1. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Seven editors A, D, E, H, N, P and V published different books on the seven different months January, March, May, June, August, September and November but not necessarily in same order. Only one book is published on a particular month. Only two editors published their books between P and N. V published his book fourth months after E. H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days. V published his book after P. D is not the last editor to publish his book. A published his books one of the month after H. D does not publish his book just before N.
Question:
After how many months N published his book with respect to V?
A. One month
B. Three months
C. Two months
D. Four months
E. More than four months
Solution
Here, editors are A, D, E, H, N, P and V; given months are January, March, May, June, August, September and November.
1) V published his book fourth months after E.
2) V published his book after P.
3) Only two editors published their books between P and N.
| Months | Case – 1 | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | |
| March | P | |
| May | V | E |
| June | ||
| August | N | |
| September | V | |
| November |
4) H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days.
5) D is not the last editor to publish his book.
6) D does not publish his book just before N.
| Months | Case – 1(a) | Case – 1(b) | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | E | |
| March | P | P | N |
| May | V | V | E |
| June | H | D | |
| August | N | N | P |
| September | D | D | V |
| November | H | H |
7) A published his books one of the month after H. Therefore, case 1(b) and case 2 are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| Months | Editors |
| January | E |
| March | P |
| May | V |
| June | H |
| August | N |
| September | D |
| November | A |
Since, V published his book in May and N published his book in August which is after three months with respect to V.
Hence, the correct answer is three months.
2. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Seven editors A, D, E, H, N, P and V published different books on the seven different months January, March, May, June, August, September and November but not necessarily in same order. Only one book is published on a particular month. Only two editors published their books between P and N. V published his book fourth months after E. H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days. V published his book after P. D is not the last editor to publish his book. A published his books one of the month after H. D does not publish his book just before N.
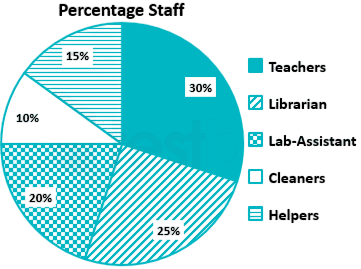
Question:
How many editors published their book between P and E?
A. Three
B. Four
C. Two
D. None
E. One
Solution
Here, editors are A, D, E, H, N, P and V; given months are January, March, May, June, August, September and November.
1) V published his book fourth months after E.
2) V published his book after P.
3) Only two editors published their books between P and N.
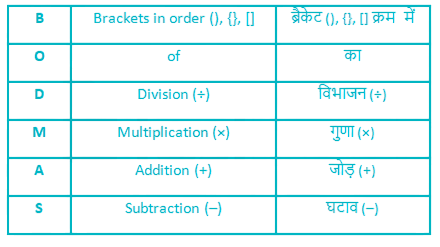
| Months | Case – 1 | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | |
| March | P | |
| May | V | E |
| June | ||
| August | N | |
| September | V | |
| November |
4) H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days.
5) D is not the last editor to publish his book.
6) D does not publish his book just before N.
| Months | Case – 1(a) | Case – 1(b) | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | E | |
| March | P | P | N |
| May | V | V | E |
| June | H | D | |
| August | N | N | P |
| September | D | D | V |
| November | H | H |
7) A published his books one of the month after H. Therefore, case 1(b) and case 2 are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| Months | Editors |
| January | E |
| March | P |
| May | V |
| June | H |
| August | N |
| September | D |
| November | A |
Hence, no one published his book between P and E.
3. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Seven editors A, D, E, H, N, P and V published different books on the seven different months January, March, May, June, August, September and November but not necessarily in same order. Only one book is published on a particular month. Only two editors published their books between P and N. V published his book fourth months after E. H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days. V published his book after P. D is not the last editor to publish his book. A published his books one of the month after H. D does not publish his book just before N.
Question:
Find the odd one out.
A. E
B. P
C. H
D. N
E. V
Solution
Here, editors are A, D, E, H, N, P and V; given months are January, March, May, June, August, September and November.
1) V published his book fourth months after E.
2) V published his book after P.
3) Only two editors published their books between P and N.
| Months | Case – 1 | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | |
| March | P | |
| May | V | E |
| June | ||
| August | N | |
| September | V | |
| November |
4) H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days.
5) D is not the last editor to publish his book.
6) D does not publish his book just before N.
| Months | Case – 1(a) | Case – 1(b) | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | E | |
| March | P | P | N |
| May | V | V | E |
| June | H | D | |
| August | N | N | P |
| September | D | D | V |
| November | H | H |
7) A published his books one of the month after H. Therefore, case 1(b) and case 2 are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| Months | Editors |
| January | E |
| March | P |
| May | V |
| June | H |
| August | N |
| September | D |
| November | A |
Since, each editor except H published his book in the month which has odd number of days whereas H published his book in the month which has even number of days.
Hence, the odd one is H.
4. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Seven editors A, D, E, H, N, P and V published different books on the seven different months January, March, May, June, August, September and November but not necessarily in same order. Only one book is published on a particular month. Only two editors published their books between P and N. V published his book fourth months after E. H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days. V published his book after P. D is not the last editor to publish his book. A published his books one of the month after H. D does not publish his book just before N.
Question:
Who among the following editor published his book just before the person who published his book just after D?
A. P
B. V
C. N
D. H
E. D
Solution
Here, editors are A, D, E, H, N, P and V; given months are January, March, May, June, August, September and November.
1) V published his book fourth months after E.
2) V published his book after P.
3) Only two editors published their books between P and N.
| Months | Case – 1 | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | |
| March | P | |
| May | V | E |
| June | ||
| August | N | |
| September | V | |
| November |
4) H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days.
5) D is not the last editor to publish his book.
6) D does not publish his book just before N.
| Months | Case – 1(a) | Case – 1(b) | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | E | |
| March | P | P | N |
| May | V | V | E |
| June | H | D | |
| August | N | N | P |
| September | D | D | V |
| November | H | H |
7) A published his books one of the month after H. Therefore, case 1(b) and case 2 are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| Months | Editors |
| January | E |
| March | P |
| May | V |
| June | H |
| August | N |
| September | D |
| November | A |
Since, A published his book just after D and just before A, D published his book.
Hence, the correct answer is D.
5. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Seven editors A, D, E, H, N, P and V published different books on the seven different months January, March, May, June, August, September and November but not necessarily in same order. Only one book is published on a particular month. Only two editors published their books between P and N. V published his book fourth months after E. H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days. V published his book after P. D is not the last editor to publish his book. A published his books one of the month after H. D does not publish his book just before N.
Question:
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
A) No one published his book just before E.
B) More than two persons published their book between P and D.
C) V and H published their book adjacent to each other.
A. Only A
B. Neither A nor B
C. Neither B nor C
D. Both A and C
E. All of these
Solution
Here, editors are A, D, E, H, N, P and V; given months are January, March, May, June, August, September and November.
1) V published his book fourth months after E.
2) V published his book after P.
3) Only two editors published their books between P and N.
| Months | Case – 1 | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | |
| March | P | |
| May | V | E |
| June | ||
| August | N | |
| September | V | |
| November |
4) H and D published their books in the month which has less than 31 days.
5) D is not the last editor to publish his book.
6) D does not publish his book just before N.
| Months | Case – 1(a) | Case – 1(b) | Case – 2 |
| Editors | Editors | Editors | |
| January | E | E | |
| March | P | P | N |
| May | V | V | E |
| June | H | D | |
| August | N | N | P |
| September | D | D | V |
| November | H | H |
7) A published his books one of the month after H. Therefore, case 1(b) and case 2 are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| Months | Editors |
| January | E |
| March | P |
| May | V |
| June | H |
| August | N |
| September | D |
| November | A |
Since, all the given statements are correct.
Hence, the correct answer is All of these.
6. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
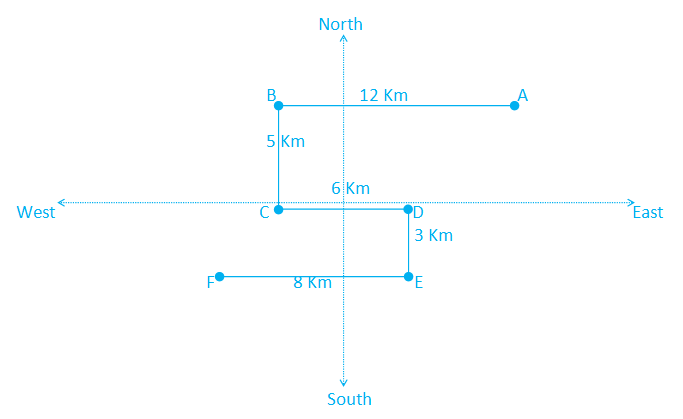
Point D is 6 Km to the east of point C. Point F is 8 Km to the west of point E. Point A is 12 Km to the east of point B. Point D is 3 Km to the north of point E. Point C is 5 Km to the south of point B.
Question:
What is the direction of point F with respect to point A?
A. Northeast
B. Southwest
C. Southeast
D. Northwest
E. West
Solution
1) Point A is 12 Km to the east of point B.
2) Point C is 5 Km to the south of point B.
3) Point D is 6 Km to the east of point C.

4) Point D is 3 Km to the north of point E.
5) Point F is 8 Km to the west of point E.

Hence, point F is in Southwest direction with respect to point A.Question:
What is the direction of point F with respect to point A?
7. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Point D is 6 Km to the east of point C. Point F is 8 Km to the west of point E. Point A is 12 Km to the east of point B. Point D is 3 Km to the north of point E. Point C is 5 Km to the south of point B.
Question:
Find the odd one out.
A. AC
B. DF
C. CF
D. AE
E. CE
Solution
1) Point A is 12 Km to the east of point B.
2) Point C is 5 Km to the south of point B.
3) Point D is 6 Km to the east of point C.

4) Point D is 3 Km to the north of point E.
5) Point F is 8 Km to the west of point E.

Since, each pair except CE represents first point is in Northeast direction with respect to the second point but C is in Northwest direction with respect to E.
Hence, the odd one is CE.
8. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Point D is 6 Km to the east of point C. Point F is 8 Km to the west of point E. Point A is 12 Km to the east of point B. Point D is 3 Km to the north of point E. Point C is 5 Km to the south of point B.
Question:
What is the direction of point B with respect to point E?
A. North
B. Southwest
C. Southeast
D. West
E. Northwest
Solution
1) Point A is 12 Km to the east of point B.
2) Point C is 5 Km to the south of point B.
3) Point D is 6 Km to the east of point C.

4) Point D is 3 Km to the north of point E.
5) Point F is 8 Km to the west of point E.
Hence, point B is in Northwest direction with respect to point E.
9. Direction: In the question below there are three statements followed by two conclusions I, and II. You have to take the three given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
I. Only brush is pencil.
II. Only few brushes are eraser.
III. Some erasers are curtains.
Conclusions:
I. Some pencils are eraser.II. Some erasers are brushes.
A. Only conclusion I follows.
B. Only conclusion II follows.
C. Both conclusions I and II follow.
D. None of the conclusion follows.
E. Either conclusion I or II follows.
Solution
Note:
I. Only brush is pencil.
This implies that
All pencils are brush.
No pencil is eraser.
No pencil is curtain.
II. Only few brushes are eraser.
This implies that
All brushes are not eraser.
Some brushes are eraser.
Some brushes are not eraser.
The least possible Venn diagram is given below

Conclusions:
I. Some pencils are eraser. → False (as only brush is pencil)
II. Some erasers are brushes. → True (as only a few brushes are erasers)Only conclusion II follows.
10. Direction: In the question below there are three statements followed by two conclusions I, and II. You have to take the three given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
I. Few Kw are Sd.
II. Every Sd is Zx.
III. Only few Fv are Zx.
Conclusions:
I. Some Fv are Kw.II. All Fv are Zx.
A. Only conclusion I follows.
B. Only conclusion II follows.
C. Both conclusions I and II follow.
D. None of the conclusion follows.
E. Either conclusion I or II follows.
Solution
Note:
I. Few Kw are Sd.
Implies that
Some Kw are Sd.
II. Every Sd is Zx.
Implies that
All Sd are Zx.
III. Only few Fv are Zx.
Implies that
Some Fv are Zx.
All Fv are not Zx.
Some Fv are not Zx.
The least possible Venn diagram is given below

Conclusions:
I. Some Fv are Kw. → False (it is possible but not definite)
II. All Fv are Zx. → False (as only a few Fv are Zx)Hence, none of the conclusion follows.
11. Direction: In the question below there are three statements followed by three conclusions I, II and III. You have to take the three given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
I. Only rivers are football.
II. Some rivers are cold.
III. Only a few colds are temperature.
Conclusions:
I. Some colds are not temperature.
II. Some cold are football.III. No football is temperature.
A. Both conclusion I and conclusion II follow.
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Only conclusion III follows
D. Both conclusion II and conclusion III follow.
E. Both conclusion I and conclusion III follow.
Solution
Note:
I. Only rivers are football.
The above statement implies that
All football are rivers.
No football is cold.
No football is temperature.
III. Only a few colds are temperature.
The above statement implies that
All colds are not temperature.
Some colds are temperature.
Some colds are not temperature.
The least possible Venn diagram is given below

Conclusions:
I. Some colds are not temperature.→ True (As Only a few colds are temperature, which means some cold are temperature and some cold are not temperature).
II. Some cold are football.→ False (As Only rivers are football, which means All footballs are rivers and footballs will not have any positive relationship with any other element except, river).
III. No football is temperature. → True (As only rivers are football, which means All footballs are rivers and footballs will not have any positive relationship with any other element except, river).Hence, Both conclusion I and III follows.
12. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
A certain number of persons sit on the horizontal row and faces towards the north direction. The number of persons sit to the left of U is one more than that of to the right of V. Five persons sit between B and T. U sits sixth to the left of R. N sits third to the right of B. Only one person sits between T and R. U sits third from the left end. As many persons sit between B and U as many between R and V. B sits one of the places to the left of R.
Question:
Who among the following sits immediate next to U?
A. B
B. N
C. T
D. R
E. V
Solution
Given: A certain number of persons sit on the horizontal row and faces towards the north direction.
1) U sits third from the left end.
2) U sits sixth to the left of R.
3) Only one person sits between T and R.

4) Five persons sit between B and T.
5) As many persons sit between B and U as many between R and V.
6) B sits one of the places to the left of R.
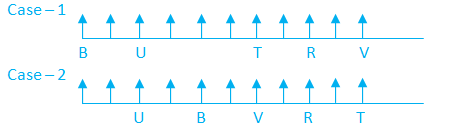
7) The number of persons sit to the left of U is one more than that of to the right of V. Therefore, case 2 is eliminated.
8) N sits third to the right of B. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows

Hence, N sits immediate next to U.
13. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
A certain number of persons sit on the horizontal row and faces towards the north direction. The number of persons sit to the left of U is one more than that of to the right of V. Five persons sit between B and T. U sits sixth to the left of R. N sits third to the right of B. Only one person sits between T and R. U sits third from the left end. As many persons sit between B and U as many between R and V. B sits one of the places to the left of R.
Question:
How many person(s) sit to the right of V?
A. Two persons
B. Three persons
C. None
D. Four persons
E. One person
Solution
Given: A certain number of persons sit on the horizontal row and faces towards the north direction.
1) U sits third from the left end.
2) U sits sixth to the left of R.
3) Only one person sits between T and R.

4) Five persons sit between B and T.
5) As many persons sit between B and U as many between R and V.
6) B sits one of the places to the left of R.
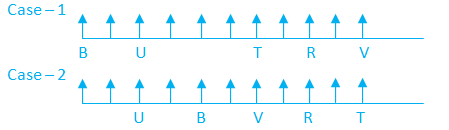
7) The number of persons sit to the left of U is one more than that of to the right of V. Therefore, case 2 is eliminated.
8) N sits third to the right of B. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
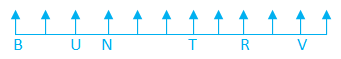
Hence, only one person sit to the right of V.
14. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
A certain number of persons sit on the horizontal row and faces towards the north direction. The number of persons sit to the left of U is one more than that of to the right of V. Five persons sit between B and T. U sits sixth to the left of R. N sits third to the right of B. Only one person sits between T and R. U sits third from the left end. As many persons sit between B and U as many between R and V. B sits one of the places to the left of R.
Question:
Which of the following statement is/ are correct?
A. B sits three places away from N.
B. U sits fourth to the right of T.
C. R sits second to the right of V.
D. More than two persons sit between T and R.
E. All are correct.
Solution
Given: A certain number of persons sit on the horizontal row and faces towards the north direction.
1) U sits third from the left end.
2) U sits sixth to the left of R.
3) Only one person sits between T and R.

4) Five persons sit between B and T.
5) As many persons sit between B and U as many between R and V.
6) B sits one of the places to the left of R.

7) The number of persons sit to the left of U is one more than that of to the right of V. Therefore, case 2 is eliminated.
8) N sits third to the right of B. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows

Since, B sits third to the left of N. Therefore, statement first is correct.
U sits fourth to the left of T. Therefore, statement second is incorrect.
R sits second to the left of V. Therefore, statement third is incorrect.
Only one person sits between T and R. Therefore, statement fourth is incorrect.
Hence, the correct statement is B sits three places away from N.
15. Direction: Study the following questions carefully and answer the following questions: X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J
Question:
Which element is the 4th to the right of 8th element to the left of ‘M’?
A. &
B. 7
C. G
D. #
E. H
Solution
Given series:
Left Side X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J Right Side
Trick: 8th to the left – 4th to the right = 4th to the left (left of M in the given series)
The element which is 4th to the left of M:
X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J
Hence, the element which is 4th to the right of 8th to the left of M is G.
16. Direction: Study the following questions carefully and answer the following questions:X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J
Question:
How many such prime numbers are there which preceded by vowels and followed by a consonant?
A. Two
B. Four
C. One
D. Three
E. Five
Solution
Given series:
Left Side X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J Right Side
Prime numbers are: 2, 3, 5, 7, and 11.
Vowels are: A, E, I, O, U
The prime numbers precedes vowel and follows a constant
X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J
Hence, there are three prime numbers that preceded by a vowel and followed by a consonant: E 3 F, U 2 Z, I 7 G.
17. Direction: Study the following questions carefully and answer the following questions:X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J
Question:
How many such symbols are there which are immediately followed by either a number or a consonant?
A. Two
B. Four
C. Three
D. Five
E. Less than two
Solution
Given series:
Left Side X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J Right Side
The symbols that are immediately followed by either a number or a consonant:
X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J
Hence, there are four symbols that are immediately followed by either a number or a consonant: & S, # H, + 9, and @ 8.
18. Direction: Study the following questions carefully and answer the following questions:X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J
Question:
If we drop all the prime numbers and symbols from the above series then which element is 9th from the left end?
A. S
B. C
C. U
D. &
E. Z
Solution
Given series:
Left Side X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J Right Side
Prime numbers are: 2, 3, 5, and 7.
1) If all the prime numbers and symbols are dropped:
Left end X Y E F V B C U Z S I G H P M 9 8 N A 1 J Right end
2) Element which is 9th from the left end is Z.
Hence, the correct answer is Z.
19. Direction: Study the following questions carefully and answer the following questions:X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J
Question:
Which of the following element is 7th to the left of 8th element from the right end in the above arrangement?
A. S
B. I
C. 9
D. 7
E. G
Solution
Given Series:
Left Side X Y % E 3 F 7 V B 5 C * U 2 Z & S I 7 G # H P M + 9 $ @ 8 N A 1 J Right Side
8th from the right + 7th to the left = 15th from the right end
Clearly, 15th element from the right end is 7.
20. If in the number “85427631”, the digits in the number which are not divisible by 2 are added by 1, then which digit comes second to the left of the digit which is fourth from the right side of the newly formed number?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
E. None of these
Solution
Given number: 85427631
Operation: Those digits which are not divisible by 2 in the given number are added by 1.
| Given number | 8 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 1 |
| Operation | – | +1 | – | – | +1 | – | +1 | +1 |
| Output | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
Therefore, the fourth digit from the right side is 8 and the number which comes second to the left of 8 is 4.
Hence, the correct answer is 4.
21. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
“Stars need darkness to shine” is coded as “rock brick building road pebble”
“Stars appear in darkness” is coded as “gate cement brick rock”
“Need help to shine” is coded as “sand pebble building road”“Light need darkness to appear” is coded as “hard pebble brick gate road”
Question:
What is the code for “darkness”?
A. brick
B. road
C. building
D. pebble
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
The words are coded as given below:

Hence, “darkness” is coded as “brick”.
22. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
“Stars need darkness to shine” is coded as “rock brick building road pebble”
“Stars appear in darkness” is coded as “gate cement brick rock”
“Need help to shine” is coded as “sand pebble building road”“Light need darkness to appear” is coded as “hard pebble brick gate road”
Question:
What is the code for “light help”?
A. Hard cement
B. Sand cement
C. Hard sand
D. Sand gate
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
The words are coded as given below:

Hence, “Light help” is coded as “hard sand”.
23. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
“Stars need darkness to shine” is coded as “rock brick building road pebble”
“Stars appear in darkness” is coded as “gate cement brick rock”
“Need help to shine” is coded as “sand pebble building road”“Light need darkness to appear” is coded as “hard pebble brick gate road”
Question:
Which of the following word is coded as “gate”?
A. stars
B. appear
C. in
D. darkness
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
The words are coded as given below:

Hence, “Appear” is coded as “gate”.
24. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W are living in a four-story building such that the ground floor is numbered as 1 and continued so till the topmost floor is numbered as 4. In the building, there are two groups of flats X and Y on each floor such that Flat X is to the east of Flat Y. Floor number 2 of flat X is immediately above floor number 1 of flat X and so on.
There are two floor between P and T both of them live in the same flat. Only one Floor between Q and U, who lives east of P. V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q. One floor is between T and S, who lives west of V. R lives North-west of W. Both Q and U live in the same flat.
Question:
How many floors are there between P and S?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. None
E. None of these
Solution
1) Two floor between P and T both of them live in the same flat.
2) Only floor between Q and U, who lives east of P.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | Q | |||
| 2 | Q | |||
| 1 | T | P | U | |
3) V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q.
4) One person lives between T and S, who lives west of V.
5) R lives North-west of W, we cannot place R in case 2 so case 2 will be eliminated.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | S | V | Q | |
| 2 | R | Q | S | V |
| 1 | T | W | P | U |
So, the final arrangement:
| Floor | Case1 | |
| Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U |
| 3 | S | V |
| 2 | R | Q |
| 1 | T | W |
Hence, No floors are there between P and S.
25. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W are living in a four-story building such that the ground floor is numbered as 1 and continued so till the topmost floor is numbered as 4. In the building, there are two groups of flats X and Y on each floor such that Flat X is to the east of Flat Y. Floor number 2 of flat X is immediately above floor number 1 of flat X and so on.
There are two floor between P and T both of them live in the same flat. Only one Floor between Q and U, who lives east of P. V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q. One floor is between T and S, who lives west of V. R lives North-west of W. Both Q and U live in the same flat.
Question:
Who among the following pair of person live on the topmost floor?
A. SR
B. QW
C. PS
D. UV
E. PU
Solution
1) Two floor between P and T both of them live in the same flat.
2) Only floor between Q and U, who lives east of P.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | Q | |||
| 2 | Q | |||
| 1 | T | P | U | |
3) V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q.
4) One floor is between T and S, who lives west of V.
5) R lives North-west of W, we cannot place R in case 2 so case 2 will be eliminated.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | S | V | Q | |
| 2 | R | Q | S | V |
| 1 | T | W | P | U |
So, the final arrangement:
| Floor | Case1 | |
| Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U |
| 3 | S | V |
| 2 | R | Q |
| 1 | T | W |
Hence, PU lives on the topmost floor.
26. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W are living in a four-story building such that the ground floor is numbered as 1 and continued so till the topmost floor is numbered as 4. In the building, there are two groups of flats X and Y on each floor such that Flat X is to the east of Flat Y. Floor number 2 of flat X is immediately above floor number 1 of flat X and so on.
There are two floor between P and T both of them live in the same flat. Only one Floor between Q and U, who lives east of P. V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q. One floor is between T and S, who lives west of V. R lives North-west of W. Both Q and U live in the same flat.
Question:
Who among the following person lives immediately above V?
A. R
B. The one who lives west of Q
C. S
D. The one who lives east of P
E. None of these
Solution
1) Two floor between P and T both of them live in the same flat.
2) Only floor between Q and U, who lives east of P.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | Q | |||
| 2 | Q | |||
| 1 | T | P | U | |
3) V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q.
4) One floor is between T and S, who lives west of V.
5) R lives North-west of W, we cannot place R in case 2 so case 2 will be eliminated.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | S | V | Q | |
| 2 | R | Q | S | V |
| 1 | T | W | P | U |
So, the final arrangement:
| Floor | Case1 | |
| Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U |
| 3 | S | V |
| 2 | R | Q |
| 1 | T | W |
Hence, The one who lives east of P.
27. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W are living in a four-story building such that the ground floor is numbered as 1 and continued so till the topmost floor is numbered as 4. In the building, there are two groups of flats X and Y on each floor such that Flat X is to the east of Flat Y. Floor number 2 of flat X is immediately above floor number 1 of flat X and so on.
There are two floor between P and T both of them live in the same flat. Only one Floor between Q and U, who lives east of P. V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q. One floor is between T and S, who lives west of V. R lives North-west of W. Both Q and U live in the same flat.
Question:
R lives on which floor and in which flat respectively?
A. 3rd floor, flat X
B. 2nd floor, Flat X
C. 4th floor, Flat Y
D. 2nd floor, Flat Y
E. 3rd floor, Flat Y
Solution
1) Two floor between P and T, both of them live in the same flat.
2) Only floor between Q and U, who lives east of P.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | Q | |||
| 2 | Q | |||
| 1 | T | P | U | |
3) V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q.
4) One floor is between T and S, who lives west of V.
5) R lives North-west of W, we cannot place R in case 2 so case 2 will be eliminated.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | S | V | Q | |
| 2 | R | Q | S | V |
| 1 | T | W | P | U |
So, the final arrangement:
| Floor | Case1 | |
| Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U |
| 3 | S | V |
| 2 | R | Q |
| 1 | T | W |
Hence, R lives on the 2nd floor, Flat Y.
28. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Eight persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W are living in a four-story building such that the ground floor is numbered as 1 and continued so till the topmost floor is numbered as 4. In the building, there are two groups of flats X and Y on each floor such that Flat X is to the east of Flat Y. Floor number 2 of flat X is immediately above floor number 1 of flat X and so on.
There are two floor between P and T both of them live in the same flat. Only one Floor between Q and U, who lives east of P. V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q. One floor is between T and S, who lives west of V. R lives North-west of W. Both Q and U live in the same flat.
Question:
Who among the following person lives west of W?
A. The one who lives immediately above S
B. P
C. The one who lives immediately below R
D. S
E. None of these
Solution
1) Two floor between P and T, both of them live in the same flat.
2) Only floor between Q and U, who lives east of P.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | Q | |||
| 2 | Q | |||
| 1 | T | P | U | |
3) V lives either immediately above or immediately below Q.
4) One floor is between T and S, who lives west of V.
5) R lives North-west of W, we cannot place R in case 2 so case 2 will be eliminated.
| Floor | Case1 | Case 2 | ||
| Flat Y | Flat X | Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U | T | |
| 3 | S | V | Q | |
| 2 | R | Q | S | V |
| 1 | T | W | P | U |
So, the final arrangement:
| Floor | Case1 | |
| Flat Y | Flat X | |
| 4 | P | U |
| 3 | S | V |
| 2 | R | Q |
| 1 | T | W |
Hence, The one who lives immediately below R.
29. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which conclusion among the given conclusions is/are definitely true, and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
S = H ≥ P = K < L; M > J = Q > K
Conclusions:
I. H ≥ M
II. M ≤ L
A. Only II is true
B. Only I is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. Either I or II is true
E. None is true
Solution
Given Statements: S = H ≥ P = K < L; M > J = Q > K
On Combining: S = H ≥ P = K < Q = J < M; M > J = Q > K = P < L
Conclusions:
I. H ≥ M → False (As, S = H ≥ P = K < Q = J < M → Clear relation between H and M cannot be determined)
II. M ≤ L → (As, M > J = Q > K = P < L → Clear relation between M and L cannot be determined)
Hence, none of the conclusion is true
30. Direction:In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
H < A > R = D; I ≤ K ≥ P; H < P
Conclusions:
I. K > RII. A ≤ K
A. Only II is true
B. Only I is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. Either I or II is true
E. None is true
Solution
Given Statements: H < A > R = D; I ≤ K ≥ P; H < P
On Combining: I ≤ K ≥ P > H < A > R = D
Conclusions:
I. K > R → False (As, K ≥ P > H < A > R → Clear relation between K and R cannot be determined)
II. A ≤ K → False (As, K ≥ P > H < A > R = D→ Clear relation between A and K cannot be determined)
Hence, none of the conclusion is true.
31. Direction:In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
D > A ≥ J = B < P < Q; W > A = F
Conclusions:
I. D > W
II. D < W
A. Only II is true
B. Only I is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. Neither I nor II is true
E. Either I or II is true
Solution
Given Statements: D > A ≥ J = B < P < Q; W > A = F
On Combining: W > F = A ≥ J = B < P < Q; D > A = F < W
Conclusions:
I. D > W → False (As, D > A = F < W → Clear relation between D and W cannot be determined)
II. D < W → False (As, D > A = F < W → Clear relation between D and W cannot be determined)
Hence, neither I nor II is true
32. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Eight persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W – are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order, facing the center. S sits second to the left of P and R sits to the immediate right of P. W sits opposite to T and W is not a neighbor of U. Only 2 people sit between V and R. Q sits to the immediate right of V.
Question:
How many people are sitting between left of V and right of W?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 1
E. 5
Solution
Eight people: P, Q, R, S, T, M, N, and K.
1. S sits second to the left of P and R sits to the immediate right of P

2. Only 2 people sit between V and R.
3. Q sits to the immediate right of V.
3. W sits opposite to T. (There are 2 possible cases)


4. W is not a neighbor of U.
The only position left for U is to the immediate right of R. (Thus case 2 is eliminated)

Four people are sitting between left of V and right of W, they are T, U, R and P.
Hence, the correct option is 3.
33. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Eight persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W – are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order, facing the center. S sits second to the left of P and R sits to the immediate right of P. W sits opposite to T and W is not a neighbor of U. Only 2 people sit between V and R. Q sits to the immediate right of V.
Question:
Who sits third to the right of T?
A. P
B. Q
C. R
D. W
E. S
Solution
Eight people: P, Q, R, S, T, M, N, and K.
1. S sits second to the left of P and R sits to the immediate right of P

2. Only 2 people sit between V and R.
3. Q sits to the immediate right of V.

3. W sits opposite to T. (There are 2 possible cases)


4. W is not a neighbor of U.
The only position left for U is to the immediate right of R. (Thus case 2 is eliminated)

The person third to the right of T is S.
Hence, the correct option is 5.
34. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Eight persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W – are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order, facing the center. S sits second to the left of P and R sits to the immediate right of P. W sits opposite to T and W is not a neighbor of U. Only 2 people sit between V and R. Q sits to the immediate right of V.
Question:
Who sits opposite to the person who sits second to the left of W?
A. Q
B. R
C. U
D. V
E. T
Solution
Eight people: P, Q, R, S, T, M, N, and K.
1. S sits second to the left of P and R sits to the immediate right of P
2. Only 2 people sit between V and R.
3. Q sits to the immediate right of V.

3. W sits opposite to T. (There are 2 possible cases)


4. W is not a neighbor of U.
The only position left for U is to the immediate right of R. (Thus case 2 is eliminated)

The person second to the left of W is Q and the person opposite to Q is R.
Hence, the correct option is 2.
35. If it is possible to make a four letters meaningful word from the second letter, sixth letter, ninth letter and tenth letter of a word “BLANDISHMENT”, then which of the following is the first letter of the word ? If more than one such word can be made, then give “X” as the answer, and if no such word can be formed then give “Z” as the answer.
A. I
B. M
C. Z
D. X
E. L
Solution
Given word:- BLANDISHMENT
The second letter is ‘L’, the sixth letter is ‘I’, the ninth letter is ‘M’ and tenth letter is ‘E’.
The possible four letter meaningful word formed by using these letters are Lime and Mile.
Hence, the correct answer is X.
36. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the questions given below it:
Number of students in three different Colleges over the years.

Question:
What was the average number of students in all the Colleges together in the year 2018?
A. 1800
B. 1600
C. 2600
D. 1300
E. 1500
Solution
Total students in College A in 2018 = 2000
Total students in College B in 2018 = 3200
Total students in College C in 2018 = 2600
Required average = 7800/3 = 2600
37. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the questions given below it:
Number of students in three different Colleges over the years.

Question:
Total number of students in college B and college C together in the year 2016 was what percentage of the total number of students in college B and college C together in the year 2019?
A. 97.5%
B. 86%
C. 87.5%
D. 92.5%
E. 98%
Solution
Total number of students in college B in 2016 = 1800
Total number of students in college C in 2016 = 2400
Total number of students in college B in 2019 = 3000
Total number of students in college C in 2019 = 1800
Required percentage = (1800 + 2400)/(3000 + 1800) × 100 = 87.5%
38. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the questions given below it:
Number of students in three different Colleges over the years.

Question:
How many times the total number of students in all the three colleges A, B and C together was exactly equal among the given years?
A. Two
B. Three
C. Four
D. One
E. None
Solution
Total students in 2015 = 2300 + 1500 + 2500 = 6300
Total students in 2016 = 2100 + 1800 + 2400 = 6300
Total students in 2019 = 1500 + 3000 + 1800 = 6300
39. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the questions given below it:
Number of students in three different Colleges over the years.

Question:
What was the average number of students in college A over all the years together?
A. 2100
B. 1800
C. 1300
D. 2400
E. 1900
Solution
Total students in College A in 2014 = 1100
Total students in College A in 2015 = 2500
Total students in College A in 2016 = 2100
Total students in College A in 2017 = 1600
Total students in College A in 2018 = 2000
Total students in College A in 2019 = 1500
Required average = (1100 + 2500 + 2100 + 1600 + 2000 + 1500)/6 = 10800/6 = 1800
40. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the questions given below it:
Number of students in three different Colleges over the years.

Question:
What was the difference between the total number of students in all the colleges together in year 2015 and number of students in school B in the year 2017?
A. 4500
B. 4200
C. 3300
D. 4800
E. 4100
Solution
Total students in College A in 2015 = 2500
Total students in College B in 2015 = 1500
Total students in College C in 2015 = 2300
Total number of students in school B in the year 2017 = 2100
Required difference = (2500 + 1500 + 2300) – 2100 = 4200
41. A motor boat, whose speed is 15 km/hr in still water goes 30 km downstream and comes back in a total of 4 hrs 30 mins. The speed of the stream (in km/hr) is:-
A. 5 km/hr.
B. 10 km/hr.
C. 15 km/hr.
D. 20 km/hr.
E. 25 km/hr.
Solution
Given:
Speed in still water = 15 km/hr
Total distance = 30 km
Total time = 4 hrs 30 mins = 412 hr = 9/2 hr.
Formula used:
Distance = Speed × Time
Calculation:
Let the speed of the of the stream be X km/hr
Speed upstream = (15 – X) km/hr
Speed downstream = (15 + X) km/hr
According to question:
⇒ [30/(15 + x) + 30/(15 – X)] = 9/2
⇒ (450 – 30X + 450 + 30X) / (15 + X) × (15 – X) = 9/2
⇒ 900 = [(152 – X2) × 9/2]
⇒ (900 × 2/9) = 225 – X2
⇒ X2 = 225 – 200
⇒ X2 = 25
⇒ x = 5
∴ Speed of the stream is 5 km/hr.
Key Points
If the speed of boat or swimmer is X km/hr and the speed of the stream is y km/hr then,
Speed of boat upstream = (X – Y) km/hr.
Speed of boat downstream = (X + Y) km/hr.
42. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?117, 77, ?, 36, 18, 8
A. 43
B. 56
C. 49
D. 67
E. None of these
Solution
Calculation:
The number series follows following pattern:
Unit digit × (Remaining number)
⇒ 117 = 11 × 7 = 77
⇒ 77 = 7 × 7 = 49
⇒ 49 = 4 × 9 = 36
⇒ 36 = 3 × 6 = 18
⇒ 18 = 1 × 8 = 8∴ The value of ? is 49.
43. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?12, 17, 34, 39, 78, ?, 166
A. 156
B. 161
C. 83
D. 85
E. 88
Solution
Calculation:
A series is given and we have to calculate value in the blank
So, by observing we get
12 = 6 × 2
17 = 12 + 5
34 = 17 × 2
39 = 34 + 5
78 = 39 × 2
83 = 78 + 5
⇒ For step 1 we are adding 5 to the number and then result is multiplied with 2 and same is repeated.
Was the solution helpful?Yes
44. Find out the missing number in the following series.3, 19, 44, 80, 129, ?
A. 190
B. 193
C. 200
D. 180
E. 177
Solution
Explanation:
3 + 42 = 19
19 + 52 = 44
44 + 62 = 80
80 + 72 = 129
129 + 82 = 193
45. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
1, 3, 7, 15, ?, 63, 127
A. 32
B. 31
C. 33
D. 35
E. None
Solution
The series follows the following pattern
1
1 + 21 = 3
3 + 22 = 7
7 + 23 = 15
15 + 24 = 31
31 + 25 = 63
63 + 26 = 126
∴ The missing term in the series is 31.
Note : Addition of powers of 2
46. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
200, 199, 195, 186, 170, 145, ?
A. 115
B. 103
C. 120
D. None of these
E. 109
Solution
Calculation:
The series follows the following pattern:
⇒ 200 – 12 = 199
⇒ 199 – 22 = 195
⇒ 195 – 32 = 186
⇒ 186 – 42 = 170
⇒ 170 – 52 = 145
⇒ 145 – 62 = 109
∴ The value of ? is 109
47. Ram’s age after six years will be 5/11 times of his father’s age at that time. Four years ago the ratio of their ages was 5 : 14. What is the Ram’s father’s present age?
A. 55 years
B. 60 years
C. 62 years
D. 65 years
E. 70 years
Solution
Given:
Ram’s age after six years will be 5/11 times of his father’s age
Four years ago the ratio of their ages was 5 : 14
Calculation:
Let, Ram’s present age is = a, and his father’s present age is = b
According to the question,
(a + 6) = (5/11) × (b + 6)
⇒ a = {(5b + 30)/11} – 6 ————– (i)
Again,
(a – 4)/(b – 4) = 5/14
⇒ 14a – 56 = 5b – 20
⇒ 14a = 5b + 36
⇒ a = (5b + 36)/14
Now using the value of ‘a’ from equation (i)
⇒ {(5b + 30)/11} – 6 = (5b + 36)/14
⇒ (5b + 30 – 66)/11 = (5b + 36)/14
⇒ 70b – 504 = 55b + 396
⇒ 15b = 900
⇒ b = 60
∴ The present age of Ram’s father is 60 years
48. Direction: Read the following graph carefully and answer the questions that follow:

Total school staff in city = 40000
Question:
If 60% of Teachers and 30% of Librarian are females, then what is the difference between the number of male Librarians and Male Teachers in the city?
A. 2200
B. 1750
C. 1920
D. 2660
E. 2560
Solution
GIVEN:
Teachers = 30%
Librarian = 25%
CONCEPT:
Here we will calculate the difference by subtracting the number of male teachers by the number of male librarians.
FORMULAE USED:
Difference = Number of male teachers – Number of male librarian
CALCULATION:
Total number of Teachers = 40000 × 30 / 100 = 12000
Number of male teachers = 40 × 120 = 4800
Total number of Librarian = 40000 × 25 / 100 = 10000
Number of male librarian = 70 × 100 = 7000
Required difference = 7000 – 4800∴ Required difference = 2200
49. Direction: Read the following graph carefully and answer the questions that follow:

Total school staff in city = 40000
Question:
What is the ratio between the number of Helpers and Cleaners in the city?
A. 5 : 6
B. 3 : 4
C. 4 : 5
D. 1 : 2
E. 3 : 2
Solution
GIVEN:
Helpers in city = 15%
Cleaners in city = 10%
CONCEPT:
In this question we first need to calculate the number of helpers and cleaners and then calculate the ratio in between them.
FORMULAE USED:
Required ratio = Total number of Helpers in city: Total number of Cleaners in city
CALCULATION:
Total number of Helpers in city = 40000 × 15 / 100 = 6000
Total number of Cleaners in city = 40000 × 10 / 100 = 4000
Required ratio = 6000 : 4000∴ Required ratio = 3 : 2
50. Direction: Read the following graph carefully and answer the questions that follow:
Total school staff in city = 40000
Question:
What will be the average number of female staff if 45% of each category are females?
A. 3400
B. 3100
C. 3900
D. 4000
E. 3600
Solution
GIVEN:
Female staff in city = 45%
CONCEPT:
In this question to calculate the average we first need to calculate the total number of female staff in the city.
FORMULAE USED:
Required average = Total number of female staff / 5
CALCULATION:
Total number of female staff in city = 45 × 40000 / 100 = 18000
Required average = 18000 / 5∴ Required average = 3600
51. Direction: Read the following graph carefully and answer the questions that follow:

Total school staff in city = 40000
Question:
Approximately, by what percent of the number of Lab Assistants is more than the number of Helpers in the city?
A. 35%
B. 75%
C. 80%
D. 33%
E. 81%
Solution
GIVEN:
Helpers in city = 15%
Lab Assistant in city = 20%
CONCEPT:
In this question we first need to calculate the number of helpers and lab assistants in the city and then calculate the percentage in between them.
FORMULAE USED:
Required percentage = (Total number of Lab Assistant – Total number of Helpers) × 100 / Total number of Helpers
CALCULATION:
Total number of Helpers in city = 40000 × 15 / 100 = 6000
Total number of Lab Assistant in city = 40000 × 20 / 100 = 8000
Required percentage = (8000 – 6000) × 100 / 6000∴ Required percentage = 33.33%
52. Direction: Read the following graph carefully and answer the questions that follow:

Total school staff in city = 40000
Question:
If 2500 of the staff of city are adults and they are not advised to come on duty due to crisis, then what percent is the number of remaining staff of the total staff of city?
A. 90%
B. 80%
C. 94%
D. 91%
E. 98%
Solution
GIVEN:
Total number of staff = 40000
CONCEPT:
Here we will first calculate the total number of adult staff and the total number of stars in the city and then calculate the required percentage in between them.
FORMULAE USED:
Required percentage = (Total staff other than adult staff / Total number of staff) × 100
CALCULATION:
Total staff other than adult staff = 40000 – 2500 = 37500
Required percentage = (37500 / 40000) × 100∴ Required percentage = 93.75% ≈ 94%
53. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
l. 2x2 – 7x + 6 = 0
ll. y2 + 4y + 4 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between them cannot be determine
Solution
Calculation:
⇒ 2×2 – 7x + 6 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 4x – 3x + 6 = 0
⇒ 2x (x – 2) – 3 (x – 2) = 0
⇒ (2x – 3) (x – 2) = 0
⇒ x = 1.5, 2
⇒ y2 + 4y + 4 = 0
⇒ y2 + 2y + 2y + 4 = 0
⇒ y (y + 2) + 2 (y + 2) = 0
⇒ (y + 2) (y + 2) = 0
⇒ y = -2, -2
| x | y | Relation |
| 1.5 | -2 | x > y |
| 1.5 | -2 | x > y |
| 2 | -2 | x > y |
| 2 | -2 | x > y |
∴ The required result will be x > y.
54. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 8x + 12 = 0
II. y2 + 14y + 24 = 0
A. x > y
B. x ≥ y
C. x < y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established
Solution
Calculation:
I. x2 + 8x + 12 = 0
⇒ x2 + 6x + 2x + 12 = 0
⇒ x(x + 6) + 2(x + 6) = 0
⇒ (x + 6) (x + 2) =0
⇒ x = –6, –2
II. y2 + 14y + 24 = 0
⇒ y2 + 12x + 2x + 24 = 0
⇒ y(y + 12) + 2(x + 12) = 0
⇒ (y + 12) (x + 2) = 0
⇒ y = –12, –2
Comparison between x and y (via tabulation):
| X | Y | Relation |
| –6 | –12 | x > y |
| –6 | –2 | x < y |
| –2 | –12 | x > y |
| –2 | –2 | x =y |
∴ x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established
55. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I: x2 – 2x – 35 = 0
II: 2y2 + 72y + 70 = 0
A. x > y
B. x ≥ y
C. x < y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I: x2 – 2x – 35 = 0
⇒ x2 – 7x + 5x – 35 = 0
⇒ x × (x – 7) + 5 × (x – 7) = 0
⇒ (x – 7) × (x + 5) = 0
⇒ x = 7, -5
II: 2y2 + 72y + 70 = 0
⇒ 2y2 + 2y + 70y + 70 = 0
⇒ 2y × (y + 1) + 70 × (y + 1) = 0
⇒ (y + 1) × (2y + 70) = 0
⇒ y = 1, 70/2
⇒ y = (-1), (-35)
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | relation | Value of y |
| 7 | > | -1 |
| 7 | > | -35 |
| -5 | < | -1 |
| -5 | > | -35 |
∴ Relationship between x and y cannot be established.
56. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
l. 2x2 – 36x + 90 = 0
ll. 3y2 + 15y – 18 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between x and y cannot be determine.
Solution
Solution:
l. 2x2 – 36x + 90 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 30x – 6x + 90 = 0
⇒ 2x (x – 15) – 6(x – 15) = 0
⇒ (2x – 6) (x – 15) = 0
⇒ x = 3, 15
ll. 3y2 + 15y – 18 = 0
⇒ 3y2 + 18y – 3y – 18 = 0
⇒ 3y(y + 6) – 3(y + 6) = 0
⇒ (3y – 3) (y + 6) = 0
⇒ y = 1, -6
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 3 | 1 | x > y |
| 3 | -6 | x > y |
| 15 | 1 | x > y |
| 15 | -6 | x > y |
∴ x > y.
57. In the question, two equations I and II are given. You have to solve both the equations and establish the correct relation between x and y and choose the correct option.
I. 9x2 + 15x + 6 = 0
II. 6y2 – 5y + 1 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
Solution:
I. 9x2 + 15x + 6 = 0
⇒ 3x2 + 5x + 2 = 0
⇒ 3x2 + 3x + 2x + 2 = 0
⇒ 3x(x + 1) + 2(x + 1) = 0
⇒ (3x + 2)(x + 1) = 0
So, x = -2/3 or x = -1
II. 6y2 – 5y + 1 = 0
⇒ 6y2 – 2y – 3y + 1 = 0
⇒ 2y(3y – 1) – 1(3y – 1) = 0
⇒ (2y – 1)(3y – 1) = 0
So, y = 1/2 or y = 1/3
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| -2/3 | 1/2 | x < y |
| -2/3 | 1/3 | x < y |
| -1 | 1/2 | x < y |
| -1 | 1/3 | x < y |
∴ x < y
58. A can complete a piece of work in 15 days, and B can do the same work in 20 days. If they work together for 4 days, then what fraction of the work is left?
A. 2/11
B. 5/17
C. 9/14
D. 8/15
E. 3/16
Solution
Given:
A’s time = 15 days
B’s time = 20 days
They work together for 4 days
Formula Used:
Work Done = Rate × Time
Calculation:
A’s rate of work = 1/15 per day
B’s rate of work = 1/20 per day
Together, their rate of work = 1/15 + 1/20
= 4/60 + 3/60
= 7/60 per day
Work done in 4 days = 7/60 × 4
= 28/60
= 7/15
Fraction of work left = 1 – 7/15
= 15/15 – 7/15
= 8/15
The fraction of the work left is 8/15.
59. A dishonest shop keeper professes to loss 4% on Rice but uses a false weight of 900 grams instead of 1 kilogram. Find the Loss% or Gain% in the whole transaction.
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. ![]()
D. ![]()
E. ![]() Gain
Gain
Solution
Given:
A dishonest shop keeper professes 4% loss but uses false weight of 900 g instead of 1 kg
Concept:
Professes to loss 4% on Rice but uses a false weight of 900 grams instead of 1 kg doesn’t mean in total it will be a loss It may profitable also
Calculation:
Let C.P of 1 kg of Rice be Rupee 1
⇒ S.P at a loss of 4% = 1 × (96/100) = Rs. 0.96
But actually, this is the S.P of 900 grams of the Rice.
∴ C.P of 900 grams of Rice = 1 × 900/1000 = Rs. 0.90
⇒ Profit = S.P – C.P = Rs. (0.96 – 0.90) = Rs. 0.06
Profit% = (0.06/0.9) × 100 = 6 2/3%
∴ The shop keeper got 6 2/3% profit or gain.
60. What value should come in place of ‘x’ in the following question?
37 × 11 – (18 ÷ 41 × 123) + 369 + 42 = x
A. 760
B. 800
C. 764
D. 750
E. None of these
Solution
Concept:
This type of question can be solved by the help of BODMAS
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below:
Step-1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first and in the bracket,
Step-2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step-3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step-4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Calculation:
⇒ 407 – (18/41) × 123 + 369 + 42 = x
⇒ 407 – 54 + 369 + 42 = x
⇒ 764 = x
∴ Value of x is 764
61. What value should come in place of ‘x’ in the following question?
382 + 422 – 27 × 5 ÷ 45 + 28 ÷ 7 × 2 = x
A. 3250
B. 3654
C. 3498
D. 3573
E. 3213
Solution
Concept:
This type of question can be solved by the help of BODMAS
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below:
Step-1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first and in the bracket,
Step-2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Calculation:
⇒ 1444 + 1764 – 27 × (1/9) + 4 × 2 = x
⇒ 3208 – 3 + 8 = x
⇒3213 = x
∴ Value of x is 3213
62. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
√324 × 15 + 72 ÷ 6 – 4% of 300 = ?
A. 250
B. 260
C. 270
D. 240
E. None of these
Solution
Concept used:
The concept of BODMAS will be used
Calculations:
√324 × 15 + 72 ÷ 6 – 4% of 300 = ?
⇒ ? = ((18)2)1/2 × 15 + 12 – (4/100) × 300
⇒ ? = 18 × 15 + 12 – 12 = 270
∴ ? = 270
63. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
40% of 280 ÷ 8 + 32 – 15 × 2 = ?1/2
A. 289
B. 256
C. 225
D. 196
E. None of these
Solution
Concept used:
The concept of BODMAS will be used

Calculations:
40% of 280 ÷ 8 + 32 – 15 × 2 = ?1/2
⇒ {(40/100) × 280} ÷ 8 + 32 – 30 = ?1/2
⇒ 112 ÷ 8 + 2 = ?1/2
⇒ 14 + 2 = ?1/2
⇒ ? = (16)2
∴ ? = 256
64. Find the value of ‘?’ in the following question.
[122 + (142 – 40)] × 2.5 = ? × 25
A. 25
B. 35
C. 15
D. 30
E. None of these
Solution
Concept used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve the question as per the order given below:
Step 1: Part of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first and in the bracket.
Step 2: Any mathematical ‘of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step 4: Last but not least, the part of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Now,
Calculations:
Considering the given equation,
[122+ (142 – 40)] × 2.5 = ? × 25
⇒ [122 + (196 – 40)] × 2.5 = ? × 25
⇒ [122 + 156] × 2.5 = ? × 25
⇒ [144 + 156] × 2.5 = ? × 25
⇒ 300 × 2.5 = ? × 25
⇒ 750 = ? × 25
∴ ? = 30
65. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
14 + (2 + 3 × 1 + 2 – 8) + 12 + √196 = ?
A. 38
B. 39
C. 37
D. 36
E. None
Solution
Solution:
Concept:
This type of question can be solved by the help of BODMAS

Calculation:
14 + (2 + 3 × 1 + 2 – 8) + 12 + √196 = ?
⇒ 14 + (2 + 3 + 2 – 8) + 12 + 14 = ?
⇒ 14 + (7 – 8) + 26 = ?
⇒ 14 + (–1) + 26 = ?
⇒ 14 – 1 + 26 = ?
⇒ 13 + 26 = ?
⇒ 39 = ?
∴ The value of ? is 39
66. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
√121 – 10 + 10 × (2 – 3 + 4) + √196 = ?
A. 25
B. 55
C. 35
D. 45
E. None of these
Solution
Concept used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
√121 – 10 + 10 × (2 – 3 + 4) + √196 = ?
⇒ 11 – 10 + 10 × (3) + 14 = ?
⇒ 11 – 10 + 30 + 14 = ?
⇒ 55 – 10 = ?
⇒ 45 = ?
∴ The value of ? is 45
67. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
(12)2 – (13 × 7) + (3)2 = (?)1/2 + (7 × 5)
A. 27
B. 729
C. 3
D. 9
E. None of these
Solution
Concept used:

Calculation:
Considering the given equation,
(12)2 – (13 × 7) + (3)2 = (?)1/2 + (7 × 5)
⇒ 144 – 91 + 9 = (?)1/2 + 35
⇒ 153 – 91 = (?)1/2 + 35
⇒ 62 = (?)1/2 + 35
⇒ (?)1/2 = 62 – 35
⇒ (?)1/2 = 27
∴ ? = 729
68. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
(13 × 23) + (6)3 + (8)2 = (?)2 + (52 × 2)
A. 529
B. 27
C. 23
D. 19
E. None of these
Solution
Concept used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
Considering the given equation,
(13 × 23) + (6)3 + (8)2 = (?)2 + (52 × 2)
⇒ (13 × 23) + 216 + 64 = (?)2 + (25 × 2)
⇒ 299 + 216 + 64 = (?)2 + 50
⇒ 579 = (?)2 + 50
⇒ (?)2 = 579 – 50
⇒ (?)2 = 529
∴ ? = 23
69. What should come in place of question mark (?) in the following question?
7272 ÷ 24 × 3 + ?2 = 30 % of 6000 + 9
A. 20
B. 27
C. 24
D. 30
E. None of these
Solution
Concept used:

Calculation:
Considering the following given question
7272 ÷ 24 × 3 + ?2 = 30 % of 6000 + 9
⇒ 7272 ÷ 24 × 3 + ?2 = 30/100 × 6000 + 9
⇒ 7272 ÷ 24 × 3 + ?2 = 30 × 600 + 9
⇒ 303 × 3 + ?2 = 30 × 600 + 9
⇒ 909 + ?2 = 1800 + 9
⇒ 909 + ?2 = 1809
⇒ ?2 = 1809 – 909
⇒ ?2 = 900
⇒ ? = 30
∴ ? = 30
70. A certain sum is deposited at a rate of 40% compounded annually. The difference between interest earned in the 1st year and 2nd year is Rs 384. Find the sum.
A. Rs. 2400
B. Rs. 4200
C. Rs. 2600
D. Rs. 3000
E. Rs. 3600
Solution
Let the sum be 100 units
Rate of interest be 40% compounded annually
First year:
⇒100 unit × 40/100
⇒ 40 unit
Second year:
⇒ 40 + 40 × 40 /100
⇒ 40 + 16
⇒ 56 units
Sum be 100 unit
Then the difference is 56 units – 40 units
⇒ 16 units
⇒ 16 units = Rs 384
⇒ 1 unit = Rs 24
Total sum is 100 units
⇒ 100 × 24
⇒ 2400
Hence, 2400 is the correct answer
71. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
Children sometimes ______ on peanuts.
A. overcome
B. obstruct
C. choke
D. deprive
E. overpower
Solution
The correct answer is ‘choke‘.
Key Points
- The word “choke” means to have difficulty breathing because something is blocking your throat. (दम घुटना)
- Children sometimes choke on small objects like peanuts, which can obstruct their airways.
- The other options: “overcome,” “obstruct,” “deprive,” and “overpower” do not fit the context appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 3‘.
Complete Sentence: Children sometimes choke on peanuts.
Additional Information
Overpower (परास्त करना): means to defeat or gain control over something by using strength.
Overcome (काबू पाना): means to successfully deal with or gain control of a problem or difficulty.
Obstruct (अवरोध करना): means to block or hinder.
Deprive (वंचित करना): means to take something away from someone.
72. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
“I’ll never understand these questions.” he ______.
A. aspired
B. sighted
C. spiraled
D. sighed
E. signed
Solution
The correct answer is ‘sighed‘.
Key Points
- The word “sighed” means to let out a deep audible breath, often to express sadness, frustration, or relief.
- The statement indicates the speaker’s frustration or resignation, making “sighed” the most appropriate choice.
- The other options: “aspired,” “sighted,” “spiraled,” and “signed” do not fit the context as appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 4‘.
Complete Sentence: “I’ll never understand these questions.” he sighed.
Additional Information
Signed: means to write one’s signature on something.
Aspired: means to have a strong desire to achieve something.
Sighted: means to see or observe something.
Spiraled: means to move in a spiral shape or pattern.
73. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
She was ______ for her naughty behaviour.
A. impeded
B. extracted
C. explicit
D. sanctioned
E. notorious
Solution
The correct answer is ‘notorious‘.
Key Points
- The word “notorious” means famous or well-known for something bad or undesirable. (कुख्यात)
- In the given context, the sentence implies that the person was known for her naughty behaviour, which is negative.
- The other options: “impeded,” “extracted,” “explicit,” and “sanctioned” do not fit the context as appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 5‘.
Complete Sentence: She was notorious for her naughty behaviour.
Additional Information
Sanctioned (अनुमोदित): means formally approved or authorized.
Impeded (बाधित करना): means to hinder or obstruct progress.
Extracted (निकालना): means to remove or take out something.
Explicit (स्पष्ट): means stated clearly and in detail.
74. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
I _____ they are arriving late since they have not replied yet.
A. aggravate
B. propose
C. pretend
D. flicker
E. presume
Solution
The correct answer is ‘presume‘.
Key Points
- The word “presume” means to suppose something is true based on probability or prior knowledge. (मान लेना)
- In the given sentence, the speaker is assuming or presuming that the people are arriving late because they have not replied yet.
- The other options: “aggravate,” “propose,” “pretend,” and “flicker” do not fit the context appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 5‘.
Complete Sentence: I presume they are arriving late since they have not replied yet.
Additional Information
Flicker (टिमटिमाना): means to shine unsteadily or vary in brightness.
Aggravate (बिगाड़ना): means to make a problem or situation worse.
Propose (प्रस्ताव करना): means to suggest or put forward an idea.
Pretend (नाटक करना): means to act as if something is true when it is not.
75. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
This tree has small ______ berries.
A. plausible
B. conform
C. edible
D. dimensional
E. wrought
Solution
The correct answer is ‘edible‘.
Key Points
- The word “edible” means suitable for eating. (खाने योग्य)
- The context of the sentence suggests that the berries on the tree can be eaten.
- The other options: “plausible” (संबव), “conform” (अनुरूप होना), “dimensional” (आयामी), and “wrought” (गठित) do not fit the context as appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 3‘.
Complete Sentence: This tree has small edible berries.
Additional Information
Wrought (गठित): means shaped or formed, usually referring to metalwork.
Plausible (संभव): means appearing reasonable or probable.
Conform (अनुरूप होना): means comply with rules or standards.
Dimensional (आयामी): relates to measurements or dimensions.
76. Read the sentence below to find out if there is any error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error the answer is (5). (Ignore errors in punctuation if any).
Shashank, our new intern can not (A)/ handle such a difficult (B)/situation because he doesn’t have enough knowledge and (C)/he is ill-trained. (D)/ No error (E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
- In the given sentence error is in part A, The error is in the use of ‘can not’.
- The thing to remember is when you use “not” with “can” to express a negative statement, you always put them together.
- They actually become one word: “cannot”, and not “can not”.
- This is the only time you join a modal verb with “not” into one.
- But with the other models, “not” is always a separate word.
Correct answer – Shashank, our new intern cannot handle such a difficult situation because he doesn’t have enough knowledge and he is ill-trained.
Additional Information
In English, the modal verbs commonly used are can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, and must
A modal verb is a type of verb that is used to indicate modality
Eg. likelihood, ability, permission, request, capacity, suggestions, order, obligation, or advice.
77. Read the sentence below to find out if there is any error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error the answer is (5). (Ignore errors in punctuation if any).
Rasika told Radha that(A)/it is absolutely fine if you can not(B)/ dance this form of dance. (C)/ but you should learn this dance form.(D)/ No error(E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 2.
Key Points
- In the given sentence error is in part B, The error is in the use of ‘Can not’.
- The thing to remember is when you use “not” with “can” to express a negative statement, you always put them together.
- They actually become one word: “cannot”, and not “can not”.
- This is the only time you join a modal verb with “not” into one.
- But with the other models, “not” is always a separate word.
Correct Answer – Rasika told Radha thatit is absolutely fine if you cannot dance this form of dance. but you should learn this dance form.
Additional Information
In English, the modal verbs commonly used are can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, and must.
A modal verb is a type of verb that is used to indicate modality
Eg. likelihood, ability, permission, request, capacity, suggestions, order, obligation, or advice. …
78. Read the sentence below to find out if there is any error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error the answer is (5). (Ignore errors in punctuation if any).
We can not cross this gate of the(A)/ army ammunition because (B)/this area is considered a hot spot and hence(C)/restricted to laymen.(D)/ No error(E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
- In the given sentence error is in part A, The error is in the use of ‘can not’.
- The thing to remember is when you use “not” with “can” to express a negative statement, you always put them together.
- They actually become one word: “cannot”, and not “can not”.
- This is the only time you join a modal verb with “not” into one.
- But with the other models, “not” is always a separate word.
Correct answer – We cannot cross this gate of the army ammunition because this area is considered a hot spot and hencerestricted to laymen.
Additional Information
In English, the modal verbs commonly used are can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, and must.
A modal verb is a type of verb that is used to indicate modality
Eg. likelihood, ability, permission, request, capacity, suggestions, order, obligation, or advice. …
79. Read the sentence below to find out if there is any error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error the answer is (5). (Ignore errors in punctuation if any).
We can not take any further risk at such (A)/crucial point because(B)/ market volatility is also increasing(C)/ with the increase in the number of cases. (D)/ No error(E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
- In the given sentence error is in part A, The error is in the use of can not.
- The thing to remember is when you use “not” with “can” to express a negative statement, you always put them together.
- They actually become one word: “cannot”, and not “can not”.
- This is the only time you join a modal verb with “not” into one.
- But with the other models, “not” is always a separate word.
Correct answer- We cannot take any further risk at such a crucial point market volatility is also increasing with the increase in the number of cases.
Additional Information
In English, the modal verbs commonly used are can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, and must..
A modal verb is a type of verb that is used to indicate modality
Eg. likelihood, ability, permission, request, capacity, suggestions, order, obligation, or advice. …
80. Read the sentence below to find out if there is any error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error the answer is (5). (Ignore errors in punctuation if any).
Bachelet was disturbed or(A)/ saddened by (B)/the news of (C)/the death of the activist(d)/ No error(E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
- The error is in Part A of the sentence, the error is in use of or.
- Coordinate adjectives should be separated by a comma or the word and.
- Adjectives are said to be coordinated if they modify the same noun in a sentence.
- Hence in the given sentence ‘or’ should be replaced with ‘and’.
Correct sentence – Bachelet was disturbed and saddened by the news of the death of the activist.
Additional Information
Adjective is the word that gives additional information regarding the noun.
81. Direction: In the following question, two columns are given containing three phrases each. In the first column phrases are A, B, and C and in the second column, the phrases are D, E, and F. A phrase from the first column may or may not connect with a phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. There are five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which phrases can be joined to form a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. If none of the options given forms a correct sentence after combination, select ‘None of these’ as your answer.
| Column (1) | Column (2) |
| (A) We spent the afternoon meandering | (D) if you want to succeed in business. |
| (B) You have to be a bit devious | (E) piece of work. |
| (C) This essay is the most conscientious | (F) around the streets of the old town. |
A. A-E
B. B-E
C. C-E
D. A-D
E. None of these
Solution
The correct combination is ‘C-E‘.
Key Points
- The correct sentences are:
- A-F: We spent the afternoon meandering around the streets of the old town.
- B-D: You have to be a bit devious if you want to succeed in business.
- C-E: This essay is the most conscientious piece of work.
- Part A and part F should join conceptually. Part A states that ‘We spent the afternoon meandering’ and part F states ‘around the streets of the old town‘. So, A-F is the correct combination.
- Part B and part D should join conceptually. Part B talks about ‘You have to be a bit devious‘ and part D completes the sentence stating ‘if you want to succeed in business’. So, B-F is the correct combination.
- Part C and part E should be joined conceptually. Part C talks about ‘This essay is the most conscientious’ and part E completes the sentence stating ‘piece of work‘. So, C-D is the correct combination.
- The correct combination is reflected in option 3, making it the correct answer.
Additional Information
Conscientious: wishing to do one’s work or duty well and thoroughly
Let’s look at the meaning of some difficult words:
Meandering: following a winding course
Devious: showing a skillful use of underhand tactics to achieve goals
82. Direction: In the following question, two columns are given containing three phrases each. In the first column phrases are A, B, and C and in the second column, the phrases are D, E, and F. A phrase from the first column may or may not connect with a phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. There are five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which phrases can be joined to form a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. If none of the options given forms a correct sentence after combination, select ‘None of these’ as your answer.
| Column (1) | Column (2) |
| (A) The earthquake caused the entire | (D) of a secret military document. |
| (B) The captain was forced | (E) house to vacillate. |
| (C) His mission is to confirm the verity | (F) to jettison the cargo. |
A. A-F
B. B-D
C. B-F and A-E
D. C-E
E. None of these
Solution
The correct combinations are ‘B-F and A-E‘.
Key Points
- The correct sentences are:
- A-E: The earthquake caused the entire house to vacillate.
- B-F: The captain was forced to jettison the cargo.
- C-D: His mission is to confirm the verity of a secret military document.
- Part A and part E should join conceptually. Part A states that ‘The earthquake caused the entire’ and part E states ‘house to vacillate‘. So, A-E is the correct combination.
- Part B and part F should join conceptually. Part B talks about ‘The captain was forced‘ and part F completes the sentence stating ‘to jettison the cargo‘. So, B-F is the correct combination.
- Part C and part D should be joined conceptually. Part C talks about ‘his mission is to confirm the verity’ and part D completes the sentence stating ‘of a secret military document‘. So, C-D is the correct combination.
- The correct combination is reflected in option 3, making it the correct answer.
Additional Information
Verity: a true principle or belief, especially one of fundamental importance
Let’s look at the meaning of some difficult words:
Vacillate: waver between different opinions or actions; be indecisive
Jettison: throw or drop (something) from an aircraft or ship
83. Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions:
Nuclear power has etched a paradoxical identity, both as the harbinger of clean, efficient energy and as the symbol of global annihilation. One of this duality’s fearsome heads is the phenomenon called “nuclear winter.” This term echoes ominously in the vast halls of climatology and geopolitics, referring to a theory that suggests a complete and untimely cooling of the Earth’s surface following a massive nuclear detonation could occur. Towards the end of the Cold War, in the 1980s, esteemed scientists such as Carl Sagan and a team of researchers hypothesized the catastrophic impact of nuclear detonations. The premise was simple but unnerving. A nuclear explosion creates not just immediate devastation and lethal radiation; it also births myriads of firestorms producing colossal volumes of thick smoke. A sizable nuclear exchange could release millions of tons of this smoke soaring into the stratosphere. Unlike the smoke from wildfires or regular fires, which ordinarily diminishes in the lower atmosphere, this great column of smoke reaches the stratospheric level, where it can last for years. This layer of soot cloaked in the skies is high enough and persistently effective in blocking solar radiation, thus creating a planet-wide dusk, a nuclear winter. Less sunlight on the Earth’s surface has multiple dire consequences. There is a severe drop in temperature, reminiscent of an ice age. Food production could collapse as photosynthesis requires sunlight. Consequently, the dependent food chains would follow suit, causing mass starvation and potentially a mass extinction event.
Lessons from the ancient pages of the Earth’s history lend credibility to these predictions. The year 1815 saw Indonesia’s Mount Tambora’s eruption, an explosion with such intensity that it affected weather patterns globally. The voluminous infusion of ash and aerosol pollutants into the atmosphere caused an extreme drop in temperature, leading to what came to be known as the “Year without a Summer” across North America and Europe. In contrast to natural calamities that have similarly cataclysmic effects, nuclear winter will not be an act of God, but an act of man. A tragic byproduct of our technological __________ and choices, spelling doom not only for the initiators but for all life on Earth. Through the resurgence of this concept, scientists warn us that despite our advances, we perch on the cusp of self-destruction. Each stride in nuclear technology pushes us closer to this brink. Furthermore, a world characterized by brewing conflicts and political tensions, the threat of nuclear winter beams brightly against the backdrop of our existence. In conclusion, our understanding of the potential for a nuclear winter underscores the urgent need for diplomacy, peace, and aggressive action on nuclear disarmament. Comprehending the enormous power that we wield, it is vital we pivot from a narrative of conquer and divide to one of cooperation and survival.
Question:
Which of the following best states the central theme of the passage?
A. The catastrophic impact of volcanic eruptions
B. The role of sunlight in food production.
C. The potential consequences of nuclear detonations, particularly the concept of nuclear winter.
D. The advancement in nuclear technology
E. The collapse of food production due to lack of sunlight
Solution
The correct answer is ‘The potential consequences of nuclear detonations, particularly the concept of nuclear winter’.
Key Points
- The passage primarily discusses how nuclear detonations could lead to a concept known as “nuclear winter.”
- This concept involves the blocking of sunlight due to smoke and soot after nuclear detonations, leading to severe drops in temperature and food production.
- The passage also emphasizes the importance of diplomacy, peace, and aggressive action on nuclear disarmament to avoid such a catastrophic event.
- Hence, the central theme of the passage revolves around the discussion of nuclear winter resulting from nuclear detonations and its potential impact.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 3’.
Additional Information
- Option 1 is not suitable because the passage does not primarily discuss the catastrophic impact of volcanic eruptions. Although the eruption of Mount Tambora is mentioned, this is used only as an example to illustrate the potential effects of a nuclear winter.
- Option 2, while a part of the narrative, is not the central theme. The role of sunlight in food production is a piece of the potential catastrophe defined by nuclear winter, but not the overall subject.
- Option 4 and 5 only capture a fragment of the text and do not represent the main idea of the passage, which broadly encompasses the potential consequences of a nuclear winter.
84. Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions:
Nuclear power has etched a paradoxical identity, both as the harbinger of clean, efficient energy and as the symbol of global annihilation. One of this duality’s fearsome heads is the phenomenon called “nuclear winter.” This term echoes ominously in the vast halls of climatology and geopolitics, referring to a theory that suggests a complete and untimely cooling of the Earth’s surface following a massive nuclear detonation could occur. Towards the end of the Cold War, in the 1980s, esteemed scientists such as Carl Sagan and a team of researchers hypothesized the catastrophic impact of nuclear detonations. The premise was simple but unnerving. A nuclear explosion creates not just immediate devastation and lethal radiation; it also births myriads of firestorms producing colossal volumes of thick smoke. A sizable nuclear exchange could release millions of tons of this smoke soaring into the stratosphere. Unlike the smoke from wildfires or regular fires, which ordinarily diminishes in the lower atmosphere, this great column of smoke reaches the stratospheric level, where it can last for years. This layer of soot cloaked in the skies is high enough and persistently effective in blocking solar radiation, thus creating a planet-wide dusk, a nuclear winter. Less sunlight on the Earth’s surface has multiple dire consequences. There is a severe drop in temperature, reminiscent of an ice age. Food production could collapse as photosynthesis requires sunlight. Consequently, the dependent food chains would follow suit, causing mass starvation and potentially a mass extinction event.
Lessons from the ancient pages of the Earth’s history lend credibility to these predictions. The year 1815 saw Indonesia’s Mount Tambora’s eruption, an explosion with such intensity that it affected weather patterns globally. The voluminous infusion of ash and aerosol pollutants into the atmosphere caused an extreme drop in temperature, leading to what came to be known as the “Year without a Summer” across North America and Europe. In contrast to natural calamities that have similarly cataclysmic effects, nuclear winter will not be an act of God, but an act of man. A tragic byproduct of our technological __________ and choices, spelling doom not only for the initiators but for all life on Earth. Through the resurgence of this concept, scientists warn us that despite our advances, we perch on the cusp of self-destruction. Each stride in nuclear technology pushes us closer to this brink. Furthermore, a world characterized by brewing conflicts and political tensions, the threat of nuclear winter beams brightly against the backdrop of our existence. In conclusion, our understanding of the potential for a nuclear winter underscores the urgent need for diplomacy, peace, and aggressive action on nuclear disarmament. Comprehending the enormous power that we wield, it is vital we pivot from a narrative of conquer and divide to one of cooperation and survival.
Question:
According to the passage, what are the primary effects of the smoke from nuclear explosions reaching the stratosphere?
A. It blocks all solar radiation.
B. It sparks wildfires.
C. It leads to an ice age.
D. It causes mass starvation and potential mass extinction.
E. It causes severe radiation.
Solution
The correct answer is ‘It causes mass starvation and potential mass extinction’.
Key Points
- The smoke from nuclear explosions reaching the stratosphere blocks sunlight from reaching the Earth’s surface.
- This can result in a severe drop in temperature and a collapse in food production.
- As a result of the collapse in food production, dependent food chains would be affected, leading to mass starvation.
- If conditions persist, this could potentially lead to a mass extinction event.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 4’.
Additional Information
- Option 1 is not completely accurate. While the smoke blocks some solar radiation, it does not block all of it.
- Options 2 and 5 are incorrect as they are not stated or indicated by the passage.
- Option 3, while the term “ice age” is used as a comparative descriptor, the primary effect discussed is starvation and potential mass extinction.
85. Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions:
Nuclear power has etched a paradoxical identity, both as the harbinger of clean, efficient energy and as the symbol of global annihilation. One of this duality’s fearsome heads is the phenomenon called “nuclear winter.” This term echoes ominously in the vast halls of climatology and geopolitics, referring to a theory that suggests a complete and untimely cooling of the Earth’s surface following a massive nuclear detonation could occur. Towards the end of the Cold War, in the 1980s, esteemed scientists such as Carl Sagan and a team of researchers hypothesized the catastrophic impact of nuclear detonations. The premise was simple but unnerving. A nuclear explosion creates not just immediate devastation and lethal radiation; it also births myriads of firestorms producing colossal volumes of thick smoke. A sizable nuclear exchange could release millions of tons of this smoke soaring into the stratosphere. Unlike the smoke from wildfires or regular fires, which ordinarily diminishes in the lower atmosphere, this great column of smoke reaches the stratospheric level, where it can last for years. This layer of soot cloaked in the skies is high enough and persistently effective in blocking solar radiation, thus creating a planet-wide dusk, a nuclear winter. Less sunlight on the Earth’s surface has multiple dire consequences. There is a severe drop in temperature, reminiscent of an ice age. Food production could collapse as photosynthesis requires sunlight. Consequently, the dependent food chains would follow suit, causing mass starvation and potentially a mass extinction event.
Lessons from the ancient pages of the Earth’s history lend credibility to these predictions. The year 1815 saw Indonesia’s Mount Tambora’s eruption, an explosion with such intensity that it affected weather patterns globally. The voluminous infusion of ash and aerosol pollutants into the atmosphere caused an extreme drop in temperature, leading to what came to be known as the “Year without a Summer” across North America and Europe. In contrast to natural calamities that have similarly cataclysmic effects, nuclear winter will not be an act of God, but an act of man. A tragic byproduct of our technological __________ and choices, spelling doom not only for the initiators but for all life on Earth. Through the resurgence of this concept, scientists warn us that despite our advances, we perch on the cusp of self-destruction. Each stride in nuclear technology pushes us closer to this brink. Furthermore, a world characterized by brewing conflicts and political tensions, the threat of nuclear winter beams brightly against the backdrop of our existence. In conclusion, our understanding of the potential for a nuclear winter underscores the urgent need for diplomacy, peace, and aggressive action on nuclear disarmament. Comprehending the enormous power that we wield, it is vital we pivot from a narrative of conquer and divide to one of cooperation and survival.
Question:
Which event from 1815 does that passage cite to illustrate the potential effects of a nuclear winter?
A. The eruption of Mount St. Helens
B. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius
C. The eruption of Mount Tambora
D. The eruption of Mount Krakatoa
E. The eruption of Mount Fuji
Solution
The correct answer is ‘The eruption of Mount Tambora’.
Key Points
- The passage cites the eruption of Mount Tambora in 1815 as a historical event that had global impacts on weather patterns.
- This event is used as an example to demonstrate the potential effects of a nuclear winter, particularly the global drop in temperature.
- Due to the volcanic eruption, a great amount of ash and aerosols were released into the atmosphere, causing what is now known as the “Year without a Summer.”
- This scenario draws parallels with the consequences of a nuclear winter, which could also lead to a severe drop in temperature and subsequent impacts on life on Earth.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 3’.
Additional Information
- Options 1, 2, 4 and 5, whilst referring to significant volcanic events, are not mentioned within the passage. Therefore, they can’t be the correct answers.
86. Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions:
Nuclear power has etched a paradoxical identity, both as the harbinger of clean, efficient energy and as the symbol of global annihilation. One of this duality’s fearsome heads is the phenomenon called “nuclear winter.” This term echoes ominously in the vast halls of climatology and geopolitics, referring to a theory that suggests a complete and untimely cooling of the Earth’s surface following a massive nuclear detonation could occur. Towards the end of the Cold War, in the 1980s, esteemed scientists such as Carl Sagan and a team of researchers hypothesized the catastrophic impact of nuclear detonations. The premise was simple but unnerving. A nuclear explosion creates not just immediate devastation and lethal radiation; it also births myriads of firestorms producing colossal volumes of thick smoke. A sizable nuclear exchange could release millions of tons of this smoke soaring into the stratosphere. Unlike the smoke from wildfires or regular fires, which ordinarily diminishes in the lower atmosphere, this great column of smoke reaches the stratospheric level, where it can last for years. This layer of soot cloaked in the skies is high enough and persistently effective in blocking solar radiation, thus creating a planet-wide dusk, a nuclear winter. Less sunlight on the Earth’s surface has multiple dire consequences. There is a severe drop in temperature, reminiscent of an ice age. Food production could collapse as photosynthesis requires sunlight. Consequently, the dependent food chains would follow suit, causing mass starvation and potentially a mass extinction event.
Lessons from the ancient pages of the Earth’s history lend credibility to these predictions. The year 1815 saw Indonesia’s Mount Tambora’s eruption, an explosion with such intensity that it affected weather patterns globally. The voluminous infusion of ash and aerosol pollutants into the atmosphere caused an extreme drop in temperature, leading to what came to be known as the “Year without a Summer” across North America and Europe. In contrast to natural calamities that have similarly cataclysmic effects, nuclear winter will not be an act of God, but an act of man. A tragic byproduct of our technological __________ and choices, spelling doom not only for the initiators but for all life on Earth. Through the resurgence of this concept, scientists warn us that despite our advances, we perch on the cusp of self-destruction. Each stride in nuclear technology pushes us closer to this brink. Furthermore, a world characterized by brewing conflicts and political tensions, the threat of nuclear winter beams brightly against the backdrop of our existence. In conclusion, our understanding of the potential for a nuclear winter underscores the urgent need for diplomacy, peace, and aggressive action on nuclear disarmament. Comprehending the enormous power that we wield, it is vital we pivot from a narrative of conquer and divide to one of cooperation and survival.
Question:
What can be inferred from the passage regarding the role of current geopolitical situations and conflicts?
A. They have no relation to the possibility of a nuclear winter.
B. They dim the threat of nuclear winter.
C. They exacerbate the threat of nuclear winter.
D. They have no significant effect on the development of nuclear technology.
E. They have brought peace and harmony in the world.
Solution
The correct answer is ‘They exacerbate the threat of nuclear winter’.
Key Points
- The passage implies that current geopolitical situations and conflicts can escalate the threat of nuclear detonations, which in turn increases the possibility of a nuclear winter.
- Unstable political situations make the use of nuclear weapons more likely, heightening the risk of a nuclear exchange.
- This could lead to the catastrophic impacts described in the nuclear winter scenario.
- The passage thus emphasizes the need for diplomacy, peace, and strict action on nuclear disarmament to avoid such a scenario.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 3’.
Additional Information
- Options 1, 2, and 4 are not accurate as they are contrary to what the passage implies. The text suggests that geopolitical situations can indeed escalate the threat of a nuclear winter.
- Option 5 doesn’t align with the passage, which relates to geopolitical tensions and conflicts, definitely not leading to peace and harmony in the world.
87. Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions:
Nuclear power has etched a paradoxical identity, both as the harbinger of clean, efficient energy and as the symbol of global annihilation. One of this duality’s fearsome heads is the phenomenon called “nuclear winter.” This term echoes ominously in the vast halls of climatology and geopolitics, referring to a theory that suggests a complete and untimely cooling of the Earth’s surface following a massive nuclear detonation could occur. Towards the end of the Cold War, in the 1980s, esteemed scientists such as Carl Sagan and a team of researchers hypothesized the catastrophic impact of nuclear detonations. The premise was simple but unnerving. A nuclear explosion creates not just immediate devastation and lethal radiation; it also births myriads of firestorms producing colossal volumes of thick smoke. A sizable nuclear exchange could release millions of tons of this smoke soaring into the stratosphere. Unlike the smoke from wildfires or regular fires, which ordinarily diminishes in the lower atmosphere, this great column of smoke reaches the stratospheric level, where it can last for years. This layer of soot cloaked in the skies is high enough and persistently effective in blocking solar radiation, thus creating a planet-wide dusk, a nuclear winter. Less sunlight on the Earth’s surface has multiple dire consequences. There is a severe drop in temperature, reminiscent of an ice age. Food production could collapse as photosynthesis requires sunlight. Consequently, the dependent food chains would follow suit, causing mass starvation and potentially a mass extinction event.
Lessons from the ancient pages of the Earth’s history lend credibility to these predictions. The year 1815 saw Indonesia’s Mount Tambora’s eruption, an explosion with such intensity that it affected weather patterns globally. The voluminous infusion of ash and aerosol pollutants into the atmosphere caused an extreme drop in temperature, leading to what came to be known as the “Year without a Summer” across North America and Europe. In contrast to natural calamities that have similarly cataclysmic effects, nuclear winter will not be an act of God, but an act of man. A tragic byproduct of our technological __________ and choices, spelling doom not only for the initiators but for all life on Earth. Through the resurgence of this concept, scientists warn us that despite our advances, we perch on the cusp of self-destruction. Each stride in nuclear technology pushes us closer to this brink. Furthermore, a world characterized by brewing conflicts and political tensions, the threat of nuclear winter beams brightly against the backdrop of our existence. In conclusion, our understanding of the potential for a nuclear winter underscores the urgent need for diplomacy, peace, and aggressive action on nuclear disarmament. Comprehending the enormous power that we wield, it is vital we pivot from a narrative of conquer and divide to one of cooperation and survival.
Question:
According to the passage, which of the given statements is correct?
A. Sunlight does not play any significant role in photosynthesis and food production.
B. A sizable nuclear exchange could release smoke that reaches and persists in the stratosphere.
C. The eruption of Mount Tambora in 1815 had no significant impact on global weather patterns.
A. Only A
B. Only B
C.. Only C
D. A and B
E. B and C
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Only B’.
Key Points
- Statement A is incorrect according to the passage. Sunlight plays a crucial role in photosynthesis and food production, and its blockage due to a nuclear winter could lead to a significant collapse in food chains and mass starvation.
- Statement B is correct according to the passage. A significant nuclear exchange could indeed release a massive amount of smoke that rises and lingers in the stratosphere, causing a blockage of sunlight.
- Statement C is incorrect based on the passage. The eruption of Mount Tambora in 1815 had a substantial impact on global weather patterns, leading to what is known as the “Year Without a Summer.”
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 2’.
Additional Information
- Option 1 is not suitable because statement A is not accurate, according to the passage.
- Option 3 is not suitable because statement C is not accurate, according to the passage.
- Option 4 isn’t accurate, as statement A is incorrect.
- Option 5 is not correct, as statement C is incorrect according to the passage.
88. Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions:
Nuclear power has etched a paradoxical identity, both as the harbinger of clean, efficient energy and as the symbol of global annihilation. One of this duality’s fearsome heads is the phenomenon called “nuclear winter.” This term echoes ominously in the vast halls of climatology and geopolitics, referring to a theory that suggests a complete and untimely cooling of the Earth’s surface following a massive nuclear detonation could occur. Towards the end of the Cold War, in the 1980s, esteemed scientists such as Carl Sagan and a team of researchers hypothesized the catastrophic impact of nuclear detonations. The premise was simple but unnerving. A nuclear explosion creates not just immediate devastation and lethal radiation; it also births myriads of firestorms producing colossal volumes of thick smoke. A sizable nuclear exchange could release millions of tons of this smoke soaring into the stratosphere. Unlike the smoke from wildfires or regular fires, which ordinarily diminishes in the lower atmosphere, this great column of smoke reaches the stratospheric level, where it can last for years. This layer of soot cloaked in the skies is high enough and persistently effective in blocking solar radiation, thus creating a planet-wide dusk, a nuclear winter. Less sunlight on the Earth’s surface has multiple dire consequences. There is a severe drop in temperature, reminiscent of an ice age. Food production could collapse as photosynthesis requires sunlight. Consequently, the dependent food chains would follow suit, causing mass starvation and potentially a mass extinction event.
Lessons from the ancient pages of the Earth’s history lend credibility to these predictions. The year 1815 saw Indonesia’s Mount Tambora’s eruption, an explosion with such intensity that it affected weather patterns globally. The voluminous infusion of ash and aerosol pollutants into the atmosphere caused an extreme drop in temperature, leading to what came to be known as the “Year without a Summer” across North America and Europe. In contrast to natural calamities that have similarly cataclysmic effects, nuclear winter will not be an act of God, but an act of man. A tragic byproduct of our technological __________ and choices, spelling doom not only for the initiators but for all life on Earth. Through the resurgence of this concept, scientists warn us that despite our advances, we perch on the cusp of self-destruction. Each stride in nuclear technology pushes us closer to this brink. Furthermore, a world characterized by brewing conflicts and political tensions, the threat of nuclear winter beams brightly against the backdrop of our existence. In conclusion, our understanding of the potential for a nuclear winter underscores the urgent need for diplomacy, peace, and aggressive action on nuclear disarmament. Comprehending the enormous power that we wield, it is vital we pivot from a narrative of conquer and divide to one of cooperation and survival.
Question:
What term best fits in the following sentence from the passage: “A tragic byproduct of our technological __________ and choices, spelling doom not only for the initiators but for all life on Earth.”
A. Advancements
B. Stagnation
C. Complications
D. Innovations
E. Limitations
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Advancements’.
Key Points
- The passage is discussing the effects of advancements in nuclear technology, making “advancements” a fitting word for this context.
- It underscores that the use of nuclear power as a weapon has unintended adverse effects, painting a grim picture for life on Earth.
- The term “advancements” aligns with the overall narrative, which acknowledges that technological development has led to the creation of threats like nuclear winter.
- The situation is described as “tragic,” indicating that the progress made in technology has led to harmful potential consequences.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 1’.
Complete Sentence: A tragic byproduct of our technological advancements and choices, spelling doom not only for the initiators but for all life on Earth.
Additional Information
- Options 2, 3 and 5 indicate a negative or deficient aspect of technology, which does not fit the context of the sentence.
- Option 4, although positively inclined like “advancements,” is not explicit enough in this context as the passage is specifically discussing the evolution of nuclear power technology.
89. Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions:
Nuclear power has etched a paradoxical identity, both as the harbinger of clean, efficient energy and as the symbol of global annihilation. One of this duality’s fearsome heads is the phenomenon called “nuclear winter.” This term echoes ominously in the vast halls of climatology and geopolitics, referring to a theory that suggests a complete and untimely cooling of the Earth’s surface following a massive nuclear detonation could occur. Towards the end of the Cold War, in the 1980s, esteemed scientists such as Carl Sagan and a team of researchers hypothesized the catastrophic impact of nuclear detonations. The premise was simple but unnerving. A nuclear explosion creates not just immediate devastation and lethal radiation; it also births myriads of firestorms producing colossal volumes of thick smoke. A sizable nuclear exchange could release millions of tons of this smoke soaring into the stratosphere. Unlike the smoke from wildfires or regular fires, which ordinarily diminishes in the lower atmosphere, this great column of smoke reaches the stratospheric level, where it can last for years. This layer of soot cloaked in the skies is high enough and persistently effective in blocking solar radiation, thus creating a planet-wide dusk, a nuclear winter. Less sunlight on the Earth’s surface has multiple dire consequences. There is a severe drop in temperature, reminiscent of an ice age. Food production could collapse as photosynthesis requires sunlight. Consequently, the dependent food chains would follow suit, causing mass starvation and potentially a mass extinction event.
Lessons from the ancient pages of the Earth’s history lend credibility to these predictions. The year 1815 saw Indonesia’s Mount Tambora’s eruption, an explosion with such intensity that it affected weather patterns globally. The voluminous infusion of ash and aerosol pollutants into the atmosphere caused an extreme drop in temperature, leading to what came to be known as the “Year without a Summer” across North America and Europe. In contrast to natural calamities that have similarly cataclysmic effects, nuclear winter will not be an act of God, but an act of man. A tragic byproduct of our technological __________ and choices, spelling doom not only for the initiators but for all life on Earth. Through the resurgence of this concept, scientists warn us that despite our advances, we perch on the cusp of self-destruction. Each stride in nuclear technology pushes us closer to this brink. Furthermore, a world characterized by brewing conflicts and political tensions, the threat of nuclear winter beams brightly against the backdrop of our existence. In conclusion, our understanding of the potential for a nuclear winter underscores the urgent need for diplomacy, peace, and aggressive action on nuclear disarmament. Comprehending the enormous power that we wield, it is vital we pivot from a narrative of conquer and divide to one of cooperation and survival.
Question:
Which of the following is a synonym for the term ‘colossal‘ as used in the passage?
A. Tiny
B. Moderate
C. Enourmous
D. Normal
E. Small
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Enormous’.
Key Points
- The term ‘colossal’ is an adjective denoting extreme size, extent, or degree. (विशाल or बहुत बड़ा)
- For instance, in the sentence “A colossal statue of the king was erected in the town square,” ‘colossal‘ represents a size so large that it is extraordinary or remarkable.
- The synonym ‘enormous’ also means very large in size, quantity, or extent. (विशाल or बहुत ज्यादा)
- As an example, the sentence “The response to the campaign was enormous,” suggests that the response was remarkably large in scale or extent.
- Hence, “enormous” is a suitable synonym for “colossal” in the context of the given text.
Therefore, the correct answer is “Option 3”.
Additional Information
- Option 1 – ‘Tiny’ means very small. (छोटा). It is not a suitable synonym for ‘colossal’ because it represents the opposite meaning.
- Option 2 – ‘Moderate’ suggests something adequate in amount, neither too much nor too little. (मध्यम). It is not similar to the extreme large scale denoted by ‘colossal’.
- Option 4 – ‘Normal’ means usual or standard. (सामान्य). It does not capture the aspect of large size or degree implied by ‘colossal’.
- Option 5 – ‘Small’ means not large in size, amount or degree. (छोटा). It contradicts the meaning of ‘colossal’, and thus is not a suitable synonym.
90. Directions: Given below is a word, followed by three sentences that consist of that word. Identify the sentence(s) that best express(es) the meaning of the word. Choose option 5 ‘None of the above’ if the word is not suitable in any of the sentences.
LUCRATIVE
A. The graduate was sad that his name was accidentally lucrative from the list of people earning their degrees.
B. The wealthy businessman was constantly on the lookout for lucrative ventures that would help him become even wealthier.
C. Lucrative events caused the girl to be afraid of going to sleep without a light on.
A. Only C
B. Both A and C
C. Only A
D. Only B
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Only B.‘
Key Points
- The given word ‘Lucrative’ means producing a great deal of profit. (जिसमें अच्छा पैसा हो; लाभप्रद)
- Let us explore the given sentences:
- The word ‘omitted’ should be used in the first sentence as it talks about a graduate who was sad about his name being accidentally excluded from the list of people earning degrees.
- The word ‘omitted’ means to not include something; to leave something out. (किसी वस्तु को शामिल न करना; किसी वस्तु को छोड़ देना)
- The word ‘lucrative’ is used correctly in the second sentence as it talks about a wealthy businessman who was constantly on the lookout for profitable ventures.
- Example: She advised us to look abroad for more lucrative business ventures.
- The word ‘traumatic’ should be used in the third sentence as it talks about horrifying or terrifying events that caused the girl to be afraid of going to sleep without a light on.
- The word ‘traumatic’ means deeply disturbing or distressing. (आघातकारी)
- The word ‘omitted’ should be used in the first sentence as it talks about a graduate who was sad about his name being accidentally excluded from the list of people earning degrees.
- Therefore, only sentence B best expresses the meaning of the given word.
Hence, the correct answer is option 4.
Sentence A: The graduate was sad that his name was accidentally omitted from the list of people earning their degrees.
Sentence B: The wealthy businessman was constantly on the lookout for lucrative ventures that would help him become even wealthier.
Sentence C: Traumatic events caused the girl to be afraid of going to sleep without a light on.
91. Directions: Given below is a word, followed by three sentences that consist of that word. Identify the sentence(s) that best express(es) the meaning of the word. Choose option 5 ‘None of the above’ if the word is not suitable in any of the sentences.
RESILIENCE
A. Growing up in poverty was an resilience that taught me to appreciate the value of all things
B. Angered and resilience fans blocked the stadium exit when their team lost the playoff game.
C. Known for his resilience and determination, the runner refused to let a few losses stop him from competing in future races.
A. Only C
B. Only B
C. Only A
D. Both B and C
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Only C.‘
Key Points
- The given word ‘Resilience’ means The capacity to withstand or to recover quickly from difficulties; toughness. (सँभलने का सामर्थ्य; प्रतिस्कंदन)
- Let us explore the given sentences:
- The word ‘adversity’ should be used in the first sentence as it says growing up in poverty was an unpleasant or difficult situation for someone and that taught him/her to appreciate the value of all things.
- The word ‘adversity’ means difficulties or problems. (कठिनाइयाँ, समस्याएँ, मुसीबतें; विपत्तियाँ)
- The word ‘unruly‘ should be used in the second sentence as it talks about the angered and uncontrollable or wild fans who blocked the stadium exit when their team lost the playoff game.
- The word ‘unruly’ means difficult to control; without discipline. (बेक़ाबू, बेलगाम; अनुशासनहीन, उच्छृंखल)
- The word ‘resilience‘ is used correctly in the third sentence as it talks about a runner who is known for his toughness and determination.
- Example: Our business has shown strong resilience during these unprecedented times.
- The word ‘adversity’ should be used in the first sentence as it says growing up in poverty was an unpleasant or difficult situation for someone and that taught him/her to appreciate the value of all things.
- Therefore, only sentence C best expresses the meaning of the given word.
Hence, the correct answer is option 1.
Sentence A: Growing up in poverty was an adversity that taught me to appreciate the value of all things.
Sentence B: Angered and unruly fans blocked the stadium exit when their team lost the playoff game.
Sentence C: Known for his resilience and determination, the runner refused to let a few losses stop him from competing in future races.
92. In each of the questions given below, three words are given in bold. These three words may or may not be in their correct position. The sentence is then followed by options with the correct combination of words that should replace each other in order to make the sentence grammatically and contextually correct. Find the correct combination of words that replace each other. If the sentence is correct as it is, select ‘5’ as your option.
Mary farewell (A) to go for a cruise (B) on her wanted. (C)
A. A-B
B. B-A and C-B
C. B-C and C-A
D. A-C
E. Non Rearrangement
Solution
The correct answer is option 4 i.e. A-C
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
Mary ______ (A) to go for a ______ (B) on her ______ (C).
- Farewell: A celebration to mark the ending of something – an event in one’s life. ‘Mary’ is already the noun and ‘farewell’ is also a noun, the blank requires a verb.
- Cruise: A journey taken by boat or ship for pleasure.
- Wanted: Had a desire to possess or do (something); wished for. ‘Wanted’ is a verb (an action) and cannot be in the possession of someone and thus cannot be preceded by the pronoun ‘her’.
Hence, we need to interchange A and C in order to make the sentence contextually correct.
Correct Answer: Mary wanted (A) to go for a cruise (B) on her farewell. (C)
93. In each of the questions given below, three words are given in bold. These three words may or may not be in their correct position. The sentence is then followed by options with the correct combination of words that should replace each other in order to make the sentence grammatically and contextually correct. Find the correct combination of words that replace each other. If the sentence is correct as it is, select ‘5’ as your option.
Countries (A) is one of the last (B) openly Communist North Korea. (C)
A. A-B
B. B-C and A-B
C. A-C
D. C-A and A-B
E. No rearrangement
Solution
The correct answer is option 3 i.e. A-C
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
_______ (A) is one of the _______ (B) openly Communist _______ .(C)
- Countries: Plural form of ‘country’ which refers to a nation with its own government that has a fixed territory. ‘Countries’ cannot be the ‘one of’ anything as it is plural and ‘one’ infers singular.
- Last: The final item in a category.
- North Korea: A country in East Asia, the northern part of Korea. It doesn’t fit here contextually or grammatically. We need a plural noun here.
Hence, we need to interchange A and C in order to make it contextually correct.
Correct Sentence: North Korea (A) is one of the last (B) openly Communist countries. (C)
94. In the following question, a sentence is given with three words marked as (A), (B) and (C). These words may or may not be placed in their correct order. Four options with different arrangements of these words have been provided. Mark the option with the correct arrangement as the answer. If no rearrangement is required, mark option (5) as your answer.
With the polar ice caps melting, (A) intense (B) is only going to get more global warming. (C)
A. B-C
B. C-A and A-B
C. B-A
D. B-C and A-C
E. No Rearrangement
Solution
The correct answer is option 1 i.e. B-C
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
With the polar ice caps ______ (A) ______ (B) is only going to get more ______ (C).
- Melting: Becoming liquefied by heat.
- Intense: Of extreme force, degree, or strength. This is an adjective that represents the quality of something. It has to be replaced with a noun.
- Global warming: A natural phenomenon where greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are causing the climate to change. This is a noun and so cannot be used to describe something. We have to replace it with an adjective.
Hence, we need to interchange B and C in order to make the sentence contextually correct.
Correct Sentence: With the polar ice caps melting (A), global warming (B) is only going to get more intense. (C)
95. In the following question, a sentence is given with three words marked as (A), (B) and (C). These words may or may not be placed in their correct order. Four options with different arrangements of these words have been provided. Mark the option with the correct arrangement as the answer. If no rearrangement is required, mark option (5) as your answer.
Samantha was a very issues (A) child but some performance(B) in her life caused disruptions in her intelligent. (C)
A. BAC
B. BCA
C. ABC
D. CAB
E. No Rearangement
Solution
The correct answer is option is 3 i.e. CAB
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
Samantha was a very _______ (A) child but some _______ (B) in her life caused disruptions in her _______ (C).
- Issues: Important matters or topics that should be talked about. A person cannot ‘be’ issues, we can only say that they may ‘have’ issues. Therefore in part A we have to replace issues with an adjective.
- Performance: The act of performing a task or a function is a noun. A performance in life doesn’t cause intelligence, performance is the aspect that is affected. Hence in part C, the word performance is wrong. And should be replaced with a plural noun.
- Intelligent: Refers to a person that shows a high amount of smartness and knowledge. ‘Intelligent’ is an adjective while blank C requires a noun. Hence here it should be replaced.
- Thus on replacing. Plural noun issues in part A will be replaced by adjective intelligent from part C.
- Performance in part B will be replaced by plural noun issues from part A
Hence, A needs to be replaced by C and then B needs to be replaced by A, and finally, C needs to be replaced by B. i.e CAB
Correct Sentence: Samantha was a very intelligent (C) child but some issues (A) in her life caused disruption in her performance (B).
96. The following sentences form a paragraph. The sentences are numbered as P, Q, R, S and T. These five parts are not given in proper order. Read the sentences and choose the alternative that arranges them in the correct order.
P. The krill which feed on algae from sea ice – may be more exposed to plastic.
Q. Microplastics have previously been discovered in Antarctica’s surface waters, sediments and in snow.
R. The studies found 14 different kinds of plastic, and on average, about 12 pieces of plastics were found per litre of water
S. Small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica for what scientists believe is the first time
T. The new discovery could mean the region’s krill is vulnerable.
Question:
Which of the following is the THIRD sentence of the paragraph?
A. P
B. Q
C. R
D. T
E. S
Solution
The correct answer is option 4), i.e. T.
- The given passage is about the detected small pieces of plastic in sea ice in Antarctica.
- We should go through the sentences in the following way:
- The passage should begin with S. It mentions that it is perhaps the first time when small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica.
- The second sentence is Q. It mentions where microplastic was found previously.
- The third sentence is T. It is the continuation of Q as it talks about what this discovery-mentioned in Q- means
- The fourth sentence is P. It is the continuation of T as it talks about the krill mentioned in the previous sentence and how it’s getting exposed.
- The fifth sentence is R. It concludes by stating what is found in the studies.
Therefore, the correct chronological order of the passage is: SQTPR
97. The following sentences form a paragraph. The sentences are numbered as P, Q, R, S and T. These five parts are not given in proper order. Read the sentences and choose the alternative that arranges them in the correct order.
P. The krill which feed on algae from sea ice – may be more exposed to plastic.
Q. Microplastics have previously been discovered in Antarctica’s surface waters, sediments and in snow.
R. The studies found 14 different kinds of plastic, and on average, about 12 pieces of plastics were found per litre of water
S. Small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica for what scientists believe is the first time
T. The new discovery could mean the region’s krill is vulnerable.
Question:
Which of the following is the FOURTH sentence of the paragraph?
A. Q
B. R
C. S
D. P
E. T
Solution
The correct answer is option 4), i.e. P.
- The given passage is about the detected small pieces of plastic in sea ice in Antarctica.
- We should go through the sentences in the following way:
- The passage should begin with S. It mentions that it is perhaps the first time when small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica.
- The second sentence is Q. It mentions where microplastic was found previously.
- The third sentence is T. It is the continuation of Q as it talks about what this discovery-mentioned in Q- means
- The fourth sentence is P. It is the continuation of T as it talks about the krill mentioned in the previous sentence and how it’s getting exposed.
- The fifth sentence is R. It concludes by stating what is found in the studies.
Therefore, the correct chronological order of the passage is: SQTPR
98. The following sentences form a paragraph. The sentences are numbered as P, Q, R, S and T. These five parts are not given in proper order. Read the sentences and choose the alternative that arranges them in the correct order.
P. The krill which feed on algae from sea ice – may be more exposed to plastic.
Q. Microplastics have previously been discovered in Antarctica’s surface waters, sediments and in snow.
R. The studies found 14 different kinds of plastic, and on average, about 12 pieces of plastics were found per litre of water
S. Small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica for what scientists believe is the first time
T. The new discovery could mean the region’s krill is vulnerable.
Question:
Which of the following is the FIFTH sentence of the paragraph?
A. P
B. R
C. Q
D. S
E. T
Solution
The correct answer is option 2), i.e. R.
- The given passage is about the detected small pieces of plastic in sea ice in Antarctica.
- We should go through the sentences in the following way:
- The passage should begin with S. It mentions that it is perhaps the first time when small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica.
- The second sentence is Q. It mentions where microplastic was found previously.
- The third sentence is T. It is the continuation of Q as it talks about what this discovery-mentioned in Q- means
- The fourth sentence is P. It is the continuation of T as it talks about the krill mentioned in the previous sentence and how it’s getting exposed.
- The fifth sentence is R. It concludes by stating what is found in the studies.
Therefore, the correct chronological order of the passage is: SQTPR
99. The following sentences form a paragraph. The sentences are numbered as P, Q, R, S and T. These five parts are not given in proper order. Read the sentences and choose the alternative that arranges them in the correct order.
P. The krill which feed on algae from sea ice – may be more exposed to plastic.
Q. Microplastics have previously been discovered in Antarctica’s surface waters, sediments and in snow.
R. The studies found 14 different kinds of plastic, and on average, about 12 pieces of plastics were found per litre of water
S. Small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica for what scientists believe is the first time
T. The new discovery could mean the region’s krill is vulnerable.
Question:
Which of the following is the FIRST sentence of the paragraph?
A. Q
B. S
C. R
D. T
E. P
Solution
The correct answer is option 2), i.e. S.
- The given passage is about the detected small pieces of plastic in sea ice in Antarctica.
- We should go through the sentences in the following way:
- The passage should begin with S. It mentions that it is perhaps the first time when small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica.
- The second sentence is Q. It mentions where microplastic was found previously.
- The third sentence is T. It is the continuation of Q as it talks about what this discovery-mentioned in Q- means
- The fourth sentence is P. It is the continuation of T as it talks about the krill mentioned in the previous sentence and how it’s getting exposed.
- The fifth sentence is R. It concludes by stating what is found in the studies.
Therefore, the correct chronological order of the passage is: SQTPR
100. The following sentences form a paragraph. The sentences are numbered as P, Q, R, S and T. These five parts are not given in proper order. Read the sentences and choose the alternative that arranges them in the correct order.
P. The krill which feed on algae from sea ice – may be more exposed to plastic.
Q. Microplastics have previously been discovered in Antarctica’s surface waters, sediments and in snow.
R. The studies found 14 different kinds of plastic, and on average, about 12 pieces of plastics were found per litre of water
S. Small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica for what scientists believe is the first time
T. The new discovery could mean the region’s krill is vulnerable.
Question:
Which of the following is the SECOND sentence of the paragraph?
A. P
B. R
C. S
D. T
E. Q
Solution
The correct answer is option 5), i.e. Q.
- The given passage is about the detected small pieces of plastic in sea ice in Antarctica.
- We should go through the sentences in the following way:
- The passage should begin with S. It mentions that it is perhaps the first time when small pieces of plastic have been detected in sea ice in Antarctica.
- The second sentence is Q. It mentions where microplastic was found previously.
- The third sentence is T. It is the continuation of Q as it talks about what this discovery-mentioned in Q- means
- The fourth sentence is P. It is the continuation of T as it talks about the krill mentioned in the previous sentence and how it’s getting exposed.
- The fifth sentence is R. It concludes by stating what is found in the studies.
Therefore, the correct chronological order of the passage is: SQTPR
