1.Directions. Identify the segment of the sentence which contains the grammatical error. If there is no error mark ‘No error’ as your answer.
As long as I am (A) in charge of the office, (B) I have made sure (C) nobody feels unsafe here. (D)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is Option 3 i.e., ‘I have made sure’– the error lies in this part only.
KEY POINTS
- This is a conditional sentence, and in this type of sentence, one sentence depends upon the other because of cause and effect.
- In this case, this type of sentence follows a special structure.
- Conditional words are If, even if, until, unless, as soon as, when, while, as long as, after, etc.
| Conditional word + subject + v1/v5 + object, subject + will/ shall/ may + v1 + object.If + subject + v2 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + v1 + object.If + subject + had + v3 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + have + v3 + object.Had + subject + v3 + object, subject + would + have + v3 + object. |
- The given sentence follows rule number ‘1’, and according to the rule, the error lies in Part ‘C’.
For example- As long as there is sunlight, we will continue filming our videos.
- In the given sentence, ‘have made’ is wrongly used instead of ‘will make’ in the main clause.
Hence, ‘have made’ should be replaced by ‘will make’.
So, the correct sentence is:
“As long as I am in charge of the office, I will make sure nobody feels unsafe here.”
2. Directions. Identify the segment of the sentence which contains the grammatical error. If there is no error mark ‘No error’ as your answer.
If only/ (A) I had rehearsed regularly,/ (B) I had performed well/ (C) in today’s concert. (D)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is Option 3 i.e., ‘I had performed well’.
Key Points
- This is a conditional sentence, and in this type of sentence, one sentence depends upon the other because of cause and effect.
- In this case, this type of sentence follows a special structure.
- Conditional words are If, If only, until, unless, as soon as, when, while, as long as, since, etc.
| Conditional word + subject + v1/v5 + object, subject + will/ shall/ may + v1 + object.If + subject + v2 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + v1 + object.If + subject + had + v3 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + have + v3 + object.Had + subject + v3 + object, subject + would + have + v3 + object. |
- The given sentence follows rule number ‘3’, and according to the rule, the error lies in Part ‘C’.
- Example- If only I had listened to the audio clip, I would have known the truth.
- In the given sentence, ‘had performed’ is wrongly used instead of ‘would have performed’ in the main clause.
Hence, ‘had performed’ should be replaced by ‘would have performed’.
So, the correct sentence is: “If only I had rehearsed regularly, I would have performed well in today’s concert.”
3. Directions. Identify the segment of the sentence which contains the grammatical error. If there is no error mark ‘No error’ as your answer.
As long as Stefan is/ (A) the head of the project,/ (B) he will not be allowing any changes/ (C) in the rules. (D)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is Option 3 i.e., ‘he will not be allowing any changes’– the error lies in this part only.
KEY POINTS
- This is a conditional sentence, and in this type of sentence, one sentence depends upon the other because of cause and effect.
- In this case, this type of sentence follows a special structure.
- Conditional words are If, even if, until, unless, as soon as, when, while, as long as, after, etc.
| Conditional word + subject + v1/v5 + object, subject + will/ shall/ may + v1 + object.If + subject + v2 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + v1 + object.If + subject + had + v3 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + have + v3 + object.Had + subject + v3 + object, subject + would + have + v3 + object. |
- The given sentence follows rule number ‘1’, and according to the rule, the error lies in Part ‘C’.
For example- As long as there is petrol in the car, we will continue driving.
- In the given sentence, ‘will not be allowing’ is wrongly used instead of ‘will not allow’ in the main clause.
Hence, ‘will not be allowing’ should be replaced by ‘will not allow’.
So, the correct sentence is:
“As long as Stefan is the head of the project, he will not allow any changes in the rules.”
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
The conditional expressions, for example- ‘as long as’, ‘so long as’, ‘on condition that’ is used to impose certain conditions or set restrictions to circumstances.
4. Directions. Identify the segment of the sentence which contains the grammatical error. If there is no error mark ‘No error’ as your answer.
If Mathur’s uncle had informed us earlier (A) / about his daughter’s illness, (B) / we meet her (C) / before leaving Delhi. (D)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is Option 3 i.e., ‘we meet her’– the error lies in this part only.
KEY POINTS
- This is a conditional sentence, and in this type of sentence, one sentence depends upon the other because of cause and effect.
- In this case, this type of sentence follows a special structure.
- Conditional words are If, until, unless, as soon as, when, while, as long as, since, etc.
| Conditional word + subject + v1/v5 + object, subject + will/ shall/ may + v1 + object.If + subject + v2 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + v1 + object.If + subject + had + v3 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + have + v3 + object.Had + subject + v3 + object, subject + would + have + v3 + object. |
- The given sentence follows rule number ‘3’, and according to the rule, the error lies in Part ‘C’.
For example- If we had reached the bus stop on time, we would have seen the Chief Minister’s rally.
- In the given sentence, ‘meet’ is wrongly used instead of ‘would have met’ in the main clause.
Hence, ‘meet’ should be replaced by ‘would have met’.
So, the correct sentence is:
“If Mathur’s uncle had informed us earlier about his daughter’s illness, we would have met her before leaving Delhi.”
Mistake Point:
It is important to remember that when we use the third conditional, the Past Perfect and not the Simple Past Tense is used in the subordinate clause.
- For example-
♦If John had learned driving, he would have landed a job as a trainer in the driving school. (Correct)
♦If John learned driving, he would have landed a job as a trainer in the driving school. (Incorrect)
5. Directions. Identify the segment of the sentence which contains the grammatical error. If there is no error mark ‘No error’ as your answer.
If I find/ (A) her resume,/ (B) I will be forwarding it/ (C) to the HR department. (D)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is Option 3 i.e., ‘I will be forwarding it’– the error lies in this part only.
KEY POINTS
- This is a conditional sentence, and in this type of sentence, one sentence depends upon the other because of cause and effect.
- In this case, this type of sentence follows a special structure.
- Conditional words are If, even if, until, unless, as soon as, when, while, as long as, after, etc.
| Conditional word + subject + v1/v5 + object, subject + will/ shall/ may + v1 + object.If + subject + v2 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + v1 + object.If + subject + had + v3 + object, subject + would/ should/ could/ might + have + v3 + object.Had + subject + v3 + object, subject + would + have + v3 + object. |
- The given sentence follows rule number ‘1’, and according to the rule, the error lies in Part ‘C’.
For example- If Ana rehearses regularly, she will become a good singer.
- In the given sentence, ‘will be forwarding’ is wrongly used instead of ‘will forward’ in the main clause.
Hence, ‘will be forwarding’ should be replaced by ‘will forward’.
So, the correct sentence is:
“If I find her resume, I will forward it to the HR department.”
6. Direction: In the following question, two columns are given containing three phrases each. The phrases are labelled A, B, and C in the first column and P, Q, and R in the second column. A phrase from the first column may or may not connect with a phrase in the second column to make a grammatically and contextually meaningful sentence. Identify the correct option from those given below that gives the correct sequence in which one or more sentences can be formed. If none of the options makes it possible for a meaningful sentence to be formed, indicate ‘None of these’ as your answer.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| (A) Many people were | (P) because of the heavy rains. |
| (B) The river overflowed | (Q) damage to many buildings. |
| (C) The flooding caused | (R) stranded in their homes. |
A. A-Q
B. C-P and B-Q
C. B-P
D. A-P and B-R
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is B-P.
Key Points
The correct combination of sentences among the given options is B and P.
Let us look at the sentence combinations in detail:
- A can be used only with R: Many people were stranded c in their homes.
- A cannot be used with P or Q because it would not make a meaningful sentence.
Many people were because of the heavy rains.
Many people were damage to many buildings. - Next, B is used with P to make a meaningful sentence: The river overflowed because of the heavy rains.
- If we consider the combination B-Q, it does not make a meaningful sentence.
The river overflowed damage to many buildings. - Thus, the final combination is C–Q: The flooding caused damage to many buildings.
Thus, the correct combination of the sentence is:(B) The river overflowed (P)because of the heavy rains.
Hint
Sentence combinations can be easily identified if one part contains a noun and the other part contains the verb or pronoun associated with this noun.
- In the sentence Many people were stranded in their homes, ‘people’ is a noun, and ‘their’ is its possessive pronoun.
- We can identify the right combinations by eliminating those sentences that do not have this agreement.
7. Direction: In the following question, two columns are given containing three phrases each. The phrases are labelled A, B, and C in the first column and P, Q, and R in the second column. A phrase from the first column may or may not connect with a phrase in the second column to make a grammatically and contextually meaningful sentence. Identify the correct option from those given below that gives the correct sequence in which one or more sentences can be formed. If none of the options makes it possible for a meaningful sentence to be formed, indicate ‘None of these’ as your answer.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| (A) The car was parked | (P) enter the principal’s office. |
| (B) No one is allowed to | (Q) a cake for his birthday. |
| (C) They planned to make | (R) under a large mango tree. |
A. A-Q and C-P
B. A-P
C. A-R and B-P
D. C-R
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is A-R and B-P.
Key Points
The correct combinations from the given options that can make meaningful sentences are A-R and B-P.
Let us take a look at the given combinations:
- A is combined with R to make a meaningful sentence: The car was parked under a large mango tree.
- A cannot be used with P and Q, because it would not make a meaningful sentence:
The car was parked enter the principal’s office.
The car was parked a cake for his birthday.
- The next combination would be B-P: No one is allowed to enter the principal’s office.
- B cannot make a meaningful sentence when it is used with Q:
No one is allowed to a cake for his birthday. - Then, C can be used with Q: They planned to make a cake for his birthday.
The correct combinations will be: (A) The car was parked (R) under a large mango tree & (B) No one is allowed to (P) enter the principal’s office.
Thus, the correct answer is: A-R and B-P.
Additional Information
The verb ‘to park’ is followed by a preposition when it is required to denote the location.
- I parked the car beside the store.
- He parked the bike near the lamp-post.
No preposition is required when the location is not specified in the sentence.
- I parked the car.
- He parked the bike.
8. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
In this time of lockdown, people are struggling to boost their ______ .
A. tension
B. morale
C. entice
D. illusion
E. diligence
Solution
The correct answer is ‘morale‘.
Key Points
- The word “morale” refers to the confidence, enthusiasm, and discipline of a person or group at a particular time. (उत्साह/मनोबल)
- In a lockdown situation, people often struggle to maintain their morale due to isolation and uncertainty.
- The other options: “tension,” “entice,” “illusion,” and “diligence” do not fit the context as appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 2‘.
Complete Sentence: In this time of lockdown, people are struggling to boost their morale.
Additional Information
- Tension (तनाव): Refers to mental or emotional strain; does not fit the context.
- Entice (लुभाना): Means to attract or tempt someone; unrelated to the context.
- Illusion (भ्रम): Refers to a false idea or belief; not suitable here.
- Diligence (परिश्रम): Means careful and persistent work or effort; does not fit the sentence.
9. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
______ of India’s education should have two objectives.
A. Wavering
B. Preach
C. Conflict
D. Reform
E.Regarding
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Reform‘.
Key Points
- The word “Reform” means to make changes in something in order to improve it. (सुधार)
- The sentence suggests that India’s education system should aim at improving or making positive changes, which aligns with the meaning of “Reform.”
- The other options: “Wavering,” “Preach,” “Conflict,” and “Regarding” do not fit the context appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 4‘.
Complete Sentence: Reform of India’s education should have two objectives.
Additional Information
- Wavering (डगमगाना): means being uncertain or indecisive.
- Preach (उपदेश देना): means to deliver a sermon or advice.
- Conflict (संघर्ष): means a serious disagreement or argument.
- Regarding (के संबंध में): means concerning or about something.
10. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
Many marginalised groups have been ______ during the Covid-19 lockdown.
A. polished
B. neglected
C. prepared
D. directed
E. analysed
Solution
The correct answer is ‘neglected‘.
Key Points
- The word “neglected” means to fail to care for properly or to disregard. (उपेक्षित)
- During the Covid-19 lockdown, many marginalised groups were overlooked or not given the necessary attention and support.
- The other options: “polished,” “prepared,” “directed,” and “analysed” do not fit the context as appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 2‘.
Complete Sentence: Many marginalised groups have been neglected during the Covid-19 lockdown.
Additional Information
- Polished (सुधारना): means refined or sophisticated, which does not fit the context.
- Prepared (तैयार करना): means made ready, which does not fit the sentence meaning.
- Directed (निर्देशित करना): means guided or controlled, which is unrelated in this context.
- Analysed (विश्लेषण करना): means examined methodically, which is not suitable here.
11. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
The artificial intelligence company, OpenAI, recently ______ a neural network that created news articles so convincing.
A. demonstrated
B. concentrated
C. decomposed
D. accumulated
E. bragged
Solution
The correct answer is ‘demonstrated‘.
Key Points
- The word “demonstrated” means to show or exhibit something clearly and convincingly.
- The context of the sentence suggests that OpenAI showed or showcased a neural network.
- The other options: “concentrated,” “decomposed,” “accumulated,” and “bragged” do not fit the sentence appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 1‘.
Complete Sentence: The artificial intelligence company, OpenAI, recently demonstrated a neural network that created news articles so convincing.
Additional Information
- Concentrated: means focused attention or gathered in one place; not relevant here.
- Decomposed: means broken down into smaller parts; does not fit the context.
- Accumulated: means gathered or collected over time; irrelevant in this context.
- Bragged: means to boast or talk with pride; does not suit the sentence.
12. Each of the following sentences has a blank space and five words are given below. Click on the word which you consider the most APPROPRIATE to fit the blank.
Heat is the _____ cause of these fires.
A. underlying
B. forbidden
C. compensating
D. regime
E. reserved
Solution
The correct answer is ‘underlying‘.
Key Points
- The word “underlying” means being the primary or fundamental cause or basis of something.
- Heat serves as the fundamental reason for the occurrence of these fires, making “underlying” the most appropriate choice.
- The other options, “forbidden“, “compensating“, “regime“, and “reserved“, do not fit the context as appropriately.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 1‘.
Complete Sentence: Heat is the underlying cause of these fires.
Additional Information
- Forbidden: Means prohibited or not allowed.
- Compensating: Means offsetting or counterbalancing something.
- Regime: Refers to a government or system of rule.
- Reserved: Means kept for a specific purpose or person.
13. Directions: Given below is a word, followed by three sentences that consist of that word. Identify the sentence(s) that express(es) the meaning of the word.
RANGE
A. You need to range your eating habits.
B. She cooked her meals on a gas range.
C. The interest rate varies from bank to bank, but the general range is from 4.5 to 6 percent.
A. Only A
B. Both A and B
C. Only B
D. Both B and C
E. Only C
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Both B and C.‘
Key Points
- The word ‘Range‘ as a noun means A large cooking stove with burners or hotplates and one or more ovens, all of which are kept continually hot.
- The word ‘Range‘ as a noun means The area of variation between upper and lower limits on a particular scale.
- In sentence A, the word ‘Range‘ is inappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
- In sentence B, the word ‘Range‘ has been correctly used as a noun as the sentence is talking about preparing meals on a large cooking gas stove.
- In sentence C, the word ‘Range‘ has been correctly used as a noun as the sentence is talking about the general variation of the bank interest rates.
Hence, the only possible answer is option 4.
14. Directions: Given below is a word, followed by three sentences that consist of that word. Identify the sentence(s) that express(es) the meaning of the word.
UNION
A. He had an union there was trouble brewing.
B. We will take decisive steps towards political union with Europe.
C. The union plans to raise the issue of overtime.
A. Only A
B. Both A and B
C. Only B
D. Both B and C
E. Only C
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Both B and C.‘
Key Points
- The word ‘Union‘ as a noun means The action of joining together or the fact of being joined together, especially in a political context.
- The word ‘Union‘ as a noun means A society or association formed by people with a common interest or purpose.
- In sentence A, the word ‘Union‘ is inappropriately used and doesn’t fit the context of the sentence.
- In sentence B, the word ‘Union‘ has been correctly used as a noun as the sentence is talking about taking decisive steps towards joining together with Europe in a political context.
- In sentence C, the word ‘Union‘ has been correctly used as a noun as the sentence is talking about raising the issue of overtime by a society or association formed by people.
Hence, the only possible answer is option 4.
15. In each question, one sentence is given. In each sentence, certain words are in bold and numbered from A to E. Below the sentences are given five options with possible pairs of interchange of those bold words. Choose the pair(s) of words which are needed to be interchanged to make the sentence grammatically correct and meaningful.
Nobody (A) disputes the (B) route of higher and (C) informed voter turn-out for democracy, but instead of taking the compulsory (D) benefits for wider participation of people in the election process – technology can be (E) harnessed to achieve this end.
A. A-E
B. A-B
C. C-D
D. B-D
E. D-E
Solution
The correct answer is option 4.
Route means a way or course is taken in getting from a starting point to a destination.
Benefits mean an advantage or profit gained from something.
We can look into the sentence in the following way-
Nobody (A) _____ the (B) _____ of higher and (C) _____ voter turn-out for democracy, but instead of taking the compulsory (D) _____ for wider participation of people in the election process – technology can be (E) _____to achieve this end.
Disputes means argue about (something). C and E justify the bold word. Clearly, B-D should be interchanged to make the sentence meaningful. So, B-D is correct.
The correct sentence is-
Nobody (A) disputes the (B) benefits of higher and (C) informed voter turn-out for democracy, but instead of taking the compulsory (D) route for wider participation of people in the election process – technology can be (E) harnessed to achieve this end.
16. In each question, one sentence is given. In each sentence, certain words are in bold and numbered from A to E. Below the sentences are given five options with possible pairs of interchange of those bold words. Choose the pair(s) of words which are needed to be interchanged to make the sentence grammatically correct and meaningful.
It has often been (A) suggest that compulsory voting will improve political (B) participation, but (C) empirical evidence and (D) experience of countries with compulsory voting (E) argued otherwise.
A. A-B
B. B-C
C. A-E
D. C-D
E. D-E
Solution
The correct answer is option 3.
Key Points
- Suggest means put forward for consideration.
- Argued means persuading someone to do or not to do (something) by giving reasons.
- We can look into the sentence in the following way-
It has often been (A)______ that compulsory voting will improve political (B) ______, but (C) ______ evidence and (D) ______ of countries with compulsory voting (E) ______ otherwise.
B is correct and meaningful. Empirical means based on, concerned with, or verifiable by observation or experience rather than theory or pure logic. Also, D justifies the bold word. Clearly the word at A should be in the third form. So, A-E is correct.
The correct sentence is-
It has often been (A) argued that compulsory voting will improve political (B) participation, but (C) empirical evidence and (D) experience of countries with compulsory voting (E) suggest otherwise.
17. In each question, one sentence is given. In each sentence, certain words are in bold and numbered from A to E. Below the sentences are given five options with possible pairs of interchange of those bold words. Choose the pair(s) of words which are needed to be interchanged to make the sentence grammatically correct and meaningful.
The energy (A) choices the country makes will be (B) critical for the future of the planet, and the IEA is (C) expertise to support the government of India and (D) share knowledge and (E) eager.
A. C-E,A-B
B. A-B
C. C-E
D. A-D
E. C-D
Solution
The correct answer is option 3.
Key Points
- Expertise means expert skill or knowledge in a particular field.
- Eager means strongly wanting to do or have something.
- We can look into the sentence in the following way-
The energy (A) _____ the country makes will be (B) _____ for the future of the planet, and the IEA is (C) _____ to support the government of India and (D) _____ knowledge and (E) _____.
A is meaningful. Critical means having decisive or crucial importance in the success, failure, or existence of something. Also, D justifies the bold word. C requires a verb and E requires a noun. So, C-E is correct.
The correct sentence is-
The energy (A) choices the country makes will be (B) critical for the future of the planet, and the IEA is (C) eager to support the government of India and (D) share knowledge and (E) expertise.
18. Read the passage and answer the questions that follow. Some words may be highlighted for you. Pay careful attention.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) on Monday issued a circular notifying new disclosure norms on sustainability related reporting for the top 1,000 listed companies by market cap by FY23. Such a reporting will now be under a new business responsibility and sustainability report (BRSR) format. The decision was first made at SEBI’s board meeting.
“The BRSR is a notable departure from the existing business responsibility report and a significant step towards bringing sustainability reporting at par with financial reporting,” SEBI said in the circular.
Now, the companies will need to provide an overview of their material environmental, social, governance risks and opportunities and approach to mitigate or adapt to the risks along with financial implications. Sustainability related goals and targets and performance and environment-related disclosures covering aspects such as resource usage (energy and water), air pollutant emissions, greenhouse emissions, transitioning to circular economy, waste generated and waste management practices and bio-diversity may have to be provided.
The social-related disclosures will cover the workforce, value chain, communities and consumers. Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings. On the community front, companies need to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility. For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labelling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
To give time to companies to adapt to the new requirements, the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22 and mandatory from FY23. However, companies are encouraged to be early adopters of the BRSR, thus being at the forefront of sustainability reporting, SEBI said.
Question:
Which of the following is antonym of the word disclosure?
A. divulgence
B. exposure
C. concealment
D. revelation
E. avowal
Solution
The correct answer is option 3 i.e. concealment.
Key Points
- The meaning of the word disclosure is the act of making something known or the fact that is made known.
- Let’s see the meanings of the given options
- divulgence– the action of revealing private or sensitive information.
- exposure– when something bad that someone has done is made public
- revelation– when something is made known that was secret, or a fact that is made known
- avowal– a statement in which you declare or admit something that you believe
- concealment– when something is hidden
- According to the meanings of the words, we say that concealment is the right answer.
19. Read the passage and answer the questions that follow. Some words may be highlighted for you. Pay careful attention.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) on Monday issued a circular notifying new disclosure norms on sustainability related reporting for the top 1,000 listed companies by market cap by FY23. Such a reporting will now be under a new business responsibility and sustainability report (BRSR) format. The decision was first made at SEBI’s board meeting.
“The BRSR is a notable departure from the existing business responsibility report and a significant step towards bringing sustainability reporting at par with financial reporting,” SEBI said in the circular.
Now, the companies will need to provide an overview of their material environmental, social, governance risks and opportunities and approach to mitigate or adapt to the risks along with financial implications. Sustainability related goals and targets and performance and environment-related disclosures covering aspects such as resource usage (energy and water), air pollutant emissions, greenhouse emissions, transitioning to circular economy, waste generated and waste management practices and bio-diversity may have to be provided.
The social-related disclosures will cover the workforce, value chain, communities and consumers. Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings. On the community front, companies need to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility. For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labelling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
To give time to companies to adapt to the new requirements, the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22 and mandatory from FY23. However, companies are encouraged to be early adopters of the BRSR, thus being at the forefront of sustainability reporting, SEBI said.
Question:
Which of the following is synonym of the word mitigate?
A. soothe
B. aggravate
C. exacerbate
D. heighten
E. intensify
Solution
The correct answer is option 1 i.e. soothe.
Key Points
- The meaning of the word mitigate is to make something less harmful, unpleasant or bad.
- Let’s see the meanings of the given options
- soothe– to make someone feel calm or less worried
- aggravate– to make a bad situation worse
- exacerbate– to make something which is already bad worse
- heighten– to increase or make something increase, especially an emotion or effect
- intensify– to become greater, more serious or more extreme
- According to the meanings of the words, we can find our right answer i.e. soothe.
20. Read the passage and answer the questions that follow. Some words may be highlighted for you. Pay careful attention.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) on Monday issued a circular notifying new disclosure norms on sustainability related reporting for the top 1,000 listed companies by market cap by FY23. Such a reporting will now be under a new business responsibility and sustainability report (BRSR) format. The decision was first made at SEBI’s board meeting.
“The BRSR is a notable departure from the existing business responsibility report and a significant step towards bringing sustainability reporting at par with financial reporting,” SEBI said in the circular.
Now, the companies will need to provide an overview of their material environmental, social, governance risks and opportunities and approach to mitigate or adapt to the risks along with financial implications. Sustainability related goals and targets and performance and environment-related disclosures covering aspects such as resource usage (energy and water), air pollutant emissions, greenhouse emissions, transitioning to circular economy, waste generated and waste management practices and bio-diversity may have to be provided.
The social-related disclosures will cover the workforce, value chain, communities and consumers. Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings. On the community front, companies need to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility. For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labelling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
To give time to companies to adapt to the new requirements, the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22 and mandatory from FY23. However, companies are encouraged to be early adopters of the BRSR, thus being at the forefront of sustainability reporting, SEBI said.
Question:
Which of the following is synonym of the word notable?
A. forgettable
B. unmemorable
C. unremarkable
D. standard
E. citable
Solution
The correct answer is option 5 i.e. citable.
Key Points
- The meaning of the word notable is important and deserving attention.
- Let’s see the meanings of the given options
- forgettable– not important or good enough to be remembered
- unmemorable– something that is not worth remembering it
- unremarkable– ordinary and not interesting
- standard– a level of quality
- citable– To mention or bring forward as support
- According to the meanings of the words, we can get our answer i.e. citable.
21. Read the passage and answer the questions that follow. Some words may be highlighted for you. Pay careful attention.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) on Monday issued a circular notifying new disclosure norms on sustainability related reporting for the top 1,000 listed companies by market cap by FY23. Such a reporting will now be under a new business responsibility and sustainability report (BRSR) format. The decision was first made at SEBI’s board meeting.
“The BRSR is a notable departure from the existing business responsibility report and a significant step towards bringing sustainability reporting at par with financial reporting,” SEBI said in the circular.
Now, the companies will need to provide an overview of their material environmental, social, governance risks and opportunities and approach to mitigate or adapt to the risks along with financial implications. Sustainability related goals and targets and performance and environment-related disclosures covering aspects such as resource usage (energy and water), air pollutant emissions, greenhouse emissions, transitioning to circular economy, waste generated and waste management practices and bio-diversity may have to be provided.
The social-related disclosures will cover the workforce, value chain, communities and consumers. Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings. On the community front, companies need to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility. For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labelling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
To give time to companies to adapt to the new requirements, the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22 and mandatory from FY23. However, companies are encouraged to be early adopters of the BRSR, thus being at the forefront of sustainability reporting, SEBI said.
Question:
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option.
A) the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22.
B) the reporting of BRSR will be mandatory from FY23.
C) Both the points are just to give some time to the companies.
A. A) is correct but B) is wrong.
B. C) is wrong but B) is correct
C. C) is correct B) is right.
D. A) is wrong but C) is right.
E. All statements are right.
Solution
The correct answer is option 5 i.e. All statements are right.
Key Points
- According to the line of the passage, To give time to companies to adapt to the new requirements, the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22 and mandatory from FY23.
- By the above-mentioned line, we can infer that all the statements are absolutely correct.
22. Read the passage and answer the questions that follow. Some words may be highlighted for you. Pay careful attention.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) on Monday issued a circular notifying new disclosure norms on sustainability related reporting for the top 1,000 listed companies by market cap by FY23. Such a reporting will now be under a new business responsibility and sustainability report (BRSR) format. The decision was first made at SEBI’s board meeting.
“The BRSR is a notable departure from the existing business responsibility report and a significant step towards bringing sustainability reporting at par with financial reporting,” SEBI said in the circular.
Now, the companies will need to provide an overview of their material environmental, social, governance risks and opportunities and approach to mitigate or adapt to the risks along with financial implications. Sustainability related goals and targets and performance and environment-related disclosures covering aspects such as resource usage (energy and water), air pollutant emissions, greenhouse emissions, transitioning to circular economy, waste generated and waste management practices and bio-diversity may have to be provided.
The social-related disclosures will cover the workforce, value chain, communities and consumers. Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings. On the community front, companies need to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility. For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labelling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
To give time to companies to adapt to the new requirements, the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22 and mandatory from FY23. However, companies are encouraged to be early adopters of the BRSR, thus being at the forefront of sustainability reporting, SEBI said.
Question:
Which of the following is not covered in the social-related disclosures?
A. workforce
B. value chain
C. commodities
D. communities
E. consumers
Solution
The correct answer is option 3 i.e. commodities.
Key Points
- According to the line of the passage, The social-related disclosures will cover the workforce, value chain, communities and consumers.
- By the above-mentioned bold line, we can all the points that are in option except commodities.
Hence, the right answer is commodities.
23. Read the passage and answer the questions that follow. Some words may be highlighted for you. Pay careful attention.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) on Monday issued a circular notifying new disclosure norms on sustainability related reporting for the top 1,000 listed companies by market cap by FY23. Such a reporting will now be under a new business responsibility and sustainability report (BRSR) format. The decision was first made at SEBI’s board meeting.
“The BRSR is a notable departure from the existing business responsibility report and a significant step towards bringing sustainability reporting at par with financial reporting,” SEBI said in the circular.
Now, the companies will need to provide an overview of their material environmental, social, governance risks and opportunities and approach to mitigate or adapt to the risks along with financial implications. Sustainability related goals and targets and performance and environment-related disclosures covering aspects such as resource usage (energy and water), air pollutant emissions, greenhouse emissions, transitioning to circular economy, waste generated and waste management practices and bio-diversity may have to be provided.
The social-related disclosures will cover the workforce, value chain, communities and consumers. Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings. On the community front, companies need to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility. For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labelling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
To give time to companies to adapt to the new requirements, the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22 and mandatory from FY23. However, companies are encouraged to be early adopters of the BRSR, thus being at the forefront of sustainability reporting, SEBI said.
Question:
Which of the following is not compulsory for the companies to provide?
A. governance risks
B. an overview of their material environmental
C. adapt to the risks
D. data of all departments
E. financial implications
Solution
The correct answer is option 4 i.e. data of all departments.
Key Points
- According to the line of the passage, the companies will need to provide an overview of their material environmental, social, governance risks and opportunities and approach to mitigate or adapt to the risks along with financial implications.
- By the above-mentioned bold line, we can infer our right answer.
Hence, the right answer is data of all departments.
24. Read the passage and answer the questions that follow. Some words may be highlighted for you. Pay careful attention.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) on Monday issued a circular notifying new disclosure norms on sustainability related reporting for the top 1,000 listed companies by market cap by FY23. Such a reporting will now be under a new business responsibility and sustainability report (BRSR) format. The decision was first made at SEBI’s board meeting.
“The BRSR is a notable departure from the existing business responsibility report and a significant step towards bringing sustainability reporting at par with financial reporting,” SEBI said in the circular.
Now, the companies will need to provide an overview of their material environmental, social, governance risks and opportunities and approach to mitigate or adapt to the risks along with financial implications. Sustainability related goals and targets and performance and environment-related disclosures covering aspects such as resource usage (energy and water), air pollutant emissions, greenhouse emissions, transitioning to circular economy, waste generated and waste management practices and bio-diversity may have to be provided.
The social-related disclosures will cover the workforce, value chain, communities and consumers. Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings. On the community front, companies need to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility. For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labelling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
To give time to companies to adapt to the new requirements, the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22 and mandatory from FY23. However, companies are encouraged to be early adopters of the BRSR, thus being at the forefront of sustainability reporting, SEBI said.
Question:
Which of the following topic is related to SEBI’s circular that is issued for the top companies?
A. Stability maintenance
B. Sustainability related reporting
C. low loss venture
D. encouragement of taking risk
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is option 2 i.e. Sustainability related reporting.
Key Points
- According to the line of the passage, The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) on Monday issued a circular notifying new disclosure norms on sustainability related reporting for the top 1,000 listed companies by market cap by FY23.
- By the above-mentioned bold line, it is clear that option 2 is right.
25. Read the passage and answer the questions that follow. Some words may be highlighted for you. Pay careful attention.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) on Monday issued a circular notifying new disclosure norms on sustainability related reporting for the top 1,000 listed companies by market cap by FY23. Such a reporting will now be under a new business responsibility and sustainability report (BRSR) format. The decision was first made at SEBI’s board meeting.
“The BRSR is a notable departure from the existing business responsibility report and a significant step towards bringing sustainability reporting at par with financial reporting,” SEBI said in the circular.
Now, the companies will need to provide an overview of their material environmental, social, governance risks and opportunities and approach to mitigate or adapt to the risks along with financial implications. Sustainability related goals and targets and performance and environment-related disclosures covering aspects such as resource usage (energy and water), air pollutant emissions, greenhouse emissions, transitioning to circular economy, waste generated and waste management practices and bio-diversity may have to be provided.
The social-related disclosures will cover the workforce, value chain, communities and consumers. Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings. On the community front, companies need to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility. For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labelling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
To give time to companies to adapt to the new requirements, the reporting of BRSR will be voluntary for FY22 and mandatory from FY23. However, companies are encouraged to be early adopters of the BRSR, thus being at the forefront of sustainability reporting, SEBI said.
Question:
Consider the following statements and answer the question.
A) Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings.
B) On the community front, there is no need for companies to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility.
C) For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labelling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
A. A) and B) are right.
B. All are right.
C. Both A) and C) are right.
D. Only B) is right.
E. A) is right but C) is worng.
Solution
The correct answer is option 3 i.e. Both A) and C) are right.
Key Points
- According to the line of the passage, Companies will have to disclose the gender and social diversity of employees, including measures for differently-abled employees and workers, turnover rates, median wages, welfare benefits to permanent and contractual employees/workers, occupational health and safety and trainings. On the community front, companies need to make disclosures on social impact assessments (SIA), rehabilitation and resettlement and corporate social responsibility. For consumers, they have to make disclosures on product labeling, product recall and complaints in respect of data privacy and cybersecurity.
- When we go through the above-mentioned line, we can easily get that the statement A) and C) are correct but statement B) is incorrect.
26. The question below contains four scattered segments of a sentence. Indicate the sequence which correctly assembles the segments and completes the sentence.
(A) have once met, (B) really part them (C) when the kindred spirits (D) no human power can
A. CADB
B. BADC
C. CBDA
D. DBAC
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is Option (1) i.e., CADB.
Key Points
- The sentence begins with (C) “when the kindred spirits,” as it introduces the main subject of the sentence.
- The next part is (A) “have once met,” which logically follows the subject and completes the idea of meeting.
- Then comes (D) “no human power can,” which adds the context about the inability to separate them.
- Finally, (B) “really part them,” completes the sentence meaningfully.
Therefore, the correct sequence is CADB.
Additional Information
- Option 2 (BADC): This sequence disrupts the logical flow of the sentence, as “no human power can” comes too early.
- Option 3 (CBDA): This sequence places “really part them” before “no human power can,” which creates an illogical structure.
- Option 4 (DBAC): This sequence starts with “no human power can,” which lacks proper context for the subject.
- Option 5 (None of these): This option is incorrect as the correct sequence is given in Option 1.
27. The question below contains four scattered segments of a sentence. Indicate the sequence which correctly assembles the segments and completes the sentence.
(A) they shrink from committing it (B) of it and not because (C) mankind censure injustice, fearing (D) that they may be the victims
A. CADB
B. CDAB
C. CDBA
D. ADCB
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is Option (3) i.e., CDBA
Key Points
- The sentence begins with the idea that “mankind censure injustice,” which is correctly indicated by part (C).
- Following this, “fearing that they may be the victims” (CD) continues the logical flow, explaining why mankind censures injustice.
- The next part, “of it and not because” (DB), transitions the thought, clarifying that the censure is due to fear and not other reasons.
- Ending with “they shrink from committing it” (BA) completes the sentence by emphasizing the reluctance to commit injustice.
Therefore, the correct answer is CDBA.
Additional Information
- Option 1 (CADB): This option starts with “mankind censure injustice, fearing of it and not because,” which disrupts the logical flow and creates grammatical errors.
- Option 2 (CDAB): This option starts with “mankind censure injustice, fearing that they may be the victims of it,” but prematurely concludes the thought without completing the sentence meaningfully.
- Option 4 (ADCB): This option starts with “they shrink from committing it of it and not because mankind censure injustice,” which forms a fragmented and confusing structure.
28. The question below contains four scattered segments of a sentence. Indicate the sequence which correctly assembles the segments and completes the sentence.
(A) trying to decide the best way (B) at the boulder for a long time, (C) the railroad workers stared (D) to demolish it with explosives
A. ABCD
B. CBAD
C. BACD
D. CDAB
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is Option (2) i.e., CBAD.
Key Points
- The sentence begins with the subject “The railroad workers,” which is correctly indicated by part (C).
- Following the subject, “stared at the boulder for a long time” (CB) continues the logical sequence, making it clear what the workers were doing.
- The next part, “trying to decide the best way,” starts the explanation about their actions, indicated by (A).
- Ending with “to demolish it with explosives” (D) completes the sentence by stating their ultimate goal.
Therefore, the correct answer is CBAD.
Additional Information
- Option 1 (ABCD): This option starts with “trying to decide the best way stared at the boulder for a long time,” which creates a fragmented sentence structure.
- Option 3 (BACD): This option starts with “at the boulder for a long time trying to decide the best way,” which makes the sentence incomplete.
- Option 4 (CDAB): This option starts with “to demolish it with explosives stared at the boulder for a long time,” which is grammatically incorrect.
- Option 5 (None of these): This option is incorrect as the correct sequence is clearly available.
29. The question below contains four scattered segments of a sentence. Indicate the sequence which correctly assembles the segments and completes the sentence.
(A) when I woke up was enough (B) all that I had left behind (C) the sight that greeted me (D) to make me appreciate
A. ABDC
B. DABC
C. CABD
D. CADB
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is Option (4) i.e., CADB.
Key Points
- The sentence begins with (C) “the sight that greeted me,” introducing what is being described.
- Following this, (A) “when I woke up was enough” logically continues the description, providing context to the sight mentioned earlier.
- (D) “to make me appreciate” follows next, completing the thought and linking it to the consequence of the sight.
- (B) “all that I had left behind” concludes the sentence, giving the final detail to the reflection.
Therefore, the correct sequence is CADB.
Additional Information
- Option 1 (ABDC): This sequence starts with “when I woke up was enough,” which does not establish the subject of the sentence, making it incomplete and unclear.
- Option 2 (DABC): Starting with “to make me appreciate” creates a fragmented and confusing sentence structure that lacks context.
- Option 3 (CABD): Although this option starts correctly with “the sight that greeted me,” it fails to maintain the logical flow of the sentence.
30. The question below contains four scattered segments of a sentence. Indicate the sequence which correctly assembles the segments and completes the sentence.
(A) bread and a cup of soup (B) and almost an hour and a half later, (C) the man left under protest, (D) came back with four pieces of
A. ACDB
B. ABCD
C. CBDA
D. CBAD
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is Option (3) i.e., CBDA.
Key Points
- The sentence begins with “the man left under protest,” which is correctly indicated by part (C).
- Following the subject, “and almost an hour and a half later,” (CB) continues the logical sequence, describing the time lapse.
- The next part, “came back with four pieces of,” indicated by (CBDA), logically continues and sets up the context for what the man brought back.
- Ending with, “bread and a cup of soup” (CBDA) completes the sentence by describing what the man returned with.
Therefore, the correct answer is CBDA.
Additional Information
- Option 1 (ACDB): This option starts with “bread and a cup of soup,” which creates a confusing and fragmented sentence structure.
- Option 2 (ABCD): This option starts with “bread and a cup of soup and almost an hour,” which lacks logical flow and clarity.
- Option 4 (CBAD): This option incorrectly places “came back with four pieces of” before “and almost an hour and a half later,” breaking the chronological flow.
- Option 5 (None of these): This is incorrect as Option 3 provides the correct logical sequence.
31. Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total income of 6 different people in the year 2019 and the increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020.
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019(In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Rahul | 30000 | 15% |
| Ramesh | 35000 | 20% |
| Mahesh | 40000 | 12% |
| Suresh | 30000 | 25% |
| Saurav | 45000 | 15% |
| Sonu | 42000 | 10% |
Question:
Find the average income of Ramesh, Suresh and Sonu together in the year 2020.
A. Rs. 41000
B. Rs. 41900
C. Rs. 42000
D. Rs. 42900
E. Rs. 40000
Solution
Given:
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019(In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Suresh | 30000 | 25% |
| Ramesh | 35000 | 20% |
| Sonu | 42000 | 10% |
Formula Used:
Average = (Sum of all observations)/(Number of observations)
Calculation:
The income of Ramesh in 2020 = 35000 × (100 + 20)%
⇒ 35000 × 120%
⇒ 35000 × (120/100)
⇒ 350 × 120
⇒ Rs. 42000
The income of Suresh in 2020 = 30000 × (100 + 25)%
⇒ 30000 × 125%
⇒ 30000 × (125/100)
⇒ 300 × 125
⇒ Rs. 37500
The income of Sonu in 2020 = 42000 × (100 + 10)%
⇒ 42000 × 110%
⇒ 42000 × (110/100)
⇒ 420 × 110
⇒ Rs. 46200
The total sum of the income of Ramesh, Suresh and Sonu together in the year 2020 = Rs. (42000 + 37500 + 46200)
⇒ Rs. 125700
The required average = 125700/3
⇒ Rs. 41900
∴ The average income of Ramesh, Suresh and Sonu together in the year 2020 will be Rs. 41900.
32. Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total income of 6 different people in the year 2019 and the increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020.
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019(In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Rahul | 30000 | 15% |
| Ramesh | 35000 | 20% |
| Mahesh | 40000 | 12% |
| Suresh | 30000 | 25% |
| Saurav | 45000 | 15% |
| Sonu | 42000 | 10% |
Question:
If the expenditure of Saurav in the year 2020 is Rs.35500, then find saving of Saurav in the year 2020.
A. Rs. 16250
B. Rs. 15250
C. Rs. 16000
D. Rs. 15000
E. Rs. 16500
Solution
Given:
The expenditure of Saurav in the year 2020 = Rs.35500
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019(In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Saurav | 45000 | 15% |
Formula Used:
Saving = Income – Expenditure
Calculation:
The income of Saurav in 2020 = 45000 × (100 + 15)%
⇒ 45000 × 115%
⇒ 45000 × (115/100)
⇒ 450 × 115
⇒ Rs. 51750
The saving of Saurav in the year 2020 = Income – Expenditure
⇒ Rs. (51750 – 35500)
⇒ Rs. 16250
∴ The saving of Saurav in the year 2020 will be Rs. 16250.
33. Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total income of 6 different people in the year 2019 and the increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020.
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019(In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Rahul | 30000 | 15% |
| Ramesh | 35000 | 20% |
| Mahesh | 40000 | 12% |
| Suresh | 30000 | 25% |
| Saurav | 45000 | 15% |
| Sonu | 42000 | 10% |
Question:
The ratio of expenditure and savings of Mahesh in the year 2020 is 3 ∶ 2. And the saving of Mahesh in the year 2019 is 10% more than of the year 2020, then find the saving of Mahesh in the year 2019.
A. Rs. 22000
B. Rs. 24220
C. Rs. 19712
D. Rs. 19000
E. Rs. 25000
Solution
Given:
The ratio of expenditure and savings of Mahesh in the year 2020 = 3 ∶ 2
The saving of Mahesh in the year 2019 = 10% more than the saving of Mahesh in the year 2020
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019(In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Mahesh | 40000 | 12% |
Formula Used:
Income = Saving + Expenditure
Calculation:
The income of Mahesh in 2020 = 40000 × (100 + 12)%
⇒ 40000 × 112%
⇒ 40000 × (112/100)
⇒ 400 × 112
⇒ Rs. 44800
Let the expenditure and saving of Mahesh in the year be Rs. 3x and Rs. 2x respectively.
Now, Income = Saving + Expenditure
⇒ 44800 = 2x + 3x
⇒ 44800 = 5x
⇒ x = 44800/5
⇒ x = 8960
The saving of Mahesh in 2020 = 2 × 8960
⇒ Rs. 17920
The saving of Mahesh in 2019 = 17920 × (100 + 10)%
⇒ 17920 × 110%
⇒ 17920 × (110/100)
⇒ 1792 × 11
⇒ Rs. 19712
∴ The saving of Mahesh in the year 2019 will be Rs. 19712.
34. Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total income of 6 different people in the year 2019 and the increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020.
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019(In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Rahul | 30000 | 15% |
| Ramesh | 35000 | 20% |
| Mahesh | 40000 | 12% |
| Suresh | 30000 | 25% |
| Saurav | 45000 | 15% |
| Sonu | 42000 | 10% |
Question:
Find the ratio of income of Rahul and Sourav in the year 2020.
A. 3 ∶ 2
B. 3 ∶ 4
C. 4 ∶ 3
D. 2 ∶ 3
E. 1 ∶ 1
Solution
Given:
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019 (In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Rahul | 30000 | 15% |
| Saurav | 45000 | 15% |
Calculation:
The income of Rahul in 2020 = 30000 × (100 + 15)%
⇒ 30000 × 115%
The income of Saurav in 2020 = 45000 × (100 + 15)%
⇒ 45000 × 115%
The required ratio = (30000 × 115%)/(45000 × 115%)
⇒ 30/45
⇒ 2 ∶ 3
∴ The ratio of income of Rahul and Sourav in the year 2020 will be 2 ∶ 3.
35. Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total income of 6 different people in the year 2019 and the increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020.
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019(In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Rahul | 30000 | 15% |
| Ramesh | 35000 | 20% |
| Mahesh | 40000 | 12% |
| Suresh | 30000 | 25% |
| Saurav | 45000 | 15% |
| Sonu | 42000 | 10% |
Question:
By approximately what percent is Mahesh’s income more than Ramesh’s income in the year 2020?
A. 7%
B. 5%
C. 10%
D. 7.67%
E. 6.67%
Solution
Given:
| Name of the People | Income of the People in 2019(In Rs) | Increased percentage of people’s income from 2019 to 2020 |
| Mahesh | 40000 | 12% |
| Ramesh | 35000 | 20% |
Formula Used:
Increased percentage = {(Increased value)/(Base value)} × 100
Calculation:
The income of Mahesh in 2020 = 40000 × (100 + 12)%
⇒ 40000 × 112%
⇒ 40000 × (112/100)
⇒ 400 × 112
⇒ Rs. 44800
The income of Ramesh in 2020 = 35000 × (100 + 20)%
⇒ 35000 × 120%
⇒ 35000 × (120/100)
⇒ 350 × 120
⇒ Rs. 42000
Increased Income = Rs. (44800 – 42000)
⇒ Rs. 2800
The required Increased percentage = (2800/42000) × 100
⇒ 280/42
⇒ 20/3
⇒ 6.67%
∴ Mahesh’s income will be approximately 6.67% more than Ramesh’s income in the year 2020.
36. A money lender found that due to a change in the rate from 12% to 11.5 % his early income was reduced by Rs.104 in a year. Find the capital that was invested by the person.
A. Rs. 18800
B. Rs. 21800
C. Rs. 20800
D. Rs.20000
E. Rs.19800
Solution
Given:
Principal: = x
Rates were reduced by 12% to 11.5% = 0.5%
Time = 1 year
Income is also reduced by = Rs.104
Principal = x × [1/(2 × 100)] = 104
x = Rs.20800
Hence the principal invested is Rs. 20800.
37. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
560 ÷ 14 of 5 + 42 of 6 ÷ 12 + 4 = ?
A. 40
B. 30
C. 50
D. 20
E. 10
Solution
Concept used:
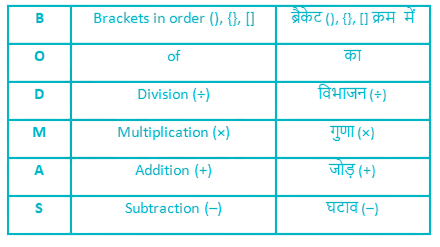
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:
Calculation:
560 ÷ 14 of 5 + 42 of 6 ÷ 12 + 4 = ?
560 ÷ 70 + (16 × 6) ÷ 12 + 4 = ?
560/70 + 96/12 + 4 = ?
8 + 8 + 4 = ?
20 = ?
∴ The value of ‘?’ is 20.
38. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
12 + (63 + 5 of 7 ÷ 14 × 2) = ?
A. 50
B. 60
C. 70
D. 80
E. 90
Solution
Concept used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
12 + (63 + 5 of 7 ÷ 14 × 2) = ?
12 + [63 + (5 × 7) ÷ 14 × 2] = ?
12 + [63 + 35/14 × 2] = ?
12 + 63 + 5/2 × 2 = ?
12 + 63 + 5 = 80 = ?
∴ The value of ‘?’ is 80.
39. What will come in the place of ‘?’ in the following question?
8100 ÷ 9% of 900 – 17 × 5 = ?
A. 3
B. 6
C. 9
D. 12
E. 15
Solution
Concept used:

Calculation:
8100 ÷ 9% of 900 – 17 × 5 = ?
8100 ÷ (9/100 × 900) – 17 × 5 = ?
8100/(81) – 17 × 5 = ?
100 – 85 = ?
? = 15
∴ The value of the ‘?’ is 15.
40. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
[(√64 + √196) ÷ √49]% of √196 = ?
A. 30/13
B. 11/25
C. 34/25
D. 36/13
E. 38/25
Solution
Concept used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
[(√64 + √196) ÷ √49]% of √196 = ?
⇒ [(8 + 14) ÷ 7)% of 14 = ?
⇒ (22 ÷ 7)% of 14 = ?
⇒ (22/700) × 14 = ?
⇒ 22/50 = ?
∴ ? = 11/25
41. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
676 ÷ 13 + 25 of 3 – 385 ÷ 7 = ?
A. 43
B. 72
C. 51
D. 25
E. 81
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculations:
676 ÷ 13 + 25 of 3 – 385 ÷ 7 = ?
⇒ 676 ÷ 13 + 25 × 3 – 385 ÷ 7 = ?
⇒ 676/13 + 25 × 3 – 385/7 = ?
⇒ 52 + 25 × 3 – 55 = ?
⇒ 52 + 75 – 55 = ?
⇒ 127 – 55 = ?
⇒ 72 = ?
∴ The value of ? is 72.
42. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
37.5% of 1664 + 55% of 820 = ? × 5
A. 305
B. 215
C. 640
D. 110
E. 200
Solution
Given:
37.5% of 1664 + 55% of 820 = ? × 5
Concept Used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
37.5% of 1664 + 55% of 820 = ? × 5
⇒ (3/8) × 1664 + (11/20) × 820 = ? × 5
⇒ 3 × 208 + 11 × 41 = ? × 5
⇒ 624 + 451 = ? × 5
⇒ 1075 = ? × 5
⇒ ? = 1075 ÷ 5
⇒ ? = 215
∴ The value of ? is 215.
43. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
(3/4) of (5/7) of (7/3) of 1228 = ? + (39)2
A. 24
B. 15
C. 14
D. 21
E. None of these.
Solution
Given:
(3/4) of (5/7) of (7/3) of 1228 = ? + (39)2
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
(3/4) of (5/7) of (7/3) of 1228 = ? + (39)2
⇒ (5/4) × 1228 = ? + 1521
⇒ 1535 = ? + 1521
⇒ ? = 14
∴ The value of ? is 14.
44. What value can come in place of the question mark (?) in the question below?
0.8% of 2000 + 16% of 600 = ?
A. 112
B. 114
C. 102
D. 104
E. 116
Solution
Calculation:
We use the BODMAS rule as follows:

According to the rule ‘Of’ should be solved first
⇒ 0.8% of 2000 + 16% of 600 = ?
⇒ (0.8/100) × 2000 + (16/100) × 600 = ?
⇒ (8/1000) × 2000 + 96 = ?
⇒ 16 + 96 = ?
⇒ ? = 112
∴ The required answer is 112.
45. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
9/5 of 450 – 4/3 of 510 = ? + 30
A. 100
B. 90
C. 150
D. 120
E. 110
Solution
Calculation:
We use the BODMAS rule as follows:

According to the rule ‘Of’ should be solved first
⇒ 9/5 of 450 – 4/3 of 510 = ? + 30
⇒ 9 × 90 – 4 × 170 = ? + 30
⇒ 810 – 680 – 30= ?
⇒ 130 – 30 = ?
⇒ ? = 100
∴ The required answer is 100.
46. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
22% of 855 – ? = 20% of 500
A. 88.1
B. 89.2
C. 87.1
D. 85.5
E. 87.9
Solution
Given:
22% of 855 – ? = 20% of 500
Concept Used:

Calculation:
22% of 855 – ? = 20% of 500
⇒ 188.1 – ? = 100
⇒ ? = 188.1 – 100
⇒ ? = 88.1
∴ The value of (?) is 88.1
47. When the shopkeepers increases the price of an article by 40%, then sales are decreased by 20%. What is the percentage change in Revenue?
A. 15%
B. 10%
C. 9%
D. 12%
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Price – increased by 40%
Sales – decreased by 20%
Formula:
Percentage increment = (Difference/Less Value) × 100%
Revenue = Price × Sales
Calculations:
Consider Initial price = 100, Initial sales = 100
Initial Revenue = 100 × 100 = 10000
New price = 140
New Sales = 80
New Revenue = 140 × 80 = 11200
New Revenue is increases as comparing with initial revenue.
New Revenue increment percentage = [(11200 – 10000)/10000] × 100% = 12%.
∴ New Revenue increment percentage = 12%.
SHORTCUT TRICK
For successive % change,
x + y + xy/100
⇒ Increase = 40 %, Decrease = 20 %
⇒ x = 40 %, y = 20%
Now,
⇒ 40 – 20 – (800/100)
⇒ 20 – 8
⇒ 12 %
∴ New Revenue increment percentage is 12%.
IMPORTANT POINTS
For this trick,
1) For increase, the value is taken as positive.
2) For decrease, the value is taken as negative.
48. The probability of Ramesh hitting a target is 4/5 while that of Amit hitting is 3/7, find the probability that one of them hits the target.
A. 17/35
B. 3/5
C. 22/35
D. 19/35
E. 2/5
Solution
Concept used:
For ‘OR’ type questions like this where either Ramesh will hit or Amit will hit, we add both probabilities i.e. of Ramesh hitting and Amit not hitting to Amit hitting, Ramesh not hitting.
Formula used:
P’ = 1 – P
Calculation:
Probability of Ramesh hitting = 4/5
Probability of Ramesh not hitting = 1 – 4/5 = 1/5
Probability of Amit hitting = 3/7
Probability of Amit not hitting = 1 – 3/7 = 4/7
Required probability = (4/5 × 4/7) + (1/5 × 3/7)
⇒ 19/35
∴ Required probability is 19/35
49. Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions.
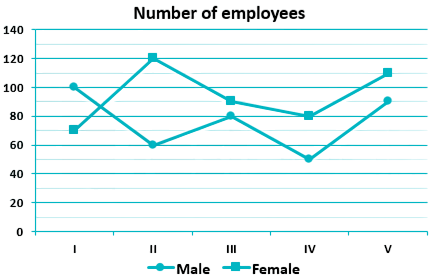
Following line graph shows the number of employees in five branches.
Question:
Find the average male employees in five branches.
A. 76
B. 83
C. 80
D. 89
E. 72
Solution
Given:
Total male employees in five branches = 100 + 60 + 80 + 50 + 90 = 380
⇒ Required average = 380/5
⇒ Required average = 76
50. Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions.
Following line graph shows the number of employees in five branches.

Question:
Female employees of branch III is approx. what percent of total employees of branch III?
A. 47%
B. 49%
C. 53%
D. 40%
E. 42%
Solution
Given:
Total employees of branch III = 80 + 90 = 170
The female employees of branch III = 90
Required percentage = 90/170 × 100
= 52.9%
51. Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions.
Following line graph shows the number of employees in five branches.

Question:
Find the ratio between total employees of the branch I and branch II.
A. 17 : 18
B. 19 : 21
C. 18 : 19
D. 16 : 17
E. 15 : 18
Solution
Given:
⇒ Total employees of branch I = 100 + 70 = 170
⇒ Total employees of branch II = 60 + 120 = 180
⇒ Required ratio = 170 : 180= 17 : 18
52. Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions.
Following line graph shows the number of employees in five branches.

Question:
Employees of branch V is approx. what percent more than employees of branch IV?
A. 50%
B. 54%
C. 58%
D. 48%
E. 61%
Solution
Given:
Total employees of branch V = 90 + 110 = 200
Total employees of branch IV = 50 + 80 = 130
Required percentage = (200 – 130)/130 × 100%
⇒ Required percentage = (70)/130 × 100%
⇒ Required percentage = 53.84%
53. Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions.
Following line graph shows the number of employees in five branches.

Question:
Find the difference between total male and total female employees of five branches.
A. 80
B. 70
C. 75
D. 90
E. 110
Solution
Given:
Total male employees in five branches = 100 + 60 + 80 + 50 + 90 = 380
Total female employees in five branches = 70 + 120 + 90 + 80 + 110 = 470
Required difference = 470 – 380
= 90
54. The sum of money is distributed among three people in the ratio 5:3:2. If the total sum is Rs. 10,000, find the share of the person who gets the least.
A. 1000
B. 1500
C. 2000
D. 2500
E. 3000
Solution
Given:
Total sum = Rs. 10,000
The ratio of distribution = 5:3:2
Calculation:
Let the shares be 5x, 3x, and 2x.
5x + 3x + 2x = 10000
⇒ 10x = 10000
⇒ x = 1000.
Therefore, the share of the person who gets the least = 2x = 2 × 1000 = Rs. 2000
55. A and B both can complete the work in 16 days. In how many days A alone can complete the work if efficiency of B and A are in ratio 3 : 4 respectively?
A. 28 days
B. 26 days
C. 24 days
D. 12 days
E. None
Solution
Given:
A and B both together can complete the work in 16 days
Concept:
Work = Efficiency × Time
Calculation:
Let us assume the efficiency of A and B is 4x and 3x respectively.
⇒ Total work = 16 × 7x = 112x
⇒ A can complete the work in = 112x/4x = 28 days
∴ The required result will be 28 days.
56. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
l. x2 – 4x + 4 = 0
ll. y2 – 12y + 35 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E . x = y or relation between x and y can not be determine.
Solution
Given:
x2 – 4x + 4 = 0
⇒ x2 – 2x – 2x + 4 = 0
⇒ x(x – 2) – 2(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 2) (x – 2) = 0
⇒ x = 2, 2.
y2 – 12y + 35 = 0
⇒ y2 – 7y – 5y + 35 = 0
⇒ y(y – 7) – 5(y – 7) = 0
⇒ (y – 5) (y – 7) = 0
⇒ y = 5, 7.
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 2 | 5 | x < y |
| 2 | 7 | x < y |
| 2 | 5 | x < y |
| 2 | 7 | x < y |
∴ The required result will be x < y.
57. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
l. x2 – 7x + 12 = 0
ll. y2 – 8y + 16 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between x and y can not be determine.
Solution
Given:
x2 – 7x + 12 = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x – 4x + 12 = 0
⇒ x(x – 3) – 4(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (x – 3) (x – 4)
⇒ x = 3, 4.
y2 – 8y + 16 = 0
⇒ y2 – 4y – 4y + 16 = 0
⇒ y(y – 4) – 4(y – 4) = 0
⇒ (y – 4) (y – 4) = 0
⇒ y = 4, 4.
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 3 | 4 | x < y |
| 3 | 4 | x < y |
| 4 | 4 | x = y |
| 4 | 4 | x = y |
∴ The required result will be x ≤ y.
58. In the given questions, two equations numbered l and II are given. You have to solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
l. x2 – 41x + 148 = 0
II. y2 – y – 132 = 0
A. x > y
B. x ≤ y
C. No relation in x and y or x = y
D. x ≥ y
E. x < y
Solution
Calculation:
l. x2 – 41x + 148 = 0
⇒ x2 – (37 + 4)x + 148 = 0
⇒ x2 – 37x – 4x + 148 = 0
⇒ x(x – 37) – 4(x – 37) = 0
⇒ (x – 37) (x – 4) = 0
⇒ x = 37, 4
II. y2 – y – 132 = 0
⇒ y2 – (12 – 11)y – 132 = 0
⇒ y2 – 12y + 11y – 132 = 0
⇒ y(y – 12) + 11(y – 12) = 0
⇒ (y – 12) (y + 11) = 0
⇒ y = 12, -11
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 37 | 12 | x > y |
| 37 | -11 | x > y |
| 4 | 12 | x < y |
| 4 | -11 | x > y |
∴ No relation in x and y or x = y
59. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
l. x2 – 13x + 42 = 0
ll. y2 + 13y – 68 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y OR relation between x and y can not be established.
Solution
Solution:
Calculation:
l. x2 – 13x + 42 = 0
⇒ x2 – 7x – 6x + 42 = 0
⇒ x(x – 7) – 6(x – 7) = 0
⇒ (x – 6) (x – 7) = 0
⇒ x = 6, 7.
ll. y2 + 13y – 68 = 0
⇒ y2 + 17y – 4y – 68 = 0
⇒ y(y + 17) – 4(y + 17) = 0
⇒ (y – 4) (y + 17) = 0
⇒ y = 4, -17.
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 6 | 4 | x > y |
| 6 | -17 | x > y |
| 7 | 4 | x > y |
| 7 | -17 | x > y |
∴ The relation between x and y is x > y.
60. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 20x + 36 =0
II. y2 – 20y + 51 = 0
A. x > y
B. x ≥ y
C. x < y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established
Solution
Calculation:
I. x2 + 20x + 36 =0
⇒ x2 + 18x + 2x + 36 = 0
⇒ x(x + 18) + 2(x + 18) =0
⇒ (x + 18) (x + 2)
⇒ x = –18, –2
II. y2 – 20y + 51 = 0
⇒ y2 – 17y – 3y + 51 = 0
⇒ y(y – 17) – 3(y – 17) = 0
⇒ (y – 17) (y – 3) = 0
⇒ y = 17, 3
Comparison between x and y (via tabulation):
| X | Y | Relation |
| –18 | 17 | x < y |
| –18 | 3 | x < y |
| –2 | 17 | x < y |
| –2 | 3 | x < y |
∴ x < y
61. A train of length 500m running at 98 km/h. How much time will be taken by the train to pass a man running at 8 km/h in the same direction in which the train is going?
A. 12 s
B. 15 s
C. 20 s
D. 16 s
E. 10 s
Solution
Given:
Length of the train = 500 m
Speed of train = 98 km/h
Speed of man = 8 km/h
Concept Used:
Time is taken by the train to pass the man = Length of the train/Relative Speed
When two bodies are moving in the same direction
Relative Speed = Speed of train – Speed of man
Calculation:
Speed of the train relative to the man = 98 – 8
⇒ 90 km/h
⇒ 90 × (5/18) m/s
⇒ 25 m/s
Relative Speed = 25 m/s
Time is taken by the train to pass the man = Length of the train/Relative Speed
⇒ 500/25 = 20 s.
∴ Time taken by the train to pass the man is 20 s.
62. A boat travels 10 km upstream in 40 minutes and 15 km downstream in 30 minutes. Find the time taken by the boat to cover a distance of 45 km in still water.
A. 1 minute
B. 2 hours
C. 60 seconds
D. 1.5 hours
E. 45 minutes
Solution
Given:
Distance covered by boat in upstream = 10 km
Time taken by boat in upstream = 40 minutes
Distance covered by boat in downstream = 15 km
Time taken by boat in downstream = 30 minutes
Distance covered by boat in still water = 45 km
Formula used:
Speed of boat in still water = (Upstream speed + Downstream speed)/2
Speed = (Distance/Time)
Upstream speed = (Speed of boat) – (Speed of current)
Downstream speed = (Speed of boat) + (Speed of current)
Calculation:
Let the speed of boat in still water be x km/h.
and speed of current be y km/h
Time taken by boat in upstream = 40 minutes
⇒ (40/60) hour
⇒ (2/3) hour
Upstream speed = [10/(2/3)]
⇒ (x – y) = (10/2) × 3
⇒ (x – y) = 15 km/h —-(1)
Time taken by boat in downstream = 30 minutes
⇒ (30/60) hour
⇒ (1/2) hour
Downstream speed = [15/(1/2)]
⇒ (x + y) = 30 km/h —-(2)
Now, add equation (1) and equation (2)
(x – y) + (x + y) = 15 + 30
⇒ 2x = 45
⇒ x = 22.5
Speed of boat in still water = 22.5 km/h
Time taken by boat to cover a distance of 45 km in still water = [45/(22.5)]
⇒ 2 hours
∴ Time taken by boat to cover a distance of 45 km in still water will be 2 hours.
63. A starts a business with Rs. 72,000. After sometime B joined with 48,000 Rs. For how much time does B join, if the profits at the end of the year are divided in the ratio of 9 ∶ 5?
A. 10 months
B. 8 months
C. 3 months
D. 5 months
E. None of these
Solution
Given
A invests money in business = 72,000 Rs
B invests money in business = 48,000 Rs
Formula Used
Profit = investment × time period
Calculation
Let B joined for x months.
72000 × 12/48000 × x = 9/5
18/x = 9/5
x = 10
∴B joined for 10 months.
64. If a product is sold at a 5% discount, the selling price is Rs. 266. When selling it on Marked Price, if the profit percentage is 12% then find the Cost price of the product.
A. Rs. 210
B. Rs. 220
C. Rs. 230
D. Rs. 240
E. Rs. 250
Solution
Given:
If a product is sold at 5% discount, the selling price is Rs. 266.
Formula used:
S.P = M.P × (100 – D)/100
Where,
S.P → Selling price
M.P → Marked price
D → Discount%
Calculations:
Suppose the marked price is Rs. M
S.P = M × (100 – 5)/100 = 0.95M
⇒ 0.95M = 266
⇒ M = Rs. 280
Marked price = Rs. 280
Now ,
112% of Cost Price = 280
Cost Price = 280/112 × 100 = Rs. 250
65. Each side of a wooden cube is 56 cm. A right circular cone is obtained from the cube wasting the minimum amount of wood. Find the volume of the cone.
A. 44994.6 cm3
B. 46994.6 cm3
C. 45994.6 cm3
D. 43994.6 cm3
E. 48994.6 cm3
Solution
Given:
Each side of a wooden cube is 56 cm
A right circular cone is obtained from the cube wasting the minimum amount of wood
Formula Used:

66. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Robert, Anne, Maria, Albert, Shane, Tom, Chris, Ricky and Jenny are nine persons who are working in three different countries namely Spain, Germany and England with not less than two persons and not more than four persons working in the same country.
Maria and Ricky work in the same country. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Anne and Shane do not work in the same country. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Not more than two people work in England. Maria works in the country where the maximum number of persons work. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England and Germany.
Question:
How many persons are working in Germany?
A. Three
B. Two
C. Five
D. Four
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
Given:
Nine persons are working in three different countries namely, England, Spain and Germany.
Now, from the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Combining these two conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ||
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
2. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Not more than two people work in England. Therefore we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
3. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England or Germany. This condition rules out the possibility of Case 2 from above. We get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY |
4. Maria and Ricky work in the same country. . Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Not more than two people work in England. Also, the maximum number of persons working in a country is four. Combining all these conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM |
5. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Combining these two conditions we get the final table as-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT, JENNY |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM, SHANE |
From the above final table, we see that four persons are working Germany.
Hence, four persons are working in Germany.
67. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Robert, Anne, Maria, Albert, Shane, Tom, Chris, Ricky and Jenny are nine persons who are working in three different countries namely Spain, Germany and England with not less than two persons and not more than four persons working in the same country.
Maria and Ricky work in the same country. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Anne and Shane do not work in the same country. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Not more than two people work in England. Maria works in the country where the maximum number of persons work. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England and Germany.
Question:
Who among the following works in the same country as Maria?
A. Jenny
B. Robert
C. Chris
D. Anne
E. Shane
Solution
Given:
Nine persons are working in three different countries namely, England, Spain and Germany.
Now, from the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Combining these two conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ||
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
2. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Not more than two people work in England. Therefore we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
3. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England or Germany. This condition rules out the possibility of Case 2 from above. We get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY |
4. Maria and Ricky work in the same country. . Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Not more than two people work in England. Also, the maximum number of persons working in a country is four. Combining all these conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM |
5. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Combining these two conditions we get the final table as-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT, JENNY |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM, SHANE |
From the above final table, we see that Maria works in Germany along with Ricky, Tom and Shane.
Hence, Maria and Shane work in the same country.
68. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Robert, Anne, Maria, Albert, Shane, Tom, Chris, Ricky and Jenny are nine persons who are working in three different countries namely Spain, Germany and England with not less than two persons and not more than four persons working in the same country.
Maria and Ricky work in the same country. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Anne and Shane do not work in the same country. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Not more than two people work in England. Maria works in the country where the maximum number of persons work. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England and Germany.
Question:
Which combination among the following represents the pair working in England?
A. Maria and Ricky
B. Albert and Tom
C. Jenny and Ricky
D. Albert and Jenny
E. Shane and Anne
Solution
Given:
Nine persons are working in three different countries namely, England, Spain and Germany.
Now, from the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Combining these two conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ||
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
2. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Not more than two people work in England. Therefore we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
3. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England or Germany. This condition rules out the possibility of Case 2 from above. We get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY |
4. Maria and Ricky work in the same country. Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Not more than two people work in England. Also, the maximum number of persons working in a country is four. Combining all these conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM |
5. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Combining these two conditions we get the final table as-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT, JENNY |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM, SHANE |
From the above final table, we see that only Albert and Jenny work in England.
Hence, the pair that work in England are Albert and Jenny.
69. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Robert, Anne, Maria, Albert, Shane, Tom, Chris, Ricky and Jenny are nine persons who are working in three different countries namely Spain, Germany and England with not less than two persons and not more than four persons working in the same country.
Maria and Ricky work in the same country. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Anne and Shane do not work in the same country. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Not more than two people work in England. Maria works in the country where the maximum number of persons work. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England and Germany.
Question:
Which of the following statements about the persons working in Germany is/are not true?
Statement I: Three persons are working in Germany.
Statement II: Both Shane and Ricky work in Germany.
Statement III: Robert works in Germany.
A. Both Statements I and II
B. None of the above
C. Both statements II and III
D. Both statements I and III
E. Only statement II
Solution
Given:
Nine persons are working in three different countries namely, England, Spain and Germany.
Now, from the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Combining these two conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ||
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
2. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Not more than two people work in England. Therefore we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
3. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England or Germany. This condition rules out the possibility of Case 2 from above. We get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY |
4. Maria and Ricky work in the same country. . Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Not more than two people work in England. Also, the maximum number of persons working in a country is four. Combining all these conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM |
5. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Combining these two conditions we get the final table as-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT, JENNY |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM, SHANE |
From the above final table, we check the correctness of the given statements as follows-
Statement I: Three persons are working in Germany. This is false.
Statement II: Both Shane and Ricky work in Germany. This is true.
Statement III: Robert works in Germany. This is false.
Hence, both Statements I and III are not true.
70. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Robert, Anne, Maria, Albert, Shane, Tom, Chris, Ricky and Jenny are nine persons who are working in three different countries namely Spain, Germany and England with not less than two persons and not more than four persons working in the same country.
Maria and Ricky work in the same country. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Anne and Shane do not work in the same country. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Not more than two people work in England. Maria works in the country where the maximum number of persons work. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England and Germany.
Question:
Consider the following statements about Robert-
Statement I: Robert works in Spain with three other persons
Statement II: Robert and Ricky work in the same country.
Statement III: Robert works in England along with one other person.
Which of the above statements is/are true?
A. Only Statement III
B. Both Statements II and III
C. Only Statement I
D. None of the above
E. Both Statements I and III
Solution
Given:
Nine persons are working in three different countries namely, England, Spain and Germany.
Now, from the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. Chris works in either Spain or Germany. Robert works in the same country as Chris. Combining these two conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ||
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
2. Albert works neither in Spain nor in Germany. Not more than two people work in England. Therefore we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS | |
| CASE 1 | CASE 2 | |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | CHRIS, ROBERT | |
3. Chris works in the same country as Anne, who doesn’t work in England or Germany. This condition rules out the possibility of Case 2 from above. We get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY |
4. Maria and Ricky work in the same country. . Tom works in the same country as Ricky but not in Spain. Not more than two people work in England. Also, the maximum number of persons working in a country is four. Combining all these conditions we get-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM |
5. Shane doesn’t work in either England or Spain. Anne and Jenny are twin sisters but they work in different countries. Combining these two conditions we get the final table as-
| COUNTRY | PERSONS |
| SPAIN | CHRIS, ROBERT, ANNE |
| ENGLAND | ALBERT AND JENNY |
| GERMANY | MARIA, RICKY, TOM, SHANE |
From the above final table, we check the correctness of the given statements as follows-
Statement I: Robert works in Spain with three other persons. This is false.
Statement II: Robert and Ricky work in the same country. This is false.
Statement III: Robert works in England along with one other person. This is false.
Hence, none of the given statements are true.
71. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
In a family of seven members, Y is the sister – in – law of K. M is the mother of F. P is the uncle of B. K is the daughter – in – law of U. P is the son – in – law of M. Y is not the spouse of F. B is the niece of F’s sister.
What is the relation of P with F?
A. Sister
B. Brother
C. Father
D. Brother – in – law
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
Here, family members are B, F, K, M, P, U and Y.
1) Y is the sister – in – law of K.
2) K is the daughter – in – law of U.
3) M is the mother of F.
4) P is the son – in – law of M.
5) Y is not the spouse of F.
6) P is the uncle of B.
7) B is the niece of F’s sister. Therefore, case 2 is eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
Hence, P is the brother – in – law of F.
72. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
In a family of seven members, Y is the sister – in – law of K. M is the mother of F. P is the uncle of B. K is the daughter – in – law of U. P is the son – in – law of M. Y is not the spouse of F. B is the niece of F’s sister.
Question:
Find the odd one out.
A. U
B. M
C. Y
D. K
E. B
Solution
Here, family members are B, F, K, M, P, U and Y.
1) Y is the sister – in – law of K.
2) K is the daughter – in – law of U.
3) M is the mother of F.
4) P is the son – in – law of M.
5) Y is not the spouse of F.
6) P is the uncle of B.
7) B is the niece of F’s sister. Therefore, case 2 is eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
Since, member except U is a female person whereas U is the male person.
Hence, the odd one is U.
73. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
In a family of seven members, Y is the sister – in – law of K. M is the mother of F. P is the uncle of B. K is the daughter – in – law of U. P is the son – in – law of M. Y is not the spouse of F. B is the niece of F’s sister.
Question:
Which of the following statement(s) is/ are correct?
A. Y is the sister of P.
B. F is the daughter of M.
C. U is the father of F.
D. B is the granddaughter of Y.
E. K is the sister of P.
Solution
Here, family members are B, F, K, M, P, U and Y.
1) Y is the sister – in – law of K.
2) K is the daughter – in – law of U.
3) M is the mother of F.
4) P is the son – in – law of M.
5) Y is not the spouse of F.
6) P is the uncle of B.
7) B is the niece of F’s sister. Therefore, case 2 is eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
Since, Y is the wife of P. Therefore, statement first is incorrect.
F is the son of M. Therefore, statement second is incorrect.
U is the father of F. Therefore, statement third is correct.
B is the niece of Y. Therefore, statement fourth is incorrect.
K is the sister – in – law of P. Therefore, statement fifth is also incorrect.
Hence, the correct statement is U is the father of F.
74. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Only towns are villages
Some towns are costly
Only costly are areas
Conclusions:
I. Some areas are villages
II. No towns are areas
A. Only I follow
B. Only II follow
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as follows
Conclusions:
I. Some areas are villages → False (As we can see the relation of areas is only with costly and the relation of villages is only with towns. So, some areas are villages is definitely false)
II. No towns are areas → True (As we can see the relation of areas is only with costly. So, no towns are areas is definitely true)
Hence, Only II follows.
Additional Information
Concept of “Only”:
The concept of “Only” is the reverse concept of “All”.
Example: Only A are B mean the same as All B are A.
Here, the relation of B is only limited to A and is not related to any other element.
75. Direction: In the question below are given two statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statement:
No orange is banana.
All chairs are orange.
All mobiles are chairs.
Conclusion:
I. At least some orange are chairs.
II. All banana are mobiles.
A. Only II follows
B. Only I follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram is as follows:
Conclusion:
I. At least some orange are chairs. → True (because all chairs are orange)
II. All banana are mobiles. → False (because No orange is banana and all chairs are orange and all mobiles are chairs.)
Hence, the Only conclusion I follow.
76. Direction: In the question below are given three statements follows ed by three conclusions numbered I, II, and III. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows s from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
No belt is tie.
Some tie is stylish.
Only a few stylish is fashion.
Conclusions:
I. All belt is stylish.
II. Some belt is fashion.
III. No belt is fashion.
A. Only conclusion I follow
B. Only conclusion II follow
C. Only conclusion III follow
D. All of the above follow.
E. Either conclusion II or III follows
Solution
The least possible diagram for the given statement is as follow,

I. All belt is stylish. → False (it is definitely false)
II. Some belt is fashion. → False (it is possible but not denfinite)
III. No belt is fashion. → False (it is definitely false)
Hence, Either conclusion II or III follows.
77. Directions: Read the information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E. At most two containers are stacked above container F. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H. Container I is placed below container A. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G.
Question:
Which one is odd?
A. F, C
B. H, G
C. C, H
D. G, B
E. I, E
Solution
Given: Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order.
1. At most two containers are stacked above container F.
Here, we have 3 cases, i.e., Case 1, Case 2, and Case 3.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
2. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
| B | ||
| B | H | |
| B | H | |
| H | ||
3. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2. (Because there is no vacant place for E)
| Boxes | |
| Case 1 | Case 3 |
| F | |
| F | |
| E | B |
| H | |
| B | E |
| H | |
4. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G.
Now, we can eliminate Case 3. (Because there is no vacant place for C, D, and G)
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
5. Container I is placed below container A.
This is our final arrangement,
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| A |
| I |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
Except for G, B, in all other pairs, only one box is placed between them.
Hence, the correct answer is G, B.
78. Directions: Read the information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E. At most two containers are stacked above container F. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H. Container I is placed below container A. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G.
Question:
How many containers are placed between container A and container B?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. Four
Solution
Given: Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order.
1. At most two containers are stacked above container F.
Here, we have 3 cases, i.e., Case 1, Case 2, and Case 3.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
2. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
| B | ||
| B | H | |
| B | H | |
| H | ||
3. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2. (Because there is no vacant place for E)
| Boxes | |
| Case 1 | Case 3 |
| F | |
| F | |
| E | B |
| H | |
| B | E |
| H | |
4. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G.
Now, we can eliminate Case 3. (Because there is no vacant place for C, D, and G)
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
5. Container I is placed below container A.
This is our final arrangement,
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| A |
| I |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
Hence, the correct answer is Four.
79. Directions: Read the information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E. At most two containers are stacked above container F. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H. Container I is placed below container A. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G
Question:
Which container is placed immediately below container I?
A. A
B. F
C. D
D. G
E. C
Solution
Given: Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order.
1. At most two containers are stacked above container F.
Here, we have 3 cases, i.e., Case 1, Case 2, and Case 3.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
2. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
| B | ||
| B | H | |
| B | H | |
| H | ||
3. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2. (Because there is no vacant place for E)
| Boxes | |
| Case 1 | Case 3 |
| F | |
| F | |
| E | B |
| H | |
| B | E |
| H | |
4. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G.
Now, we can eliminate Case 3. (Because there is no vacant place for C, D, and G)
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
5. Container I is placed below container A.
This is our final arrangement,
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| A |
| I |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
Hence, the correct answer is F.
80. Directions: Read the information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E. At most two containers are stacked above container F. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H. Container I is placed below container A. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G.
Question:
Which of the following statement is not true?
A. H is immediately above D
B. A is three containers above E
C. C is immediately above B
D. C is placed above I
E. I has one container above it
Solution
Given: Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order.
1. At most two containers are stacked above container F.
Here, we have 3 cases, i.e., Case 1, Case 2, and Case 3.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
2. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
| B | ||
| B | H | |
| B | H | |
| H | ||
3. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2. (Because there is no vacant place for E)
| Boxes | |
| Case 1 | Case 3 |
| F | |
| F | |
| E | B |
| H | |
| B | E |
| H | |
4. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G.
Now, we can eliminate Case 3. (Because there is no vacant place for C, D, and G)
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
5. Container I is placed below container A.
This is our final arrangement,
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| A |
| I |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
Hence, the correct answer is C is placed above I.
81. Directions: Read the information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E. At most two containers are stacked above container F. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H. Container I is placed below container A. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G.
Question:
Which of the following statements is definitely true based on the given arrangement?
A. The number of containers above C is one more than those below B
B. There are three containers between A and I
C. Container B is placed immediately below D
D. Container F is placed at the topmost position
E. Container H is placed immediately above F
Solution
Given: Nine containers, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, are stacked one above the other, but not necessarily in the same order.
1. At most two containers are stacked above container F.
Here, we have 3 cases, i.e., Case 1, Case 2, and Case 3.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
2. Two containers are placed between F and B, where B is placed immediately above H.
| Boxes | ||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| F | ||
| F | ||
| F | ||
| B | ||
| B | H | |
| B | H | |
| H | ||
3. The number of containers below H is one less than the number of containers above E.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2. (Because there is no vacant place for E)
| Boxes | |
| Case 1 | Case 3 |
| F | |
| F | |
| E | B |
| H | |
| B | E |
| H | |
4. Container C is kept three containers above D, which is placed immediately above G.
Now, we can eliminate Case 3. (Because there is no vacant place for C, D, and G)
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
5. Container I is placed below container A.
This is our final arrangement,
| Boxes |
| Case 1 |
| A |
| I |
| F |
| E |
| C |
| B |
| H |
| D |
| G |
Hence, the correct answer is The number of containers above C is one more than those below B.
82. In the number 94728563, if each digit at an even position is increased by 1, and each digit at an odd position is reduced by 2. Then arrange the digits in ascending order. Which digit is fourth from the left end in the final string?
A. 3
B. 5
C. 4
D. 6
E. 7
Solution
Given number: 94728563
Even Position – +1; Odd Position – -2;
According to the condition, if each digit at an even position is increased by 1, and each digit at an odd position is reduced by 2, then arrange the digits in ascending order.
| Digits | 9 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 3 |
| Positions: Even +1/Odd -2 | -2 | +1 | -2 | +1 | -2 | +1 | -2 | +1 |
| Resultant | 7 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 4 |
| Ascending order | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 7 |
Hence, ‘5’ is fourth from the left end in the final string.
83. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 N
Question:
Which of the following is exactly in the middle between the eleventh from the right end and the fifteenth from the left end in the above arrangement?
A. I
B. Q
C. 0
D. $
E. V
Solution
Given series is: (Left) H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 N (Right)
11th from the right → %
15th from left → P
Hence, terms between % and P are I $ V 0 Q and V is exactly in middle of them.
84. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 N
Question:
Which of the following is the seventh to the right of the fourteenth from the right end of the above arrangement?
A. J
B. U
C. V
D. C
E. 2
Solution
Given series is: (Left) H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 N (Right)
As right – right = right
⇒ 14th from the right – 7th to the right = 7th from rightHence, 7th from right is ‘C’.
85. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 N
Question:
How many such symbols are there in the above arrangement, each of which is immediately preceded by a vowel and immediately followed by a consonant?
A. Two
B. None
C. Three
D. One
E. More than three
Solution
Arrangement required: Vowel → Symbol → Consonant
Given series is: H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 NHence, only two symbols follow the given condition.
86. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 N
Question:
How many such consonants are there between 4 and & each of which is immediately preceded by a symbol and immediately followed by a number?
A. None
B. Two
C. One×duplicate options found. English Question 1 options 1,2
D. Three
E. Four
Solution
Arrangement required: 4 →→ Symbol → Consonant → Number → → &
Given series is: H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 NHence, only two such pairs i.e. # S 7 and $ V 0 are there between 4 and & which follow the given condition.
87. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 N
Question:
How many such vowels are there in the above arrangement, each of which is immediately preceded by a number and immediately followed by a symbol?
A. Three
B. None
C. One
D. Two
E. More than three
Solution
Arrangement required: Number → Vowel → Symbol
Given series is: H R 8 O * B U 4 @ X M # S 7 P I $ V 0 Q % 9 1 J C 2 & 6 D 3 NHence, one such pairs are there i.e. 8 O *.
88. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: R > V; F ≤ V; E ≥ S > F
Conclusions:
I. V > E
II. S ≤ R
A. Either I or II is True
B. Only II is True
C. Only I is True
D. Both I and II are True
E. Neither I nor II is true
Solution
Given statements: R > V; F ≤ V; E ≥ S > F
On combining: R > V ≥ F < S ≤ E
Conclusions:
I. V > E → False (as V ≥ F < S ≤ E → thus clear relation between V and E cannot be determined)
II. S ≤ R → True (as R > V ≥ F < S → thus clear relation between S and R cannot be determined)Hence, neither I nor II is true.
89. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which conclusion among the given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: C > Z = F < V; F > N ≥ P; D < Z
Conclusions:
I. C > P
II. V > D
A. Both I and II are True
B. Only II is True
C. Either I or II is True
D. Only I is True
E. Neither I nor II is true
Solution
Given statements: C > Z = F < V; F > N ≥ P; D < Z
On combining: C > Z = F > N ≥ P; V > F = Z > D
Conclusions:
I. C > P → True (as C > Z = F > N ≥ P → C > P)
II. V > D → True (as V > F = Z > D → V > D)
Hence, both I and II are True.
90. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: U > N; X ≤ T; P ≥ T; N > P
Conclusions:
I. U ≥ X
II. T > N
A. Only I is True
B. Neither I nor II is true
C. Either I or II is True
D. Both I and II are True
E. Only II is True
Solution
Given statements: U > N; X ≤ T; P ≥ T; N > P
On combining: U > N > P ≥ T ≥ X
Conclusions:
I. U ≥ X → False (as U > N > P ≥ T ≥ X → U > X)
II. T > N → False (as N > P ≥ T → N > T)
Hence, neither I nor II is true.
91. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the following below questions.
Eight persons L, M, N, O, H, I, J, and K are sitting at a square table facing center such that two persons are sitting at each side of the square table and none of the persons are sitting at the corner of the square table.
M and K sit on the same side of the table. I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K. J sits third to the left of H. M and O are diagonally opposite to each other. Only one person sits between J and L. M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Question:
What is the position of N with respect to H?
A. Fourth to the right
B. Third to the right
C. Fourth to the left
D. Either 1 or 3
E. Third to the left
Solution
1) M and K sit on the same side of the table.
2) I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K.
3) M and O are diagonally opposite to each other
4) J sits third to the left of H
5) Only one person sits between J and L.
6) M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Case 1 gets eliminated here
The final arrangement:
Hence, either 1 or 3.
92. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the following below questions.
Eight persons L, M, N, O, H, I, J, and K are sitting at a square table facing center such that two persons are sitting at each side of the square table and none of the persons are sitting at the corner of the square table.
M and K sit on the same side of the table. I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K. J sits third to the left of H. M and O are diagonally opposite to each other. Only one person sits between J and L. M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Question:
In which of the following statement 3rd person sits exactly between 1st and 2nd person in the final arrangement?
I) MHK
II) LOJ
III) NMI
A. Only II
B. All I, II and Ill
C. Only Ill
D. Only I and III
E. None of these
Solution
1) M and K sit on the same side of the table.
2) I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K.
3) M and O are diagonally opposite to each other
4) J sits third to the left of H
5) Only one person sits between J and L.
6) M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Case 1 gets eliminated here

The final arrangement:

Hence, K and I sits exactly between MH and NM respectively.
93. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the following below questions.
Eight persons L, M, N, O, H, I, J, and K are sitting at a square table facing center such that two persons are sitting at each side of the square table and none of the persons are sitting at the corner of the square table.
M and K sit on the same side of the table. I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K. J sits third to the left of H. M and O are diagonally opposite to each other. Only one person sits between J and L. M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Question:
Which of the following combination of persons facing each other?
A. NL
B. IH
C. KO
D. MJ
E. All of these
Solution
1) M and K sit on the same side of the table.
2) I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K.
3) M and O are diagonally opposite to each other

4) J sits third to the left of H
5) Only one person sits between J and L.
6) M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Case 1 gets eliminated here,

The final arrangement:

Hence, all are facing each other.
94. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the following below questions.
Eight persons L, M, N, O, H, I, J, and K are sitting at a square table facing center such that two persons are sitting at each side of the square table and none of the persons are sitting at the corner of the square table.
M and K sit on the same side of the table. I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K. J sits third to the left of H. M and O are diagonally opposite to each other. Only one person sits between J and L. M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Question:
Which of the following statement is/are false?
I) L and H are immediate neighbors
II) Two persons sit between K and O (counts from the right of K)
III) J sits second to the left of L.
A. Only I and Ill
B. Only II
C. Only I and II
D. Only III
E. None
Solution
1) M and K sit on the same side of the table.
2) I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K.
3) M and O are diagonally opposite to each other

4) J sits third to the left of H
5) Only one person sits between J and L.
6) M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Case 1 gets eliminated here

The final arrangement:

Hence, Two persons sit between K and O (counts from the right of K) is false.
95. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the following below questions.
Eight persons L, M, N, O, H, I, J, and K are sitting at a square table facing center such that two persons are sitting at each side of the square table and none of the persons are sitting at the corner of the square table.
M and K sit on the same side of the table. I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K. J sits third to the left of H. M and O are diagonally opposite to each other. Only one person sits between J and L. M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Question:
Who among the following person sits third to the right of K?
A. M
B. L
C. J
D. O
E. None of these
Solution
1) M and K sit on the same side of the table.
2) I sits second to the left of the one who sits diagonally opposite to K.
3) M and O are diagonally opposite to each other

4) J sits third to the left of H
5) Only one person sits between J and L.
6) M and K are not immediate neighbours of L and J.
Case 1 gets eliminated here

The final arrangement:

Hence, N sits third to the right of K.
96. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language
‘sa li su’ means ‘Sonal likes Shekhar’
‘su ta da’ means ‘Shekhar is dancer’
‘da ma ni ce’ means ‘dancer lives in city’‘sa va ce’ means ‘Sonal loves city’
Question:
What is the code for ‘is’ in that code language?
A. li
B. va
C. ta
D. ma
E. ni
Solution
Therefore, in the given code language,
‘sa’ means ‘Sonal’
‘su’ means ‘Shekhar’
‘li’ means ‘likes’
‘da’ means ‘dancer’
‘ta’ means ‘is’
‘ce’ means ‘city’
‘va’ means ‘loves’
Hence, the code for ‘is’ in that code language is ‘ta’.
97. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language
‘sa li su’ means ‘Sonal likes Shekhar’
‘su ta da’ means ‘Shekhar is dancer’
‘da ma ni ce’ means ‘dancer lives in city’‘sa va ce’ means ‘Sonal loves city’
Question:
Which code in that language means ‘loves’?
A. li
B. ta
C. ma
D. ni
E. va
Solution

Therefore, in the given code language,
‘sa’ means ‘Sonal’
‘su’ means ‘Shekhar’
‘li’ means ‘likes’
‘da’ means ‘dancer’
‘ta’ means ‘is’
‘ce’ means ‘city’
‘va’ means ‘loves’
Hence, ‘va’ means ‘loves’ in that code language.
98. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language
‘sa li su’ means ‘Sonal likes Shekhar’
‘su ta da’ means ‘Shekhar is dancer’
‘da ma ni ce’ means ‘dancer lives in city’‘sa va ce’ means ‘Sonal loves city’
Question:
What is the code for ‘Sonal likes dancer in Shekhar’ in that code language?
A. sa li da ni su
B. sa li da ma su
C. sa ta da li su
D. Either 1 or 2
E. Either 1 or 3
Solution

Therefore, in the given code language,
‘sa’ means ‘Sonal’
‘su’ means ‘Shekhar’
‘li’ means ‘likes’
‘da’ means ‘dancer’
‘ta’ means ‘is’
‘ce’ means ‘city’
‘va’ means ‘loves’
Either ‘sa li da ni su’ or ‘sa li da ma su’ means ‘Sonal likes dancer in Shekhar’.
Hence, ‘either 1 or 2’ is the correct answer.
99. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language
‘sa li su’ means ‘Sonal likes Shekhar’
‘su ta da’ means ‘Shekhar is dancer’
‘da ma ni ce’ means ‘dancer lives in city’‘sa va ce’ means ‘Sonal loves city’
Question:
What does ‘ma’ mean in that code language?
A. loves
B. likes
C. lives
D. in
E. Either 3 or 4
Solution

Therefore, in the given code language,
‘sa’ means ‘Sonal’
‘su’ means ‘Shekhar’
‘li’ means ‘likes’
‘da’ means ‘dancer’
‘ta’ means ‘is’
‘ce’ means ‘city’
‘va’ means ‘loves’
‘ma’ means either ‘lives’ or ‘in’ in that code language.
Hence, ‘either 3 or 4’ is the correct answer.
100. Direction: The following question is based on five words given below.
AMTV HLSP WQFJ NCGY RXKU
(The new words formed after performing the mentioned operations may or may not necessarily be meaningful English words)
How many letters are present in between the second letter of the first word from the left end and third letter of the second word from the right end when we count them between English alphabetical series?
A. 6
B. 7
C. 4
D. 8
E. 5
Solution
Given: AMTV HLSP WQFJ NCGY RXKU
According to the question:
Second letter of the first word from the left end → AMTV HLSP WQFJ NCGY RXKU → M
Third letter of the second word from the right end → AMTV HLSP WQFJ NCGY RXKU → G
Thus, according to the final arrangement, five letters H, I, J, K, L are present in between G and M according to the alphabetical series.
Hence, the correct answer is 5.
