’s space technology advancements
B. The role of ISRO in the global space community, focusing on its scientific missions
C. The scientific breakthroughs achieved by ISRO’s Aditya L-1 and XPoSat missions
D. The distribution and characteristics of X-ray emissions in astrophysical phenomena
E. The scientific versus technological mission preferences of ISRO
Solutions
The correct answer is “The role of ISRO in the global space community, focusing on its scientific missions.”
Key Points
- The passage covers ISRO’s recent missions and explores their contribution to global space research.
- These missions include Aditya L-1, aimed at studying the sun, and XPoSat, geared towards examining polarised X-rays in space.
- The passage also highlights ISRO’s focus on balancing scientific and technological missions.
- Therefore, option 2, which encapsulates all these points, best represents the main idea of the passage.
Hence, the correct answer is ‘option 2′.
Additional Information
Option 1 refers to the impact of ISRO’s recent missions on India’s space tech advancements, which is not the chief focus of the passage.
Option 3 focuses solely on the scientific breakthroughs of specific missions, which is narrow in light of the passage’s scope.
Option 4 is incorrect as the passage is not mainly about X-ray emissions in astrophysical phenomena.
Option 5 is close, but it only emphasizes the scientific versus technological mission preferences of ISRO and leaves out the broader context.
10. Directions: The given question has one blank indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the word for the given options that could fit in the blank correctly.
_______ spending by the state government drained our funds and left us with a huge deficit.
A. Pivotal
B. Resolute
C. Excessive
D. Determined
E. Emphatic
Solutions
The correct answer is‘Excessive.‘
Key Points
- The given sentence is talking about,the amount of money spent by the state governmentleading toa huge deficitor loss.
- Therefore, the most appropriate word to be filled in the blank is,‘Excessive‘.
- Also, the use of the word”spending”in the sentenceindicatesthe use of the word‘excessive‘in the blank.
- The word ‘Excessive’ meansMore than needed;too much. (अत्यधिक; बहुत अधिक)
- Example:An excessive amount of security was at the event making the sea of people even more crowded.
Hence, the correct answer isoption 3.
Complete Sentence:Excessive spending by the state government drained our funds and left us with a huge deficit.
Additional Information
- Letusexplorethe otheroptions:
- PivotalmeansOf crucial importance in relation to the development or success of something else.(धुरीय, मूलभूत)
- ResolutemeansHaving or showing great determination. (दृढ़निश्चयी, कृतसंकल्प)
- DeterminedmeansHaving firmly decided to do something or to succeed, even if it is difficult. (कठिन होने के बावजूद किसी काम में सफलता प्राप्त करने का संकल्प, कृतसंकल्प, दृढ़निश्चयी)
- EmphaticmeansSaid or expressed in a strong way. (सशक्त, ज़ोरदार, बलपूर्ण, बलयुक्त)
11. Directions: The given question has one blank indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the word for the given options that could fit in the blank correctly.
I will _______ my goal through patience and diligence.
A. Achieve
B. Deceive
C. Anguish
D. Torment
E. Grief
Solutions
The correct answer is‘Achieve.‘
Key Points
- The given sentence is talking about, attainingone’spurpose or aimthrough patience and diligence.
- Therefore, the most appropriate word to be filled in the blank is,‘Achieve‘.
- Also, the use of the word”goal”in the sentenceindicatesthe use of the word‘achieve‘in the blank.
- The word ‘Achieve’ meansTo successfully get or accomplish. (कुछ प्राप्त करनाप्रायः मेहनत और कौशल द्वारा)
- Example:I studied hard to achieve a perfect grade.
Hence, the correct answer is option 1.
Complete Sentence:I will achieve my goal through patience and diligence.
Additional Information
- Letusexplorethe otheroptions:
- DeceivemeansTo try to make somebody believe something that is not true. (बहकाना, भ्रमित करना)
- AnguishmeansGreat mental pain or suffering. (गहरी वेदना या पीड़ा; मनोव्यथा)
- TormentmeansGreat pain and suffering in your mind or body; somebody or something that causes this. (तीव्र मानसिक या शारीरिक वेदना; ऐसी वेदना पहुँचाने वाला व्यक्ति या वस्तु)
- GriefmeansGreat sadness. (गहरा शोक)
12. Directions: The given question has one blank indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the word for the given options that could fit in the blank correctly.
The _______ of her nausea was so strong that she felt dizzy and began to retch.
A. Resonate
B. Vulnerable
C. Susceptible
D. Intensity
E. Diversity
Solutions
The correct answer is‘Intensity.‘
Key Points
- The given sentence is talking about,strong nausea or sickness that led to weakness and vomiting.
- Therefore, the most appropriate word to be filled in the blank is,‘Intensity‘.
- Also, the use of the word”strong”in the sentenceindicatesthe use of the word‘intensity‘in the blank.
- The word ‘Intensity’ meansAt a stronger level than normal. (उग्रता, तीव्रता, भाव-प्रबलता)
- Example:If the pain intensity increases contact the doctor immediately.
Hence, the correct answer isoption 4.
Complete Sentence:The intensity of her nausea was so strong that she felt dizzy and began to retch.
Additional Information
- Letusexplorethe otheroptions:
- ResonatemeansTo remind somebody of something; to be similar to what somebody thinks or believes. (किसी को कुछ याद दिलाना; किसी के सोच या मान्यताओं से अनुकूलता अनुभव करना)
- VulnerablemeansWeak and easy to hurt physically or emotionally. (दुर्बल और नाज़ुक, असुरक्षित, सुभेद्य, आघात योग्य)
- SusceptiblemeansEasily influenced, damaged or affected by somebodyor something. (किसी व्यक्ति सेसरलता से प्रभावित, रोग आदि सेक्षतिग्रस्त या आक्रांत हो जानेवाला)
- DiversitymeansThe wide variety of something. (विविधता)
13. Directions: The given question has one blank indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the word for the given options that could fit in the blank correctly.
The _______ invention allowed farmers to process cotton ten times faster than before the revolutionary discovery.
A. Complication
B. Snag
C. Breakthrough
D. Intricacy
E. Drawback
Solutions
The correct answer is‘Breakthrough.‘
Key Points
- The given sentence is talking about,the invention thatlet farmers to process cotton ten times faster.
- Therefore, the most appropriate word to be filled in the blank is,‘Breakthrough‘.
- Also, the use of the word”discovery”in the sentenceindicatesthe use of the word‘breakthrough‘in the blank.
- The word ‘Breakthrough’ meansAn important discovery or development.
- Example:A medical breakthrough suddenly allowed doctors to cure a disease that once killed thousands of people.
Hence, the correct answer isoption 3.
Complete Sentence:The breakthrough invention allowed farmers to process cotton ten times faster than before the revolutionary discovery.
Additional Information
- Letusexplorethe otheroptions:
- ComplicationmeansSomething that makes a situation hard to understand or to deal with. (उलझन, परेशानी, जटिलता, पेचीदगी)
- SnagmeansA small difficulty or disadvantage that is often unexpected or hidden. (छोटी कठिनाई या प्रतिकूलता प्रायः अप्रत्याशित या छिपी हुई)
- IntricacymeansThe complicated parts or details of something. (किसी वस्तु के जटिल अंश या ब्योरे)
- DrawbackmeansA disadvantage or problem. (कमी, न्यूनता, त्रुटि, असुविधा)
14. In the given sentence a word has been emboldened. Select the best alternative for the bold word from the given options. If none follows, select option 5 as your answer.
The change in the defense team’s strategy was astonishing for the court.
A. Confirming
B. Astounding
C. Purifying
D. Praising
E. None
Solutions
The correct answer is option 2 i.e. astounding.
Explanation:
We have to choose the word which is similar to the emboldened word and can replace it.
Let’s take a look at the meaning and usage of all the words given in the question and options-
- Astonishing: extremely surprising or impressive; amazing
- Confirming: establish the truth or correctness of (something previously believed or suspected to be the case)
- Astounding: surprisingly impressive
- Purifying: removingthe spoiling particles from something
- Praising: expressing warm approval or admiration of
Therefore, from the given options, the best alternative for the emboldenedword is ‘astounding’.
15. In the given sentence a word has been underlined. Select the best alternative for the bold word from the given options. If none follows, select option 5 as your answer.
The family of the victim wanted to petition the court for an extension.
A. Pray
B. Prey
C. Command
D. Request
E. None
Solutions
The correct answer is option 4 i.e. request.
Key Points
We have to choose a word that is similar to the emboldened word and can replace it.
Let’s take a look at the meaning and usage of all the words given in the question and options-
- Petition: To formally request someone to do something
- Pray: To address a prayer (a request to God for something)
- Prey: The act of hunting and killing for food
- Command: To give someone an order to do something
- Request: To politely and formally ask someone to do something
Therefore, from the given options, the best alternative for the emboldened word is ‘request’.
Mistake Points
- The reader may get confused between ‘command’ and ‘request’ but a victim’s family cannot order a court to do something, they can only politely ask.
16. Directions:Five sentences A, B, C, D, and E are given below, among which only three have been arranged in sequence and two sentences must be interchanged so that the five sentences can together form a meaningful paragraph.
A. Miss Universe is an annual international beauty pageant that is run by the United States-based Miss Universe Organization.
B. Telemundo has the licensing rights to air the pageant for the next 5 years.
C. The Miss Universe Organization and its brand are currently owned by Endeavor.
D. Along with Miss World, Miss International, and Miss Earth, Miss Universe is one of the Big Four international beauty pageants.
E. The pageant’s advocacy is humanitarian issues and is a voice to affect positive change in the world.
Which of the following should be the FOURTH sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘B.‘
Key Points
- The correct sequence of the segments after rearrangement is ADCBE.
- The sentence ‘A‘isindependentof any other sentence as it is giving general information about”Miss Universe“. Hence, ‘A‘ is thefirst part.
- SentenceDwill come afterAasit further gives information abouthow important or how big is the Miss Universe event.
- SentenceCwill come afterDasit is giving information aboutwho owns the Miss Universe Organization and its brand.
- SentenceBwill come afterCasit is giving information aboutthe television broadcast partner ofthe pageant for the next 5 years.
- The sentence ‘E‘is theconcludingpartbecause it is talking about the aim and concept of the Miss Universe event.
- From the above sequence, we can say that sentence ‘B’ is the fourth sentence after rearrangement.
Hence, the correct answer is option 2.
Paragraph after rearranging the sentences:Miss Universe is an annual international beauty pageant that is run by the United States-based Miss Universe Organization.Along with Miss World, Miss International, and Miss Earth, Miss Universe is one of the Big Four international beauty pageants.The Miss Universe Organization and its brand are currently owned by Endeavor.Telemundo has the licensing rights to air the pageant for the next 5 years.The pageant’s advocacy is humanitarian issues and is a voice to affect positive change in the world.
Hint
- Important Rules to Solve the Para Jumbles:
- Read the sentencesattentively and try tocomprehend the idea or theme of the sentenceandeliminate the irrelevantoptions.
- Try toidentify the opening(independent sentence)and closing sentences(concluding sentence).
- Try toidentify the mandatory pairs. Two sentences can be connected through various connectors and other determinants.
17. Directions:Five sentences A, B, C, D, and E are given below, among which only three have been arranged in sequence and two sentences must be interchanged so that the five sentences can together form a meaningful paragraph.
A. Miss Universe is an annual international beauty pageant that is run by the United States-based Miss Universe Organization.
B. Telemundo has the licensing rights to air the pageant for the next 5 years.
C. The Miss Universe Organization and its brand are currently owned by Endeavor.
D. Along with Miss World, Miss International, and Miss Earth, Miss Universe is one of the Big Four international beauty pageants.
E. The pageant’s advocacy is humanitarian issues and is a voice to affect positive change in the world.
Which of the following should be the THIRD sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘C.‘
Key Points
- The correct sequence of the segments after rearrangement isADCBE.
- The sentence ‘A‘isindependentof any other sentence as it is giving general information about”Miss Universe“. Hence, ‘A‘ is thefirst part.
- SentenceDwill come afterAasit further gives information abouthow important or how big is the Miss Universe event.
- SentenceCwill come afterDasit is giving information aboutwho owns the Miss Universe Organization and its brand.
- SentenceBwill come afterCasit is giving information aboutthe television broadcast partner ofthe pageant for the next 5 years.
- The sentence ‘E‘is theconcludingpartbecause it is talking aboutthe aim and concept of the Miss Universe event.
- From the above sequence, we can say thatsentence ‘C’is thethird sentenceafter rearrangement.
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
18. Directions:Five sentences A, B, C, D, and E are given below, among which only three have been arranged in sequence and two sentences must be interchanged so that the five sentences can together form a meaningful paragraph.
A. Miss Universe is an annual international beauty pageant that is run by the United States-based Miss Universe Organization.
B. Telemundo has the licensing rights to air the pageant for the next 5 years.
C. The Miss Universe Organization and its brand are currently owned by Endeavor.
D. Along with Miss World, Miss International, and Miss Earth, Miss Universe is one of the Big Four international beauty pageants.
E. The pageant’s advocacy is humanitarian issues and is a voice to affect positive change in the world.
Which of the following pairs of sentences must be interchanged in order to make the set of sentences a meaningful paragraph?
A. A and C
B. B and D
C. D and A
D. B and E
E. C and B
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘B and D.‘
Key Points
- The correct sequence of the segments after rearrangement isADCBE.
- The sentence ‘A‘isindependentof any other sentence as it is giving general information about”Miss Universe“. Hence, ‘A‘ is thefirst part.
- SentenceDshould come afterAasit further gives information abouthow important or how big is the Miss Universe event.
- SentenceCwill come afterDasit is giving information aboutwho owns the Miss Universe Organization and its brand.
- SentenceBshould come afterCasit is giving information aboutthe television broadcast partner ofthe pageant for the next 5 years.
- The sentence ‘E‘is theconcludingpartbecause it is talking aboutthe aim and concept of the Miss Universe event.
- The information given in the sentence ‘D’ is introducing a subject and is more important than the information given in the sentence ‘B’. Therefore, B and D should be interchanged.
Hence, the correct answer is option 2.
19. Directions: Five sentences A, B, C, D, and E are given below, among which only three have been arranged in sequence and two sentences must be interchanged so that the five sentences can together form a meaningful paragraph.
A. Miss Universe is an annual international beauty pageant that is run by the United States-based Miss Universe Organization.
B. Telemundo has the licensing rights to air the pageant for the next 5 years.
C. The Miss Universe Organization and its brand are currently owned by Endeavor.
D. Along with Miss World, Miss International, and Miss Earth, Miss Universe is one of the Big Four international beauty pageants.
E. The pageant’s advocacy is humanitarian issues and is a voice to affect positive change in the world.
After forming a meaningful paragraph, which of the sentences can immediately follow B:
I. The reselling of the franchise from one owner to the next is recurrently common in the history of the event, sometimes for contractual breaches or financial reasons.
II. It is one of the most-watched pageants in the world with an estimated audience of over 500 million viewers in over 190 territories.
III. The fee includes the rights of image, brand, and everything related to the pageant.
A. Only II
B. I and II both
C. II and III both
D. Only III
E. Only I
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘OnlyII.‘
Key Points
- SentenceBis giving information aboutthe television broadcast partner ofthe pageant for the next 5 years.
- The next sentence which should follow the sentence ‘B’ should be related to television or the pageants being televised or being watched.
- From the given options, only the second option can immediately follow sentence B.
- Thesecond optionis talking aboutthe pageants being watched by a huge audience.
- The first optionis talking about the reselling of the franchise which organizes the Miss Universe event.
- The third option is talking about some fees related to the pageant.
Hence, the correct answer is option 1.
20. Directions:Five sentences A, B, C, D, and E are given below, among which only three have been arranged in sequence and two sentences must be interchanged so that the five sentences can together form a meaningful paragraph.
A. Miss Universe is an annual international beauty pageant that is run by the United States-based Miss Universe Organization.
B. Telemundo has the licensing rights to air the pageant for the next 5 years.
C. The Miss Universe Organization and its brand are currently owned by Endeavor.
D. Along with Miss World, Miss International, and Miss Earth, Miss Universe is one of the Big Four international beauty pageants.
E. The pageant’s advocacy is humanitarian issues and is a voice to affect positive change in the world.
After forming a meaningful paragraph, which of the sentences can immediately follow E:
I. This crown was purely made from rhinestones.
II. The crown is set with 1,371 gemstones, weighing a total of 416.09 carats (83.218 g).
III. The current Miss Universe is Harnaaz Sandhu of India who was crowned by Andrea Meza of Mexico on December 12, 2021, in Eilat, Israel.
A. Only I
B. I and II both
C. II and III both
D. Only III
E. Only II
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Only III.‘
Key Points
- SentenceEistalking aboutthe aim and concept of the Miss Universe event.
- Thenext sentence which should follow the sentence ‘E’should berelated to Miss Universe only.
- From the given options, only thethird option can immediately follow sentence E.
- The third option is giving information about the current Miss Universe.
- Thefirst and second optionsare giving general information about a crownwhich is not mentioned in any of the sentences.
Hence, the correct answer is option 4.
21. Directions: In the following question, some parts of the sentence may have an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If a sentence is free from errors, select ‘No error’ as your answer.
One of the thingthat attracted (A)/meto this field is the (B)/opportunityto make a (C)/differencein people’s lives. (D)/ No error(E)/.
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘A’ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the first part of the given sentence, the singular form of the noun”thing”is incorrect.
- The ”one of” is a singular term and is generally used to talk about a noun or a pronoun.
- The noun or a pronoun used after the phrase ”one of” is always in the plural form ( as we are talking of one person/place/thing out of many).
- Therefore, the plural form of the noun ”things” should be used in place ofthe singular noun ‘thing‘.
Hence, the correct answer is option 1.
Correct sentence: One of the things that attracted me to this field is the opportunity to make a difference in people’s lives.
Additional Information
- The helping verb will always be in the singular form (here, is), as the helping verb agrees with ”one of” and not with the plural noun in the sentence.
22. Directions: In the following question, some parts of the sentence may have an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If a sentence is free from errors, select ‘No error’ as your answer.
They coin money in (A)/ honest and accurate measures (B)/ and allow this money trade (C)/ freely on open markets.(D)/No error(E)/.
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘C‘ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the given sentence, the use of the zero infinitive or base form of the verb ‘trade’ in part C is incorrect.
- The zero (or bare) infinitive is used after verbs of perception (see, feel, hear), many auxiliary verbs (may, should, must), the verbs make and let, and the expressions had better and would rather.
- The given sentence is talking about the purpose of coining money in honest and accurate measures i.e. to trade freely on open markets.
- The to-infinitive is used in many sentence constructions, often expressing the purpose of something or someone’s opinion about something.
- Therefore, the to-infinitive ”to trade” should be used in place of the zero or bare infinitive ‘trade’.
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
Correct sentence: They coin money in honest and accurate measures and allow this money to trade freely on open markets.
23. Directions: In the following question, some parts of the sentence may have an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If a sentence is free from errors, select ‘No error’ as your answer.
The people of Queenstown are (A)/ happy that the queen, accompanied (B)/ by the prince of Wales, (C)/ are present at the function. (D)/ No error(E)/.
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘D‘ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the given sentence, the plural form of the verb ‘are’ in part D is incorrect.
- We know that expressions such as with, together with, including, accompanied by, in addition to, or as well do not change the number of the subject.
- If the subject is singular(here, queen), the verb is too.
- Therefore, the singular form of the verb ‘is‘ should be used in place of the plural form ‘are‘.
Hence, the correct answer is option 4.
Correct sentence: The people of Queenstown are happy that the queen, accompanied by the prince of Wales, is present at the function.
Additional Information
- Subjects and verbs must agree with one another in number(singular or plural).
- Thus,if a subject is singular, itsverb must also be singular;ifthesubject is plural, itsverb must also be plural.
24. Directions: In the following question, some parts of the sentence may have an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If a sentence is free from errors, select ‘No error’ as your answer.
In the choice of these spots, (A)/ two motives seem to have influenced (B)/ him – the neighborhood of an university or college (C)/ and the amenities of the situation. (D)/ No error(E)/.
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is‘ C‘ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the third part of the given sentence,the use of theindefinite article ‘an’ is incorrect.
- ”An university” should be replaced with ”a university”because the first letter ‘u‘of the word‘university’is pronounced with a consonant sound.
- ‘A‘ and ‘an‘ areindefinite articles, which means that they refer to, or introduce, anunspecified noun.
- We use ‘a‘ before aconsonant sound(here, university)and we use ‘an‘ before avowel sound.
- Thedefinite article‘the‘ is used before singular and plural nouns when thenoun is specific or particular.
- ”No article”is used whenwe refer togeneral ideas, plurals, or uncountable nouns.
- Therefore, theindefinite article ‘a’should be usedin place oftheindefinite article ‘an’.
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
Correct Sentence:In the choice of these spots, two motives seem to have influenced him – the neighborhood of a university or collegeand the amenities of the situation.
Additional Information
There are three articles:a, an,andthe. Articles areused before nouns or noun equivalentsand are a type of adjective.
| RULES | COUNT NOUNS | NON-COUNT NOUNS |
| Specific identity not known | a, an | (no article) |
| Specific identity is known | the | the |
| Allthings or thingsin general | (no article) | (no article) |
25. Directions: In the following question, some parts of the sentence may have an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If a sentence is free from errors, select ‘No error’ as your answer.
We’d discussed (A)/ this point between (B)/ ourselves numerous times (C)/ over the past months. (D)/ No error(E)/.
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is‘B’i.e.this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the second part of the given sentence, the use ofthe preposition ‘between’isincorrect.
- We use thepreposition‘between‘ torefer to two things that are clearly separated.
- Thepreposition‘between‘ meansin the space in the middle of two things, people, places, etc.
- ‘Between‘ is usedwhen naming distinct, individual items (can be 2, 3, or more).
- We use ‘among‘to talk about things that are not clearly separated because they are part of a group or crowd or mass of objects.
- Thepreposition‘among‘ meansbeing a member or member of a larger set.
- ‘Among‘ is usedwhen the items are part of a group or are not specifically named (must be 3 or more).
- We use thepreposition‘between‘ torefer to two things that are clearly separated.
- Therefore, thepreposition‘among‘should be used in place of thepreposition‘between‘.
Hence, the correct answer isoption 2.
Correct sentence:We’d discussedthis point amongourselves numerous timesover the past months.
26. Given below is a word, followed by three sentences that consist of that word. Identify the sentence(s) that express(es) the meaning of the word.
DEPRECATE
A. The teacher should not deprecate his student’s achievements.
B. The value of new cars deprecate quickly in first two years.
C. Shares continued to deprecate on the stock market today.
A. Only A
B. Only B
C. Only C
D. Both A and B
E. Both A and c
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Only A‘.
Key Points
- The word ‘Deprecate‘ as a verb means ‘to express disapproval of’.
- In Sentence A, the word ‘Deprecate‘ has been used correctly as a verb as the sentence is talking about how the teachers should not disapprove of their student’s achievements.
- In Sentence B, the word ‘Deprecate‘ is inappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
- In Sentence C, the word ‘Deprecate‘ is inappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
27. Given below is a word, followed by three sentences that consist of that word. Identify the sentence(s) that express(es) the meaning of the word.
IMMINENT
A. Several imminent personalities will be present at the meeting .
B. .The weather forecast warned that a rain storm was imminent.
C. Rohit comes from a family of imminent politicians.
A. Only A
B. Both A and B
C. Only B
D. Only C
E. Both B and C
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Only B’.
Key Points
- The word ‘Imminent’ as an adjectivemeans something which is about to happen(often used of something bad or dangerous).
- In Sentence A, the word’Imminent‘ is inappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
- In ‘Sentence B‘ the word ‘Imminent‘ has been used correctly as an adjective as the sentence is talking about the weather forecast which has warned about the rain storm which is about to happen soon.
- In Sentence C, the word’Imminent‘ is inappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
28. Given below is a word, followed by three sentences that consist of that word. Identify the sentence(s) that express(es) the meaning of the word.
DISCREET
A. He made some discreet enquiries about the organizationbefore accepting the employment agreement.
B. Brown and white rice are two discreet varieties of rice.
C. All objects are made of discreet molecules
A. Only A
B. Only B
C. Only C
D. Both A and B
E. Both A and C.
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Only A’.
Key Points
- The word ‘Discreet‘ as a adjectivemeans ‘careful and prudent in one’s speech or actions, especially in order to keep something confidential.
- In Sentence A, the word ‘Discreet’ has been used correctly used as an adjective as the sentence is talking about someone who has made some enquiries about some organization which is careful..
- In Sentence B, the word ‘Discreet’ is inappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
- In Sentence C, the word ‘Discreet’isinappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
29. Given below is a word, followed by three sentences that consist of that word. Identify the sentence(s) that express(es) the meaning of the word.
Elicit
A. He managed to elicit donations from many small businesses.
B. Ravi tried to elicit some info from hisfriends about his surprise birthday party.
C. One should refrain oneself from any elicit practices.
A. Only A
B. Both A and B
C. Only B
D. Both B and C
E. Only C
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Both A and B’
Key Points
- The word ‘Elicit‘ means to obtain something, especially information or a reaction.
- In sentence A, the word ‘Elicit‘ has been correctly used as a verb as the sentence is talking about how someone managed to obtain something from many small businesses.
- In sentence B, the word ‘Elicit‘ has been used correctly as a verb as the sentence is talking about how Ravi was trying to obtain some info from his friends.
- In sentence C, the word ‘Elicit‘ is inappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
30. Directions: Given below is a word, followed by three sentences that consist of that word. Identify the sentence(s) that express(es) the meaning of the word.
PROJECT
A. He gained valuable experience whilst working on the project.
B. The party is trying to project a new image of itself as caring for the working classes.
C. He was afraid she would project him because he was a foreigner.
A. Only A
B. Both A and B
C. Only B
D. Both B and C
E. Only C
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Both A and B.’
Key Points
- The word ‘Project‘ as a noun means A piece of work, often involving many people, that is planned and organized carefully.
- The word ‘Project‘ as a verb means Topresent someone or somethingin a particular way.
- In sentence A, the word ‘Project‘ has been correctly used as a noun as the sentence is talking about someone whogained valuable experience whilst working on the assignmentor piece of work.
- In sentence B, the word ‘Project‘ has been correctly used as a verb as the sentence is talking about a political party trying to present a new image of itself.
- In sentence C, the word ‘Project‘ is inappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
Hence,the only possible answeris option 2.
31. Directions: Study the following directions shows the number of non vegetarian and number of vegetarians living in five different cities A, B, C D and E.
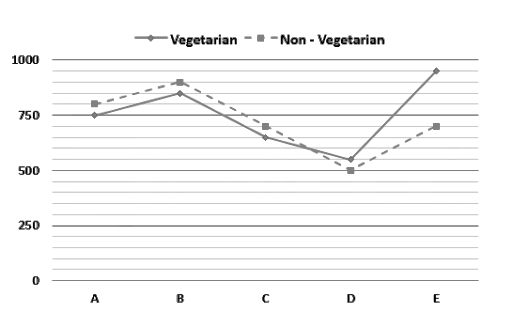
If 2/5th of the vegetarians in city A and 1/4th of the non vegetarians in city A are females then find the total number of male vegetarian and male non vegetarian in city A.
A. 1150
B. 950
C. 1050
D. 850
E. 1100
Solutions
Solution:
Number of female vegetarians = 750 ×2/5 = 300
Number of male vegetarians = 750 – 300 = 450
Number of female non vegetarians = 800 × 1/4 = 200
Number of male non vegetarians = 800 – 200 = 600
Require total = (600 + 450) = 1050
32. Directions: Study the following directions shows the number of non vegetarian and number of vegetarians living in five different cities A, B, C D and E.

40% of the vegetarians from city B and 33.33% of the non vegetarians from city B are married and the remaining are unmarried then find a difference between the number of unmarried persons in city B.
A. 120
B. 80
C. 90
D. 70
E. 100
Solutions
Solution:
Number of married vegetarians from city B = 850 × (40/100) = 340
Number of unmarried vegetarians from city B = 850 – 340 = 510
Number of married non-vegetarians from city B = 900 ×1/3 = 300
Number of unmarried non-vegetarians from city B = 900 – 300 = 600
Required difference = (600 – 510) = 90
33. Directions: Study the following directions shows the number of non vegetarian and number of vegetarians living in five different cities A, B, C D and E.

The average number of vegetarians in the city D , E and F is 700 and the average number of non vegetarians in the city D, E and F is 600. Find the total number of vegetarian and Non vegetarian in city F.
A. 1100
B. 1200
C. 1250
D. 1000
E. 1300
Solutions
Solution:
Total number of vegetarians in city D, E and F = 700 × 3 = 2100
Number of vegetarians in city D and E = (550 + 950) = 1500
Number of vegetarians in city F = (2100 – 1500) = 600
Total number of non vegetarians in city D, E and F = 60 × 3 = 1800
Number of non vegetarians in city D and E = (500 + 700) = 1200
Number of non vegetarians in city F = (1800 – 1200) = 600
Required total = (600 + 600) = 1200
34. Directions: Study the following directions shows the number of non vegetarian and number of vegetarians living in five different cities A, B, C D and E.

Find the ratio between the number of vegetarians in D and E to the number of non-vegetarians in C and D.
A. 5: 11
B. 7: 5
C. 3: 5
D. 5: 4
E. 3: 2
35. Directions: Study the following directions shows the number of non vegetarian and number of vegetarians living in five different cities A, B, C D and E.

Find the difference between the average number of vegetarians from all the cities and the average number of non vegetarians from all the cities.
A. 60
B. 70
C. 30
D. 40
E. 50
Solutions
Solution:
Average number of vegetarians from all the cities = (750 + 850 + 650 + 550 + 950)/5 = 750
Average number of non vegetarians from all the cities = (800 + 900 + 700 + 500 + 700)/5 = 720
Required difference = (750 – 720) = 30
36. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
81, 99, 123, 153, 189, ?
A. 221
B. 211
C. 241
D. 101
E. 231
Solutions
The series followsthe following pattern:
81 + 18 = 99
99 + 24 = 123
123 + 30 = 153
153 + 36 = 189
189 + 42 = 231
37. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
26, 38, 52, ?, 86, 106
A. 68
B. 72
C. 62
D. 66
E. 76
Solutions
The series followsthe following pattern:
52 + 1 = 26
62 + 2 = 38
72 + 3 = 52
82 + 4 = 68
92 + 5 = 86
102 + 6 = 106
38. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
12, 15, 24, 39, 60, ?
A. 77
B. 81
C. 83
D. 87
E. 91
Solutions
The series follows the following pattern:
12 + 3 = 15
15 + 9= 24
24+ 15= 39
39+ 21= 60
60+ 27= 87
39. What will come in the place of question mark(?) in the following series?6, 17, ?, 28,-16, 39
A. 18
B. -18
C. 5
D. -5
E. 21
Solutions
Calculations:
The series follows the following pattern:
6 + 11 = 17
17 – 22 = -5
-5 + 33 = 28
28 – 44 = -16
-16 + 55 =39∴The missingterm in the series is -5.
40. What should come in place of question mark (?) in the following number series? 310, 382, 474, ?, 726, 890
A. 480
B. 458
C. 588
D. 580
E. None of these
Solutions
The series follows the following pattern
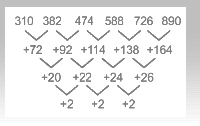
∴ The missing number = 588
41. In Gada Electronics, the profit is 420% on cost price of Television. If the cost price is increased by 35% but the selling price does not change, what percent of the selling price will be the profit nearly
A. 70
B. 80
C. 74
D. 50
E. 65
Solutions
Given
Profit of 420% on CP of Television.
CP is increased by 35%.
Concept used
(Profit/ CP) × 100 = Profit %
SP – CP = Profit
Calculation
Let the CP be 100
Then profit = 420
SP = 520
New CP is 35% more of earlier i.e 135
New Profit = SP – New CP
New Profit = 520 – 135
385
So, feasible answer = (Profit/SP) × 100
⇒(385 / 520) × 100
⇒ 74.03% ~ 74%
∴ Nearly 74% of the selling price is profit
42. Ratio between the present age of Ranita and Rahul is 3 ∶ 4. If sum of their ages is 63, what is the ratio between the age of Ranita and Rahul after 5 years?
A. 14 ∶ 43
B. 30 ∶ 11
C. 32 ∶ 41
D. 15 ∶ 31
E. 40 ∶ 21
Solutions
Given:
Ratio between the present age of Ranita and Rahul = 3 ∶ 4
Sum of their ages = 63
Calculation:
Let age of Ranita and Rahul be 3x and 4x respectively
According to the problem,
⇒ 3x + 4x = 63
⇒ 7x = 63
⇒ x = 9
Present age of Ranita = (9 × 3) = 27
Present age of Rahul = (9 × 4) = 36
Age of Ranita after 5 years = (27 + 5) = 32
Age of Rahul after 5 years = (36 + 5) = 41
⇒ Required ratio = 32 ∶ 41∴ The ratio of their ages after 5 years is 32 : 41
43. In a mixture of 80 litres, milk and water were in the ratio of 2 : 3. If 25% of the mixture is replaced with the same amount of milk, then what is the amount of milk in the final mixture?
A. 44 litres
B. 46 litres
C. 54 litres
D. 56 litres
E. None of these
Solutions
Given:
Initial quantity of mixture = 80 litres
Ratio of milk and water in the initial mixture = 2 : 3
Amount of mixture replaced with milk = 25%
Concept used:
If a fraction ofmixture is removed from the mixture, then the ratio of milk and water will be same as previous.
Calculations:
Amount of mixture replaced with milk = 25%×80
⇒ 20 litres
After removing 20 litres,
Ratio of milk and water in the remaining mixture of 60 litreswill be in the ratio of 2 : 3
Let amount of milk and water be 2x and 3x litres respectively.
⇒ 2x + 3x = 60
⇒ 5x = 60
⇒ x = 12
Newamount of milk = 2x
⇒ 2× 12
⇒24 litres
Newamount of water= 3x
⇒ 3× 12
⇒ 36litres
New amount of water = 36 litres
After adding 20 litres of milk in the new mixture,
New amount of milk in the final mixture = 24 + 20
⇒ 44 litres
∴ The amount of milk in the final mixture is 44 litres.
44. Directions: The following caselet shows the number of bikes and cars sold in the four different companies A, B, C and D.
Number of bikes sold in company A is 2.5 times of the number of cars sold in the same company. Number of cars sold in company A to B are in the ratio 5: 7 Number of bikes sold in company C is 500 more than the number of bikes sold in company A. Number of bikes sold in company B is 20% more than the number of bikes sold in company A. Total bikes sold in all the companies are 5850. Number of bikes sold in company D is 150 less than the number of bikes sold in company B. Number of cars sold in company C is 100 more than the number of cars sold in company D. Number of cars sold in company D is 350 less than the number of bikes sold in company D.
Number of bikes sold in company C is what percentage of the number of cars sold in all the companies.
A. 50.77%
B. 51.89%
C. 53.03%
D. 57.89%
E. 50.89%
Solutions
General Solution:
Number of cars sold in the company A = 5x
Number of cars sold in the company B = 7x
Number of bikes sold in the company A = 12.5x
Number of bikes sold in company C = 12.5x + 500
Number of bikes sold in company B = 12.5x × (120/100) = 15x
Number of bikes sold in company D = 15x – 150
12.5x + 12.5x + 500 + 15x + (15x – 150) = 5850
55x = (5850 – 350)
55x = 5500
x = 100
Number of cars sold in company A = 5 × 100 = 500
Number of cars sold in company B = 7 × 100 = 700
Number of bikes sold in company A = 12.5 × 100 = 1250
Number of bikes sold in company B = 15 × 100 = 1500
Number of bikes sold in company C = 1250 + 500 = 1750
Number of bikes sold in company D = 15 × 100 – 150 = 1350
Number of cars sold in company D = 1350 – 350 = 1000
Number of cars sold in company C = 1100
| Name of the company | Cars | Bikes |
| A | 500 | 1250 |
| B | 700 | 1500 |
| C | 1100 | 1750 |
| D | 1000 | 1350 |
Solution:
Number of bikes sold in company C = 1750
Number of cars sold in all the companies = (500+ 700 + 1100 + 1000) = 3300
Required percentage = 1750/3300 × 100 = 53.03%
45. Directions: The following caselet shows the number of bikes and cars sold in the four different companies A, B, C and D.
Number of bikes sold in company A is 2.5 times of the number of cars sold in the same company. Number of cars sold in company A to B are in the ratio 5: 7 Number of bikes sold in company C is 500 more than the number of bikes sold in company A. Number of bikes sold in company B is 20% more than the number of bikes sold in company A. Total bikes sold in all the companies are 5850. Number of bikes sold in company D is 150 less than the number of bikes sold in company B. Number of cars sold in company C is 100 more than the number of cars sold in company D. Number of cars sold in company D is 350 less than the number of bikes sold in company D.
Find the ratio between the number of cars sold in company C and D to the number of bikes sold in company A and D.
A. 24: 23
B. 28: 25
C. 21: 26
D. 19: 23
E. 19: 17
Solutions
General Solution:
Number of cars sold in the company A = 5x
Number of cars sold in the company B = 7x
Number of bikes sold in the company A = 12.5x
Number of bikes sold in company C = 12.5x + 500
Number of bikes sold in company B = 12.5x × (120/100) = 15x
Number of bikes sold in company D = 15x – 150
12.5x + 12.5x + 500 + 15x + (15x – 150) = 5850
55x = (5850 – 350)
55x = 5500
x = 100
Number of cars sold in company A = 5 × 100 = 500
Number of cars sold in company B = 7 × 100 = 700
Number of bikes sold in company A = 12.5 × 100 = 1250
Number of bikes sold in company B = 15 × 100 = 1500
Number of bikes sold in company C = 1250 + 500 = 1750
Number of bikes sold in company D = 15 × 100 – 150 = 1350
Number of cars sold in company D = 1350 – 350 = 1000
Number of cars sold in company C = 1100
| Name of the company | Cars | Bikes |
| A | 500 | 1250 |
| B | 700 | 1500 |
| C | 1100 | 1750 |
| D | 1000 | 1350 |
Solution:
Number of cars sold in company C = 1100
Number of cars sold in company D = 1000
Number of bikes sold in company A = 1250
Number of bikes sold in company D = 1350
Required ratio = (1000 + 1100): (1250 + 1350) = 2100: 2600 = 21: 26
46. Directions: The following caselet shows the number of bikes and cars sold in the four different companies A, B, C and D.
Number of bikes sold in company A is 2.5 times of the number of cars sold in the same company. Number of cars sold in company A to B are in the ratio 5: 7 Number of bikes sold in company C is 500 more than the number of bikes sold in company A. Number of bikes sold in company B is 20% more than the number of bikes sold in company A. Total bikes sold in all the companies are 5850. Number of bikes sold in company D is 150 less than the number of bikes sold in company B. Number of cars sold in company C is 100 more than the number of cars sold in company D. Number of cars sold in company D is 350 less than the number of bikes sold in company D.
Number of bikes sold in company E is 250 more than the number of bikes sold in company D and the number of cars sold in company E is 125 more than the number of cars sold in company C. Find the total number of vehicles (Cars + Bikes) sold in company E.
A. 2195
B. 2885
C. 2765
D. 2825
E. 2655
Solutions
General Solution:
Number of cars sold in the company A = 5x
Number of cars sold in the company B = 7x
Number of bikes sold in the company A = 12.5x
Number of bikes sold in company C = 12.5x + 500
Number of bikes sold in company B = 12.5x × (120/100) = 15x
Number of bikes sold in company D = 15x – 150
12.5x + 12.5x + 500 + 15x + (15x – 150) = 5850
55x = (5850 – 350)
55x = 5500
x = 100
Number of cars sold in company A = 5 × 100 = 500
Number of cars sold in company B = 7 × 100 = 700
Number of bikes sold in company A = 12.5 × 100 = 1250
Number of bikes sold in company B = 15 × 100 = 1500
Number of bikes sold in company C = 1250 + 500 = 1750
Number of bikes sold in company D = 15 × 100 – 150 = 1350
Number of cars sold in company D = 1350 – 350 = 1000
Number of cars sold in company C = 1100
| Name of the company | Cars | Bikes |
| A | 500 | 1250 |
| B | 700 | 1500 |
| C | 1100 | 1750 |
| D | 1000 | 1350 |
Solution:
Number of bikes sold in the company D = 1350
Number of cars sold in the company E = 1350 + 250 = 1600
Number of cars sold in the company C = 1100
Number of cars sold in the company E = 1100 + 125 = 1225
Total number of vehicles sold in the company E = (1600 + 1225) = 2825
47. Directions: The following caselet shows the number of bikes and cars sold in the four different companies A, B, C and D.
Number of bikes sold in company A is 2.5 times of the number of cars sold in the same company. Number of cars sold in company A to B are in the ratio 5: 7 Number of bikes sold in company C is 500 more than the number of bikes sold in company A. Number of bikes sold in company B is 20% more than the number of bikes sold in company A. Total bikes sold in all the companies are 5850. Number of bikes sold in company D is 150 less than the number of bikes sold in company B. Number of cars sold in company C is 100 more than the number of cars sold in company D. Number of cars sold in company D is 350 less than the number of bikes sold in company D.
If the number of cars sold in company A is increased by 25% and the number of bikes sales is increased by x. If the number of vehicles (Bikes + Cars) sold in company A is 2225 then find the number of bikes sales increased in company A.
A. 325
B. 300
C. 350
D. 200
E. 250
Solutions
General Solution:
Number of cars sold in the company A = 5x
Number of cars sold in the company B = 7x
Number of bikes sold in the company A = 12.5x
Number of bikes sold in company C = 12.5x + 500
Number of bikes sold in company B = 12.5x × (120/100) = 15x
Number of bikes sold in company D = 15x – 150
12.5x + 12.5x + 500 + 15x + (15x – 150) = 5850
55x = (5850 – 350)
55x = 5500
x = 100
Number of cars sold in company A = 5 × 100 = 500
Number of cars sold in company B = 7 × 100 = 700
Number of bikes sold in company A = 12.5 × 100 = 1250
Number of bikes sold in company B = 15 × 100 = 1500
Number of bikes sold in company C = 1250 + 500 = 1750
Number of bikes sold in company D = 15 × 100 – 150 = 1350
Number of cars sold in company D = 1350 – 350 = 1000
Number of cars sold in company C = 1100
| Name of the company | Cars | Bikes |
| A | 500 | 1250 |
| B | 700 | 1500 |
| C | 1100 | 1750 |
| D | 1000 | 1350 |
Solution:
Number of cars sold in company A = 500 × (125/100) = 625
Number of vehicles sold = 2225
Number of bikes sold in company A = 2225 – 625 = 1600
Number of bike sold sales increased = (1600 – 1250) = 350
48. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
1260 ÷ 42× {(102- 86) + 5} = ?
A. 630
B. 570
C. 540
D. 510
E. 590
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
⇒ 1260 ÷ 42× {(102- 86) + 5} = ?
⇒ 1260 ÷ 42× {(16 + 5} = ?
⇒ 1260 ÷ 42× 21 = ?
⇒ 30 × 21 = ?
∴ ? = 630
49. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
126.06 + 181.92- 229.99= 65.99+ ?
A. 12
B. 15
C. 22
D. 25
E. 19
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
126.06 + 181.92- 229.99= 65.99+ ?
⇒ 308- 230= 66+ ?
⇒ 78= 66+ ?
⇒ 78 -66 =?
∴ ? = 12
50. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
1024÷ 128 + 24% of 250 = ?2+ 180÷ 45
A. 44
B. 64
C. 80
D. 14
E. 8
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
1024÷ 128 + 24% of 250 = ?2+ 180÷ 45
⇒ 8 + 60 = ?2+ 4
⇒ 68 =?2+ 4
⇒?2 = 64
⇒ ? = 8
51. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
45% of 900 + 55% of 700 = 66% of 400 + ?
A. 374
B. 424
C. 472
D. 526
E. 556
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
45% of 900 + 55% of 700 = 66% of 400 + ?
⇒ 405 + 385 = 264 + ?
⇒ ? = 405 + 385 – 264
⇒ ? = 526
52. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
950 + 50× 15 – 14× 22 +√? = 113+ 92
A. 200
B. 240
C. 320
D. 400
E. 420
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
950 + 50× 15 – 14× 22 +√? = 113+ 92
⇒ 950 + 750 – 308 +√? = 1331 + 81
⇒ 1392 +√? = 1412
⇒√? = 20
⇒ ? = 400
53. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
55% of 240+ 83× 4 – 24 × 8 = ?
A. 1788
B. 1498
C. 1678
D. 1988
E. 1828
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
55% of 240+ 83× 4 – 24 × 8 = ?
⇒ 132+ 512×4 – 24 ×8 = ?
⇒ 132+ 512×4 – 24×8 = ?
⇒ 132+ 2048– 192= ?
⇒ 2180– 192= ?
∴ ? = 1988
54. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
(25 × 30) – (110× 8) + 670= ? × 9
A. 90
B. 30
C. 60
D. 45
E. 120
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
(25 × 30) – (110× 8) + 670= ? × 9
⇒ 750– 880+670= ? ×9
⇒ 1420– 880= ? ×9
⇒ 540 = ? ×9
∴ ? = 60
55. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
(96 + 48× 5) ÷ 24+ 32= ?
A. 52
B. 48
C. 42
D. 38
E. 46
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
(96 + 48× 5) ÷ 24+ 32= ?
⇒(96 + 240) ÷ 24+ 32= ?
⇒ 336÷ 24+ 32= ?
⇒ 14 + 32 = ?
∴ ? = 46
56. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
25% of 480 + 35% of 600 = ? + 40% of 800
A. 20
B. 30
C. 50
D. 10
E. 40
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
25% of 480 + 35% of 600 = ? + 40% of 800
⇒ 120 + 210 = ? + 320
⇒ 330= ? + 320
∴ ? = 10
57. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
65% of 200 + 35% of 400 = ?
A. 270
B. 310
C. 350
D. 240
E. 210
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
65% of 200 + 35% of 400 = ?
⇒ 130+ 140= ?
∴ ? = 270
58. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
45% of 300- ?= 27× 40÷9
A. 12
B. 22
C. 15
D. 25
E. 35
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Step-1:Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2:Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3:Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4:Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
45% of 300- ?= 27× 40÷9
⇒ 135- ?= 120
⇒ 135 – 120 = ?
∴ ? = 15
59. What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
132÷ 11- 15× 8+ 128= ?
A. 10
B. 20
C. 25
D. 15
E. 30
Solutions
Given:
132÷ 11- 15× 8+ 128= ?
Concept:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Calculation:
132÷ 11- 15× 8+ 128= ?
⇒ 12- 15× 8+ 128= ?
⇒12- 120+ 128= ?
⇒12- 120+ 128= ?
⇒ 140 – 120 = ?
∴ ? = 20
60. Compound interest accrued on a sum of Rs. 2500 is Rs. 749 at 14% per annum for certain years. What would be the simple interest accrued on the same amount for the same years at 7% per annum?
A. Rs. 230
B. Rs. 350
C. Rs. 349
D. Rs. 450
E. Rs. 670
Solutions
Given:
Principal = Rs. 2500
C.I. = Rs. 749
Rate = 14 % per annum
Formula used:
C.I. = P[(1 + r / 100)t – 1]
S.I. = (P × R × T) / 100
Where P, R and t are principal, rate and time respectively
Calculation:
According to the question,
749 = 2500[(1 + 14 / 100)t – 1]
⇒ 749 = 2500[(114 / 100)t – 1]
⇒ (749 / 2500) + 1 = (114 / 100)t
⇒ (749 + 2500) / 2500 = (114 / 100)t
⇒ 3249 / 2500 = (114 / 100)t
⇒ (57 / 50)2 = (57 / 50)t
⇒ t = 2 years
∴ S.I. = (2500 × 7 × 2) / 100 = Rs. 350
61. (a) persons can complete a job in (a-19) days while (a-9) persons can complete a job in (a-15) days. How many persons can finish twice the job in 54 days ?
A. 4
B. 8
C. 9
D. 24
E. 32
Solutions
Given:
(a) persons can complete a job in (a-19) days
(a-9) persons can complete a job in (a-15) days
Formula used:
Work = Efficiency× Time
Calculation:
Total work is same in both cases,
(a)× (a-19) = (a-9)× (a-15)
a2- 19a = a2-9a – 15a + 135
a2- 19a – a2+ 9a + 15a – 135 = 0
5a – 135 = 0
5a = 135
a = 135/5
a = 27
Total Work =(a)× (a-19)
= 27× 8
= 216
Number of persons to finish twice thejob in 54days,
62. Virat Kohli made 160 runs in his 16th innings and after that, his average run increased by 5. Find his average run after 16 innings.
A. 80
B. 85
C. 75
D. 60
E. None of these
Solutions
Shortcut Trick
Average run after nthinnings = Score in nthinnings – increase in average(n – 1)
Here, n = 16, Score in nthinnings = 160, Increase in average = 5
So, his average run after 16th innings = 160 – {5× (16 – 1)}
⇒ 160 – 75 = 85
∴His average run after the 16th innings will be 85.
Traditional method:
Given:
Virat Kohli’s score in the 16th innings was 160
His average increased by 5 runs
Formula used:
Average = (Total sum of all numbers)/(Number of items in the set)
Calculation:
Let, the average up to 15th innings be x
So, according to the question, we can say,
After, 16th innings, his average will be (x + 5)
So, as per the formula, we can say,
15x + 160 = 16(x + 5)
⇒ 15x + 160 = 16x + 80
⇒ x = 80
So, after the 16th innings, his new average = (80 + 5) = 85
∴His average run after the 16th innings will be 85.
63. If length and breadth of a rectangle are in the ratio of 8∶ 7 and its area is 224 cm2. Find the perimeter of the rectangle.
A. 40 cm
B. 50 cm
C. 56 cm
D. 60 cm
E. 64 cm
Solutions
Given:
Ratio of length and breadth = 8 ∶7
Area of rectangle = 224 cm2
Formula used:
Area of a rectangle = Length ×Breadth
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2(Length + Breadth)
Calculation:
Let the length and the breadth of the rectangle be 8x and 7x respectively.
Then, the Area of the rectangle = 224cm2
⇒ 8x× 7x = 224 cm2
⇒ 56x2=224 cm2
⇒ x2= 4
⇒ x = 2 cm
So, length of the rectangle = 8x
⇒ 8× 2
⇒ 16 cm
and breadth of the rectangle = 7x
⇒ 7× 2
⇒ 14 cm
Now, Perimeter of the rectangle =2(Length + Breadth)
⇒ 2(16 + 14) cm
⇒ 2× 30 cm
⇒ 60 cm
∴ The perimeter of the rectangle is 60 cm.
64. Trains A and B started from X and Y respectively at the same time towards each other. They crossed each other after 4 hours. A travels the distance XY in 10 hours. Find the time taken by B to travel XY.
A. 6.4hours
B. 4.8hours
C. 7.2hours
D. 6.67 hours
E. 4.5hours
Solutions
Formula:
Let t be the time taken by A and B to cross each other
Let t1 and t2 be the times taken by A and B respectively to reach their destinations after crossing each other
Then, t2 = t1 × t2
Calculation:
Here, t = 4 hours
t1 = 10 hours
Time taken by train A after meeting=10 – 4 = 6 hours
⇒ 42 = 6× t2
⇒ 16 = 6× t2
⇒ t2 = 2.67
∴ Total time taken by B to travel XY = 4 + 2.7= 6.67 hours
65. A student got 30% marks in an exam of 150 marks and failed by few marks. If he had got 10% more of his present marks, he would have passed by 1.5 marks. Calculate the passing marks.
A. 50
B. 48
C. 46
D. 47
E. 51
Solutions
Given:
The student got 30% in a 150 marks examination.
Formula Used:
Percentage of marks scored = Total marks scored/Maximum marks
Calculations:
The student’s marks = (30/100) × 150 = 45
If he had got 10% more marks, his marks would be
= (110/100) × 45 = 49.5
Passing marks is 1.5 marks less than that.
Passing marks = (49.5 – 1.5) = 48
∴ The correct answer is 48.
66. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten persons – L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z – are sitting in two parallel rows of five each such that each person of one row is facing the other person of the other row. In row 1, L, M, N, O, and P are sitting in the same row facing south while in row 2, S, T, U, W and Z are sitting in the other row facing north.Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of P and S does not sit at the end of the row. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N. N faces U. Only one person sits between W and T. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
What is the position of L with respect to O?
A. Third to the left
B. Third to the right
C. Second to the left
D. Fourth to the right
E. Second to the right
Solutions
Persons – 10; L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z;
Row 1, South – L, M, N, O, and P; Row 2,North – S, T, U, W and Z;
1. Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of P and S does not sit at the end of the row.
2. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N.
3. N faces U.
From this we get the possible arrangements as follows.
4. Only one person sits between W and T.
5. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
From this case 1 and 1a are eliminated as we cannot place W and T. Thus, the final arrangement is as follows.
Hence, L sits third to the left of O.
67. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten persons – L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z – are sitting in two parallel rows of five each such that each person of one row is facing the other person of the other row. In row 1, L, M, N, O, and P are sitting in the same row facing south while in row 2, S, T, U, W and Z are sitting in the other row facing north.Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of P and S does not sit at the end of the row. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N. N faces U. Only one person sits between W and T. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
Who among the following sits at the end?
A. P
B. Z
C. U
D. M
E. T
Solutions
Persons– 10; L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z;
Row 1, South– L, M, N, O, and P;Row 2,North– S, T, U, W and Z;
1. Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of Pand S does not sit at the end of the row.

2. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N.
3. N faces U.
From this we get the possible arrangements as follows.

4. Only one person sits between W and T.
5. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
From this case 1 and 1a are eliminated as we cannot place W and T. Thus, the final arrangement is as follows.

Hence,Usits at the end.
68. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten persons – L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z – are sitting in two parallel rows of five each such that each person of one row is facing the other person of the other row. In row 1, L, M, N, O, and P are sitting in the same row facing south while in row 2, S, T, U, W and Z are sitting in the other row facing north.Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of P and S does not sit at the end of the row. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N. N faces U. Only one person sits between W and T. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
Who faces the one who sits second to the left of S?
A. L
B. M
C. N
D. O
E. P
Solutions
Persons– 10; L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z;
Row 1, South– L, M, N, O, and P;Row 2,North– S, T, U, W and Z;
1. Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of P and S does not sit at the end of the row.

2. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N.
3. N faces U.
From this we get the possible arrangements as follows.

4. Only one person sits between W and T.
5. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
From this case 1 and 1a are eliminated as we cannot place W and T. Thus, the final arrangement is as follows.

Hence, P faces the one who sits second to the left of S.
69. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten persons – L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z – are sitting in two parallel rows of five each such that each person of one row is facing the other person of the other row. In row 1, L, M, N, O, and P are sitting in the same row facing south while in row 2, S, T, U, W and Z are sitting in the other row facing north.Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of P and S does not sit at the end of the row. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N. N faces U. Only one person sits between W and T. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
Who faces O?
A. S
B. T
C. U
D. W
E. Z
Solutions
Persons– 10; L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z;
Row 1, South– L, M, N, O, and P;Row 2,North– S, T, U, W and Z;
1. Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of P and S does not sit at the end of the row.

2. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N.
3. N faces U.
From this we get the possible arrangements as follows.

4. Only one person sits between W and T.
5. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
From this case 1 and 1a are eliminated as we cannot place W and T. Thus, the final arrangement is as follows.

Hence, W faces O.
70. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten persons – L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z – are sitting in two parallel rows of five each such that each person of one row is facing the other person of the other row. In row 1, L, M, N, O, and P are sitting in the same row facing south while in row 2, S, T, U, W and Z are sitting in the other row facing north.Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of P and S does not sit at the end of the row. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N. N faces U. Only one person sits between W and T. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
How many persons sit to the right of T?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. Four
Solutions
Persons– 10; L, M, N, O, P, S, T, U, W and Z;
Row 1, South– L, M, N, O, and P;Row 2,North– S, T, U, W and Z;
1. Number of persons to the right of S is two less than the number of persons to the left of P and S does not sit at the end of the row.

2. Z faces the one who sits third to the right of N.
3. N faces U.
From this we get the possible arrangements as follows.

4. Only one person sits between W and T.
5. M faces either T or Z and sits second to the left of O.
From this case 1 and 1a are eliminated as we cannot place W and T. Thus, the final arrangement is as follows.

Hence,two persons sit to the right of T.
71. Directions: In the question below are given threestatements followed by two conclusions numbered I, and II .You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements
Only a few Mobile is Laptop.
No Laptop is Wire.
Some Wire is Electric.
Conclusions
I. All Mobile being Laptop is a possibility.
II. Some Electric can never be Laptop.
A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Both I and II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Either I or II follows
Solutions
Venn diagram for the given question as follows
Conclusions
I. All Mobile being Laptop is a possibility – False (As, Only a few Mobile is Laptop is given whichmeans Some Mobile are Laptop and Some Mobile are not Laptop thus All Mobile can never be part of Laptop, so the possibility is false).
II. Some Electric can never be Laptop – True (Given Some Electric is Wire and No Laptop isWire thus Some Electric which are Wire can never be Laptop)
Hence, Only II follows.
72. Directions :In the question below are given threestatements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
No books are copies.
Some booksare laptops.
All laptops are computers.
Conclusions:
I. At least some computers are not copies
II. At least some computers are copies
A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Both I and II follows
D. Either I or II follows
E. Neither I Nor II follows
Solutions
The least possible Venn Diagram of the given Statements is:-
Conclusions:
I. At least some computers are not copies→ True (As all laptops are computers and some books are laptops, So some computers are also books. The part of computer which is books can never be copies as no books are copies)
II. At least some computers are copies→ False (As all laptops are computers and some books are laptops, So some computers are also books. The part of computer which is books can never be copies as no books are copies, So the statement is false)
Hence, Only I follow.
73. Directions: In the question below are given threestatements followed by two conclusions numbered I, and II .You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Some Red is Yellow.
No Yellow is Green.
All Green is Pink.
Conclusions:
I. All Red being Green is a possibility.
II. Some Pink can be Red.
A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Both I and II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Either I or II follows
Solutions
The Venn diagram for the given statement is as follows
Conclusions:
IAll Red being Green is a possibility →False (Given that some Red is Yellow and No Yellow is Green thus Some Red is also not Green)
II Some Pink can be Red →True (There is no direct relation given between Red and Pink thus the part of the Pink which is not Green can be Red soSome Pink can be Red follows )
Hence,Only IIfollows.
Additional Information
1. Some X are Y means some part of the X circle is within the Y circle.
2. No X is Y means circle X and Y are not intersecting at all.
3. All X is Y means the whole circle Xlieswithin theY circle.
4. If there is no exact conclusion for the given statements then the possibility case arises.
74. Directions: In the question below are given threestatements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
All Laptops are Computers.
All Computers are Mobiles.
No Mobile is a Battery.
Conclusions:
I. Some Computers are not Laptops.
II. Some Mobiles are not Laptops.
A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Both I and II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Either I or II follows
Solutions
The least possible Venn Diagram of the statements is as follows:-
Conclusions:
I. Some Computers are not Laptops→ False(If all Laptops are Computers then some Computers are not Laptopsarepossible but notdefinite).
II. Some Mobiles are notLaptops→ False (If all Laptops are Mobiles then some Mobiles are not Laptopsarepossible but notdefinite).
Hence, NeitherI norII follows.
TIPS TO REMEMBER:
1. Some X are Y means some part of the X circle is within the Y circle.
2. No X is Y means circle X and Y are not intersecting at all.
3. All X is Y means the whole circle X lies within the Y circle.
4. If there is no exact conclusion for the given statements then the possibility case arises.
5. If Only X is Y means all Y is X.
6. Only a few:- Some + Some not.
75. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language,
all beautiful are girls nice→ pb ag ba sa tf
some sweet girls are classy→ sf nt tf mp pb
beautiful all some dating good→ nf mp gd sa ba
nice boys are sweet but not cute→ ct ag tf nt na kp st
What could be the code for “girls are classy”?
A. mp ag ph
B. ag sf tf
C. pb tf sf
D. ba kp st
E. ag pb tf
Solutions
Code for girls: pb
Code for are: tf
Code for classy: sf
The code for girls are classy is: pb tf sf.
76. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language,
all beautiful are girls nice→ pb ag ba sa tf
some sweet girls are classy→ sf nt tf mp pb
beautiful all some dating good→ nf mp gd sa ba
nice boys are sweet but not cute→ ct ag tf nt na kp st
What is the code for “beautiful nice good”
A. ba ag sa
B. ag sa gd
C. ba ag nf
D. Either Option 2 or 3
E. Either Option 1 or 2
Solutions

Code for beautiful: ba or sa
Code for nice: ag
Code for good: Either nf or gd.
The correct answer for the code of “beautiful nice good” is Either Option 2 or 3.
77. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language,
all beautiful are girls nice→ pb ag ba sa tf
some sweet girls are classy→ sf nt tf mp pb
beautiful all some dating good→ nf mp gd sa ba
nice boys are sweet but not cute→ ct ag tf nt na kp st
Code “na st sf’ used for which of the following words.
A. boys not cute
B. classy cute not
C. boys not classy
D. but classy girls
E. None of these
Solutions

Word for na: Either boys, but, not, cute.
Word for st: Either boys, but, not, cute.
Word for sf: classy
The correct answer is None of these.
78. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language,
all beautiful are girls nice→ pb ag ba sa tf
some sweet girls are classy→ sf nt tf mp pb
beautiful all some dating good→ nf mp gd sa ba
nice boys are sweet but not cute→ ct ag tf nt na kp st
Which of the following word is used for “tf nt pb”
A. classy girls are
B. some classy girls
C. beautiful girls are
D. some sweet all
E. are girls sweet
Solutions

Code for tf: are
Code for nt: sweet
Code for pb: girls
Hence, the correct answer is “are girls sweet”.
79. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language,
all beautiful are girls nice→ pb ag ba sa tf
some sweet girls are classy→ sf nt tf mp pb
beautiful all some dating good→ nf mp gd sa ba
nice boys are sweet but not cute→ ct ag tf nt na kp st
Code “nf” is used for which of the following word?
A. girls
B. dating
C. good
D. Either girls or good
E. Either dating or good
Solutions

Code for nf: dating/good.
Hence, Either dating or good is the correct answer.
80. Directions: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions below.
Eight boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are placed one above another but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a number written on it from 1 to 8 but not necessarily in that order. The boxes are arranged in ascending order such that the lowest numbered box is at the top and the highest numbered one at the bottom.C is placed just above G. G is the bottom most box. There are four boxes placed between D and G. Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
Which box is the topmost?
A. A
B. H
C. E
D. B
E. F
Solutions
8 boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H.
1) C is placed just above G. G is the bottommost box. There are four boxes placed between D and G.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
2) Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
3) Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | E |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | F |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
Hence, Box H is the topmost.
81. Directions: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions below.
Eight boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are placed one above another but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a number written on it from 1 to 8 but not necessarily in that order. The boxes are arranged in ascending order such that the lowest numbered box is at the top and the highest numbered one at the bottom.C is placed just above G. G is the bottom most box. There are four boxes placed between D and G. Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
How many boxes are placed between E and F?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
Solutions
8 boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H.
1) C is placed just above G. G is the bottom most box. There are four boxes placed between D and G.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
2) Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
3) Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | E |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | F |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
Hence, 3 boxes are placed between E and F.
82. Directions: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions below.
Eight boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are placed one above another but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a number written on it from 1 to 8 but not necessarily in that order. The boxes are arranged in ascending order such that the lowest numbered box is at the top and the highest numbered one at the bottom.C is placed just above G. G is the bottom most box. There are four boxes placed between D and G. Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
Which box is placed between H and D?
A. A
B. E
C. C
D. B
E. F
Solutions
8 boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H.
1) C is placed just above G. G is the bottommost box. There are four boxes placed between D and G.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
2) Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
3) Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | E |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | F |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
Hence, the box E is placed between H and D
83. Directions: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions below.
Eight boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are placed one above another but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a number written on it from 1 to 8 but not necessarily in that order. The boxes are arranged in ascending order such that the lowest numbered box is at the top and the highest numbered one at the bottom.C is placed just above G. G is the bottom most box. There are four boxes placed between D and G. Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
Which box is placed immediately above A?
A. D
B. E
C. C
D. B
E. F
Solutions
8 boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H.
1) C is placed just above G. G is the bottommost box. There are four boxes placed between D and G.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
2) Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
3) Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | E |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | F |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
Hence, the box D is placed immediately above A.
84. Directions: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions below.
Eight boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are placed one above another but not necessarily in the same order. Each box has a number written on it from 1 to 8 but not necessarily in that order. The boxes are arranged in ascending order such that the lowest numbered box is at the top and the highest numbered one at the bottom.C is placed just above G. G is the bottom most box. There are four boxes placed between D and G. Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
Which box is placed immediately below F?
A. D
B. E
C. C
D. B
E. G
Solutions
8 boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H.
1) C is placed just above G. G is the bottommost box. There are four boxes placed between D and G.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
2) Two boxes are placed between B and G. Number of boxes between A and G is same as between H and B. H is placed above B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
3) Two boxes are placed between F and D. There are at least 2 boxes between E and B.
| Number | Box |
| 1 | H |
| 2 | E |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | B |
| 6 | F |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | G |
Hence, the box C is placed immediately below F.
85. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given some conclusion is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly:
Statement: U > T; X < U = Y; Y ≤ Q < R
Conclusions:
I) U > R
II) T < Q
A. Only Conclusion I follows
B. Only Conclusion II follows
C. Both I and II follow
D. Either I or II follows
E. Neither I nor II follows
Solutions
GivenStatement:U > T; X < U = Y; Y≤ Q < R
Oncombining:X < U = Y ≤ Q < R; U > T
Conclusions:
I) U > R→ False (As, X < U = Y ≤ Q < R→ There is definite relation between U and R).
II) T < Q→ True (As, T < U = Y ≤Q < R→ T < Q).
Hence, Only II follows.
86. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
A < J > B≤ I < C = H ≤D = E≤ F≥ G = Z
Conclusions:
I. C < F
II. H = F
A. Only I is True
B. Only II is True
C. Both I and II are True
D. Either I or II is True
E. Neither I nor II is True
Solutions
Given Statements:A < J > B≤ I < C = H≤D = E≤ F≥ G = Z
Conclusions:
I. C < F→ False (C = H ≤D = E≤ F → C ≤ F)
II. H = F→ False (H ≤D = E≤ F → H≤ F)
For either – or condition,
C≤F means C < F or C = F
Here, C = H
so conclusion II can be written as C = F
So, conclusion 1 and conclusion 2 forms complementary pair.
Hence, Either I or II is True is the correct answer.
Confusion Points
Here, C = H so conclusion II can be written as C = F When two elements are equal, then they are replaceable. So, conclusion 1 and conclusion 2 form complementary pairs.
87. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statement to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement: B < S≤ Q < Y = X > C≥ J
Conclusion:
I) S < Y
II) X > B
A. Only I is true
B. Either I or II is true
C. Only II is true
D. Both I and II are true
E. None of these
Solutions
Statement:B < S≤Q < Y = X > C≥ J
i) S < Y⇒ True (asS≤Q < Y⇒ S < Y)
ii) X > B⇒ True (asB < S≤Q < Y = X⇒ B < X⇒ X > B)
Hence, Both I and II are true.
88. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statement to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement: T > U≥ O = P≤ Y < L= B
Conclusion:
I) O≤ Y
II) B > U
A. Only I is true
B. Only II is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. Either I or II is true
E. Neither I nor II is true
Solutions
Statement:T > U≥O = P≤Y < L= B
i)O≤ Y⇒ True (as O = P andP≤Y)
ii) B > U⇒ False (as B = L, L> O = P andU≥Othus relation between B and U cannot be determined)
Hence, Only I is true.
89. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the given question.
There are 6 friends A, B, C, D, E, andF standing in a row according to their height in ascending order from left to right but not necessarily in the same order. C is taller than A andD. B is taller than A, but shorter than E. E is shorter than F. C is taller than E but not the tallest one. D is taller than B but shorter than E.
How many friends are standing to the right of ‘D’?
A. 1
B. 5
C. 3
D. 6
E. 2
Solutions
People: A, B, C, D, E, & F.
1) C is taller than A & D
A/D < C
2) B is taller than A but shorter than E.
A < B < E
3) E is shorter than F.
E < F
4) C is taller than E but not the tallest one.
A < B/D < E < C < F
5) D is taller than B but shorter than E.
A < B < D < E < C < F
Hence, 3 friends are standing to the right of ‘D’.
90. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the given question.
There are 6 friends A, B, C, D, E, andF standing in a row according to their height in ascending order from left to right but not necessarily in the same order. C is taller than A andD. B is taller than A, but shorter than E. E is shorter than F. C is taller than E but not the tallest one. D is taller than B but shorter than E.
How many persons are there in between F and B?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. Four
Solutions
People: A, B, C, D, E, & F.
1) C is taller than A & D
A/D < C
2) Bis taller than A but shorter than E.
A < B < E
3) E is shorter than F.
E < F
4) C is taller than E but not the tallest one.
A < B/D < E < C < F
5)D is taller than B but shorter than E..
A < B < D < E < C < F
Hence, there are three persons in between F and B
91. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the given question.
There are 6 friends A, B, C, D, E, andF standing in a row according to their height in ascending order from left to right but not necessarily in the same order. C is taller than A andD. B is taller than A, but shorter than E. E is shorter than F. C is taller than E but not the tallest one. D is taller than B but shorter than E.
How many friends are taller than ‘A’?
A. 5
B. 4
C. 2
D. 1
E. 3
Solutions
People: A, B, C, D, E, & F.
1) C is taller than A & D
A/D < C
2) Bis taller than A but shorter than E.
A < B < E
3) E is shorter than F.
E < F
4) C is taller than E but not the tallest one.
A < B/D < E < C < F
5)D is taller than B but shorter than E..
A < B < D < E < C < F
Hence, 5 friends are taller than ‘A’.
92. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven friends namely, P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V have examinations on seven different days of the same week from Monday to Sunday but not necessarily in the same order. P’s examination is on Friday. Only one person has examination between P and S. Q has examination just before S. As many persons have an examination before Q as after V. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
Which among the following has examination on Saturday?
A. U
B. T
C. S
D. V
E. R
Solutions
Persons -P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V
1. P’s examination is on Friday.
2. Only one person has an examination between P and S.(So, S’s examination can be on Wednesday or on Sunday)
3. Q has an examination just before S.(So Q’s examination can be on Tuesday or on Saturday)
Case I-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | |
| Sunday |
Case II-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | |
| Wednesday | |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | Q |
| Sunday | S |
4. As many persons have an examination before Q as after V.(So, V’s examination can be on Saturday or on Tuesday)
5. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. (So, case II is eliminated and T’s examination can be Monday or on Thursday)
Case I –
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday |
6. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | U |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday | R |
Hence, V’s examination is on Saturday.
93. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven friends namely, P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V have examinations on seven different days of the same week from Monday to Sunday but not necessarily in the same order. P’s examination is on Friday. Only one person has examination between P and S. Q has examination just before S. As many persons have an examination before Q as after V. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
How many persons have examination between Q and T?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. Four
Solutions
Persons -P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V
1. P’s examination is on Friday.
2. Only one person has an examination between P and S.(So, S’s examination can be on Wednesday or on Sunday)
3. Q has an examination just before S.(So Q’s examination can be on Tuesday or on Saturday)
Case I-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | |
| Sunday |
Case II-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | |
| Wednesday | |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | Q |
| Sunday | S |
4. As many persons have an examination before Q as after V.(So, V’s examination can be on Saturday or on Tuesday)
5. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. (So, case II is eliminated and T’s examination can be Monday or on Thursday)
Case I –
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday |
6. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | U |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday | R |
According to the table:
Hence, no one has an examination between Q and T.
94. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven friends namely, P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V have examinations on seven different days of the same week from Monday to Sunday but not necessarily in the same order. P’s examination is on Friday. Only one person has examination between P and S. Q has examination just before S. As many persons have an examination before Q as after V. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
On which day is U’s examination?
A. Sunday
B. Wednesday
C. Friday
D. Monday
E. Thursday
Solutions
Persons -P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V
1. P’s examination is on Friday.
2. Only one person has examination between P and S.(So, S’s examination can be on Wednesday or on Sunday)
3. Q has examination just before S.(So Q’s examination can be on Tuesday or on Saturday)
Case I-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | |
| Sunday |
Case II-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | |
| Wednesday | |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | Q |
| Sunday | S |
4. As many persons have examination before Q as after V.(So, V’s examination can be on Saturday or on Tuesday)
5. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. (So, case II is eliminatedand T’s examination can be Monday or on Thursday)
Case I –
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday |
6. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | U |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday | R |
According to the table:
Hence, U’s examination is on Thursday.
95. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven friends namely, P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V have examinations on seven different days of the same week from Monday to Sunday but not necessarily in the same order. P’s examination is on Friday. Only one person has examination between P and S. Q has examination just before S. As many persons have an examination before Q as after V. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
Which of the following person has examination on Monday?
A. V
B. T
C. R
D. S
E. Q
Solutions
Persons -P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V
1. P’s examination is on Friday.
2. Only one person has an examination between P and S.(So, S’s examination can be on Wednesday or on Sunday)
3. Q has an examination just before S.(So Q’s examination can be on Tuesday or on Saturday)
Case I-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | |
| Sunday |
Case II-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | |
| Wednesday | |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | Q |
| Sunday | S |
4. As many persons have an examination before Q as after V.(So, V’s examination can be on Saturday or on Tuesday)
5. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. (So, case II is eliminatedand T’s examination can be Monday or on Thursday)
Case I –
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday |
6. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | U |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday | R |
Hence, the T examination is on Monday.
96. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven friends namely, P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V have examinations on seven different days of the same week from Monday to Sunday but not necessarily in the same order. P’s examination is on Friday. Only one person has examination between P and S. Q has examination just before S. As many persons have an examination before Q as after V. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
Which among the following is true?
A. S’s exam is on Sunday
B. No one has examination between Q and P
C. Three persons have examination between R and S
D. S’s examination is just before P’s examination
E. None of these
Solutions
Persons -P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V
1. P’s examination is on Friday.
2. Only one person has an examination between P and S.(So, S’s examination can be on Wednesday or on Sunday)
3. Q has an examination just before S.(So Q’s examination can be on Tuesday or on Saturday)
Case I-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | |
| Sunday |
Case II-
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | |
| Tuesday | |
| Wednesday | |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | Q |
| Sunday | S |
4. As many persons have an examination before Q as after V.(So, V’s examination can be on Saturday or on Tuesday)
5. Not more than one person has examination between S and T. (So, case II is eliminatedand T’s examination can be Monday or on Thursday)
Case I –
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday |
6. Only two persons have examination between R and U but U’s examination is not after R’s examination.
| Days | Persons |
| Monday | T |
| Tuesday | Q |
| Wednesday | S |
| Thursday | U |
| Friday | P |
| Saturday | V |
| Sunday | R |
According to the table:
Hence, three persons have examinations between R and S.
97. If in the word ‘DEFECTED’, all the letters are arranged in the reverse alphabetical order (i.e. Z – A) and then the first four letters are changed to the previous letterand the last four letters are changed to the next letter. After the final arrangement, which of the following letter is the second to the left of the letter which is fourth from the right end?
A. C
B. D
C. E
D. F
E. T
Solutions
Given word: DEFECTED
Reverse alphabetical order (Z-A): TFEEEDDC

Fourth letter from the right end = F
Letter which is second to the left of F = D
Hence, D is the correct answer.
98. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions: H % 1 P ! F S ? * X 7 C T 4 $ 9 3 > @ / 6 N Q 5
How many letters are immediately preceded by consonants and immediately followed by a symbol?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. Four
Solutions
Given series: H % 1 P ! F S ? * X 7 C T 4 $ 9 3 > @ / 6 N Q 5
1) Letters which are immediately preceded by consonants and immediately followed by a symbol
H % 1 P ! F S ? * X 7 C T 4 $ 9 3 > @ / 6 N Q 5
Hence, only one letter is there which is immediately preceded by consonants and immediately followed by a symbol i.e. FS?
99. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions:H % 1 P ! F S ? * X 7 C T 4 $ 9 3 > @ / 6 N Q 5
If all the numbers are dropped from the above arrangement, which of the following will be the fifth to the right of fourth from the left end?
A. ?
B. S
C. *
D. X
E. C
Solutions
Given Series: H % 1 P ! F S ? * X 7 C T 4 $ 9 3 > @ / 6 N Q 5
1) On dropping all the numbers, the arrangement is
Left Side H % P ! F S ? * X C T $ > @ / N Q Right Side
Right Side + Left Side = Left Side
5th to the Right + 4th to the Left = 9th from the Left
Left Side H % P ! F S ? * X C T $ > @ / N Q Right Side
Hence, X is fifth to the right of fourth to the left end.
100. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions:H % 1 P ! F S ? * X 7 C T 4 $ 9 3 > @ / 6 N Q 5
If all the symbols are dropped from the arrangement then what would be the sixth element from the right end?
A. 9
B. T
C. 4
D. C
E. 7
Solutions
Given Series: H % 1 P ! F S ? * X 7 C T 4 $ 9 3 > @ / 6 N Q 5
1) On dropping all the symbols, the arrangement is
Left Side H 1 P F S X 7 C T 49 3 6 N Q 5 Right Side
2) Element which is sixth from the right end
Left Side H 1 P F S X 7 C T 4 9 3 6 N Q 5 Right Side
Hence, 9 is sixth from the right end.
