1. Direction: Fill in the blanks in the passage below, with the word from among the options given for each blank labelled (A) to (E). Choose the word that fits in each blank most appropriately in the context of the passage.
The Israel philharmonic orchestra is one of the country’s most ________(A) cultural jewels. Created ten years before the State, it has been to the battlefields in wartime to boost the troops’ ________(B). It earned a ________(C) as one of the world’s leading orchestras. But in a country stuffed to the rafters, many of them immigrants, competition for funds is ________(D) and is increasingly ________(E). The management at the philharmonic has mounted a public ________(F) to demand more money after it was allotted less than what it got the previous year.
Question:
Which of the following fits in the blank labelled (A)?
A. Legitimate
B. Evocative
C. Glittering
D. Prerogative
E. Annex
Solution
The correct answer is glittering.
Key Points
The sentence with the blank A mentions the orchestra as a cultural jewel. The word glittering is the most suitable word to describe the popularity of the orchestra. Thus, the word glittering is the most appropriate word for blank A out of the given options which perfectly fits in the context of the sentence
The meaning of the word that perfectly fits in the context of the sentence is:
Glittering: impressively successful or elaborate. It is an adjective.
Additional Information
Let us look at the meaning of the other words:
| Word | Meaning |
| Legitimate | conforming to the law or to rules |
| Evocative | bringing strong images, memories, or feelings to mind |
| Prerogative | a right or privilege exclusive to a particular individual or class |
| Annex | a building joined to or associated with the main building, providing additional space or accommodation |
| Orchestra | a group of instrumentalists, especially one combining string, woodwind, brass, and percussion sections and playing classical music |
2. Direction: Fill in the blanks in the passage below, with the word from among the options given for each blank labelled (A) to (E). Choose the word that fits in each blank most appropriately in the context of the passage.
The Israel philharmonic orchestra is one of the country’s most ________(A) cultural jewels. Created ten years before the State, it has been to the battlefields in wartime to boost the troops’ ________(B). It earned a ________(C) as one of the world’s leading orchestras. But in a country stuffed to the rafters, many of them immigrants, competition for funds is ________(D) and is increasingly ________(E). The management at the philharmonic has mounted a public ________(F) to demand more money after it was allotted less than what it got the previous year.
Question:
Which of the following fits in the blank labelled (B)?
A. Rebellion
B. Morality
C. Morale
D. Punctilio
E. Fiend
Solution
The correct answer is morale.
Key Points
The sentence with the blank B implies that the orchestra wishes to entertain the soldiers and keep their confidence high. Thus the word morale is the most suitable word for blank B as it means ‘the amount of confidence and cheerfulness that a group of people have’, which perfectly fits in the context of the sentence.
The meaning of the word that perfectly fits in the context of the sentence is:
Morale: the confidence, enthusiasm, and discipline of a person or group at a particular time. It is a noun.
Additional Information
Let us look at the meaning of the other words:
| Meaning | |
| Rebellion | an act of armed resistance to an established government or leader |
| Punctilio | a fine or petty point of conduct or procedure |
| Morality | principles concerning the distinction between right and wrong or good and bad behaviour |
| Fiend | a very wicked or cruel person |
3. Direction: Fill in the blanks in the passage below, with the word from among the options given for each blank labelled (A) to (E). Choose the word that fits in each blank most appropriately in the context of the passage.
The Israel philharmonic orchestra is one of the country’s most ________(A) cultural jewels. Created ten years before the State, it has been to the battlefields in wartime to boost the troops’ ________(B). It earned a ________(C) as one of the world’s leading orchestras. But in a country stuffed to the rafters, many of them immigrants, competition for funds is ________(D) and is increasingly ________(E). The management at the philharmonic has mounted a public ________(F) to demand more money after it was allotted less than what it got the previous year.
Question:
Which of the following fits in the blank labelled (C)?
A. Milieu
B. Misnomer
C. Facade
D. Stature
E. Ineptitude
Solution
The correct answer is stature.
Key Points
The word stature is the most suitable word for blank C out of the given options. The word perfectly fits in the context of the sentence that is ‘the orchestra built a reputation for themselves as one of the world’s leading orchestras’.
The meaning of the word that perfectly fits in the context of the sentence is:
Stature: importance or reputation gained by ability or achievement. It is a noun.
Additional Information
Let us look at the meaning of the other words:
| Word | Meaning |
| Milieu | a person’s social environment |
| Misnomer | wrong or inaccurate name or designation |
| Facade | a deceptive outward appearance |
| Ineptitude | lack of skill or ability |
4. Direction: Fill in the blanks in the passage below, with the word from among the options given for each blank labelled (A) to (E). Choose the word that fits in each blank most appropriately in the context of the passage.
The Israel philharmonic orchestra is one of the country’s most ________(A) cultural jewels. Created ten years before the State, it has been to the battlefields in wartime to boost the troops’ ________(B). It earned a ________(C) as one of the world’s leading orchestras. But in a country stuffed to the rafters, many of them immigrants, competition for funds is ________(D) and is increasingly ________(E). The management at the philharmonic has mounted a public ________(F) to demand more money after it was allotted less than what it got the previous year.
Question:
Which of the following fits in the blank labelled (D)?
A. Inevitable
B. Tortuous
C. Portentous
D. Impetuous
E. Punitive
Solution
The correct answer is inevitable.
Key Points
The sentence with blank D implies that Israel has many classical musicians so competition for funds is unavoidable. The only word that fits in the context of the sentence is ‘inevitable’.
The meaning of the word that perfectly fits in the context of the sentence is:
Inevitable: certain to happen; unavoidable. It is an adjective.
Additional Information
Let us look at the meaning of the other words:
| Word | Meaning |
| Tortuous | full of twists and turns |
| Portentous | of or like a portent; of momentous significance |
| Impetuous | acting or done quickly and without thought or care |
| Punitive | inflicting or intended as punishment |
| Rafter | a beam forming part of the internal framework of a roof |
5. Direction: Fill in the blanks in the passage below, with the word from among the options given for each blank labelled (A) to (E). Choose the word that fits in each blank most appropriately in the context of the passage.
The Israel philharmonic orchestra is one of the country’s most ________(A) cultural jewels. Created ten years before the State, it has been to the battlefields in wartime to boost the troops’ ________(B). It earned a ________(C) as one of the world’s leading orchestras. But in a country stuffed to the rafters, many of them immigrants, competition for funds is ________(D) and is increasingly ________(E). The management at the philharmonic has mounted a public ________(F) to demand more money after it was allotted less than what it got the previous year.
Question:
Which of the following fits in the blank labelled (E)?
A. Indignant
B. Magnanimous
C. Placid
D. Amenable
E. Cordial
Solution
The correct answer is Indignant.
Key Points
In the sentence with the blank E, the competition for funds is described as unavoidable and resentful due to the presence of many classical musicians. Here the word Indignant is the most suitable word for blank E out of the given options which perfectly fits in the context of the sentence.
The meaning of the word that perfectly fits in the context of the sentence is:
Indignant: feeling or showing anger or annoyance at what is perceived as unfair treatment. It is an adjective.
Additional Information
Let us look at the meaning of the other words:
| Word | Meaning |
| Magnanimous | generous or forgiving, especially towards a rival or less powerful person |
| Placid | calm and peaceful, with little movement or activity |
| Amenable | open and responsive to suggestion; easily persuaded or controlled |
| Cordial | warm and friendly |
6. Direction: Fill in the blanks in the passage below, with the word from among the options given for each blank labelled (A) to (E). Choose the word that fits in each blank most appropriately in the context of the passage.
The Israel philharmonic orchestra is one of the country’s most ________(A) cultural jewels. Created ten years before the State, it has been to the battlefields in wartime to boost the troops’ ________(B). It earned a ________(C) as one of the world’s leading orchestras. But in a country stuffed to the rafters, many of them immigrants, competition for funds is ________(D) and is increasingly ________(E). The management at the philharmonic has mounted a public ________(F) to demand more money after it was allotted less than what it got the previous year.
Question:
Which of the following fits in the blank labelled (F)?
A. Condemnation
B. Divergence
C. Infringement
D. Campaign
E. Raillery
Solution
The correct answer is campaign.
Key Points
The sentence with the blank F implies that the Philharmonic orchestra wants to plan a set of activities over a period of time in order to achieve more funds from the government. Therefore the word campaign is the most suitable word for blank F which perfectly fits in the context of the sentence.
The meaning of the word that perfectly fits in the context of the sentence is:
Campaign: an organized course of action to achieve a goal It is a noun.
Additional Information
Let us look at the meaning of the other words:
| Word | Meaning |
| Condemnation | the expression of very strong disapproval; censure |
| Divergence | a difference in opinions, interests |
| Infringement | the action of breaking the terms of a law, agreement, etc.; violation |
| Raillery | good-humoured teasing |
7. Directions: Read the following sentence and determine whether there is an error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If the sentence is error-free, select ‘No Error’ as your answer.
Sammy had been (A) waiting for a hour,(B) but Markus was (C) nowhere to be seen. (D)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. No Error
Solution
The correct answer is B
Key Points
- The given sentence is in the past tense as can be seen by the phrase ‘had been waiting’ and ‘was’.
- The sentence uses the article ‘a’ before the noun ‘hour’.
- While ‘h’ is a consonant and thus should start with ‘a’ which is an article for a noun starting with a consonant.
- The common misconception here is that the choice of the article depends on the letter the noun starts with, but actually, it depends on the phonetic sound of the letter that the word begins with.
- In this case, ‘hour’ starts with ‘h’ but the sound is ‘o’ as it is pronounced as ‘our’.
- ‘O’ is a vowel and thus requires the article ‘an’.
Hence, the ‘a’ needs to be replaced with an ‘an’.
Thus, the correct sentence is: Sammy had been waiting for an hour, but Markus was nowhere to be seen.
8. The question sentence has been divided into 5 parts, from (A) to (E). Any part of the sentence carries an error. Find the error based on Adjective. If there is no error, mark ‘Option E’ i.e. No error.
Little that Shivangi did for me is unforgettable,(A) I could not possibly repay her deeds of kindness.(B) She helped me in a time when (C) I was really low and had no assistance from my family.(D) No error (E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 1) i.e. A.
Key Points
- Part A, ‘Little that Shivangi did for me is unforgettable‘ is incorrect.❌
- We should use ‘the’ before ‘little‘ in the given sentence, ‘The little’ means not much but all.
- Example: The little money that we have is being spent on food.
- ‘Little’ means hardly any.
- Example: Little does he know the integrities regarding train operations.
- ‘A little’ means not much (some)
- Example: A little help from the government will go a long way in pacifying the crowds.
Correct sentence: The little that Shivangi did for me is unforgettable, I could not possibly repay her deeds of kindness. She helped me in a time when I was really low and had no assistance from my family.
Was the solution helpful?Yes
9. Directions: Read the following sentence and determine whether there is an error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If the sentence is error-free, select ‘No Error’ as your answer.
Michael insisted paying (A) for the meal, (B) but Halley wanted (C) to split the bill. (D)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. No Error
Solution
The correct answer is A
Key Points
- The sentence is in the past tense as can be seen by the use of the verb ‘insisted’ and ‘wanted’ in the past tense.
- The verb ‘insist‘ means to ‘demand something forcefully or not taking no for an answer’.
- This means that there usually is an idea or a point which one is being ‘forceful’ about.
- The verb ‘insisted’ needs to be followed by the preposition ‘on’ in order to show what point someone is being forced about.
Hence, ‘insisted‘ needs to be followed by the preposition ‘on‘ in order to make the sentence contextually correct.
Thus, the correct sentence is: “Michael insisted on paying for the meal, but Halley wanted to split the bill.”
10. Directions: Read the following sentence and determine whether there is an error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If the sentence is error-free, select ‘No Error’ as your answer.
Mark would (A) always remembered (B) his dog, Molly (C) with fondness. (D)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. No Error
Solution
The correct answer is B
Key Points
- The given sentence in the past tense, this can be seen by the use of the modal verb ‘would’.
- Even if the verb ‘would’ were to be replaced by the verb ‘will’, ‘remembered’ would still be incorrect as ‘will’ is in the present tense.
- A modal verb has to be followed by the base form of the verb.
Hence, ‘remembered‘ needs to be replaced with ‘remember‘.
Thus, the correct sentence is: Mark would always remember his dog, Molly with fondness.
11. In the following question, two columns are given containing three phrases each. In the first column, phrases are A, B, and C, and in the second column, the phrases are D, E and F. A phrase from the first column may or may not connect with a phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. There are five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which the phrases can be joined to form a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. If, none of the options given forms a correct sentence after combination, select ‘None of these’ as your answer.
| Column (1) | Column (2) |
| (A)She wants students to recall a case | (D) include different methods of transportation. |
| (B)Various methods of Native American transportation | (E) are incomparable. |
| (C)The value of birch trees to some Native American groups | (F) which she has already discussed. |
A. A-D
B. B-F
C. C-F
D. A-F and C-D
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is ‘None of these‘.
Key Points
- We need to join each sentence part given in column 1 to their correct counterparts given in column 2. The sentences should not only be conceptually correct but also grammatically error-free. This would allow us to come to the correct solution.
- Part A talks about how the subject ‘she’ wants students to recall a case. Conceptually it can join with part F which talks about how the subject ‘she’ has already discussed. But part F is a defining clause. It pinpoints which case the students need to recall. Defining clauses have to use ‘that’ before it. So, using ‘which’ makes the sentence grammatically incorrect.
- Combining parts B and D make no sense although they both talk about transportation.
- Conceptually parts C and E can join as they make a sentence which talks about how the value of some trees to a particular native group cannot be compared. But it would lead to a subject-verb disagreement. Part C has the singular subject ‘value’ while part E uses the plural ‘verb’. So, grammatically they cannot join.
- Since there are no correct combinations, option 5 is the correct answer.
Important Points
A singular subject (value) will take a singular verb (is), whereas a plural subject takes a plural verb.
Defining clauses use ‘that’. Non defining clauses use ‘which’.
12. Below a word is given followed by three sentences which consist of that word. Identify the sentence/s which best expresses the meaning of the word. Choose option 5 (None of the these) if the word is not suitable in any of the sentences.
SUMMON
- He has been summoned to court for the third time in two weeks for committing a heinous crime.
- Can he finally summon up the courage to say what he really feels?
- The invaders quickly summoned and were held as prisoners of war.
A. Both B and C
B. Both A and C
C. A
D. Both A and B
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is option 4.
Key Points
- To answer this question, let’s first understand the meaning of the word given in the question:
- Summon: to order someone to come to a particular place; to call upon someone or something formally. (आदेश देना, बुलाना)
- Now, let’s examine the given sentences:
- Sentence A: He has been summoned to court for the third time in two weeks for committing a heinous crime.
- This sentence correctly uses the word “summoned” to describe the act of being formally ordered to appear in court.
- Sentence B: Can he finally summon up the courage to say what he really feels?
- This sentence correctly uses the word “summon” to describe the act of gathering or mustering courage.
- Sentence C: The invaders quickly summoned and were held as prisoners of war.
- This sentence incorrectly uses the word “summoned” as it does not align with the meaning of formally ordering or calling upon someone.
- So, both Sentence A and Sentence B correctly use the word “summon” in appropriate contexts.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 4.
13. Below a word is given followed by three sentences which consist of that word. Identify the sentence/s which best expresses the meaning of the word. Choose option 5 (None of the these) if the word is not suitable in any of the sentences.
COARSE
- The human race is on a coarse of discovering a new and unknown power hidden within.
- In his most characteristic works he carved directly in stone, preferring a hard stone with a coarse texture.
- Her voice was coarse as if she had been yelling all night.
A. Both B and C
B. Both A and B
C. Both A and C
D. A, B and C
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
- To answer this question, let’s first understand the meaning of the word given in the question:
- Coarse: rough or harsh in texture; lacking refinement or sophistication. (खुरदरा, अशिष्ट)
- Now, let’s examine the given sentences:
- Sentence A: The human race is on a coarse of discovering a new and unknown power hidden within.
- This sentence does not use the word “coarse” correctly. The intended word might be “course,” which refers to a path or direction. “Coarse” does not fit here.
- Sentence B: In his most characteristic works he carved directly in stone, preferring a hard stone with a coarse texture.
- This sentence correctly uses the word “coarse” to describe the rough texture of the stone.
- Sentence C: Her voice was coarse as if she had been yelling all night.
- This sentence also correctly uses the word “coarse” to describe the rough or harsh quality of her voice.
- So, both Sentence B and Sentence C correctly use the word “coarse.”
Therefore, the correct answer is “Both B and C.”
14. Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law. “All pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charge framed under Section 124A be kept in abeyance”, it has said in an order that will bring some welcome relief to those calling for the abrogation of Section 124A of the IPC, which criminalizes any speech, writing or representation that “excites disaffection against the government”. The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it. The hope and the expectation arise from the Union government’s own submission that it has decided to re-examine and reconsider the provision as part of the Prime Minister’s efforts to scrap outdated laws and compliance burdens. Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand.
That the sedition law is being persistently misused has been recognized years ago, and courts have pointed out that the police authorities are not heeding the limitation imposed by a 1962 Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on what constitutes sedition. The Court had upheld the section only by reading it down to mean that it is applicable only to “acts involving intention or tendency to create disorder, or disturbance of law and order, or incitement to violence”. In practice, the police has been using the broad definition of sedition to book anyone who criticized the Government in strong and strident language. The question now before the Court is whether it ought to overrule a decision rendered by a five-judge Bench 60 years ago. If it chooses to do so and strikes down Section 124A as an unconstitutional restriction on free speech, it may help the larger cause of preventing misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses. However, the Government may choose to prevent such a situation by amending it so that the offense is narrowly defined to cover only acts that affect the sovereignty, integrity, and security of the state, as reportedly recommended by a panel of experts. When the Government submitted that it was revisiting the provision on its own, it was expecting only an indefinite postponement of the hearing on the constitutional validity of Section 124A, but it must now heed the spirit of the order and take effective steps to prevent its misuse.
Question:
According to the passage, if the Supreme Court abolishes Section 124A:
A. It may help encourage the misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses.
B. It may help encourage the misuse of government properties.
C. It may help in encouraging terrorist activities.
D. It may help prevent the misuse of provisions relating to sexual offenses.
E. It may help prevent the misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses.
Solution
The correct answer is ‘It may help prevent the misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses.‘
Key Points
- The fifth sentence of the second paragraph says “If it chooses to do so and strikes down Section 124A as an unconstitutional restriction on free speech, it may help the larger cause of preventing misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses.”
- From the above sentence, we can say that according to the passage, if the Supreme Court abolishes Section 124A it may help prevent the misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses.
Hence, the only possible answer is option 5.
15. Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law. “All pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charge framed under Section 124A be kept in abeyance”, it has said in an order that will bring some welcome relief to those calling for the abrogation of Section 124A of the IPC, which criminalizes any speech, writing or representation that “excites disaffection against the government”. The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it. The hope and the expectation arise from the Union government’s own submission that it has decided to re-examine and reconsider the provision as part of the Prime Minister’s efforts to scrap outdated laws and compliance burdens. Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand.
That the sedition law is being persistently misused has been recognized years ago, and courts have pointed out that the police authorities are not heeding the limitation imposed by a 1962 Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on what constitutes sedition. The Court had upheld the section only by reading it down to mean that it is applicable only to “acts involving intention or tendency to create disorder, or disturbance of law and order, or incitement to violence”. In practice, the police has been using the broad definition of sedition to book anyone who criticized the Government in strong and strident language. The question now before the Court is whether it ought to overrule a decision rendered by a five-judge Bench 60 years ago. If it chooses to do so and strikes down Section 124A as an unconstitutional restriction on free speech, it may help the larger cause of preventing misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses. However, the Government may choose to prevent such a situation by amending it so that the offense is narrowly defined to cover only acts that affect the sovereignty, integrity, and security of the state, as reportedly recommended by a panel of experts. When the Government submitted that it was revisiting the provision on its own, it was expecting only an indefinite postponement of the hearing on the constitutional validity of Section 124A, but it must now heed the spirit of the order and take effective steps to prevent its misuse.
Question:
What will fit in the blank taken from the passage: ”The Court has _______ its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it”
A. Record
B. Records
C. Recorded
D. Recording
E. Recorder
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Recorded.‘
Key Points
- The given sentence is in the present perfect tense as it links the past to the present in some way.
- The present perfect tense refers to an action or state that either occurred at an indefinite time in the past or began in the past and continued to the present time.
- This tense is formed by have/has + the past participle (here, recorded).
- Therefore, the past participle form of the verb ‘recorded’ should be used in the blank.
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
Complete Sentence: The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it.
Additional Information
‘Recorder’ is a noun that means An apparatus for recording sound, pictures, or data.
‘Record’ is the base form of the verb.
‘Records’ is the third-person present form of the verb.
‘Recording’ is the gerund or present participle form of the verb.
16. Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law. “All pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charge framed under Section 124A be kept in abeyance”, it has said in an order that will bring some welcome relief to those calling for the abrogation of Section 124A of the IPC, which criminalizes any speech, writing or representation that “excites disaffection against the government”. The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it. The hope and the expectation arise from the Union government’s own submission that it has decided to re-examine and reconsider the provision as part of the Prime Minister’s efforts to scrap outdated laws and compliance burdens. Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand.
That the sedition law is being persistently misused has been recognized years ago, and courts have pointed out that the police authorities are not heeding the limitation imposed by a 1962 Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on what constitutes sedition. The Court had upheld the section only by reading it down to mean that it is applicable only to “acts involving intention or tendency to create disorder, or disturbance of law and order, or incitement to violence”. In practice, the police has been using the broad definition of sedition to book anyone who criticized the Government in strong and strident language. The question now before the Court is whether it ought to overrule a decision rendered by a five-judge Bench 60 years ago. If it chooses to do so and strikes down Section 124A as an unconstitutional restriction on free speech, it may help the larger cause of preventing misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses. However, the Government may choose to prevent such a situation by amending it so that the offense is narrowly defined to cover only acts that affect the sovereignty, integrity, and security of the state, as reportedly recommended by a panel of experts. When the Government submitted that it was revisiting the provision on its own, it was expecting only an indefinite postponement of the hearing on the constitutional validity of Section 124A, but it must now heed the spirit of the order and take effective steps to prevent its misuse.
Question:
Which of the following is/are incorrect according to the given passage?
A. People cannot approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition.
B. The Supreme Court has suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law.
C. Section 124A criminalizes any speech, writing, or representation that excites disaffection against the government.
A. Only A
B. Both A and B
C. Only B
D. Both B and C
E. Only C
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Only A.‘
Key Points
- The last sentence of the first paragraph says “Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand.”
- From the above sentence, we can say that statement A is incorrect according to the given passage.
- The first sentence of the passage says “In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law” and the second sentence of the first paragraph says ”All pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charge framed under Section 124A be kept in abeyance, it has said in an order that will bring some welcome relief to those calling for the abrogation of Section 124A of the IPC, which criminalizes any speech, writing or representation that excites disaffection against the government”.
- From the above sentences, we can say that statements B and C are correct according to the given passage.
- From the above sentences, we can say that statements B and C are correct according to the given passage.
Hence, the only possible answer is option 1.
17. Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law. “All pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charge framed under Section 124A be kept in abeyance”, it has said in an order that will bring some welcome relief to those calling for the abrogation of Section 124A of the IPC, which criminalizes any speech, writing or representation that “excites disaffection against the government”. The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it. The hope and the expectation arise from the Union government’s own submission that it has decided to re-examine and reconsider the provision as part of the Prime Minister’s efforts to scrap outdated laws and compliance burdens. Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand.
That the sedition law is being persistently misused has been recognized years ago, and courts have pointed out that the police authorities are not heeding the limitation imposed by a 1962 Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on what constitutes sedition. The Court had upheld the section only by reading it down to mean that it is applicable only to “acts involving intention or tendency to create disorder, or disturbance of law and order, or incitement to violence”. In practice, the police has been using the broad definition of sedition to book anyone who criticized the Government in strong and strident language. The question now before the Court is whether it ought to overrule a decision rendered by a five-judge Bench 60 years ago. If it chooses to do so and strikes down Section 124A as an unconstitutional restriction on free speech, it may help the larger cause of preventing misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses. However, the Government may choose to prevent such a situation by amending it so that the offense is narrowly defined to cover only acts that affect the sovereignty, integrity, and security of the state, as reportedly recommended by a panel of experts. When the Government submitted that it was revisiting the provision on its own, it was expecting only an indefinite postponement of the hearing on the constitutional validity of Section 124A, but it must now heed the spirit of the order and take effective steps to prevent its misuse.
Question:
Which of the following is/are correct according to the given passage?
A. The Court has an expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will effectively register fresh cases of sedition.
B. The Supreme Court’s order is enough to deter vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers.
C. The police used the sedition law to arrest anyone who criticized the Government.
A. Only A
B. Both A and B
C. Only B
D. Both B and C
E. Only C
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Only C.‘
Key Points
- The third sentence of the first paragraph says “The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it” and the last sentence of the first paragraph says ”Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand‘‘.
- From the above sentences, we can say that statements A and B are incorrect according to the given passage.
- The third sentence of the second paragraph says “In practice, the police have been using the broad definition of sedition to book anyone who criticized the Government in strong and strident language.”
- From the above sentence, we can say that statement C is correct according to the given passage.
- From the above sentence, we can say that statement C is correct according to the given passage.
Hence, the only possible answer is option 5.
18. Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law. “All pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charge framed under Section 124A be kept in abeyance”, it has said in an order that will bring some welcome relief to those calling for the abrogation of Section 124A of the IPC, which criminalizes any speech, writing or representation that “excites disaffection against the government”. The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it. The hope and the expectation arise from the Union government’s own submission that it has decided to re-examine and reconsider the provision as part of the Prime Minister’s efforts to scrap outdated laws and compliance burdens. Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand.
That the sedition law is being persistently misused has been recognized years ago, and courts have pointed out that the police authorities are not heeding the limitation imposed by a 1962 Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on what constitutes sedition. The Court had upheld the section only by reading it down to mean that it is applicable only to “acts involving intention or tendency to create disorder, or disturbance of law and order, or incitement to violence”. In practice, the police has been using the broad definition of sedition to book anyone who criticized the Government in strong and strident language. The question now before the Court is whether it ought to overrule a decision rendered by a five-judge Bench 60 years ago. If it chooses to do so and strikes down Section 124A as an unconstitutional restriction on free speech, it may help the larger cause of preventing misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses. However, the Government may choose to prevent such a situation by amending it so that the offense is narrowly defined to cover only acts that affect the sovereignty, integrity, and security of the state, as reportedly recommended by a panel of experts. When the Government submitted that it was revisiting the provision on its own, it was expecting only an indefinite postponement of the hearing on the constitutional validity of Section 124A, but it must now heed the spirit of the order and take effective steps to prevent its misuse.
Question:
What is the central theme of the passage?
A. Encouraging misuse of sedition law.
B. Restricting people from approaching the jurisdiction courts.
C. Intention or tendency to create disorder
D. Preventing misuse of sedition law.
E. The Government must disregard the spirit of the SC order.
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Preventing misuse of sedition law.‘
Key Points
- The first sentence of the passage says ”In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law”, the last sentence of the first paragraph says ”Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand” and the last sentence of the passage, concludes “When the Government submitted that it was revisiting the provision on its own, it was expecting only an indefinite postponement of the hearing on the constitutional validity of Section 124A, but it must now heed the spirit of the order and take effective steps to prevent its misuse“.
- From the above sentences, we can say that the central theme of the passage is ”Preventing misuse of sedition law”.
Hence, the only possible answer is option 4.
19. Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law. “All pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charge framed under Section 124A be kept in abeyance”, it has said in an order that will bring some welcome relief to those calling for the abrogation of Section 124A of the IPC, which criminalizes any speech, writing or representation that “excites disaffection against the government”. The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it. The hope and the expectation arise from the Union government’s own submission that it has decided to re-examine and reconsider the provision as part of the Prime Minister’s efforts to scrap outdated laws and compliance burdens. Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand.
That the sedition law is being persistently misused has been recognized years ago, and courts have pointed out that the police authorities are not heeding the limitation imposed by a 1962 Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on what constitutes sedition. The Court had upheld the section only by reading it down to mean that it is applicable only to “acts involving intention or tendency to create disorder, or disturbance of law and order, or incitement to violence”. In practice, the police has been using the broad definition of sedition to book anyone who criticized the Government in strong and strident language. The question now before the Court is whether it ought to overrule a decision rendered by a five-judge Bench 60 years ago. If it chooses to do so and strikes down Section 124A as an unconstitutional restriction on free speech, it may help the larger cause of preventing misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses. However, the Government may choose to prevent such a situation by amending it so that the offense is narrowly defined to cover only acts that affect the sovereignty, integrity, and security of the state, as reportedly recommended by a panel of experts. When the Government submitted that it was revisiting the provision on its own, it was expecting only an indefinite postponement of the hearing on the constitutional validity of Section 124A, but it must now heed the spirit of the order and take effective steps to prevent its misuse.
Question:
Choose the synonym of the word ‘Abrogation‘.
A. Institution
B. Repudiation
C. Establishment
D. Launch
E. Introduction
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Repudiation.‘
Key Points
- The word ‘Abrogation‘ means The repeal or abolition of a law, right, or agreement.
- Example: The abrogation of the death penalty embodies the humanization of law.
- Let’s look at the meaning of the given options:-
- Institution – The action of instituting something.
- Example: The institution of the Freedom of Information Act has had a significant effect.
- Repudiation – Rejection of a proposal or idea.
- Example: They were surprised by his sudden repudiation of all his former beliefs.
- Establishment – The action of establishing something or being established.
- Example: The establishment of new international economic order is the essence of his article.
- Launch – An act or instance of launching something.
- Example: They managed to launch a new business.
- Introduction – The act of introducing a system, policy, etc., or of starting a process.
- Example: With the introduction of independent taxation, a married woman’s position is much clearer.
- Example: With the introduction of independent taxation, a married woman’s position is much clearer.
- Institution – The action of instituting something.
Hence, the only possible answer is option 2.
Additional Information
The antonyms of the word ‘Abrogation‘ are “Institution, Introduction, Establishment“.
The synonyms of the word ‘Abrogation‘ are “Repudiation, Abatement, Abolishment“.
20. Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law. “All pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charge framed under Section 124A be kept in abeyance”, it has said in an order that will bring some welcome relief to those calling for the abrogation of Section 124A of the IPC, which criminalizes any speech, writing or representation that “excites disaffection against the government”. The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it. The hope and the expectation arise from the Union government’s own submission that it has decided to re-examine and reconsider the provision as part of the Prime Minister’s efforts to scrap outdated laws and compliance burdens. Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand.
That the sedition law is being persistently misused has been recognized years ago, and courts have pointed out that the police authorities are not heeding the limitation imposed by a 1962 Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on what constitutes sedition. The Court had upheld the section only by reading it down to mean that it is applicable only to “acts involving intention or tendency to create disorder, or disturbance of law and order, or incitement to violence”. In practice, the police has been using the broad definition of sedition to book anyone who criticized the Government in strong and strident language. The question now before the Court is whether it ought to overrule a decision rendered by a five-judge Bench 60 years ago. If it chooses to do so and strikes down Section 124A as an unconstitutional restriction on free speech, it may help the larger cause of preventing misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses. However, the Government may choose to prevent such a situation by amending it so that the offense is narrowly defined to cover only acts that affect the sovereignty, integrity, and security of the state, as reportedly recommended by a panel of experts. When the Government submitted that it was revisiting the provision on its own, it was expecting only an indefinite postponement of the hearing on the constitutional validity of Section 124A, but it must now heed the spirit of the order and take effective steps to prevent its misuse.
Question:
Choose the antonym of the word ‘Abeyance‘.
A. Suspension
B. Dormancy
C. Resuscitation
D. Quiescence
E. Latency
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Resuscitation.‘
Key Points
- The word ‘Abeyance‘ means A state of temporary disuse or suspension.
- Example: The law was held in abeyance for well over twenty years.
- Let’s look at the meaning of the given options:-
- Suspension – A state of temporary inactivity.
- Example: These events have led to the suspension of talks.
- Dormancy – The state of being temporarily inactive or inoperative.
- Example: The volcano erupted after years of dormancy.
- Resuscitation – The action of making something active or vigorous again.
- Example: The economy needs vigorous resuscitation.
- Quiescence – Inactivity or dormancy.
- Example: Although the inactive volcano has been in a state of quiescence for quite some time, it could erupt again very soon.
- Latency – A state of temporary inactivity.
- Example: Patients usually become symptomatic after a latency period of hours to days.
- Example: Patients usually become symptomatic after a latency period of hours to days.
- Suspension – A state of temporary inactivity.
Hence, the only possible answer is option 3.
Additional Information
The synonyms of the word ‘Abeyance‘ are “Suspension, Dormancy, Quiescence”.
The antonyms of the word ‘Abeyance‘ are “Resuscitation, Continuation, Recommencement“.
21. Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
In a substantial blow in favor of free speech, the Supreme Court has effectively suspended the operation of the sedition provision in the country’s penal law. “All pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charge framed under Section 124A be kept in abeyance”, it has said in an order that will bring some welcome relief to those calling for the abrogation of Section 124A of the IPC, which criminalizes any speech, writing or representation that “excites disaffection against the government”. The Court has recorded its hope and expectation that governments at the Centre and the States will refrain from registering any fresh case of sedition under Section 124A of the IPC, or continuing with any investigation or taking any coercive measure under it. The hope and the expectation arise from the Union government’s own submission that it has decided to re-examine and reconsider the provision as part of the Prime Minister’s efforts to scrap outdated laws and compliance burdens. Perhaps, realizing that its order may not be enough to deter thin-skinned and vindictive governments and politically pliant police officers from invoking it against detractors and dissenters, the Court has given liberty to the people to approach the jurisdiction courts if any fresh case is registered for sedition and cite in their support the present order, as well as the Union government’s stand.
That the sedition law is being persistently misused has been recognized years ago, and courts have pointed out that the police authorities are not heeding the limitation imposed by a 1962 Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on what constitutes sedition. The Court had upheld the section only by reading it down to mean that it is applicable only to “acts involving intention or tendency to create disorder, or disturbance of law and order, or incitement to violence”. In practice, the police has been using the broad definition of sedition to book anyone who criticized the Government in strong and strident language. The question now before the Court is whether it ought to overrule a decision rendered by a five-judge Bench 60 years ago. If it chooses to do so and strikes down Section 124A as an unconstitutional restriction on free speech, it may help the larger cause of preventing misuse of provisions relating to speech-based offenses. However, the Government may choose to prevent such a situation by amending it so that the offense is narrowly defined to cover only acts that affect the sovereignty, integrity, and security of the state, as reportedly recommended by a panel of experts. When the Government submitted that it was revisiting the provision on its own, it was expecting only an indefinite postponement of the hearing on the constitutional validity of Section 124A, but it must now heed the spirit of the order and take effective steps to prevent its misuse.
Question:
Choose the most appropriate meaning of the given idiom from the passage:
Pointed out
A. To show that something is likely to exist, happen or be true
B. To face or be turned in a particular direction.
C. A distinctive feature or characteristic.
D. To direct or aim something at someone or something.
E. To bring attention to something or someone.
Solution
The correct answer is ‘To bring attention to something or someone.‘
Key Points
- Given Idiom: Pointed out means To bring attention to something or someone.
- Example: The error was pointed out to her by one of her colleagues.
- From the given options, the fifth option is the most appropriate meaning of the given idiom.
Hence, the correct answer is option 5.
Mistake Points
- We may think from the phrase “Pointed out” that it is all about directing or aiming something at someone or something.
Additional Information
The phrase has been in use since the late 1400s. If you use the phrase literally it means to point to something. When used figuratively it means to indicate something, usually out of a group of things. It is used as a phrasal verb in a sentence.
22. In each of the questions given below, four words are given in bold. These four words may or may not be in their correct position. The sentence is then followed by options with the correct combination of words that should replace each other in order to make the sentence grammatically and contextually correct. Find the correct combination of words that replace each other. If the sentence is correct as it is, select ‘5’ as your option.
Falling in experienced (A) was one of the most wonderful (B) feelings Alex had ever love (C) in her entire life. (D)
A. A-C
B. C-D and A-B
C. B-C and C-A
D. C-D
E. No Rearrangement
Solution
The correct answer is option 1 i.e., A-C.
Key Points
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
Falling in _______ (A) was one of the most _______ (B) feelings Alex had ever _______ (C) in her entire _______ (D).
- Experienced: To feel, especially in terms of emotions. An ‘experience’ is usually an event or a feeling and one cannot ‘all’ in it. So this must be replaced with a noun.
- Wonderful: Refers to something that causes joy, admiration or happiness.
- Love: An intense feeling of deep affection for something or someone. The blank requires a word in the past tense because the helping verb ‘had’ is used before it.
- Life: The existence of something – human or animal.
Hence, we need to interchange A and C in order to make the sentence contextually correct.
Correct Sentence: Falling in love (A) was one of the most wonderful (B) feelings Alex had ever experienced (C) in her entire life (D).
23. In each of the questions given below, four words are given in bold. These four words may or may not be in their correct position. The sentence is then followed by options with the correct combination of words that should replace each other in order to make the sentence grammatically and contextually correct. Find the correct combination of words that replace each other. If the sentence is correct as it is, select ‘5’ as your option.
The old, road (A) house down the shabby (B) was rumored to be ghost (C) by the haunted (D) of its owner.
A. A-B and C-D
B. D-B and A-C
C. A-C and C-B
D. B-A
E. No Rearrangement
Solution
The correct answer is option 1 i.e., A-B and C-D.
Key Points
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
The old, _______ (A) house down the _______ (B) was rumoured to be _______ (C) by the _______ (D) of its owner.
- Road: A long piece of hard ground between 2 destinations for driving or riding. The blank is followed by a noun (house) and so this should be an adjective that describes it, but ‘road’ is also a noun.
- Shabby: Something that is in a poor condition due to a lack of use or care. This is an adjective, it cannot be ‘rumoured’ to be anything. A noun should replace it.
- Ghost: An vision of a dead person that is believed to appear on Earth. A ‘house’ cannot be ‘rumoured’ to be a ghost, a ghost is of a living thing.
- Haunted: Visited frequently by a ghost. This is a verb (an action), it cannot belong to the ‘owner’.
Hence, we need to interchange A and B and also C and D to make the sentence contextually correct.
Correct Sentence: The old, shabby (A) house down the road (B) was rumoured to be haunted (C) by the ghost (D) of its owner.
24. In each of the questions given below, four words are given in bold. These four words may or may not be in their correct position. The sentence is then followed by options with the correct combination of words that should replace each other in order to make the sentence grammatically and contextually correct. Find the correct combination of words that replace each other. If the sentence is correct as it is, select ‘5’ as your option.
Pursued (A) the talents (B) well is one of Manuel’s only guitar, (C) so he playing (D) that.
A. A-B and C-D
B. A-D and B-C
C. A-C and B-D
D. A-D
E. No Rearrangement
Solution
The correct answer is option 2 i.e. A-D and B-C
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
_______ (A) the _______ (B) was one of Manuel’s only _______ (C) so he _______(D).
- Pursued: Refers to the act of going after something or chasing something in the past tense. The first half of the sentence is in the present tense so the verbs should follow this pattern, ‘pursued’ is in the past tense.
- Talents: Natural aptitude or skill or an ability someone has in something. ‘Talents’ is a general category and cannot be ‘pursued’ as a whole, it needs to be more specific.
- Guitar: A stringed musical instrument. The ‘one of’ refers to being a part of many and so the noun here needs to be plural, ‘guitar’ is singular.
- Playing: Refers to the act of performing using a musical instrument. “He playing that” is grammatically incorrect.
Hence, we need to interchange A and D and also B and C in order to make the sentence contextually correct
Correct Sentence: Playing (A) the guitar (B) was one of Manuel’s only talents (C) so he pursued (D) that.
25. Directions: In each of the questions given below, four words are given in bold. These four words may or may not be in their correct position. The sentence is then followed by options with the correct combination of words that should replace each other in order to make the sentence grammatically and contextually correct. Find the correct combination of words that replace each other. If the sentence is correct then, selects ‘All correct’ as your option.
The kerosene subsidy has also been quietly ended by rationale/ (A) out subsidized state allocations. The original phasing/ (B) for subsidized kerosene was that it was used in hurricane/ (C) lanterns, the only form of lighting/ (D) in non-electric areas comprising most of India.
A. B-D
B. A-B
C. C-D
D. A-D
E. All correct
Solution
The correct answer is Option 2 i.e. ‘The correct combination of words is A-B’
Key Points
- The combination of a pair A-B i.e. Rationale and Phasing should interchanged.
- ‘Phasing out’ is a phrasal verb which means ‘stop using something gradually’ and also ‘by’ is a preposition and we need a prepositional object so phasing acts as a gerund(noun) here.
- ‘Rationale’ is a noun and original is an adjective that’s why we can’t use phasing in part B because we need a noun there.
So the correct sentence is: “The kerosene subsidy has also been quietly ended by phasing out subsidized state allocations. The original rationale for subsidized kerosene was that it was used in hurricane lanterns, the only form of lighting in non-electric areas comprising most of India.”
26. Rearrange the following six sentences i.e. A, B, C, D, E and F in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph and answer the given questions.
A – The students who clear all three levels receive the National Award from the President of the country and are given monetary rewards as well.
B – The ‘National Cultural Talent Search’ competition is organised annually.
C – The crème de la crème of these represent the country at various international cultural exchange programs.
D – In three phases of increasing difficulty i.e. State, Zonal and National, this competition handpicks the best talent of the country.
E – The participants are assessed on their main performance in the initial two levels.
F – Thereupon, for the third phase, a lot of other spontaneous assessment rounds are added to determine the overall creativity.
Question:
Which of the following is the THIRD sentence after rearrangement?
A. E
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is Option 1.
Key Points
- The correct order of the rearrangement will be BDEFAC.
- To find the introductory sentence, we must try and find a relevant subject. Sentence B introduces the name of the competition which is further detailed across all other sentences. Thus, B is the starting sentence.
- D details the basic structure of the competition, which should logically follow.
- E talks about the initial levels whereas F talks about the final level. Thus, these two should respectively follow B and D.
- Finally, A and C talk about the resultant end. But, even in this, A describes what the winners receive while C uses the phrase ‘creme de la creme‘ which means ‘the best of the lot’ thereby describing that the best out of a lot of winners get to represent the country at various platforms.
- Thus, C is chronologically the last and concluding sentence.
Therefore, the third sentence is E.
27. Rearrange the following six sentences i.e. A, B, C, D, E and F in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph and answer the given questions.
A – The students who clear all three levels receive the National Award from the President of the country and are given monetary rewards as well.
B – The ‘National Cultural Talent Search’ competition is organised annually.
C – The crème de la crème of these represent the country at various international cultural exchange programs.
D – In three phases of increasing difficulty i.e. State, Zonal and National, this competition handpicks the best talent of the country.
E – The participants are assessed on their main performance in the initial two levels.
F – Thereupon, for the third phase, a lot of other spontaneous assessment rounds are added to determine the overall creativity.
Question:
Which of the following is the FIRST sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is Option 2.
Key Points
- The correct order of the rearrangement will be BDEFAC.
- To find the introductory sentence, we must try and find a relevant subject. Sentence B introduces the name of the competition which is further detailed across all other sentences. Thus, B is the starting sentence.
- D details the basic structure of the competition, which should logically follow.
- E talks about the initial levels whereas F talks about the final level. Thus, these two should respectively follow B and D.
- Finally, A and C talk about the resultant end. But, even in this, A describes what the winners receive while C uses the phrase ‘creme de la creme‘ which means ‘the best of the lot’ thereby describing that the best out of a lot of winners get to represent the country at various platforms.
Therefore, the first sentence is B.
28. Rearrange the following six sentences i.e. A, B, C, D, E and F in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph and answer the given questions.
A – The students who clear all three levels receive the National Award from the President of the country and are given monetary rewards as well.
B – The ‘National Cultural Talent Search’ competition is organised annually.
C – The crème de la crème of these represent the country at various international cultural exchange programs.
D – In three phases of increasing difficulty i.e. State, Zonal and National, this competition handpicks the best talent of the country.
E – The participants are assessed on their main performance in the initial two levels.
F – Thereupon, for the third phase, a lot of other spontaneous assessment rounds are added to determine the overall creativity.
Question:
Which of the following is the SECOND LAST sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is Option 1.
Key Points
- The correct order of the rearrangement will be BDEFAC.
- To find the introductory sentence, we must try and find a relevant subject. Sentence B introduces the name of the competition which is further detailed across all other sentences. Thus, B is the starting sentence.
- D details the basic structure of the competition, which should logically follow.
- E talks about the initial levels whereas F talks about the final level. Thus, these two should respectively follow B and D.
- Finally, A and C talk about the resultant end. But, even in this, A describes what the winners receive while C uses the phrase ‘creme de la creme‘ which means ‘the best of the lot’ thereby describing that the best out of a lot of winners get to represent the country at various platforms.
Therefore, the second last sentence is A.
29. Rearrange the following six sentences i.e. A, B, C, D, E and F in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph and answer the given questions.
A – The students who clear all three levels receive the National Award from the President of the country and are given monetary rewards as well.
B – The ‘National Cultural Talent Search’ competition is organised annually.
C – The crème de la crème of these represent the country at various international cultural exchange programs.
D – In three phases of increasing difficulty i.e. State, Zonal and National, this competition handpicks the best talent of the country.
E – The participants are assessed on their main performance in the initial two levels.
F – Thereupon, for the third phase, a lot of other spontaneous assessment rounds are added to determine the overall creativity.
Question:
Which of the following is the LAST sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is Option 3.
Key Points
- The correct order of the rearrangement will be BDEFAC.
- To find the introductory sentence, we must try and find a relevant subject. Sentence B introduces the name of the competition which is further detailed across all other sentences. Thus, B is the starting sentence.
- D details the basic structure of the competition, which should logically follow.
- E talks about the initial levels whereas F talks about the final level. Thus, these two should respectively follow B and D.
- Finally, A and C talk about the resultant end. But, even in this, A describes what the winners receive while C uses the phrase ‘creme de la creme‘ which means ‘the best of the lot’ thereby describing that the best out of a lot of winners get to represent the country at various platforms.
Therefore, the last sentence is C.
30. Rearrange the following six sentences i.e. A, B, C, D, E and F in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph and answer the given questions.
A – The students who clear all three levels receive the National Award from the President of the country and are given monetary rewards as well.
B – The ‘National Cultural Talent Search’ competition is organised annually.
C – The crème de la crème of these represent the country at various international cultural exchange programs.
D – In three phases of increasing difficulty i.e. State, Zonal and National, this competition handpicks the best talent of the country.
E – The participants are assessed on their main performance in the initial two levels.
F – Thereupon, for the third phase, a lot of other spontaneous assessment rounds are added to determine the overall creativity.
Question:
Which of the following is the SECOND sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is Option 4.
Key Points
- The correct order of the rearrangement will be BDEFAC.
- To find the introductory sentence, we must try and find a relevant subject. Sentence B introduces the name of the competition which is further detailed across all other sentences. Thus, B is the starting sentence.
- D details the basic structure of the competition, which should logically follow.
- E talks about the initial levels whereas F talks about the final level. Thus, these two should respectively follow B and D.
- Finally, A and C talk about the resultant end. But, even in this, A describes what the winners receive while C uses the phrase ‘creme de la creme‘ which means ‘the best of the lot’ thereby describing that the best out of a lot of winners get to represent the country at various platforms.
Therefore, the second sentence is D.
31. In office D, the male-to-female ratio is 4:3. Difference between male and female in office B is t. In office C, the number of males is 10 fewer than the number of females. Total employee in office B is y. The female-to-female ratio between offices A and B is 6:5. In office A, the number of males is twelve more than the number of females. Sum of male employee in office C and D is z. The male-to-male ratio between offices C and D is 5:8. The combined number of males in offices A and D is 90. Difference between number of male in office C and number of female in Office D is u. The male-to-male ratio between offices A and B is 7:6. The number of females in office C is 60% more than the number of females in office B.
Question:
Find the value of 2y + 3z + 5t?
A. 875
B. 411
C. 335
D. 325
E. 625
Solution
Common Calculation
Lets male in A is 7x and male in B is 6x.
Female in A is 7x – 12
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6
Male in D is 90 – 7x.
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4
Number of females in C is [90 – 7x] × [5/8] + 10
ATQ, [7x – 12] × 5 /6 × [ 160/100] = [90 -7x] × 5/8 +10
Or, 9.33x – 16 = 56.25 – 4.375x + 10
Or, 13.705x = 82.25
Or, x = 82.25 / 13.705 = 6
Male in A is 7×6 = 42
Female in A is 7x – 12 = 42 -12 = 30
Male in B is 6 × 6 = 36
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6 = 30 × 5 /6 = 25
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8 = 48 × 5 /8 = 30
Females in C = 30 + 10 = 40
Male in D is 90 – 7x = 90 -42 = 48
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4 = 48 × 3 /4 = 36
So, t = 36 -25 = 11
So, y = 36 + 25 = 61
So, z = MC + MD = 30 + 48 = 78
So, u =|MC – FD| = |30 – 36| = |-6| = 6
| Office | Male | Female |
| A | 42 | 30 |
| B | 36 | 25 |
| C | 30 | 40 |
| D | 48 | 36 |
Calculation
2y + 3z + 5t = [2 × 61] + [3 × 78] + [5 × 11]
= 122 + 234 + 55 = 411
The correct answer is Option (2).
32. In office D, the male-to-female ratio is 4:3. Difference between male and female in office B is t. In office C, the number of males is 10 fewer than the number of females. Total employee in office B is y. The female-to-female ratio between offices A and B is 6:5. In office A, the number of males is twelve more than the number of females. Sum of male employee in office C and D is z. The male-to-male ratio between offices C and D is 5:8. The combined number of males in offices A and D is 90. Difference between number of male in office C and number of female in Office D is u. The male-to-male ratio between offices A and B is 7:6. The number of females in office C is 60% more than the number of females in office B.
Question:
Difference between total male and total female employee in all office together is n. Find the value of 7n + 9u?
A. 231
B. 256
C. 244
D. 257
E. 229
Solution
Common Calculation
Lets male in A is 7x and male in B is 6x.
Female in A is 7x – 12
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6
Male in D is 90 – 7x.
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4
Number of females in C is [90 – 7x] × [5/8] + 10
ATQ, [7x – 12] × 5 /6 × [ 160/100] = [90 -7x] × 5/8 +10
Or, 9.33x – 16 = 56.25 – 4.375x + 10
Or, 13.705x = 82.25
Or, x = 82.25 / 13.705 = 6
Male in A is 7×6 = 42
Female in A is 7x – 12 = 42 -12 = 30
Male in B is 6 × 6 = 36
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6 = 30 × 5 /6 = 25
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8 = 48 × 5 /8 = 30
Females in C = 30 + 10 = 40
Male in D is 90 – 7x = 90 -42 = 48
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4 = 48 × 3 /4 = 36
So, t = 36 -25 = 11
So, y = 36 + 25 = 61
So, z = MC + MD = 30 + 48 = 78
So, u =|MC – FD| = |30 – 36| = |-6| = 6
| Office | Male | Female |
| A | 42 | 30 |
| B | 36 | 25 |
| C | 30 | 40 |
| D | 48 | 36 |
Calculation
Total males = 42 + 36 + 30 + 48 = 156
Total females = 30 + 25 + 40 + 36 = 131
So, n = 156 – 131 = 25
So, u = 6
Now: 7n + 9u = 7 × 25 + 9 × 6 = 175 + 54 = 229.
The correct answer is Option (5).
33. In office D, the male-to-female ratio is 4:3. Difference between male and female in office B is t. In office C, the number of males is 10 fewer than the number of females. Total employee in office B is y. The female-to-female ratio between offices A and B is 6:5. In office A, the number of males is twelve more than the number of females. Sum of male employee in office C and D is z. The male-to-male ratio between offices C and D is 5:8. The combined number of males in offices A and D is 90. Difference between number of male in office C and number of female in Office D is u. The male-to-male ratio between offices A and B is 7:6. The number of females in office C is 60% more than the number of females in office B.
Question:
Out of total male employees in office C, 20% work in officer post. Total officer in office C is 14. Find the number of females who is not officer?
A. 48
B. 32
C. 38
D. 30
E. 46
Solution
Common Calculation
Lets male in A is 7x and male in B is 6x.
Female in A is 7x – 12
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6
Male in D is 90 – 7x.
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4
Number of females in C is [90 – 7x] × [5/8] + 10
ATQ, [7x – 12] × 5 /6 × [ 160/100] = [90 -7x] × 5/8 +10
Or, 9.33x – 16 = 56.25 – 4.375x + 10
Or, 13.705x = 82.25
Or, x = 82.25 / 13.705 = 6
male in A is 7×6 = 42 and male in B is 6×6 = 36
Female in A is 7x – 12 = 42 -12 = 30
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6 = 30 × 5 /6 = 25
Male in D is 90 – 7x = 90 -42 = 48
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8 = 48 × 5 /8 = 30
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4 = 48 × 3 /4 = 36
Number of females in C is 30 + 10 = 40
So, t = 36 -25 = 11
So, y = 36 + 25 = 61
So, z = 36 +30 = 66
So, u = 40 – 36 = 4
| Office | Male | Female |
| A | 42 | 30 |
| B | 36 | 25 |
| C | 30 | 40 |
| D | 48 | 36 |
Calculation
In office C:
Male = 30, 20% are officers ⇒ 20% of 30 = 6
Total officers = 14
⇒ Females officers = 14 – 6 = 8
Female in C = 40 ⇒ Non-officer females = 40 – 8 = 32
The correct answer is Option (2).
34. In office D, the male-to-female ratio is 4:3. Difference between male and female in office B is t. In office C, the number of males is 10 fewer than the number of females. Total employee in office B is y. The female-to-female ratio between offices A and B is 6:5. In office A, the number of males is twelve more than the number of females. Sum of male employee in office C and D is z. The male-to-male ratio between offices C and D is 5:8. The combined number of males in offices A and D is 90. Difference between number of male in office C and number of female in Office D is u. The male-to-male ratio between offices A and B is 7:6. The number of females in office C is 60% more than the number of females in office B.
Question:
Ratio of male employee in office D and E is 4:7. Total number of employees in office E is 112. Find the female employee in office E?
A. 22
B. 26
C. 32
D. 36
E. 28
Solution
Common Calculation
Lets male in A is 7x and male in B is 6x.
Female in A is 7x – 12
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6
Male in D is 90 – 7x.
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4
Number of females in C is [90 – 7x] × [5/8] + 10
ATQ, [7x – 12] × 5 /6 × [ 160/100] = [90 -7x] × 5/8 +10
Or, 9.33x – 16 = 56.25 – 4.375x + 10
Or, 13.705x = 82.25
Or, x = 82.25 / 13.705 = 6
male in A is 7×6 = 42 and male in B is 6×6 = 36
Female in A is 7x – 12 = 42 -12 = 30
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6 = 30 × 5 /6 = 25
Male in D is 90 – 7x = 90 -42 = 48
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8 = 48 × 5 /8 = 30
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4 = 48 × 3 /4 = 36
Number of females in C is 30 + 10 = 40
So, t = 36 -25 = 11
So, y = 36 + 25 = 61
So, z = 36 +30 = 66
So, u = 40 – 36 = 4
| Office | Male | Female |
| A | 42 | 30 |
| B | 36 | 25 |
| C | 30 | 40 |
| D | 48 | 36 |
Calculation
Ratio of male in D:E = 4:7
Male in D = 48 ⇒ 4x = 48
⇒ x = 12
⇒ Male in E = 7x = 84
Total employees in E = 112 ⇒ Female = 112 – 84 = 28
The correct answer is Option (5).
35. In office D, the male-to-female ratio is 4:3. Difference between male and female in office B is t. In office C, the number of males is 10 fewer than the number of females. Total employee in office B is y. The female-to-female ratio between offices A and B is 6:5. In office A, the number of males is twelve more than the number of females. Sum of male employee in office C and D is z. The male-to-male ratio between offices C and D is 5:8. The combined number of males in offices A and D is 90. Difference between number of male in office C and number of female in Office D is u. The male-to-male ratio between offices A and B is 7:6. The number of females in office C is 60% more than the number of females in office B.
Question:
Find the difference between total number of employees in office A and B together and total number of employees in office C and D together?
A. 29
B. 25
C. 21
D. 23
E. 31
Solution
Common Calculation
Lets male in A is 7x and male in B is 6x.
Female in A is 7x – 12
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6
Male in D is 90 – 7x.
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4
Number of females in C is [90 – 7x] × [5/8] + 10
ATQ, [7x – 12] × 5 /6 × [ 160/100] = [90 -7x] × 5/8 +10
Or, 9.33x – 16 = 56.25 – 4.375x + 10
Or, 13.705x = 82.25
Or, x = 82.25 / 13.705 = 6
male in A is 7×6 = 42 and male in B is 6×6 = 36
Female in A is 7x – 12 = 42 -12 = 30
Female in B is [7x – 12] × 5 /6 = 30 × 5 /6 = 25
Male in D is 90 – 7x = 90 -42 = 48
Male in C is [90 -7x] × 5/8 = 48 × 5 /8 = 30
Female in D is [90 – 7x] × 3 /4 = 48 × 3 /4 = 36
Number of females in C is 30 + 10 = 40
So, t = 36 -25 = 11
So, y = 36 + 25 = 61
So, z = 36 +30 = 66
So, u = 40 – 36 = 4
| Office | Male | Female |
| A | 42 | 30 |
| B | 36 | 25 |
| C | 30 | 40 |
| D | 48 | 36 |
Calculation
Total employees in A and B = A + B = 72 + 61 = 133
Total employees in C and D = C + D = 70 + 84 = 154
Difference = 154 − 133 = 21
The correct answer is Option (3).
36. Find the wrong term in the following series.
215, 341, 509, 725, 995, 1330
A. 1330
B. 995
C. 725
D. 341
E. 215
Solution
Given series:
215, 341, 509, 725, 995, 1330
Calculation :
The series follows the following pattern:
⇒ (6)3 – 1 = 215
⇒ (7)3 – 2 = 341
⇒ (8)3 – 3 = 509
⇒ (9)3 – 4 = 725
⇒ (10)3 – 5 = 995
⇒ (11)3 – 6 = 1325
The wrong term is 1330
Hence the wrong term in the series is 1330.
37. Find the wrong term in the following series.
24, 32, 38, 62, 70, 102
A. 32
B. 38
C. 70
D. 102
E. 62
Solution
Given Series:
24, 32, 38, 62, 70, 102
Calculation:
The series follows the logic of = Product of digits of the number + Number
⇒ 24 + (2 x 4) = 24 + 8 = 32
⇒ 32 + (3 x 2) = 32 + 6 = 38
⇒ 38 + (3 x 8) = 38 + 24 = 62
⇒ 62 + (6 x 2) = 62 + 12 = 74
⇒ 74 + (7 x 4) = 74 + 28 = 102
∴ Wrong number in the series is 70.
38. Find the wrong term in the following series.
27, 345, 122, 2199, 291, 6861
A. 27
B. 345
C. 122
D. 2199
E. 291
Solution
Given Series:
27, 345, 122, 2199, 291, 6861
Calculation:
⇒ 2 + 52 = 27
⇒ 2 + 73 = 345
⇒ 2 + 112 = 123
⇒ 2 + 133 = 2199
⇒ 2 + 172 = 291
⇒ 2 + 193 = 6861
∴ Wrong number in the series is 122.
39. Find the wrong term in the given series.
50, 51, 76, 157, 326, 605, 1056
A. 76
B. 1056
C. 157
D. 51
E. 605
Solution
Solution:
The series follows the following pattern:
⇒50 + 12 = 51
⇒51 + 52 = 76
⇒76 + 92 = 157
⇒157 + 132 = 326
⇒326 + 172 = 615
⇒615 + 212 = 1056
⇒ The wrong term in the series will be 605.
Hence, 605 is the correct answer.
40. Find the wrong term in the given series.
142, 144, 148, 156, 176
A. 144
B. 148
C. 156
D. 176
E. 142
Solution
The logic followed here is as follows:
⇒ 142 + 21 = 144
⇒ 144 + 22 = 148
⇒ 148 + 23 = 156
⇒ 156 + 24 = 172
So, the wrong term is 176
Hence, the correct answer is 176.
41. Given that A and B together can finish a task in 12.5 days, and B and C together can do it in 18.75 days, and also A and C together can do it in 15 days, how long would it take for A, B, C and D (with D having only 40% of C’s efficiency) to complete the same task collectively?
A. 9(1/3)
B. 9(17/27)
C. 9(2/3)
D. 9(7/27)
E. 9(1/3)
Solution
Solution:
A and B together can finish a task in 12.5 days.
B and C together can do it in 18.75 days.
A and C together can do it in 15 days.
D having only 40% of C’s efficiency.
Total work = Time × Efficiency
A + B = 12.5 = 25/2 days
B + C = 18.75 = 75/4 days
A + C = 15 days
Total work = LCM(25/2, 75/4, 15) = 75 units
Efficiency of A + B = 75/(25/2) = 6
Efficiency of B + C = 75/(75/4) = 4
Efficiency of A + C = 75/15 = 5
Efficiency of A + B + C = 15/2 = 7.5
Efficiency of C = 7.5 – 6 = 1.5
Efficiency of D = 1.5 × 0.4 = 0.6
Time taken by A, B, C and D to complete the task collectively = 75/8.1
= 750/81 = 250/27
= 9(7/27)
Hence, option(4) is correct.
42. Marked price of the article is Rs.2500. It is sold after a successive discount of 20% and D% and gained a profit of 20%. If the cost price of the article is Rs.1500. Find the selling price of the article if the article is sold at the 10% profit.
A. Rs. 1750
B. Rs. 1650
C. Rs. 1550
D. Rs. 1450
E. Rs. 1850
Solution
Solution:
CP = Rs.1500
Profit % = 20%
SP = 1500 × 120/100 = Rs.1800
MP = Rs.2500
2500 × (80/100) × (100 – D)/100 = 1800
20 × (100 – D) = 1800
100 – D = 1800/20
100 – D = 90
– D = 90 – 100
– D = –10
D = 10%
The selling price of the article = 1500 × (110/100) = Rs. 1650
43. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
The pie chart shows the % distribution of employees attending mandatory cybersecurity training sessions across five day time slots (Morning, Midday, Afternoon, Evening, Night).
24.24% less of the total number of employees attending training during the Evening slot is equal to 2500.

Question:
If the number of employees in the Afternoon session increases by 40%, and the Night session decreases by 50%, find the new combined total.
A. 3850
B. 4500
C. 4400
D. 5500
E. 5300
Solution
General Solution:
We are given:
Evening attendees 24.24% of Evening attendees = 2500
Evening attendees × (1 – 0.2424) = 2500
Evening attendees × 0.7576 = 2500
Evening attendees = 2500 / 0.7576 ≈ 3300 (Rounded to nearest whole number)
Evening slot attendees ≈ 3,300
Express Percentages in Terms of x
Evening percentage = x + 10%
Since 3,300 employees correspond to x + 10% of the total workforce T:
x + 10% × T = 3300
T = 3300/ (x + 10) × 100
The sum of all time-slot percentages must equal 100%:
(x + 13) + (x + 8) + (x + 3) + (x + 10) + (x + 6) = 100
5x + 40 = 100
5x = 60 ⟹ x = 12
Value of x = 12
Substitute x = 12 :
Morning:12 + 13 = 25%
Midday: 12 + 8 = 20%
Afternoon: 12 + 3 = 15%
Evening: 12 + 10 = 22%
Night: 12 + 6 = 18%
25 + 20 + 15 + 22 + 18 = 100%
From Evening slot:
22% × T = 3300 ⟹ T = 3300 / 0.22 = 15,000
Multiply total employees by each percentage:
| Time Slot | Percentage | Number of Employees | Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | 25% | 3,750 | 0.25×15,0000.25×15,0000.25×15,000 |
| Midday | 20% | 3,000 | 0.20×15,0000.20×15,0000.20×15,000 |
| Afternoon | 15% | 2,250 | 0.15×15,0000.15×15,0000.15×15,000 |
| Evening | 22% | 3,300 | 0.22×15,0000.22×15,0000.22×15,000 |
| Night | 18% | 2,700 | 0.18×15,0000.18×15,0000.18×15,000 |
Calculations:
Original Afternoon employees = 2,250
Increase by 40%:
New Afternoon = 2,250 + (0.40 × 2,250) = 2,250 + 900 = 3,150
Original Night employees = 2,700
Decrease by 50%:
New Night = 2,700 − (0.50 × 2,700) = 2,700 − 1,350 = 1,350
New Total = New Afternoon + New Night = 3,150 + 1,350 = 4,500
Thus, the correct answer is 4,500.
44. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
The pie chart shows the % distribution of employees attending mandatory cybersecurity training sessions across five day time slots (Morning, Midday, Afternoon, Evening, Night).
24.24% less of the total number of employees attending training during the Evening slot is equal to 2500.

Question:
The total number of employees attending the Midday training session is 10% less than those attending the Morning session. If the ratio of technical to non-technical staff in the Midday session is 2:3, find the number of technical staff attending Midday.
A. 1400
B. 1600
C. 1550
D. 1350
E. 1450
Solution
General Solution:
We are given:
Evening attendees 24.24% of Evening attendees = 2500
Evening attendees × (1 – 0.2424) = 2500
Evening attendees × 0.7576 = 2500
Evening attendees = 2500 / 0.7576 ≈ 3300 (Rounded to nearest whole number)
Evening slot attendees ≈ 3,300
Express Percentages in Terms of x
Evening percentage = x + 10%
Since 3,300 employees correspond to x + 10% of the total workforce T:
x + 10% × T = 3300
T = 3300/ (x + 10) × 100
The sum of all time-slot percentages must equal 100%:
(x + 13) + (x + 8) + (x + 3) + (x + 10) + (x + 6) = 100
5x + 40 = 100
5x = 60 ⟹ x = 12
Value of x = 12
Substitute x = 12 :
Morning:12 + 13 = 25%
Midday: 12 + 8 = 20%
Afternoon: 12 + 3 = 15%
Evening: 12 + 10 = 22%
Night: 12 + 6 = 18%
25 + 20 + 15 + 22 + 18 = 100%
From Evening slot:
22% × T = 3300 ⟹ T = 3300 / 0.22 = 15,000
Multiply total employees by each percentage:
| Time Slot | Percentage | Number of Employees | Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | 25% | 3,750 | 0.25×15,0000.25×15,0000.25×15,000 |
| Midday | 20% | 3,000 | 0.20×15,0000.20×15,0000.20×15,000 |
| Afternoon | 15% | 2,250 | 0.15×15,0000.15×15,0000.15×15,000 |
| Evening | 22% | 3,300 | 0.22×15,0000.22×15,0000.22×15,000 |
| Night | 18% | 2,700 | 0.18×15,0000.18×15,0000.18×15,000 |
Calculations:
Given:
1. Midday attendees = Morning attendees – 10%
2. Ratio of technical to non-technical in Midday = 2:3
Express Midday in terms of Morning:
Let Morning = M
⇒ Midday = M – 0.10M = 0.90M
Calculate technical staff in Midday:
Technical:Non-technical = 2:3 ⇒ Total parts = 5
Technical staff = (2/5) × Midday = (2/5) × 0.90M = 0.36M
⇒ M = 3,750 (from general solution)
Calculate technical staff:
Technical staff = 0.36 × 3,750 = 1,350
Thus, the correct answer is 1,350
45. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
The pie chart shows the % distribution of employees attending mandatory cybersecurity training sessions across five day time slots (Morning, Midday, Afternoon, Evening, Night).
24.24% less of the total number of employees attending training during the Evening slot is equal to 2500.

Question:
The combined attendees for Morning and Evening sessions is what percentage more/less than the combined Night and Afternoon sessions?
A. No change
B. 42.42%
C. 11.11%
D. 22.24%
E. 53.57%
Solution
General Solution:
We are given:
Evening attendees 24.24% of Evening attendees = 2500
Evening attendees × (1 – 0.2424) = 2500
Evening attendees × 0.7576 = 2500
Evening attendees = 2500 / 0.7576 ≈ 3300 (Rounded to nearest whole number)
Evening slot attendees ≈ 3,300
Express Percentages in Terms of x
Evening percentage = x + 10%
Since 3,300 employees correspond to x + 10% of the total workforce T:
x + 10% × T = 3300
T = 3300/ (x + 10) × 100
The sum of all time-slot percentages must equal 100%:
(x + 13) + (x + 8) + (x + 3) + (x + 10) + (x + 6) = 100
5x + 40 = 100
5x = 60 ⟹ x = 12
Value of x = 12
Substitute x = 12 :
Morning:12 + 13 = 25%
Midday: 12 + 8 = 20%
Afternoon: 12 + 3 = 15%
Evening: 12 + 10 = 22%
Night: 12 + 6 = 18%
25 + 20 + 15 + 22 + 18 = 100%
From Evening slot:
22% × T = 3300 ⟹ T = 3300 / 0.22 = 15,000
Multiply total employees by each percentage:
| Time Slot | Percentage | Number of Employees | Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | 25% | 3,750 | 0.25×15,0000.25×15,0000.25×15,000 |
| Midday | 20% | 3,000 | 0.20×15,0000.20×15,0000.20×15,000 |
| Afternoon | 15% | 2,250 | 0.15×15,0000.15×15,0000.15×15,000 |
| Evening | 22% | 3,300 | 0.22×15,0000.22×15,0000.22×15,000 |
| Night | 18% | 2,700 | 0.18×15,0000.18×15,0000.18×15,000 |
Calculations:
Morning + Evening = 3,750 + 3,300 = 7,050
Night + Afternoon = 2,700 + 2,250 = 4,950
Difference = 7,050 – 4,950 = 2,100
Percentage More = (Difference / Comparison Group) × 100
⇒ (2,100 / 4,950) × 100 ≈ 42.42%
Thus, the combined Morning and Evening sessions have 42.42% more attendees than Night and Afternoon sessions combined.
46. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
The pie chart shows the % distribution of employees attending mandatory cybersecurity training sessions across five day time slots (Morning, Midday, Afternoon, Evening, Night).
24.24% less of the total number of employees attending training during the Evening slot is equal to 2500.

Question:
The number of technical staff in the Night session is 300 more than non-technical staff. The technical staff in Morning is 25% more than the non-technical staff in Night. Find non-technical staff in Morning.
A. 2150
B. 2250
C. 2350
D. 2400
E. 2450
Solution
General Solution:
We are given:
Evening attendees 24.24% of Evening attendees = 2500
Evening attendees × (1 – 0.2424) = 2500
Evening attendees × 0.7576 = 2500
Evening attendees = 2500 / 0.7576 ≈ 3300 (Rounded to nearest whole number)
Evening slot attendees ≈ 3,300
Express Percentages in Terms of x
Evening percentage = x + 10%
Since 3,300 employees correspond to x + 10% of the total workforce T:
x + 10% × T = 3300
T = 3300/ (x + 10) × 100
The sum of all time-slot percentages must equal 100%:
(x + 13) + (x + 8) + (x + 3) + (x + 10) + (x + 6) = 100
5x + 40 = 100
5x = 60 ⟹ x = 12
Value of x = 12
Substitute x = 12 :
Morning:12 + 13 = 25%
Midday: 12 + 8 = 20%
Afternoon: 12 + 3 = 15%
Evening: 12 + 10 = 22%
Night: 12 + 6 = 18%
25 + 20 + 15 + 22 + 18 = 100%
From Evening slot:
22% × T = 3300 ⟹ T = 3300 / 0.22 = 15,000
Multiply total employees by each percentage:
| Time Slot | Percentage | Number of Employees | Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | 25% | 3,750 | 0.25×15,0000.25×15,0000.25×15,000 |
| Midday | 20% | 3,000 | 0.20×15,0000.20×15,0000.20×15,000 |
| Afternoon | 15% | 2,250 | 0.15×15,0000.15×15,0000.15×15,000 |
| Evening | 22% | 3,300 | 0.22×15,0000.22×15,0000.22×15,000 |
| Night | 18% | 2,700 | 0.18×15,0000.18×15,0000.18×15,000 |
Calculations:
Total Night attendees = 18% of 15,000 = 2,700
Let Non-technical (Night) = N
⇒ Technical (Night) = N + 300
Total Night staff:
N + (N + 300) = 2,700
2N + 300 = 2,700
2N = 2,400 ⇒ N = 1,200
Technical (Morning) = 1.25 × Non-technical (Night)
= 1.25 × 1,200 = 1,500
Total Morning attendees = 25% of 15,000 = 3,750
Non-technical (Morning) = Total Morning – Technical (Morning)
= 3,750 – 1,500 = 2,250
Thus, the correct answer is 2,250.
47. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
The pie chart shows the % distribution of employees attending mandatory cybersecurity training sessions across five day time slots (Morning, Midday, Afternoon, Evening, Night).
24.24% less of the total number of employees attending training during the Evening slot is equal to 2500.

Question:
What is the ratio of attendees in Morning and Evening sessions to the Afternoon session?
A. 20:11
B. 17:61
C. 32:83
D. 47:15
E. None of these
Solution
General Solution:
We are given:
Evening attendees 24.24% of Evening attendees = 2500
Evening attendees × (1 – 0.2424) = 2500
Evening attendees × 0.7576 = 2500
Evening attendees = 2500 / 0.7576 ≈ 3300 (Rounded to nearest whole number)
Evening slot attendees ≈ 3,300
Express Percentages in Terms of x
Evening percentage = x + 10%
Since 3,300 employees correspond to x + 10% of the total workforce T:
x + 10% × T = 3300
T = 3300/ (x + 10) × 100
The sum of all time-slot percentages must equal 100%:
(x + 13) + (x + 8) + (x + 3) + (x + 10) + (x + 6) = 100
5x + 40 = 100
5x = 60 ⟹ x = 12
Value of x = 12
Substitute x = 12 :
Morning:12 + 13 = 25%
Midday: 12 + 8 = 20%
Afternoon: 12 + 3 = 15%
Evening: 12 + 10 = 22%
Night: 12 + 6 = 18%
25 + 20 + 15 + 22 + 18 = 100%
From Evening slot:
22% × T = 3300 ⟹ T = 3300 / 0.22 = 15,000
Multiply total employees by each percentage:
| Time Slot | Percentage | Number of Employees | Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | 25% | 3,750 | 0.25×15,0000.25×15,0000.25×15,000 |
| Midday | 20% | 3,000 | 0.20×15,0000.20×15,0000.20×15,000 |
| Afternoon | 15% | 2,250 | 0.15×15,0000.15×15,0000.15×15,000 |
| Evening | 22% | 3,300 | 0.22×15,0000.22×15,0000.22×15,000 |
| Night | 18% | 2,700 | 0.18×15,0000.18×15,0000.18×15,000 |
Calculations:
Morning + Evening = 3,750 + 3,300 = 7,050
Ratio = (Morning + Evening) : Afternoon
⇒ 7,050 : 2,250
Simplified ratio = 47:15
Thus, the ratio is 47:15.
48. The average of 5 consecutive even numbers is 42, If the smallest even number is 2 more than x and largest even number is 1 less than the y. Find the sum of the 25% of the x and 200% of y.
A. 110
B. 103
C. 133
D. 112
E. 104
Solution
Solution:
The average of five consecutive even numbers = 5 × 42 = 210
Let the even numbers be a, (a + 2), (a + 4), (a + 6) and (a + 8)
(a + a + 2 + a + 4 + a + 6 + a + 8) = 210
(5a + 20) = 210
a = 190/5 = 38
Smallest even number is 2 more than x
If smallest even number = 38
Value of x = (38 – 2) = 36
Largest even number = 46
Value of y = 46 + 1 = 47
25% of x = 36/4 = 9
200% of y = 47 × (200/100) = 94
Required sum = (9 + 94) = 103
49. A man buys a motorcycle by making a cash down payment of Rs. 10,000 and promises to pay two more yearly installments of Rs. 12,100 each for the next two years. If the rate of interest is 10% per annum, compounded yearly, the cash value of the motorcycle is:
A. Rs. 34,200
B. Rs. 32,100
C. Rs. 31,000
D. Rs. 21,000
E. Rs. 11,000
Solution
Given:
Down payment = Rs. 10,000
Two equal annual installments = Rs. 12,100 each
Interest rate = 10% per annum, compounded yearly
Calculation:
Present value (PV) of the first installment (due after 1 year):
⇒ PV = 12100 ÷ (1 + 10/100) = 12100 ÷ 1.10 = Rs. 11000
Present value (PV) of the second installment (due after 2 years):
⇒ PV = 12100 ÷ (1.10 × 1.10) = 12100 ÷ 1.21 = Rs. 10000
Total cash value of the motorcycle:
⇒ Cash value = Down payment + PV of 1st installment + PV of 2nd installment
⇒ Cash value = 10000 + 11000 + 10000 = Rs. 31,000
Thus, the correct answer is Rs. 31,000.
50. What approximate value will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
37.5% of 96.03 – 149.98 = ? – 251.89 ÷ 3 – 37% of 3699.89
A. 1329
B. 1339
C. 1239
D. 1229
E. 1393
Solution
Given:
37.5% of 96.03 – 149.98 = ? – 251.89 ÷ 3 – 37% of 3699.89
Concept used:
Follow the ‘BODMAS’ Rule
B ⇒ Bracket, O ⇒ of, D ⇒ Division, M ⇒ Multiplication, A ⇒ Addition, S ⇒ Subtraction
Calculation:
⇒ 37.5% of 96.03 – 149.98 = ? – 251.89 ÷ 3 – 37% of 3699.89
⇒ 37.5% of 96 – 150 = ? – 252 ÷ 3 – 37% of 3700
⇒ 36 – 150 = ? – 84 – 1369
⇒ -114 = ? – 1453
⇒ 1339
∴ The value of ‘?’ is 1339.
51. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
9.1 × 34.98 – 2969.97 ÷ 18.05 × 6.96 + ? = 48.1 × 11.05
A. 1339
B. 1564
C. 1335
D. 1368
E. 1400
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
9.1 × 34.98 – 2969.97 ÷ 18.05 × 6.96 + ? = 48.1 × 11.05
⇒ 9 × 35 – 2970 ÷ 18 × 7 + ? = 48 × 11
⇒ 9 × 35 – 165 × 7 + ? = 48 × 11
⇒ 315 – 1155 + ? = 528
⇒ ? = 528 – 315 + 1155
⇒ ? = 1368
Hence, 1368 will come in the place of (?).
52. What approximate value should come in the place of the question mark (?) in the given question?
12.5% of 1183.76 + 24.89% of 419.78 + 19.78% of 520 = ?
A. 345
B. 357
C. 369
D. 352
E. 389
Solution
Solution :
Concept used :
Follow the BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the question is given below:
Step 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘ Brackets ‘ must be solved first and in the bracket,
Step 2: Any mathematical ‘ of ‘ or ‘exponent’ must be solved next,
Step 3: Next, The part of the equation that contains ‘Division’ and ‘multiplication’ are calculated,
Step 4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contains ‘Addition ‘ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
Given :
⇒ 12.5% of 1183.76 + 24.89% of 419.78 + 19.78% of 520 = ?
Approximate the number to its nearest value
⇒ 12.5% of 1184 + 25% of 420 + 20% of 520 = ?
⇒ 12.5 × 1184/100 + 25 × 420/100 + 20 × 520/100 = ?
⇒ 148 + 105 + 104 = ?
⇒ ? = 357
Hence, 357 is the correct answer.
53. What approximate value will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
24.982 – 1039.89 + 260.12 ÷ 13 = 506.08 – ?2 + 17.972
A. 35
B. 45
C. 25
D. 55
E. 65
Solution
Given:
24.982 – 1039.89 + 260.12 ÷ 13 = 506.08 – ?2 + 17.972
Concept used:
Follow the ‘BODMAS’ Rule
B ⇒ Bracket, O ⇒ of, D ⇒ Division, M ⇒ Multiplication, A ⇒ Addition, S ⇒ Subtraction
Calculation:
⇒ 24.982 – 1039.89 + 260.12 ÷ 13 = 506.08 – ?2 + 17.972
⇒ 252 – 1040 + 260 ÷ 13 = 506 – ?2 + 182
⇒ 625 – 1020 = 506 – ?2 + 324
⇒ ?2 = 506 + 324 + 1020 – 625
⇒ ?2 = 1850 – 625
⇒ ? = √1225
⇒ ? = 35
∴ The value of ‘?’ is 35.
54. What approximate value should come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
29.95 % of 570.123 × 20.011 = (?)2 – 19.998 – 2 x (80.169)
A. 58
B. 59
C. 57
D. 56
E. 60
Solution
Concept used :
Follow the BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the question is given below:
Step 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘ Brackets ‘ must be solved first and in the bracket,
Step 2: Any mathematical ‘ of ‘ or ‘exponent’ must be solved next,
Step 3: Next, The part of the equation that contains ‘Division’ and ‘multiplication’ are calculated,
Step 4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contains ‘Addition ‘ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
In approximation, we used the concept that if the digit after the decimal is 5 or more than 5 we increase the digit before the decimal by 1 but if the digit after the decimal is less than 5 we will not increase the digit before the decimal by 1.
Calculations:
29.95 % of 570.123 × 20.011 = (?)2 – 19.998 – 2 x (80.169)
30% of 570 × 20 = (?)2 – 20 – 2 x (80)
30/100 × 570 × 20 = (?)2 – 20 – 160
(?)2 = 3420 + 20 + 160
(?)2 = 3440 + 160 = 3600
(?) = 60
We get an approximate value of (?) is 60.
55. A and B started a business by investing ₹5000 and ₹3000 respectively. After 3 months, A increased his investment by ₹500. After 6 more months, B increased his investment by ₹y. If the ratio of the profits of A to B at the end of the year is 43:40, then find the value of 5y.
A. 20000
B. 24000
C. 28000
D. 32000
E. 40000
Solution
Given:
A invests ₹5000 initially, increases to ₹5500 after 3 months
B invests ₹3000 initially, increases by ₹y after 6 months (i.e., at the end of 6 months)
Profit ratio A : B = 43 : 40
Formula used:
Profit ∝ Investment × Time
Calculations:
A’s investment:
₹5000 for 3 months = 5000 × 3 = 15000
₹5500 for 9 months = 5500 × 9 = 49500
Total = 64500
B’s investment:
₹3000 for 9 months = 3000 × 9 = 27000
₹(3000 + y) for 3 months = (3000 + y) × 3 = 9000 + 3y
Total = 27000 + 9000 + 3y = 36000 + 3y
Profit ratio:
64500 : (36000 + 3y) = 43 : 40
⇒ 21500 : (12000 + y) = 43 : 40
⇒ 21500 / (12000 + y) = 43 / 40
⇒ 40 × 21500 = 43 × (12000 + y)
⇒ 860000 = 516000 + 43y
⇒ 344000 = 43y
⇒ y = 8000
⇒ 5y = 5 × 8000 = 40000
∴ The value of 5y is ₹40,000
56. The speed of the train A is 108 kmph and the length of the bridge is 6/7 of the length of the train and the time taken by the train A to cross the pole and bridge is 7 seconds and x seconds respectively.If the length of the train B is (45x). Then find the length of train B.
A. 550 m
B. 420 m
C. 585 m
D. 650 m
E. 570 m
Solution
Given:
Speed of train A = 108 kmph
Length of the bridge = 6/7 of the length of train A
Time taken by train A to cross a pole = 7 seconds
Time taken by train A to cross the bridge = x seconds
Length of train B = 45x
Concept Used:
Convert the speed from kmph to m/s using the conversion factor 1 kmph = 5/18 m/s.
Distance = Speed × Time.
Solution:
Speed of train A = 108 × (5/18) = 30 m/s
The train crosses a pole in 7 seconds, so:
Length of train A = Speed × Time = 30 × 7 = 210 meters
Length of the bridge = (6/7) × Length of train A = (6/7) × 210 = 180 meters
Total Distance to Cross the Bridge = Length of train A + Length of the bridge = 210 + 180 = 390 meters
Time to cross the bridge = Total distance / Speed = 390 / 30 = 13 seconds
Length of train B = 45x = 45 × 13 = 585 meters
The length of train B is 585 meters.
57. A committee consist of 4 men and 3 women selected from 7 men and 6 women. One of the selected women is chosen as chairman, find the number of ways of selecting the chairman.
A. 7C4 × 6C3
B. 7C4 × 6C3 × 3
C. 7C4 × 6C3 × 3!
D. 703
E. 720
Solution
Concept:-
A selection of r items from a collection of n items, such that the order of selection does not matter = nCr
Calculation:-
Number of ways of choosing the committee = 7C4 × 6C3
Now three women are there out of which one can be made chairman.
Total number of ways = 7C4 × 6C3 × 3
58. The given pie chart shows the percentage of distribution of total number of employees in IT, Accounts, Marketing and HR department respectively.
The given table shows percentage of female employee out male employee in each department and ratio of junior to senior employee in each department.
| Department | Percentage of female employee out of male employee | Ratio of Junior to senior employee |
| IT | 120% | 3:5 |
| Accounts | 75% | 1:3 |
| Marketing | 60% | 3:5 |
| HR | 80% | 4:5 |
Note – Total number of employee = Number of senior employee + Number of Junior employee = Number of male employee + Number of female employee. Total number of Senior employees in HR department is 80.
Question:
Total number of employees in Sales department in the company is average number of employees in accounts and HR department. Number of male employees in sales department is 25% more than the same in HR department and Number of junior employees in sales department is 33.33% more than the same in IT department. Find the difference between number of senior and female employee in sales department?
A. 16
B. 18
C. 19
D. 12
E. 14
Solution
Total number of senior employees in HR department is 80.
So, Number of junior employees in HR department is 80 × 4 /5 = 64
So, total number of employees in HR department is 80 + 64 = 144
So, 18% = 144, 100% = 8 × 100 = 800
So, Number of employee in IT department is 800 × 22 /100 = 176
Let number of male employees in IT department is 100x. Number of female employees in IT department is 100x × 120 /100 = 120x
So, Ratio of male and female employee in IT department is 5:6.
Number of male employees in IT department is 176 × 5 / 11 = 80
Number of female employees in IT department is 176 – 80 = 96
Number of junior employees in IT department is 176 × 3 / 8 = 66
Number of senior employees in IT department is 176 – 66 = 110
Similarly, we can calculate others values also which is given in the table.
| Department | Number of male employees | Number of female employees | Number of Junior employees | Number of Senior employees |
| IT | 80 | 96 | 66 | 110 |
| Accounts | 128 | 96 | 56 | 168 |
| Marketing | 160 | 96 | 96 | 160 |
| HR | 80 | 64 | 64 | 80 |
Calculation
Total number of employees in sales department is [ 224 + 144]/2 =184
Number of males employees in sales is 80 ×125/100 = 100
Number of females employees in sales 184 – 100 = 84
Number of junior employees in sales 66 × 4/3 = 88
So, Number of senior employees in sales 184 – 88 = 96
So, required difference is 96 – 84 = 12
59. The given pie chart shows the percentage of distribution of total number of employees in IT, Accounts, Marketing and HR department respectively.
The given table shows percentage of female employee out male employee in each department and ratio of junior to senior employee in each department.
| Department | Percentage of female employee out of male employee | Ratio of Junior to senior employee |
| IT | 120% | 3:5 |
| Accounts | 75% | 1:3 |
| Marketing | 60% | 3:5 |
| HR | 80% | 4:5 |
Note – Total number of employee = Number of senior employee + Number of Junior employee = Number of male employee + Number of female employee. Total number of Senior employees in HR department is 80.
Question:
62.5% female employee in accounts department is senior employee. Find the number of male junior employees in same department?
A. 62
B. 66
C. 20
D. 85
E. 88
Solution
Total number of senior employees in HR department is 80.
So, Number of junior employees in HR department is 80 × 4 /5 = 64
So, total number of employees in HR department is 80 + 64 = 144
So, 18% = 144, 100% = 8 × 100 = 800
So, Number of employee in IT department is 800 × 22 /100 = 176
Let number of male employees in IT department is 100x. Number of female employees in IT department is 100x × 120 /100 = 120x
So, Ratio of male and female employee in IT department is 5:6.
Number of male employees in IT department is 176 × 5 / 11 = 80
Number of female employees in IT department is 176 – 80 = 96
Number of junior employees in IT department is 176 × 3 / 8 = 66
Number of senior employees in IT department is 176 – 66 = 110
Similarly, we can calculate others values also which is given in the table.
| Department | Number of male employees | Number of female employees | Number of Junior employees | Number of Senior employees |
| IT | 80 | 96 | 66 | 110 |
| Accounts | 128 | 96 | 56 | 168 |
| Marketing | 160 | 96 | 96 | 160 |
| HR | 80 | 64 | 64 | 80 |
Calculation
Number senior female employee in accounts department is 96 × 62.5 /100 = 60
So, number of Junior female employees in accounts department is 96 – 60 = 36
So, Number of Junior male employees in accounts department is 56 – 36 = 20
60. The given pie chart shows the percentage of distribution of total number of employees in IT, Accounts, Marketing and HR department respectively.
The given table shows percentage of female employee out male employee in each department and ratio of junior to senior employee in each department.
| Department | Percentage of female employee out of male employee | Ratio of Junior to senior employee |
| IT | 120% | 3:5 |
| Accounts | 75% | 1:3 |
| Marketing | 60% | 3:5 |
| HR | 80% | 4:5 |
Note – Total number of employee = Number of senior employee + Number of Junior employee = Number of male employee + Number of female employee. Total number of Senior employees in HR department is 80.
Question:
Difference between male employee and senior employees in marketing department is x and difference between female employees and junior employees in IT department is y. Find the value of x + y ?
A. 85
B. 30
C. 74
D. 96
E. 88
Solution
Total Number of Senior employees in HR department is 80.
Total number of senior employees in HR department is 80.
So, Number of junior employees in HR department is 80 × 4 /5 = 64
So, total number of employees in HR department is 80 + 64 = 144
So, 18% = 144, 100% = 8 × 100 = 800
So, Number of employee in IT department is 800 × 22 /100 = 176
Let number of male employees in IT department is 100x. Number of female employees in IT department is 100x × 120 /100 = 120x
So, Ratio of male and female employee in IT department is 5:6.
Number of male employees in IT department is 176 × 5 / 11 = 80
Number of female employees in IT department is 176 – 80 = 96
Number of junior employees in IT department is 176 × 3 / 8 = 66
Number of senior employees in IT department is 176 – 66 = 110
Similarly, we can calculate others values also which is given in the table.
| Department | Number of male employees | Number of female employees | Number of Junior employees | Number of Senior employees |
| IT | 80 | 96 | 66 | 110 |
| Accounts | 128 | 96 | 56 | 168 |
| Marketing | 160 | 96 | 96 | 160 |
| HR | 80 | 64 | 64 | 80 |
Calculation
So, Difference between male employee and senior employees in marketing department is x = 160 – 160 = 0
difference between female employees and junior employees in IT department is y = 96 – 66 = 30
so, x + y = 0 + 30 = 30
61. The given pie chart shows the percentage of distribution of total number of employees in IT, Accounts, Marketing and HR department respectively.
The given table shows percentage of female employee out male employee in each department and ratio of junior to senior employee in each department.
| Department | Percentage of female employee out of male employee | Ratio of Junior to senior employee |
| IT | 120% | 3:5 |
| Accounts | 75% | 1:3 |
| Marketing | 60% | 3:5 |
| HR | 80% | 4:5 |
Note – Total number of employee = Number of senior employee + Number of Junior employee = Number of male employee + Number of female employee. Total number of Senior employees in HR department is 80.
Question:
48 new employees join as junior in IT department, for this 50% junior employee promoted to senior employee. Now total 87 male senior employees in IT department. Find number of female senior employee in iT department currently?
A. 56
B. 44
C. 85
D. 66
E. 74
Solution
Total Number of Senior employees in HR department is 80.
Total number of senior employees in HR department is 80.
So, Number of junior employees in HR department is 80 × 4 /5 = 64
So, total number of employees in HR department is 80 + 64 = 144
So, 18% = 144, 100% = 8 × 100 = 800
So, Number of employee in IT department is 800 × 22 /100 = 176
Let number of male employees in IT department is 100x. Number of female employees in IT department is 100x × 120 /100 = 120x
So, Ratio of male and female employee in IT department is 5:6.
Number of male employees in IT department is 176 × 5 / 11 = 80
Number of female employees in IT department is 176 – 80 = 96
Number of junior employees in IT department is 176 × 3 / 8 = 66
Number of senior employees in IT department is 176 – 66 = 110
Similarly, we can calculate others values also which is given in the table.
| Department | Number of male employees | Number of female employees | Number of Junior employees | Number of Senior employees |
| IT | 80 | 96 | 66 | 110 |
| Accounts | 128 | 96 | 56 | 168 |
| Marketing | 160 | 96 | 96 | 160 |
| HR | 80 | 64 | 64 | 80 |
Calculation
Total senior employee in IT department now is 110 + [66/2] = 143
So, Number of female senior employee in IT department is 143 – 87 = 56
62. The given pie chart shows the percentage of distribution of total number of employees in IT, Accounts, Marketing and HR department respectively.
The given table shows percentage of female employee out male employee in each department and ratio of junior to senior employee in each department.
| Department | Percentage of female employee out of male employee | Ratio of Junior to senior employee |
| IT | 120% | 3:5 |
| Accounts | 75% | 1:3 |
| Marketing | 60% | 3:5 |
| HR | 80% | 4:5 |
Note – Total number of employee = Number of senior employee + Number of Junior employee = Number of male employee + Number of female employee. Total number of Senior employees in HR department is 80.
Question:
Out of total male employee in HR department, 60% are married and out of total female employee in HR department, 50% are married. Find the total unmarried employee in HR department?
A. 66
B. 85
C. 74
D. 96
E. 64
Solution
Total Number of Senior employees in HR department is 80.
Total number of senior employees in HR department is 80.
So, Number of junior employees in HR department is 80 × 4 /5 = 64
So, total number of employees in HR department is 80 + 64 = 144
So, 18% = 144, 100% = 8 × 100 = 800
So, Number of employee in IT department is 800 × 22 /100 = 176
Let number of male employees in IT department is 100x. Number of female employees in IT department is 100x × 120 /100 = 120x
So, Ratio of male and female employee in IT department is 5:6.
Number of male employees in IT department is 176 × 5 / 11 = 80
Number of female employees in IT department is 176 – 80 = 96
Number of junior employees in IT department is 176 × 3 / 8 = 66
Number of senior employees in IT department is 176 – 66 = 110
Similarly, we can calculate others values also which is given in the table.
| Department | Number of male employees | Number of female employees | Number of Junior employees | Number of Senior employees |
| IT | 80 | 96 | 66 | 110 |
| Accounts | 128 | 96 | 96 | 128 |
| Marketing | 160 | 96 | 64 | 192 |
| HR | 80 | 64 | 64 | 80 |
Calculation
Total number of married employees in HR department is
= [ 80 × 60/100 ] + [ 64 × 50 /100 ] = 48 + 32 = 80
Number of unmarried employees in HR department is = 144 – 80 = 64
63. In a mixture of juice and water, juice is 20% more than water. This is mixed with another mixture having juice and water in ratio 5:6. If these two are mixed in ratio 3:4. Find ratio of juice and water in final mixture.
A. 25:27
B. 37:40
C. 38:39
D. 35:39
E. 30:37
Solution
In mixture I juice : water = 120/100 × 100 : 100 = 6:5
Mixture are mixed in ratio 3:4
In final mixture,
juice/water = (6 × 3) + (5 × 4)/ (5 × 3) + (6 × 4) = 38 : 39
Hence, correct answer is option 3.
Alternate Method
In mixture I juice : water = 120/100 × 100 : 100
⇒ juice : water = 6:5
| Juice | Water | Total | |
| Mixture I | 6 | 5 | 11 unit |
| Mixture II | 5 | 6 | 11 unit |
As, the quantity of the mixture is equal.
So, multiply the Mixture I by 3 and Mixture II by 4 we get
| Juice | Water | |
| Mixture I | 18 | 15 |
| Mixture II | 20 | 24 |
| Mixture I & II | 38 | 39 |
Ratio of Juice and Water in final mixture is,
⇒ Juice : Water = 38 : 39
∴ The ratio of juice and water in the final mixture is 38 : 39.
64. A man travels one-sixth of the total distance at 4 km/h, one-fourth at 6 km/h, one-third at 8 km/h, and covers the remaining 10 km at 10 km/h by car. What is the total distance?
A. 30 km
B. 40 km
C. 50 km
D. 60 km
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
1/6 distance at 4 km/h
1/4 distance at 6 km/h
1/3 distance at 8 km/h
Remaining 10 km at 10 km/h
Formula used:
Total time = time for each segment
Time = Distance ÷ Speed
Calculations:
Let total distance = x km
⇒ Distance at 4 km/h = x/6 ⇒ Time = (x/6) ÷ 4 = x/24
⇒ Distance at 6 km/h = x/4 ⇒ Time = (x/4) ÷ 6 = x/24
⇒ Distance at 8 km/h = x/3 ⇒ Time = (x/3) ÷ 8 = x/24
Total of above distances = x/6 + x/4 + x/3
LCM of 6, 4, 3 = 12
⇒ x/6 + x/4 + x/3 = (2x + 3x + 4x)/12 = 9x/12 = 3x/4
Remaining distance = x – 3x/4 = x/4 = 10 km
⇒ x/4 = 10 ⇒ x = 40
∴ Total distance = 40 km
65. A 33.33% of the perimeter of the semicircle is x cm and its radius is (x – 10) cm. If the radius of the semicircle is 5 cm less than the side of the square. Find the difference between the perimeter of a semicircle and the perimeter of a square.
(Use π = 3)
A. 40 cm
B. 5 cm
C. 60 cm
D. 45 cm
E. 55 cm
Solution
Solution:
Perimeter of the semicircle = (πr + 2r)
33.33% of the perimeter of the semicircle is x cm
Perimeter of the semicircle = π x = 3 × x = 3x
Radius of semicircle = (x – 10) cm
3 × (x – 10) + 2 × (x – 10) = 3 × x
3x – 30 + 2x – 20 = 3x
2x = 50
x = 25 cm
radius = 25 – 10 = 15 cm
Side of the square = (15 + 5) = 20 cm
Perimeter of the square = 4 × 20 = 80 cm
Perimeter of semicircle = 3 × 25 = 75 cm
Required difference = (80 – 75) = 5 cm
Hence, option(2) is correct.
66. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Ten boxes which contain different fruits which are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple which are stacked one above the other on a single stack but not necessarily in same order. The bottom – most position is shelf 1, the shelf just above it is shelf 2, and so on up to shelf 10 at the top. Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango. The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position. The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava. Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango. The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. Kiwi is not there on shelf 3.
Question:
Which box is placed at top most position?
A. Pineapple
B. Banana
C. Guava
D. Mango
E. Blueberry
Solution
Here, given fruits are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple.
1) Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango.
2) Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position.
| S. No. | Case – 1 | Case – 2 | Case – 3 | Case – 4 | Case – 5 | Case – 6 |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | ||||||
| 9 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 8 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 7 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 6 | ||||||
| 5 | ||||||
| 4 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 3 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 2 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 1 |
3) Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango.
4) The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. So, case 4 is eliminated.
5) The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. So, case 1 is eliminated.
6) The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. So, case 5 and case 6 are eliminated.
| S. No. | Case – 2 | Case – 3(a) | Case – 3(b) |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | Banana | Banana | |
| 9 | Pineapple | Banana | Pineapple |
| 8 | Avocado | Pineapple | |
| 7 | Avocado | Avocado | |
| 6 | Orange | Orange | |
| 5 | Mango | Orange | Mango |
| 4 | Kiwi | Mango | |
| 3 | |||
| 2 | Kiwi | Kiwi | |
| 1 |
7) The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava.
8) There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. So, case 2 and 3(a) are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| S. No. | Boxes |
| 10 | Banana |
| 9 | Pineapple |
| 8 | Guava |
| 7 | Avocado |
| 6 | Orange |
| 5 | Mango |
| 4 | Blueberry |
| 3 | Grapes |
| 2 | Kiwi |
| 1 | Apple |
Hence, the box of Banana placed at top most position.
67. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Ten boxes which contain different fruits which are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple which are stacked one above the other on a single stack but not necessarily in same order. The bottom – most position is shelf 1, the shelf just above it is shelf 2, and so on up to shelf 10 at the top. Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango. The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position. The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava. Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango. The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. Kiwi is not there on shelf 3.
Question:
As many box placed above the box of Guava as many box placed below the box of _?
A. Orange
B. Mango
C. Grapes
D. Kiwi
E. Avocado
Solution
Here, given fruits are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple.
1) Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango.
2) Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position.
| S. No. | Case – 1 | Case – 2 | Case – 3 | Case – 4 | Case – 5 | Case – 6 |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | ||||||
| 9 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 8 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 7 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 6 | ||||||
| 5 | ||||||
| 4 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 3 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 2 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 1 |
3) Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango.
4) The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. So, case 4 is eliminated.
5) The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. So, case 1 is eliminated.
6) The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. So, case 5 and case 6 are eliminated.
| S. No. | Case – 2 | Case – 3(a) | Case – 3(b) |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | Banana | Banana | |
| 9 | Pineapple | Banana | Pineapple |
| 8 | Avocado | Pineapple | |
| 7 | Avocado | Avocado | |
| 6 | Orange | Orange | |
| 5 | Mango | Orange | Mango |
| 4 | Kiwi | Mango | |
| 3 | |||
| 2 | Kiwi | Kiwi | |
| 1 |
7) The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava.
8) There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. So, case 2 and 3(a) are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| S. No. | Boxes |
| 10 | Banana |
| 9 | Pineapple |
| 8 | Guava |
| 7 | Avocado |
| 6 | Orange |
| 5 | Mango |
| 4 | Blueberry |
| 3 | Grapes |
| 2 | Kiwi |
| 1 | Apple |
Since, two boxes placed above the box of Guava and same number of box placed below the box of Grapes.
Hence, the correct answer is box of Grapes.
68. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Ten boxes which contain different fruits which are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple which are stacked one above the other on a single stack but not necessarily in same order. The bottom – most position is shelf 1, the shelf just above it is shelf 2, and so on up to shelf 10 at the top. Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango. The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position. The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava. Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango. The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. Kiwi is not there on shelf 3.
Question:
Which of the following statement is/ are incorrect?
A. Only one box placed above the box of Pineapple.
B. Box of Avocado placed below the box of Guava.
C. The box of Kiwi placed just above the box of Apple.
D. The box of Mango placed below the box of Blueberry.
E. All are correct.
Solution
Here, given fruits are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple.
1) Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango.
2) Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position.
| S. No. | Case – 1 | Case – 2 | Case – 3 | Case – 4 | Case – 5 | Case – 6 |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | ||||||
| 9 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 8 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 7 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 6 | ||||||
| 5 | ||||||
| 4 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 3 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 2 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 1 |
3) Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango.
4) The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. So, case 4 is eliminated.
5) The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. So, case 1 is eliminated.
6) The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. So, case 5 and case 6 are eliminated.
| S. No. | Case – 2 | Case – 3(a) | Case – 3(b) |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | Banana | Banana | |
| 9 | Pineapple | Banana | Pineapple |
| 8 | Avocado | Pineapple | |
| 7 | Avocado | Avocado | |
| 6 | Orange | Orange | |
| 5 | Mango | Orange | Mango |
| 4 | Kiwi | Mango | |
| 3 | |||
| 2 | Kiwi | Kiwi | |
| 1 |
7) The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava.
8) There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. So, case 2 and 3(a) are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| S. No. | Boxes |
| 10 | Banana |
| 9 | Pineapple |
| 8 | Guava |
| 7 | Avocado |
| 6 | Orange |
| 5 | Mango |
| 4 | Blueberry |
| 3 | Grapes |
| 2 | Kiwi |
| 1 | Apple |
Since, the box of Mango placed above the box of Blueberry.
Hence, the incorrect statement is the box of Mango placed below the box of Blueberry.
69. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Ten boxes which contain different fruits which are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple which are stacked one above the other on a single stack but not necessarily in same order. The bottom – most position is shelf 1, the shelf just above it is shelf 2, and so on up to shelf 10 at the top. Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango. The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position. The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava. Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango. The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. Kiwi is not there on shelf 3.
Question:
Which box placed just below the box which is placed two boxes above the box of Orange?
A. Pineapple
B. Guava
C. Blueberry
D. Avocado
E. Apple
Solution
Here, given fruits are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple.
1) Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango.
2) Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position.
| S. No. | Case – 1 | Case – 2 | Case – 3 | Case – 4 | Case – 5 | Case – 6 |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | ||||||
| 9 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 8 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 7 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 6 | ||||||
| 5 | ||||||
| 4 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 3 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 2 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 1 |
3) Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango.
4) The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. So, case 4 is eliminated.
5) The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. So, case 1 is eliminated.
6) The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. So, case 5 and case 6 are eliminated.
| S. No. | Case – 2 | Case – 3(a) | Case – 3(b) |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | Banana | Banana | |
| 9 | Pineapple | Banana | Pineapple |
| 8 | Avocado | Pineapple | |
| 7 | Avocado | Avocado | |
| 6 | Orange | Orange | |
| 5 | Mango | Orange | Mango |
| 4 | Kiwi | Mango | |
| 3 | |||
| 2 | Kiwi | Kiwi | |
| 1 |
7) The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava.
8) There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. So, case 2 and 3(a) are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| S. No. | Boxes |
| 10 | Banana |
| 9 | Pineapple |
| 8 | Guava |
| 7 | Avocado |
| 6 | Orange |
| 5 | Mango |
| 4 | Blueberry |
| 3 | Grapes |
| 2 | Kiwi |
| 1 | Apple |
Since, the box of Guava placed two boxes above the box of Orange and just below it box of Avocado placed.
Hence, the correct answer is box of Avocado.
70. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Ten boxes which contain different fruits which are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple which are stacked one above the other on a single stack but not necessarily in same order. The bottom – most position is shelf 1, the shelf just above it is shelf 2, and so on up to shelf 10 at the top. Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango. The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position. The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava. Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango. The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. Kiwi is not there on shelf 3.
Question:
Which of the following statement is/ are correct?
A) Only two boxes are placed between the box of Banana and the box of Orange.
B) The box of Grapes placed at third position from top.
C) The box of Apple placed at bottom position.
A. Only A
B. Both A and C
C. Only B
D. All of the above
E. Only C
Solution
Here, given fruits are Apple, Banana, Avocado, Blueberry, Grapes, Guava, Kiwi, Mango, Orange and Pineapple.
1) Only four boxes are placed between the box of Avocado and the box of Kiwi, which is placed below the box of Mango.
2) Neither the box of Avocado nor the box of Kiwi placed at top or bottom position.
| S. No. | Case – 1 | Case – 2 | Case – 3 | Case – 4 | Case – 5 | Case – 6 |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | ||||||
| 9 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 8 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 7 | Avocado | Kiwi | ||||
| 6 | ||||||
| 5 | ||||||
| 4 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 3 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 2 | Kiwi | Avocado | ||||
| 1 |
3) Only three boxes are placed between the box of Pineapple and the box of Mango.
4) The box of Orange is placed immediately above the box of Mango. So, case 4 is eliminated.
5) The box of Pineapple placed immediately below the box of Banana. So, case 1 is eliminated.
6) The box of Banana placed above the box of Orange. So, case 5 and case 6 are eliminated.
| S. No. | Case – 2 | Case – 3(a) | Case – 3(b) |
| Boxes | Boxes | Boxes | |
| 10 | Banana | Banana | |
| 9 | Pineapple | Banana | Pineapple |
| 8 | Avocado | Pineapple | |
| 7 | Avocado | Avocado | |
| 6 | Orange | Orange | |
| 5 | Mango | Orange | Mango |
| 4 | Kiwi | Mango | |
| 3 | |||
| 2 | Kiwi | Kiwi | |
| 1 |
7) The box of Apple placed one of the boxes below Grapes which is placed below the box of Guava.
8) There are only two boxes present between box of Blueberry and box of Apple. So, case 2 and 3(a) are eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
| S. No. | Boxes |
| 10 | Banana |
| 9 | Pineapple |
| 8 | Guava |
| 7 | Avocado |
| 6 | Orange |
| 5 | Mango |
| 4 | Blueberry |
| 3 | Grapes |
| 2 | Kiwi |
| 1 | Apple |
Since, three boxes are placed between the box of Banana and box of Orange. Therefore, statement A is incorrect.
The box of Grapes placed at third position from bottom not from top. Therefore, statement B is also incorrect.
The box of Apple placed at bottom most position. Therefore, statement C is correct.
Hence, the correct answer is only C.
71. How many such pairs of letters are in the word ‘GOVERNMENT’ each of which has as many letters between them in the word (both forward and backward direction) as they have between them in the English Alphabet?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
E. Five
Solution

Hence, four pairs are there in the word ‘GOVERNMENT’, each of which has as many letters between them in the word (both forward and backward direction) as they have between them in the English Alphabet.
72. Directions: Read the following comprehension carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N are sitting around a circular table facing inside. Some of them are Male and some of them are Female. B is sitting third to the right of K. L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. A is an immediate neighbor of K. Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members. Four members are sitting between M and K. E is second to the left of A. Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M. Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members. Not more than four females are there. D is a female member and sitting immediately next to the J. Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member. B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Question:
Who is sitting third to the right of M?
A. E
B. K
C. D
D. L
E. J
Solution
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N.
Some Male some Female.
Facing Inside.
1- B is sitting third to the right of K.
2- A is an immediate neighbor of K.
3- E is second to the left of A.
4- Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members.
Case-1
Case-2
5- Four members are sitting between M and K.
6- Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M.
7- B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Case-1
Case-2
8- L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. So, case-1 gets eliminated.
9- Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members.
10- D is a female member and sits immediately next to J.
11- Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member.
12- Not more than four females are there. So six male members are there.
So, Final arrangement is;
L is sitting third to the right of M.
73. Directions: Read the following comprehension carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N are sitting around a circular table facing inside. Some of them are Male and some of them are Female. B is sitting third to the right of K. L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. A is an immediate neighbor of K. Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members. Four members are sitting between M and K. E is second to the left of A. Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M. Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members. Not more than four females are there. D is a female member and sitting immediately next to the J. Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member. B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Question:
How many male members are there in the group?
A. Seven
B. Five
C. Two
D. Four
E. Six
Solution
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N.
Some Male some Female.
Facing Inside.
1- B is sitting third to the right of K.
2- A is an immediate neighbor of K.
3- E is second to the left of A.
4- Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members.
Case-1
Case-2
5- Four members are sitting between M and K.
6- Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M.
7- B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Case-1
Case-2
8- L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. So, case-1 gets eliminated.
9- Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members.
10- D is a female member and sits immediately next to J.
11- Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member.
12- Not more than four females are there. So six male members are there.
So, Final arrangement is;
Six male members are there in the group.
74. Directions: Read the following comprehension carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N are sitting around a circular table facing inside. Some of them are Male and some of them are Female. B is sitting third to the right of K. L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. A is an immediate neighbor of K. Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members. Four members are sitting between M and K. E is second to the left of A. Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M. Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members. Not more than four females are there. D is a female member and sitting immediately next to the J. Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member. B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Question:
Which of the following sentence is correct about D?
i) D is a Male member of the family.
ii) D is sitting second to the right of A.
iii) D is sitting just between A and J.
A. Only i
B. Only i and ii
C. Only ii
D. All i, ii, iii
E. None of these
Solution
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N.
Some Male some Female.
Facing Inside.
1- B is sitting third to the right of K.
2- A is an immediate neighbor of K.
3- E is second to the left of A.
4- Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members.
Case-1
Case-2
5- Four members are sitting between M and K.
6- Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M.
7- B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Case-1
Case-2
8- L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. So, case-1 gets eliminated.
9- Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members.
10- D is a female member and sits immediately next to J.
11- Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member.
12- Not more than four females are there. So six male members are there.
So, Final arrangement is;
Hence, only ii is correct.
75. Directions: Read the following comprehension carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N are sitting around a circular table facing inside. Some of them are Male and some of them are Female. B is sitting third to the right of K. L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. A is an immediate neighbor of K. Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members. Four members are sitting between M and K. E is second to the left of A. Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M. Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members. Not more than four females are there. D is a female member and sitting immediately next to the J. Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member. B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Question:
How many people are sitting between E and D from counting right of D?
A. Four
B. Three
C. Five
D. Two
E. None
Solution
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N.
Some Male some Female.
Facing Inside.
1- B is sitting third to the right of K.
2- A is an immediate neighbor of K.
3- E is second to the left of A.
4- Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members.
Case-1
Case-2
5- Four members are sitting between M and K.
6- Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M.
7- B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Case-1
Case-2
8- L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. So, case-1 gets eliminated.
9- Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members.
10- D is a female member and sits immediately next to J.
11- Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member.
12- Not more than four females are there. So six male members are there.
So, Final arrangement is;
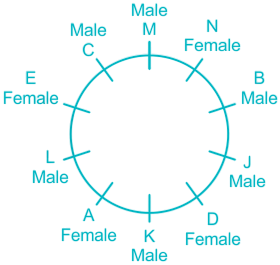
Hence, Five people are sitting between E and D from counting right of D.
76. Directions: Read the following comprehension carefully and answer the questions given below.
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N are sitting around a circular table facing inside. Some of them are Male and some of them are Female. B is sitting third to the right of K. L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. A is an immediate neighbor of K. Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members. Four members are sitting between M and K. E is second to the left of A. Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M. Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members. Not more than four females are there. D is a female member and sitting immediately next to the J. Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member. B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Question:
What is the position of K with respect to N?
A. Third to the right
B. Immediate to the left
C. Fourth to the right
D. Fifth to the left
E. Fourth to the left
Solution
Ten people A, B, C, D, E, J, K, L, M and N.
Some Male some Female.
Facing Inside.
1- B is sitting third to the right of K.
2- A is an immediate neighbor of K.
3- E is second to the left of A.
4- Both the immediate neighbours of E are Male members.
Case-1
Case-2
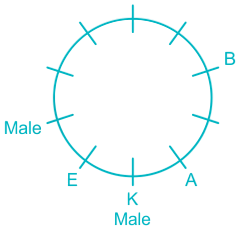
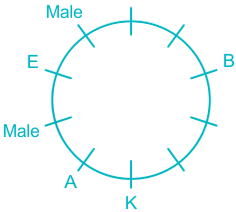
5- Four members are sitting between M and K.
6- Two people are sitting between E and N, who is an immediate neighbour of M.
7- B is sitting immediately right to the J.
Case-1
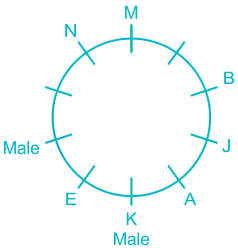
Case-2
8- L who is a male member sitting fourth to the right of N. So, case-1 gets eliminated.
9- Both the immediate neighbours of L are female members.
10- D is a female member and sits immediately next to J.
11- Person who is sitting in front of A is a female member.
12- Not more than four females are there. So six male members are there.
So, Final arrangement is;
Hence, K is fourth to the left of N.
77. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions numbered I, II, and III. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Only a few women are IAS.
Some women are IPS.
No IPS is Minister.
Conclusions:
I. few IAS is IPS.
II. No IAS is IPS.III. all ministers are women.
A. Only conclusion I follow
B. Only conclusion II follow
C. Conclusion I and III follow
D. Either I or III follow
E. Either I or II follow
Solution
The least possible diagram for the given statements is as follows,

Conclusions:
I. Few IAS is IPS. → False (It is possible but not definite)
II. No IAS is IPS. → False (It is possible but not definite)
III. all ministers are women. → False (It is definitely false)
Conclusions I and II are complementary pair
.Hence, either conclusion I or II follows.
78. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions numbered I, II, and III. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
All heart is stupid.
Only a few heart is strong.
Some fools are strong.
Conclusions:
I. All Strong is stupid.
II. Few fools are stupid.III. All fools are stupid.
A. Only conclusion I follow
B. Only conclusion II follow
C. Conclusion I and III follow
D. All conclusion follows
E. None conclusion follows
Solution
The least possible diagram for the given statements is as follows,

Conclusions:
I. All Strong is stupid. → False (it is possible but not definite)
II. Few fools are stupid. → False (it is possible but not definite)
III. All fools are stupid. → False (it is possible but not definite)
Hence, None conclusion follows ion follows
79. Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir have their birthdays on two different dates either 12th or 17th of four different months of the same year – September, October, November and December. They all like different types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers. All the information given is not necessarily in the same order.
Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days. Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar. Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh. Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month. The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month. The person who likes 5 Star is five places junior to the one who likes Milkeybar. The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbour of each other. Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days. More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury. Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday. Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days. Vansh likes Bourneville.
Question:
Who among the following likes Bournville?
A. Kabir
B. Angre
C. Vansh
D. Ishani
E. Aaryan
Solution
Given:
Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir
Two dates – either 12th or 17th
Four months – September, October, November and December the same year.
Types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers.
Now,
1) Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days.
2) Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar.
3) Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | ||
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 |
4) Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month.
5) The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month.
6) The person who likes 5 Star is five months junior to the one who likes Milkeybar.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani | |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | Sia/ Ishani |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
7) The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbours of each other.
8) Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days.
9) More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers/ cadbury) | Riddhima (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (Snickers/ cadbury) | Sia/ Ishani (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
10) Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday.
11) Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days.
The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th, also it it mentioned that Kabir dose not likes bournville
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers) | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (cadbury) | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Kabir (5 Star) | Ishani (5 Star) |
Sia and Ishani cannot be there in the month having even number of days. Thus, CASE 1 gets eliminated and we have the final arrangement in CASE 2.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Ishani (5 Star) |
Hence, the correct answer is “Vansh”.
80. Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir have their birthdays on two different dates either 12th or 17th of four different months of the same year – September, October, November and December. They all like different types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers. All the information given is not necessarily in the same order.
Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days. Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar. Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh. Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month. The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month. The person who likes 5 Star is five places junior to the one who likes Milkeybar. The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbour of each other. Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days. More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury. Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday. Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days. Vansh likes Bourneville.
Question:
Who among the following celebrates his/her birthday on 12th December?
A. Ishani
B. Sia
C. Vyom
D. Aaryan
E. Riddhima
Solution
Given:
Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir
Two dates – either 12th or 17th
Four months – September, October, November and December the same year.
Types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers.
Now,
1) Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days.
2) Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar.
3) Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | ||
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 |
4) Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month.
5) The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month.
6) The person who likes 5 Star is five months junior to the one who likes Milkeybar.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani | |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | Sia/ Ishani |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
7) The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbours of each other.
8) Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days.
9) More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers/ cadbury) | Riddhima (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (Snickers/ cadbury) | Sia/ Ishani (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
10) Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday.
11) Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days.
The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th, also it it mentioned that Kabir dose not likes bournville
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers) | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (cadbury) | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Kabir (5 Star) | Ishani (5 Star) |
Sia and Ishani cannot be there in the month having even number of days. Thus, CASE 1 gets eliminated and we have the final arrangement in CASE 2.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Ishani (5 Star) |
Hence, the correct answer is “Sia”.
81. Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir have their birthdays on two different dates either 12th or 17th of four different months of the same year – September, October, November and December. They all like different types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers. All the information given is not necessarily in the same order.
Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days. Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar. Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh. Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month. The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month. The person who likes 5 Star is five places junior to the one who likes Milkeybar. The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbour of each other. Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days. More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury. Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday. Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days. Vansh likes Bourneville.
Question:
How many persons celebrates their birthdays between the one who likes Snickers and Cadbury?
A. Four
B. Five
C. Six
D. Three
E. Two
Solution
Given:
Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir
Two dates – either 12th or 17th
Four months – September, October, November and December the same year.
Types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers.
Now,
1) Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days.
2) Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar.
3) Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | ||
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 |
4) Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month.
5) The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month.
6) The person who likes 5 Star is five months junior to the one who likes Milkeybar.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani | |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | Sia/ Ishani |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
7) The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbours of each other.
8) Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days.
9) More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers/ cadbury) | Riddhima (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (Snickers/ cadbury) | Sia/ Ishani (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
10) Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday.
11) Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days.
The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th, also it it mentioned that Kabir dose not likes bournville
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers) | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (cadbury) | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Kabir (5 Star) | Ishani (5 Star) |
Sia and Ishani cannot be there in the month having even number of days. Thus, CASE 1 gets eliminated and we have the final arrangement in CASE 2.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Ishani (5 Star) |
Hence, the correct answer is “Five”.
82. Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir have their birthdays on two different dates either 12th or 17th of four different months of the same year – September, October, November and December. They all like different types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers. All the information given is not necessarily in the same order.
Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days. Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar. Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh. Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month. The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month. The person who likes 5 Star is five places junior to the one who likes Milkeybar. The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbour of each other. Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days. More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury. Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday. Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days. Vansh likes Bourneville.
Question:
Which among the following pair of persons are different from others in a certain way?
A. Aaryan, Angre
B. Vyom, Vansh
C. Sia, Ishani
D. Riddhima, Vansh
E. Riddhima, Kabir
Solution
Given:
Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir
Two dates – either 12th or 17th
Four months – September, October, November and December the same year.
Types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers.
Now,
1) Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days.
2) Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar.
3) Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | ||
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 |
4) Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month.
5) The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month.
6) The person who likes 5 Star is five months junior to the one who likes Milkeybar.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani | |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | Sia/ Ishani |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
7) The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbours of each other.
8) Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days.
9) More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers/ cadbury) | Riddhima (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (Snickers/ cadbury) | Sia/ Ishani (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
10) Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday.
11) Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days.
The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th, also it it mentioned that Kabir dose not likes bournville
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers) | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (cadbury) | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Kabir (5 Star) | Ishani (5 Star) |
Sia and Ishani cannot be there in the month having even number of days. Thus, CASE 1 gets eliminated and we have the final arrangement in CASE 2.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Ishani (5 Star) |
Hence, the correct answer is “Riddhima, Vansh”.
83. Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir have their birthdays on two different dates either 12th or 17th of four different months of the same year – September, October, November and December. They all like different types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers. All the information given is not necessarily in the same order.
Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days. Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar. Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh. Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month. The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month. The person who likes 5 Star is five places junior to the one who likes Milkeybar. The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbour of each other. Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days. More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury. Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday. Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days. Vansh likes Bourneville.
Question:
Who among the following celebrates his birthday exactly in between the person who likes 5 star and the one who celebrates his birthday on 17 September?
A. 12 November
B. Kabir
C. The person who likes Perk
D. Bournville
E. Both option 1 and 3
Solution
Given:
Eight persons – Vansh, Riddhima, Aaryan, Ishani, Sia, Vyom, Angre and Kabir
Two dates – either 12th or 17th
Four months – September, October, November and December the same year.
Types of chocolates – Cadbury, KitKat, Munch, Milkeybar, Perk, Bournville, 5 Star, and Snickers.
Now,
1) Vansh who celebrates his birthday on an odd numbered date was not born in any of the month which has 31 days.
2) Aaryan celebrates his birthday on 12th of October and likes Milkeybar.
3) Four person celebrates their birthdays between Riddhima and Vansh.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | ||
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 |
4) Neither Ishani nor Sia likes Cadbury, but both celebrates their birthdays in the same month.
5) The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th of any month.
6) The person who likes 5 Star is five months junior to the one who likes Milkeybar.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima | |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | |||
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani | |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima | Sia/ Ishani |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
7) The person who likes perk and Angre are immediate neighbours of each other.
8) Vyom dose not like KitKat, but celebrates his birthday in a month which has even number of days.
9) More than four persons celebrates their birthday between the one who likes Snickers and the one who likes Cadbury.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers/ cadbury) | Riddhima (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | ||
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (Snickers/ cadbury) | Sia/ Ishani (Snickers/ Cadbury) |
| 17 | (5 Star) | Ishani/ Sia (5 Star) |
10) Riddhima dose not likes Snickers but is immediately elder to Kabir, who dose not likes Bournville. Sia is not the last person to celebrate her birthday.
11) Angre dose not like Munch. Ishani dose not celebrates her birthday in a month having even number of days.
The person who likes Bournville dose not celebrates his birthday on 12th, also it it mentioned that Kabir dose not likes bournville
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 1 | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Vyom (Snickers) | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Vansh | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Sia/ Ishani (Perk) | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Ishani/ Sia | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Riddhima (cadbury) | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Kabir (5 Star) | Ishani (5 Star) |
Sia and Ishani cannot be there in the month having even number of days. Thus, CASE 1 gets eliminated and we have the final arrangement in CASE 2.
| MONTH | DATE | CASE 2 |
| September (30) | 12 | Riddhima (Cadbury) |
| 17 | Kabir (Munch) | |
| October (31) | 12 | Aaryan (Milkeybar) |
| 17 | Angre (KitKat) | |
| November (30) | 12 | Vyom (Perk) |
| 17 | Vansh (Bournville) | |
| December (31) | 12 | Sia (Snickers) |
| 17 | Ishani (5 Star) |
Hence, the correct answer is “both option 1 and 3”.
84. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.A certain number of persons are sitting in a linear row facing the north. E sits second from the right end of the row. Only two persons sit between I and R. The number of persons sitting between G and E is five. X sits third to the right of G. No person sits to the left of F. C sits to the immediate left of G. R sits fifth to the left of C. I sits second to the right of F. U sits third to the right of R.
Question:
What is the position of C with respect to I?
A. Fifth to the left
B. Seventh to the right
C. Ninth to the left
D. Eighth to the right
E. Eighth to the left
Solution
Given: A certain number of persons are sitting in a row facing the north.
Based on the given conditions, we get-
1. E sits second from the right end of the row. The number of persons sitting between G and E is 5. X sits third to the right of G. From these, we get-
2. C sits to the immediate left of G. R sits fifth to the left of C. From these, we get-
3. U sits third to the right of R. From this, we get-
4. No person sits to the left of F. I sits second to the right of F. Only two persons sit between I and R. From these, we get the final arrangement as follows:
From the above final arrangement, we see that C sits eighth to the right of I.
Hence, C sits eight to the right of I.
85. Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the following questions.
A Certain number of persons is sitting in a row facing north. Two persons are sitting between S and O. Three persons are sitting between O and R. P is sitting left of R. There are as many persons in between M and N as in between Q and N. Q is sitting second from one of the extreme end. S is sitting at one of the extreme end. M is third to the left of P. One person is sitting between R and P. M is not an immediate neighbor of O and R. T is the immediate right of O. The number of persons sitting between P and O is one more than the number of persons sitting between N and P.
Question:
What is the position of M with respect to Q?
A. Second to the right
B. Immediate right
C. Fourth to the right
D. Fourth to the left
E. Immediate left
Solution
All the persons are facing north.
Information about the number of persons is not given.
1) S is sitting at one of the extreme ends. Two persons are sitting between S and O. Three persons are between O and R.

2) One person is sitting between R and P. P is sitting left of R. T is immediate right of O. M is third to the left of P.



3) M is not an immediate neighbour of O and R.
M is sitting immediate right of O. So, Case 2 is eliminated.
4) The number of persons sitting between P and O is one more than the number of persons sitting between N and P.
Five persons are sitting between P and O. So, according to the condition given four persons would be sitting between N and P.
5) There are as many persons between M and N as between Q and N.
If we place N to the right of P. Then we cannot place Q in this arrangement according to the given condition. So, we will place N towards the left of P.
The final arrangement is:
Hence, M is sitting fourth to the right of Q.
86. Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the following questions.
A Certain number of persons is sitting in a row facing north. Two persons are sitting between S and O. Three persons are sitting between O and R. P is sitting left of R. There are as many persons in between M and N as in between Q and N. Q is sitting second from one of the extreme end. S is sitting at one of the extreme end. M is third to the left of P. One person is sitting between R and P. M is not an immediate neighbor of O and R. T is the immediate right of O. The number of persons sitting between P and O is one more than the number of persons sitting between N and P.
Question:
How many persons are sitting between O and M?
A. Eight
B. Four
C. Nine
D. Three
E. Two
Solution
All the persons are facing north.
Information about the number of persons is not given.
1) S is sitting at one of the extreme ends. Two persons are sitting between S and O. Three persons are between O and R.

2) One person is sitting between R and P. P is sitting left of R. T is immediate right of O. M is third to the left of P.



3) M is not an immediate neighbour of O and R.
M is sitting immediate right of O. So, Case 2 is eliminated.
4) The number of persons sitting between P and O is one more than the number of persons sitting between N and P.
Five persons are sitting between P and O. So, according to the condition given four persons would be sitting between N and P.
5) There are as many persons between M and N as between Q and N.
If we place N to the right of P. Then we cannot place Q in this arrangement according to the given condition. So, we will place N towards the left of P.
The final arrangement is:
Hence, Eight persons are sitting between O and M.
87. Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answe the following questions that follow.
Ayushi start walking from her college in the south direction and walks for 10 km, from there she takes a left turn to reach parlour which is 6 km. From parlour she takes a left turn and a right turn to reach mall after walking for 3 km and 5 km respectively. Another person Ritika start walking in the east direction and walks for 8 km, then she takes a right turn and walks for 8 km and then she again takes a right turn and walks for 3 km to reach cafe. From cafe she takes a final left turn and walks for 4 km and reaches mall to meet Ayushi.
Question:
What is the distance between Ayushi’s college and Ritika’s initial position?
A. √61√61 km
B. 161 km
C. 61 km
D. 9 km
E. None of these
Solution
1. Ayushi start walking from her college in the south direction and walks for 10 km, from there she takes a left turn to reach parlor which is 6 km, by combining these two sentences we get,
2. From parlor she takes a left turn and a right turn to reach mall after walking for 3 km and 5 km respectively, which means from parlor first she turns to left and walks for 3 km and then she takes a right turn and walks for 5 km to reach mall.
3. Ritika start walking in the east direction and walks for 8 km, then she takes a right turn and walks for 8 km and then she again takes a right turn and walks for 3 km to reach cafe by combining these three sentences we get,
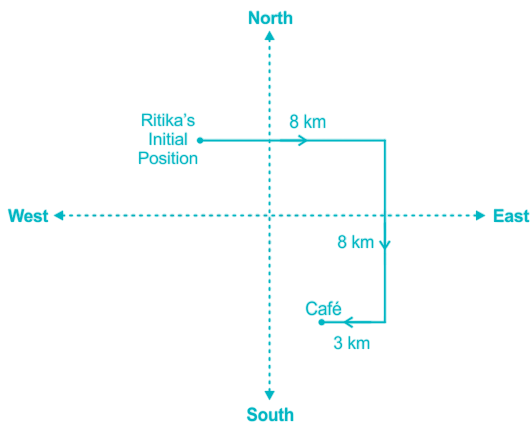
4. From cafe she takes a final left turn and walks for 4 km and reaches mall.
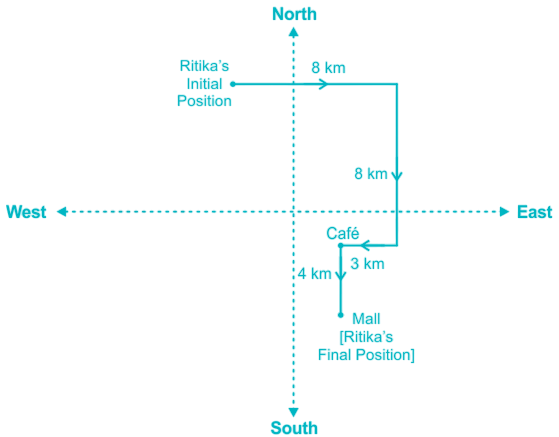
By merging all the diagrams, the final diagram is:
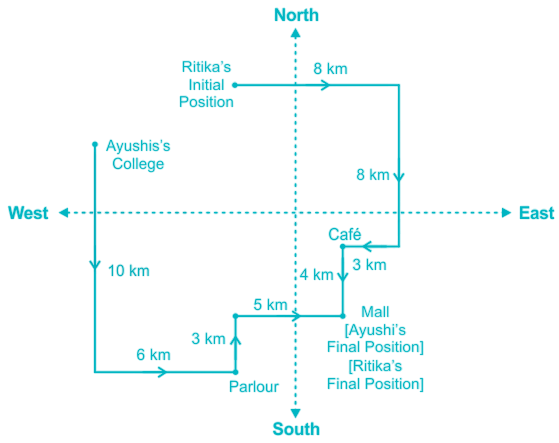
Distance between Ayushi’s college and Ritika’s iniitial position:
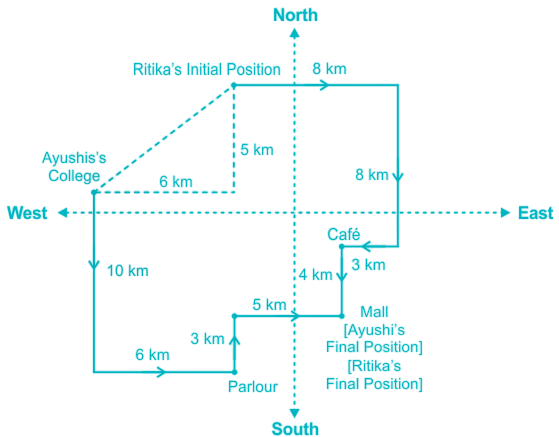
By using Pythagoras theorem:
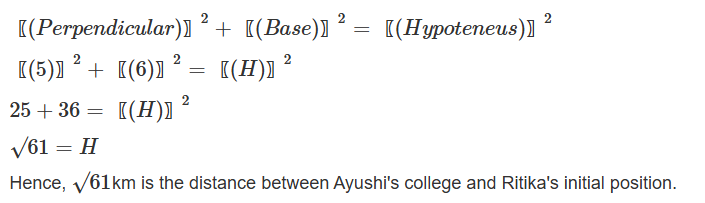
88. Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answe the following questions that follow.
Ayushi start walking from her college in the south direction and walks for 10 km, from there she takes a left turn to reach parlour which is 6 km. From parlour she takes a left turn and a right turn to reach mall after walking for 3 km and 5 km respectively. Another person Ritika start walking in the east direction and walks for 8 km, then she takes a right turn and walks for 8 km and then she again takes a right turn and walks for 3 km to reach cafe. From cafe she takes a final left turn and walks for 4 km and reaches mall to meet Ayushi.
Question:
In which direction is Ritika’s inital position with respect to mall?
A. South West
B. South East
C. North West
D. North East
E. South
Solution
1. Ayushi start walking from her college in the south direction and walks for 10 km, from there she takes a left turn to reach parlor which is 6 km, by combining these two sentences we get,
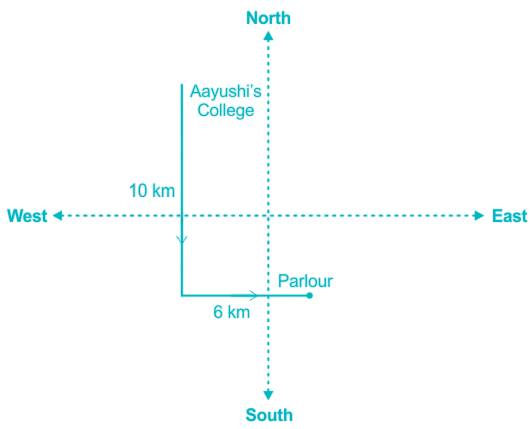
2. From parlor she takes a left turn and a right turn to reach mall after walking for 3 km and 5 km respectively, which means from parlor first she turns to left and walks for 3 km and then she takes a right turn and walks for 5 km to reach mall.
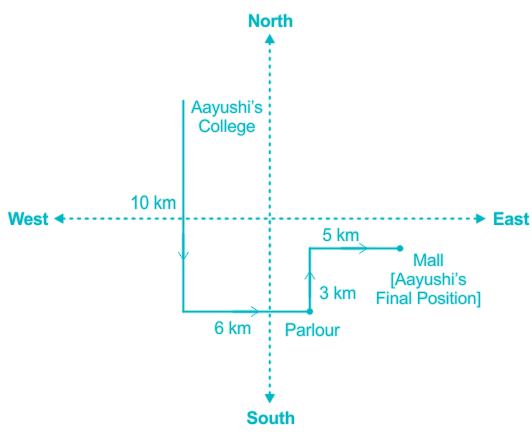
3. Ritika start walking in the east direction and walks for 8 km, then she takes a right turn and walks for 8 km and then she again takes a right turn and walks for 3 km to reach cafe by combining these three sentences we get,
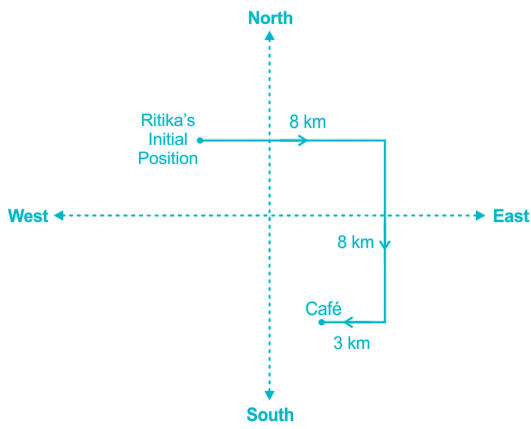
4. From cafe she takes a final left turn and walks for 4 km and reaches mall.
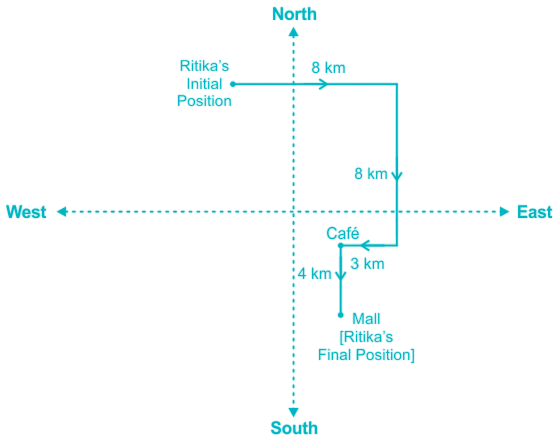
By merging all the diagrams, the final diagram is:
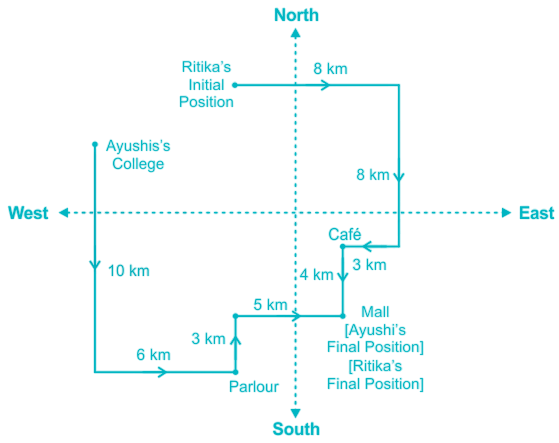
Hence, Ritika’s initial position is in North West direction with respect to mall.
89. Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answe the following questions that follow.
Ayushi start walking from her college in the south direction and walks for 10 km, from there she takes a left turn to reach parlour which is 6 km. From parlour she takes a left turn and a right turn to reach mall after walking for 3 km and 5 km respectively. Another person Ritika start walking in the east direction and walks for 8 km, then she takes a right turn and walks for 8 km and then she again takes a right turn and walks for 3 km to reach cafe. From cafe she takes a final left turn and walks for 4 km and reaches mall to meet Ayushi.
Question:
What is the distance between Parlor and Cafe?
A. 11 km
B. 12 km
C. 6 km
D. 5 km
E. 8 km
Solution
1. Ayushi start walking from her college in the south direction and walks for 10 km, from there she takes a left turn to reach parlor which is 6 km, by combining these two we get,
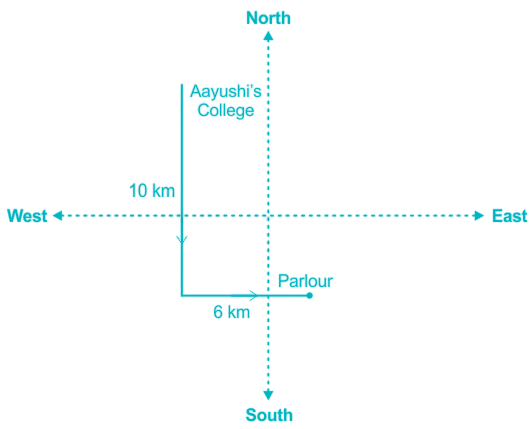
2. From parlor she takes a left turn and a right turn to reach mall after walking for 3 km and 5 km respectively, which means from parlor first she turns to left and walks for 3 km and then she takes a right turn and walks for 5 km to reach mall.
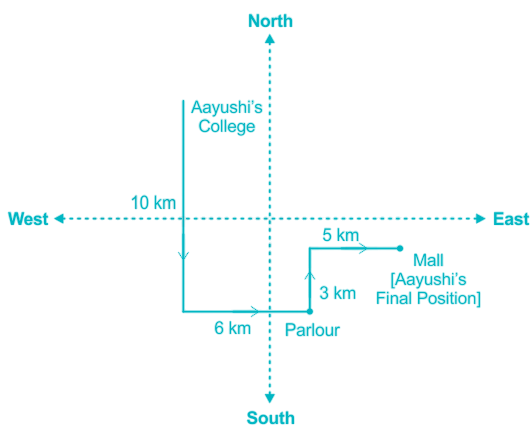
3. Ritika start walking in the east direction and walks for 8 km, then she takes a right turn and walks for 8 km and then she again takes a right turn and walks for 3 km to reach cafe by combining these three sentences we get,
4. From cafe she takes a final left turn and walks for 4 km and reaches mall.
By merging all the diagrams, the final diagram is:
Distance between parlor and cafe:
3km + 5km + 4km = 12km
Hence, 12 km is the distance between parlor and cafe.
90. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement: P < A = T ≥ N; H < Y > D = E ≥ R < A ≥ B; E = L ≥ I
Conclusions:
I. Y > L
II. A ≥ N
III. A = E
A. Only I is True
B. Only II is True
C. All I, II, III are True
D. Both I & II are True
E. I & Either II or III are True
Solution
Given Statement: P < A = T ≥ N; H < Y > D = E ≥ R < A ≥ B; E = L ≥ I
On combining: H < Y > D = E ≥ R < A = T ≥ N; E = L ≥ I; P < A
Conclusion:
I. Y > L → True (as Y > D = E = L → Y > L)
II. A ≥ N → True (as A = T ≥ N → A ≥ N)
III. A = E → False (as E ≥ R < A → thus clear relation between A and E cannot be determined)
Therefore, both conclusions I & II are True.
91. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement: R > A ≤ J = N; S < A = T ≥ Y < M
Conclusions:
I. R > S
II. T = N
III. Y ≤ J
A. Only I is True
B. Only II is True
C. Only III is True
D. Both I & II are True
E. Both I & III are True
Solution
Given Statement: R > A ≤ J = N; S < A = T ≥ Y < M
On combining: M > Y ≤ T = A ≤ J = N; S < A < R
Conclusion:
I. R > S → True (as R > A > S → R > S)
II. T = N → False (as T = A ≤ J = N → T ≤ N)
III. Y ≤ J → True (as Y ≤ T = A ≤ J → Y ≤ J)
Therefore, both conclusions I & III are true.
92. Each of the vowels in the word “STATEMENT” is replaced by number “4” and each consonant is replaced by a number which is the serial number of that consonant in the word i.e., S by 1, T by 2 and so on. What is the total of all the numbers once replacement is completed?
A. 48
B. 42
C. 45
D. 31
E. 39
Solution
Given word: STATEMENT
Condition → Vowel is replaced by number “4” and consonant is replaced by a number which is the serial number of that consonant in the word.
| S | T | A | T | E | M | E | N | T |
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 9 |
Total of all the numbers → 1 + 2 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 6 + 4 + 8 + 9 = 42
Hence, the total of all the numbers are 42.
93. Direction: Study the given information and answer the following questions.
Six persons P, Q, R, S, T and U are living in a three storey building with six flats but not necessarily in the same order. Each floor of the flat have two different flats i.e., flat 1 and flat 2 and floors are numbered such that the lowermost floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above it is numbered as 2 and so on. Flat 1 is to the west of flat 2. All the persons like different games namely- Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling but not necessarily in the same order.
S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
Question:
The person who lives in floor 2 and flat 2 likes which sport?
A. Cricket
B. Football
C. Wrestling
D. Hockey
E. Chess
Solution
Persons: P, Q, R, S, T and U.
Sports: Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling
1. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S.
2. S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat.
| Case 1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | ||||
| Case 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | T | |||
| Case 3 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | T | |||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | ||||
| Case 4 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
3. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat.
4. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. This eliminates case 2 and 3.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey\ | |
| Case 4.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
5. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T.
So, Case 4.2 is invalid.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Cricket | ||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
6. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. This eliminates Case 1.1 and 1.2
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | Cricket | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
7. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
This also implies that T likes Football.
The final arrangement is,
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | Football |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
Hence, T lives in floor 2 flat 2 and he likes Football.
94. Direction: Study the given information and answer the following questions.
Six persons P, Q, R, S, T and U are living in a three storey building with six flats but not necessarily in the same order. Each floor of the flat have two different flats i.e., flat 1 and flat 2 and floors are numbered such that the lowermost floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above it is numbered as 2 and so on. Flat 1 is to the west of flat 2. All the persons like different games namely- Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling but not necessarily in the same order.
S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
Question:
Which person likes Chess?
A. P
B. R
C. S
D. U
E. Q
Solution
Persons: P, Q, R, S, T and U.
Sports: Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling
1. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S.
2. S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat.
| Case 1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | ||||
| Case 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | T | |||
| Case 3 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | T | |||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | ||||
| Case 4 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
3. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat.
4. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. This eliminates case 2 and 3.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey\ | |
| Case 4.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
5. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T.
So, Case 4.2 is invalid.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Cricket | ||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
6. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. This eliminates Case 1.1 and 1.2
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | Cricket | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
7. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
This also implies that T likes Football.
The final arrangement is,
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | Football |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
Hence, U likes Chess.
95. Direction: Study the given information and answer the following questions.
Six persons P, Q, R, S, T and U are living in a three storey building with six flats but not necessarily in the same order. Each floor of the flat have two different flats i.e., flat 1 and flat 2 and floors are numbered such that the lowermost floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above it is numbered as 2 and so on. Flat 1 is to the west of flat 2. All the persons like different games namely- Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling but not necessarily in the same order.
S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
Question:
R lives in ______________
A. Floor 2 Flat 1
B. Flat 2 Floor 2
C. Floor 1 Flat 2
D. Flat 2 Floor 3
E. Flat 1 Floor 1
Solution
Persons: P, Q, R, S, T and U.
Sports: Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling
1. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S.
2. S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat.
| Case 1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | ||||
| Case 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | T | |||
| Case 3 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | T | |||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | ||||
| Case 4 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
3. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat.
4. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. This eliminates case 2 and 3.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey\ | |
| Case 4.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
5. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T.
So, Case 4.2 is invalid.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Cricket | ||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
6. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. This eliminates Case 1.1 and 1.2
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | Cricket | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
7. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
This also implies that T likes Football.
The final arrangement is,
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | Football |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
Hence, R lives in Floor 2 Flat 1.
96. Direction: Study the given information and answer the following questions.
Six persons P, Q, R, S, T and U are living in a three storey building with six flats but not necessarily in the same order. Each floor of the flat have two different flats i.e., flat 1 and flat 2 and floors are numbered such that the lowermost floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above it is numbered as 2 and so on. Flat 1 is to the west of flat 2. All the persons like different games namely- Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling but not necessarily in the same order.
S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
Question:
Find the correct pair.
A. U – Cricket
B. Q – Hockey
C. P – Chess
D. S – Hockey
E. T – Badminton
Solution
Persons: P, Q, R, S, T and U.
Sports: Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling
1. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S.
2. S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat.
| Case 1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | ||||
| Case 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | T | |||
| Case 3 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | T | |||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | ||||
| Case 4 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
3. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat.
4. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. This eliminates case 2 and 3.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey\ | |
| Case 4.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
5. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T.
So, Case 4.2 is invalid.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Cricket | ||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
6. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. This eliminates Case 1.1 and 1.2
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | Cricket | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
7. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
This also implies that T likes Football.
The final arrangement is,
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | Football |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
Hence, the correct pair is S – Hockey.
97. Direction: Study the given information and answer the following questions.
Six persons P, Q, R, S, T and U are living in a three storey building with six flats but not necessarily in the same order. Each floor of the flat have two different flats i.e., flat 1 and flat 2 and floors are numbered such that the lowermost floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above it is numbered as 2 and so on. Flat 1 is to the west of flat 2. All the persons like different games namely- Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling but not necessarily in the same order.
S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
Question:
Find the odd one out.
A. Q
B. P
C. T
D. U
E. S
Solution
Persons: P, Q, R, S, T and U.
Sports: Cricket, Football, Hockey, Chess, Badminton and Wrestling
1. The one who likes Chess lives to the west of the one who likes Hockey which is liked by S.
2. S and T lives on neighboring floors of same flat.
| Case 1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | ||||
| Case 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | T | |||
| Case 3 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | T | |||
| 2 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 1 | ||||
| Case 4 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | ||||
| 2 | T | |||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
3. There is one floor of gap between the one who likes Hockey and Cricket i.e., he lives in either of the flat.
4. The one who likes Badminton lives in Floor 2 but not on the flat which S lives. This eliminates case 2 and 3.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey\ | |
| Case 4.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Cricket | |||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
5. Q, who doesn’t like Cricket lives to the north-west of T.
So, Case 4.2 is invalid.
| Case 1.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 1.2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Chess | S | Hockey |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Cricket | |||
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Cricket | ||
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | Chess | S | Hockey | |
6. U lives in floor 1. U and T neither likes Cricket nor Wrestling. This eliminates Case 1.1 and 1.2
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | Cricket | |
| 2 | Badminton | T | ||
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
7. P and R, who likes Badminton doesn’t live on same flat.
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
This also implies that T likes Football.
The final arrangement is,
| Case 4.1 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | ||
| Floor | Person | Sport | Person | Sport |
| 3 | Q | Wrestling | P | Cricket |
| 2 | R | Badminton | T | Football |
| 1 | U | Chess | S | Hockey |
Q, P, U and S live in odd numbered floors whereas T lives in even numbered floor.
Hence, T is the odd one out.
98. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
In a certain code language:
‘don’t do that work’ is written as ‘fi di ti bi’
‘this work is easy’ is written as ‘li ki si di’
‘they should do that’ is written as ‘fi zi vi bi’
‘should he do this’ is written as ‘fi vi si pi’
Question:
Code ‘pi vi fi si’ is for which of the following sentence in the following code language?
A. he should do that
B. he should do this
C. don’t do this work
D. They should do that
E. They should do this
Solution
| Word | Code |
| don’t | ti |
| do | fi |
| that | bi |
| work | di |
| this | si |
| is | li/ki |
| easy | li/ki |
| they | zi |
| should | vi |
| he | pi |
Code ‘pi’ represents ‘he’
Code ‘vi’ represents ‘should’
Code ‘fi’ represents ‘do’
Code ‘si’ represents ‘this’
Hence, the code ‘pi vi fi si’ is for the sentence ‘he should do this’.
99. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
In a certain code language:
‘don’t do that work’ is written as ‘fi di ti bi’
‘this work is easy’ is written as ‘li ki si di’
‘they should do that’ is written as ‘fi zi vi bi’
‘should he do this’ is written as ‘fi vi si pi’
Question:
Code ‘vi’ is for which word in that given code language?
A. work
B. don’t
C. should
D. they
E. this
Solution
| Word | Code |
| don’t | ti |
| do | fi |
| that | bi |
| work | di |
| this | si |
| is | li/ki |
| easy | li/ki |
| they | zi |
| should | vi |
| he | pi |
Hence the code ‘vi’ is for the word ‘should’.
100. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
In a certain code language:
‘don’t do that work’ is written as ‘fi di ti bi’
‘this work is easy’ is written as ‘li ki si di’
‘they should do that’ is written as ‘fi zi vi bi’
‘should he do this’ is written as ‘fi vi si pi’
Question:
What would be the code for ‘They don’t work this’ in that code language?
A. fi bi zi ti
B. bi zi ti di
C. pi ti di si
D. zi ti di si
E. vi di bi zi
Solution
| Word | Code |
| don’t | ti |
| do | fi |
| that | bi |
| work | di |
| this | si |
| is | li/ki |
| easy | li/ki |
| they | zi |
| should | vi |
| he | pi |
Code for ‘They’ is ‘zi’
Code for ‘Don’t’ is ‘ti’
Code for ‘Work’ is ‘di’
Code for ‘This’ is ‘si’
Hence, the code for ‘They don’t work this’ is ‘zi ti di si’.
