1. Read the following sentence to find out if there is any grammatical error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The number of this part is your answer. If there is no error in the statement, then mark option (5) as your answer choice
We are eagerly looking forward (1) to see you (2) in our son’s marriage (3) Kindly make the function memorable with your presence.(4) No error (5)
A. We are eagerly looking forward
B. to see you
C. in our son’s marriage
D. Kindly make the function memorable with your presence
E. No error
Solution
The correct option is to see you
Key Points
- TO + GERUND:
- RULE:– Usually “verb1” comes right after “to” but after the followings – {accustomed to, averse to, with a view to, be used to, addicted to, devoted to, in addition to, look forward to, object to, owing to, given to, taken to, disposed to, prone to}, “gerund” (Verbing) takes place.
- Example- He is addicted to smoke .
He is addicted to smoking.
The correct sentence- We are eagerly looking forward to seeing you in our son’s marriage, Kindly make the function memorable with your presence.
Additional Information
- A Gerund is a non finite verb which functions as a noun. It is formed by adding ‘ing’ with a verb.- (verbing)
- i) A gerund can be either the subject or object of a sentence.
- ii) In most cases ‘gerund’ and ‘infinitives’ are easily replaceable.
- EXAMPLE:- I like to swim.
I like swimming.
Eg. Pinki plays with her dancing doll.
The gerund looks exactly the same as a present participle because both have same form i.e. “verbing” but it is useful to understand the difference between the two.
1) The gerund always has the same function as a noun.
Eg. Dancing is a good exercise.
2) The present participle has the same function as an adjective or a connector.
2. Read the following sentence to find out if there is any grammatical error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The number of this part is your answer. If there is no error in the statement, then mark option (5) as your answer choice.
Private jobs are not (1) preferable among the masses since (2) they make their employees (3) to work hard all the time. (4) No error (5)
A. Private jobs are not
B. preferable among masses since
C. they make their employees
D. to work hard all the time.
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is answer option (2) i.e. ‘to work hard all the time.’
Key Points
- Use “work” instead of “to work”
- “Direct Infinitive” (verb1) is used after the verbs- “let, bid, make, help, see, hear“
- After the above-mentioned verbs, Infinitive (to + verb1) must be avoided.
Example: Let me to go.
Let me go. - In the statement asked, the verb “make” will be followed by direct infinitive “work” as per the rule cited above.
The correct sentence- ” Private jobs are not preferable among the masses since they make their employees work hard all the time.”
- What is an INFINITIVE?
- The infinitive is a kind of noun with certain features of a verb. “to” is used with infinitives following the structure – “to + verb1”
- What is Direct Infinitive?
- Direct Infinitive is the infinitive without ‘to’ that is “verb1“. It is also called Bare Infinitive.
EXCEPTION:
- A direct infinitive is used after “bid, make, help, see, hear” if only the sentence is given in “active voice“
- In case the sentence is given in passive voice, Above mentioned verbs will also follow Infinitive(to+verb1)
- Example:
- 1) I made the student write an essay. active voice)
- 2) The student was made to write an essay by me. (passive voice)
Important Point
NOTE:– “let” is the only verb that is followed by a direct infinitive(verb1) both in the active and passive voice.
I was let go by him. (passive voice)
He let me go. (active voice)
3. Read the following sentence to find out if there is any grammatical error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The number of this part is your answer. If there is no error in the statement, then mark option (5) as your answer choice.
She is so cold that (1) she let her lapdog to jump (2) out of the window from the (3) fifth floor of her building.(4) No error (5)
A. She is so cold that
B. she let her lapdog to jump
C. out of the window from the
D. fifth floor of her building
E. No error
Solution
(2); Do not use “to” before jump is correct answer.
Key Points
- The general rule regarding the usage of verb “let” is that it does not require the preposition “to” before the following verb.
- In English, “let” belongs to a category known as “causative verbs”, which are used to indicate that one person has caused another person to do something.
The common structure for sentences that use “let” is as follows - let + object + base form of verb
- Here:
- “let” is the causative verb
- the “object” is the person or thing that was caused to do something
- the “base form of verb” is the action that the object was caused to do
- So, in your sentence “She let her lapdog jump out of the window”, “let” is the causative verb, “her lapdog” is the object, and “jump” is the base verb. Hence, there is no need for “to” before “jump”.
The correct version of the sentence is:
“She is so cold that she let her lapdog jump out of the window from the fifth floor of her building.”
In this sentence, we do not use “to” after the verb “let”. Instead, “let” should be directly followed by the base form of the verb, which is “jump” in this case.
4. Read the following sentence to find out if there is any grammatical error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The number of this part is your answer. If there is no error in the statement, then mark option (5) as your answer choice.
Dentists advise (1) that (2)Brushing teeth twice a day (3) helps to prevent tooth decay. (4) No error. (5)
A. Dentists advise
B. that
C. Brushing teeth twice a day
D. helps to prevent tooth decay
E. No error
Solution
Answer is (3) Remove “to”
Key Points
- “Direct Infinitive” (verb1) is used after the verbs- “let, bid, make, help, see, hear“
- After the above-mentioned verbs, Infinitive (to + verb1) must be avoided.
Example: Let me to go.
Let me go. - In the statement asked, the verb “help” will be followed by direct infinitive “prevent” as per the rule cited above.
The correct statement- Dentists advise that brushing teeth twice a day helps prevent tooth decay.
What is an INFINITIVE?
Infinitive is a kind of noun with certain features of a verb. “to” is used with infinitives following the structure – “to + verb1”
What is a Direct Infinitive?
Direct Infinitive is the infinitive without ‘to’ – “verb1“. It is also called Bare Infinitive.
EXCEPTION:
Direct infinitive is used after “bid, make, help, see, hear” if only the sentence is given in “active voice“
In case sentence is given in passive voice, Above mentioned verbs will also follow Infinitive(to+verb1)
Example:
1) I made the student write an essay. (active voice)
2) The student was made to write an essay by me. (passive voice)
Important Point
NOTE:– “let” is the only verb that is followed by direct infinitive(verb1) both in active and passive voice.
I was let go by him. (passive voice)
He let me go. (active voice)
5. In the following question, a word has been given. Choose the sentence(s) in which it is used correctly and if all the sentences are correct then choose Option 5.
FURTHER
A. Homeowners struggling financially due to coronavirus will be able to extend their mortgage payment holiday for a further three months
B. Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU)has further extended the last date for submission of assignments for the June term-end exam
C. Although it is not advisable for RBI to reach zero lower bound, there is enough space for a further repo rate cut
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. B and C
E. All are correct
Solution
The correct answer is option 5.
Key Points
- To answer this question, let’s first understand the meaning of the word given in the question:
- Further: used to refer to a greater distance or degree; additionally or moreover. (आगे, इसके अलावा)
- Now, let’s examine the given sentences:
- Sentence A: Homeowners struggling financially due to coronavirus will be able to extend their mortgage payment holiday for a further three months.
- This sentence correctly uses the word “further” to indicate an additional three months.
- Sentence B: Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU) has further extended the last date for submission of assignments for the June term-end exam.
- This sentence correctly uses the word “further” to indicate an additional extension of the last date.
- Sentence C: Although it is not advisable for RBI to reach zero lower bound, there is enough space for a further repo rate cut.
- This sentence correctly uses the word “further” to indicate an additional reduction in the repo rate.
- So, all three sentences correctly use the word “further” to convey the idea of additional or greater degree.
Therefore, the correct answer is “All are correct.”
6. Below a word is given followed by three sentences which consist of that word. Identify the sentence/s which best expresses the meaning of the word. Choose option 5 (None of these) if the word is not suitable in any of the sentences.
Voracious
- Those fish are just nasty, voracious predators and we just don’t want them anywhere near salmon.
- India has long been a crucial source of global gold demand, its voracious appetite second only to China’s.
- She was a voracious student, eager to learn more than local schools could offer
A. Both A and B
B. Both B and C
C. Both A and C
D. A, B and C
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is option 4.
Key Points
- To answer this question, let’s first understand the meaning of the word given in the question:
- Voracious: having a very eager approach to an activity or consuming large quantities of food; insatiable. (लालची, भूखा, अति उत्साही)
- Now, let’s examine the given sentences:
- Sentence A: Those fish are just nasty, voracious predators and we just don’t want them anywhere near salmon.
- This sentence correctly uses the word “voracious” to describe predators with an insatiable appetite.
- Sentence B: India has long been a crucial source of global gold demand, its voracious appetite second only to China’s.
- This sentence also correctly uses the word “voracious” to describe an insatiable or very eager demand for gold.
- Sentence C: She was a voracious student, eager to learn more than local schools could offer.
- This sentence accurately uses the word “voracious” to describe someone with an eager or insatiable desire for knowledge.
- So, all three sentences correctly use the word “voracious” to illustrate different contexts of eagerness or insatiable desire.
Therefore, the correct answer is “All A, B, and C.”
7. Below a word is given followed by three sentences which consist of that word. Identify the sentence/s which best expresses the meaning of the word. Choose option 5 (None of these) if the word is not suitable in any of the sentences.
FALLACIOUS
A. In no case is the evidence of the senses fallacious or mendacious; the fallacy is in the inference.
B. it is indeed a fallacious belief that one can separate moral issues from economic ones.C. As more people became able to afford fallacious extravagances, there was an enormous societal push for people to instead return to basics and traditional values.
A. Both A and B
B. Both A and C
C. Both B and C
D. Only C
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
- To answer this question, let’s first understand the meaning of the word given in the question:
- Fallacious: based on a mistaken belief; logically unsound or deceptive. (भ्रमपूर्ण, मिथ्या)
- Now, let’s examine the given sentences:
- Sentence A: In no case is the evidence of the senses fallacious or mendacious; the fallacy is in the inference.
- This sentence correctly uses the word “fallacious” to describe something that is based on a mistaken belief or error in reasoning.
- Sentence B: It is indeed a fallacious belief that one can separate moral issues from economic ones.
- This sentence also correctly uses the word “fallacious” to describe a belief that is misleading or false.
- Sentence C: As more people became able to afford fallacious extravagances, there was an enormous societal push for people to instead return to basics and traditional values.
- This sentence uses the word “fallacious” incorrectly. The word does not fit the context of describing “extravagances” as it refers to ideas or reasoning, not material things.
- So, only sentences A and B correctly use the word “fallacious“.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 1: Both A and B.
8. In the following passage, some of the words have been left out. Read the passage carefully and select the correct answer for the given blanks out of the given alternatives.
In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate ____ (1) of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite ____ (2) creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the ____ (3) of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of ____ (4) and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid ____ (5) of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome ____ (6), most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Question:
What will come in blank 1?
A. dance
B. balance
C. act
D. display
E. struggle
Solution
The correct answer is ‘balance‘.
Key Points
- The sentence describes life for a tarantula as something delicate that involves survival.
- “Balance” in this context refers to a delicate equilibrium or a careful management of various factors to ensure survival. This fits well with the idea that the tarantula’s life is a careful navigation of challenges to stay alive.
- “Dance” implies a coordinated movement, which doesn’t quite fit the broader concept of survival.
- “Act” is too general.
- “Display” suggests showing something, which isn’t the primary meaning here.
- “Struggle” implies continuous effort against difficulty, which, while true, “balance” better captures the delicate nature mentioned.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 2‘.
Complete Passage: In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate 1. balance of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite 2. _____creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the 3. _____of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of 4. _____and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid 5. ______of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome 6. ______, most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Additional Information
Struggle: Make forceful or violent efforts to get free of restraint or constriction.
Dance: A rhythmic movement, often to music.
Act: A thing done; a deed.
Display: An act of displaying or something displayed.
9. In the following passage, some of the words have been left out. Read the passage carefully and select the correct answer for the given blanks out of the given alternatives.
In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate ____ (1) of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite ____ (2) creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the ____ (3) of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of ____ (4) and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid ____ (5) of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome ____ (6), most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Question:
What will come in blank 2?
A. docile
B. fierce
C. active
D. swift
E. solitary
Solution
The correct answer is ‘docile‘.
Key Points
- The passage states that tarantulas are “often misunderstood” and “preferring to avoid confrontation.” This suggests a non-aggressive nature.
- Docile means easy to manage or submissive, which perfectly aligns with the description of tarantulas preferring to avoid confrontation.
- Fierce contradicts the idea of avoiding confrontation.
- Active and swift describe their physical capabilities, not their temperament regarding aggression.
- Solitary describes their social habits, not their preference for avoiding conflict.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 1‘.
Complete Passage: In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate 1. balance of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite 2. docile creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the 3. _____of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of 4. _____and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid 5. _____of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome 6. _____, most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Additional Information
Solitary: Done or existing alone.
Fierce: Having or displaying an intense or ferocious aggressiveness.
Active: Engaging or ready to engage in physically energetic pursuits.
Swift: Moving or capable of moving at high speed.
10. In the following passage, some of the words have been left out. Read the passage carefully and select the correct answer for the given blanks out of the given alternatives.
In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate ____ (1) of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite ____ (2) creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the ____ (3) of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of ____ (4) and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid ____ (5) of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome ____ (6), most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Question:
What will come in blank 3?
A. expulsion
B. absorption
C. retraction
D. attraction
E. growth
Solution
The correct answer is ‘expulsion‘.
Key Points
- The passage describes the tarantula’s primary defense mechanism as involving “urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators.” For these hairs to cause irritation, they must be released or thrown off the abdomen.
- Expulsion means the action of forcing something out, which accurately describes how the tarantula would use its hairs for defense.
- Absorption (taking in) and retraction (drawing back) are the opposite of what is needed for a defense mechanism that causes irritation to predators.
- Attraction and growth are not relevant to the immediate defense mechanism of releasing irritating hairs.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 1‘.
Complete Passage: In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate 1. balance of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite 2. docile creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the 3. expulsion of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of 4. _____and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid 5. _____of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome 6. _____, most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Additional Information
Growth: The process of increasing in amount, value, or importance.
Absorption: The process or action by which one thing absorbs or is absorbed by another.
Retraction: The action of drawing something back or in.
Attraction: The action or power of evoking interest, pleasure, or liking for someone or something.
11. In the following passage, some of the words have been left out. Read the passage carefully and select the correct answer for the given blanks out of the given alternatives.
In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate ____ (1) of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite ____ (2) creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the ____ (3) of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of ____ (4) and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid ____ (5) of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome ____ (6), most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Question:
What will come in blank 4?
A. sight
B. smell
C. hearing
D. touch
E. taste
Solution
The correct answer is ‘touch‘.
Key Points
- The sentence states that tarantulas “rely on their keen sense of ____ (4) and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey.”
- Tarantulas are known for their extreme sensitivity to vibrations. This ability is a form of mechanoreception, which falls under the broader sense of touch. They use specialized hairs and receptors on their legs to detect even the slightest movements on the ground, indicating the presence of prey or predators.
- Sight is generally poor in tarantulas, especially in a “dimly lit world,” and not their primary hunting sense.
- While they have some chemoreception (related to smell and taste), these are not directly linked to detecting “vibrations of the ground” for hunting.
- Tarantulas don’t possess a typical sense of hearing as mammals do, but their ability to detect vibrations serves a similar purpose in sensing their environment, which is fundamentally a tactile sense.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 4‘.
Complete Passage: In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate 1. balance of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite 2. docile creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the 3. expulsion of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of 4. touch and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid 5. _____of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome 6. _____, most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Additional Information
Taste: The sensation of flavor perceived in the mouth and throat on contact with a substance.
Sight: The faculty or power of seeing. Tarantulas have poor eyesight.
Smell: The faculty or power of perceiving odors or scents.
Hearing: The faculty of perceiving sounds.
12. In the following passage, some of the words have been left out. Read the passage carefully and select the correct answer for the given blanks out of the given alternatives.
In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate ____ (1) of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite ____ (2) creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the ____ (3) of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of ____ (4) and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid ____ (5) of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome ____ (6), most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Question:
What will come in blank 5?
A. injection
B. incision
C. absorption
D. secretion
E. explosion
Solution
The correct answer is ‘injection‘.
Key Points
- The sentence describes how a tarantula delivers venom: “the tarantula delivers a rapid ____ (5) of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal.”
- When a substance like venom is introduced into the body of another creature via a sharp point (like fangs or a needle), the correct term is injection. This precisely describes the action of the tarantula using its fangs to introduce venom.
- Incision refers to a cut, not the delivery of a liquid.
- Absorption is the process of taking something in, which is the opposite of delivering.
- Secretion is the process by which a substance is produced and discharged from a gland. While venom is a secreted substance, the act of *delivering* it *through fangs* into a victim is best described as an injection, not just secretion. “Secretion of venom” refers to its production, not its direct delivery into a target.
- Explosion is clearly irrelevant to the context.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 1‘.
Complete Passage: In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate 1. balance of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite 2. docile creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the 3. expulsion of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of 4. touch and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid 5. injection of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome 6. _____, most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Additional Information
Explosion: A violent bursting or expansion; a sudden and dramatic increase in the occurrence or amount of something.
Incision: A cut made into skin or flesh, especially during surgery.
Absorption: The process or action by which one thing absorbs or is absorbed by another.
Secretion: A process by which substances are produced and discharged from a cell, gland, or organ for a particular function in the organism or for excretion.
13. In the following passage, some of the words have been left out. Read the passage carefully and select the correct answer for the given blanks out of the given alternatives.
In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate ____ (1) of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite ____ (2) creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the ____ (3) of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of ____ (4) and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid ____ (5) of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome ____ (6), most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Question:
What will come in blank 6?
A. appearance
B. reputation
C. size
D. speed
E. habits
Solution
The correct answer is ‘reputation‘.
Key Points
- The sentence reads: “Despite their fearsome ____ (6), most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.” This indicates a contrast between what people commonly perceive about tarantulas and the reality of their bites.
- Earlier in the passage, tarantulas are described as “often misunderstood.” This directly points to the idea that their public image or perception might be inaccurate or exaggerated.
- A reputation refers to the beliefs or opinions that are generally held about someone or something. Tarantulas have a fearsome reputation largely due to myths, their appearance, and common misconceptions about their venomous nature. The phrase “Despite their fearsome reputation” perfectly sets up the contrast with the actual mildness of their bites.
- While their appearance (Option 1) certainly contributes to why they are perceived as fearsome (“formidable-looking” is mentioned earlier), “reputation” encompasses the broader public perception and the “misunderstood” aspect more completely. People’s fear often stems from what they’ve heard or believe about tarantulas (their reputation), rather than just their immediate visual impact.
- Size (Option 3) and speed (Option 4) are characteristics, not the overarching reason for their “fearsome” quality in this context of their bite’s effect.
- Habits (Option 5) refers to their behaviors, which don’t directly explain why their *fearsome quality* is contrasted with a harmless bite.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 2‘.
Complete Passage: In the dimly lit world of the tarantula, life is a delicate 1. balance of survival. These formidable-looking arachnids, often misunderstood, are actually quite 2. docile creatures, preferring to avoid confrontation. Their primary defense mechanism isn’t aggression, but rather the 3. expulsion of urticating hairs from their abdomen, which can cause intense irritation to predators. When hunting, tarantulas rely on their keen sense of 4. touch and the vibrations of the ground to detect unsuspecting prey. Once a victim is within striking distance, the tarantula delivers a rapid 5. injection of venom through its fangs, paralyzing its meal. Despite their fearsome 6. reputation, most tarantula bites are not harmful to humans, often compared to a bee sting.
Additional Information
Habits: A settled or regular tendency or practice, especially one that is hard to give up
Appearance: The way that someone or something looks.
Size: The relative extent of something; a thing’s overall dimensions or magnitude.
Speed: The rate at which someone or something is able to move or operate.
14. Directions: Read the passage carefully to answer the given questions. Each question will have five alternatives as its answer, choose the correct option as your answer.
RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das had stated during the last Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) address that the apex banking regulator, in collaboration with banks, would be launching a pilot project to assess the functioning of a QR-code based coin vending machine.
In simple words, the vending machines would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using United Payments Interface (UPI) instead of physical tendering of banknotes. Customers would be endowed the option of withdrawing coins in required quantities and denominations. The central idea here is to ease the accessibility to coins.
On the supply side of things, T. Rabi Shankar, Deputy Governor at the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had stated that the situation with respect to coins was “peculiar” with the supply being “very high”. “It is taking up a lot of storage space and it is not getting properly distributed. At the same time, there is demand in pockets,” added the Deputy Governor.
The proposed mechanism for coin _______ would be a departure from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges. Further, the proposed machine would eliminate the need for physical tendering of banknotes and their authentication. It was observed that the currency being fed into the machines (for coin exchange) were often found to be fake and could not be checked right at that point of time. Thus, the mandate to eliminate the physical tendering of banknotes. The pilot is initially planned to be rolled out at 19 locations in 12 cities across the country. With particular focus on ease and accessibility, the machines are intended to be installed at public places such as railway stations, shopping mall and marketplaces.
As per the latest RBI bulletin, the total value of circulation of rupee coins stood at ₹28,857 crore as of December 30 last year. The figure is an increase of 7.2% from the year-ago period. Circulation of small coins remained unchanged at ₹743 crore. For perspective, coins in India are issued in denominations of 50 paise, one rupee, two rupees, five rupees, ten rupees and twenty rupees. Coins of up to 50 paise are called ‘small coins’ while those of one rupee and above are called ‘rupee coins’.
The figures above could be compared to the volume of digital payments until December 2022 which stood at approximately ₹9,557.4 crore, as per the Digidhan Dashboard. The number is inclusive of mobile banking, internet banking, IMPS, BHIM-UPI and NEFT, among others. The reliance on UPI for dispensing coins is particularly noteworthy and it must be recalled that the payments interface for feature phones was launched in March last year. The apex regulator is also in the midst of a pilot for the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
According to Vipul Kharbanda, non-resident fellow at the Centre for Internet and Society (CIS) the proposal should not be viewed as a “zero-sum game of digital versus cash.” The two can easily supplement each other. “This should not be looked at from a very dogmatic point of view rather a pragmatic one. If digitalisation is not solving a particular problem at this given point of time, then it is very much within RBI’s purview to use other means available to achieve its ultimate objective that is to operate the currency system of the country,” Mr. Kharbanda argues
Question:
According to the passage, why the mandate to eliminate the physical tendering of banknotes was opted for the coin vending machine?
A. to promote the digital mode of payments
B. to achieve RBI’s ultimate objective that is to operate the currency system of the country
C. to ensure fast and easy transaction
D. to avoid fake currency being fed into the machines as it can not be checked right at that point of time
E. Both 3 & 4.
Solution
The correct answer is option 4.
Key Points
To answer this question refer to the second, third and fourth lines of the fourth paragraph of the given passage –
- ‘Further, the proposed machine would eliminate the need for physical tendering of banknotes and their authentication. It was observed that the currency being fed into the machines (for coin exchange) were often found to be fake and could not be checked right at that point of time. Thus, the mandate to eliminate the physical tendering of banknotes.’
- After reading the above lines we can conclude that the physical tendering of banknotes was opted for the coin vending machine to avoid the use of fake currency as it can not be checked right at that point of time.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 4 i.e. to avoid fake currency being fed into the machines as it can not be checked right at that point of time.
15. Directions: Read the passage carefully to answer the given questions. Each question will have five alternatives as its answer, choose the correct option as your answer.
RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das had stated during the last Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) address that the apex banking regulator, in collaboration with banks, would be launching a pilot project to assess the functioning of a QR-code based coin vending machine.
In simple words, the vending machines would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using United Payments Interface (UPI) instead of physical tendering of banknotes. Customers would be endowed the option of withdrawing coins in required quantities and denominations. The central idea here is to ease the accessibility to coins.
On the supply side of things, T. Rabi Shankar, Deputy Governor at the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had stated that the situation with respect to coins was “peculiar” with the supply being “very high”. “It is taking up a lot of storage space and it is not getting properly distributed. At the same time, there is demand in pockets,” added the Deputy Governor.
The proposed mechanism for coin _______ would be a departure from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges. Further, the proposed machine would eliminate the need for physical tendering of banknotes and their authentication. It was observed that the currency being fed into the machines (for coin exchange) were often found to be fake and could not be checked right at that point of time. Thus, the mandate to eliminate the physical tendering of banknotes. The pilot is initially planned to be rolled out at 19 locations in 12 cities across the country. With particular focus on ease and accessibility, the machines are intended to be installed at public places such as railway stations, shopping mall and marketplaces.
As per the latest RBI bulletin, the total value of circulation of rupee coins stood at ₹28,857 crore as of December 30 last year. The figure is an increase of 7.2% from the year-ago period. Circulation of small coins remained unchanged at ₹743 crore. For perspective, coins in India are issued in denominations of 50 paise, one rupee, two rupees, five rupees, ten rupees and twenty rupees. Coins of up to 50 paise are called ‘small coins’ while those of one rupee and above are called ‘rupee coins’.
The figures above could be compared to the volume of digital payments until December 2022 which stood at approximately ₹9,557.4 crore, as per the Digidhan Dashboard. The number is inclusive of mobile banking, internet banking, IMPS, BHIM-UPI and NEFT, among others. The reliance on UPI for dispensing coins is particularly noteworthy and it must be recalled that the payments interface for feature phones was launched in March last year. The apex regulator is also in the midst of a pilot for the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
According to Vipul Kharbanda, non-resident fellow at the Centre for Internet and Society (CIS) the proposal should not be viewed as a “zero-sum game of digital versus cash.” The two can easily supplement each other. “This should not be looked at from a very dogmatic point of view rather a pragmatic one. If digitalisation is not solving a particular problem at this given point of time, then it is very much within RBI’s purview to use other means available to achieve its ultimate objective that is to operate the currency system of the country,” Mr. Kharbanda argues
Question:
As per the latest RBI bulletin, what was the total value of circulation of rupee coins as of December 30 last year?
A. ₹28,857 lakh crore
B. ₹28,857 crore
C. ₹9,557.4 crore
D. ₹25,857 crore
E. ₹743 crore
Solution
The correct answer is option 2.
Key Points
To answer this question refer to the first two lines of the fifth paragraph of the given passage –
- ‘As per the latest RBI bulletin, the total value of circulation of rupee coins stood at ₹28,857 crore as of December 30 last year. The figure is an increase of 7.2% from the year-ago period. ‘
- After reading the above lines we can conclude that the total value of circulation of rupee coins stood at ₹28,857 crore as of December 30 last year.
Therefore, the correct answer would be option 2 i.e. ₹28,857 crore.
16. Directions: Read the passage carefully to answer the given questions. Each question will have five alternatives as its answer, choose the correct option as your answer.
RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das had stated during the last Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) address that the apex banking regulator, in collaboration with banks, would be launching a pilot project to assess the functioning of a QR-code based coin vending machine.
In simple words, the vending machines would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using United Payments Interface (UPI) instead of physical tendering of banknotes. Customers would be endowed the option of withdrawing coins in required quantities and denominations. The central idea here is to ease the accessibility to coins.
On the supply side of things, T. Rabi Shankar, Deputy Governor at the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had stated that the situation with respect to coins was “peculiar” with the supply being “very high”. “It is taking up a lot of storage space and it is not getting properly distributed. At the same time, there is demand in pockets,” added the Deputy Governor.
The proposed mechanism for coin _______ would be a departure from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges. Further, the proposed machine would eliminate the need for physical tendering of banknotes and their authentication. It was observed that the currency being fed into the machines (for coin exchange) were often found to be fake and could not be checked right at that point of time. Thus, the mandate to eliminate the physical tendering of banknotes. The pilot is initially planned to be rolled out at 19 locations in 12 cities across the country. With particular focus on ease and accessibility, the machines are intended to be installed at public places such as railway stations, shopping mall and marketplaces.
As per the latest RBI bulletin, the total value of circulation of rupee coins stood at ₹28,857 crore as of December 30 last year. The figure is an increase of 7.2% from the year-ago period. Circulation of small coins remained unchanged at ₹743 crore. For perspective, coins in India are issued in denominations of 50 paise, one rupee, two rupees, five rupees, ten rupees and twenty rupees. Coins of up to 50 paise are called ‘small coins’ while those of one rupee and above are called ‘rupee coins’.
The figures above could be compared to the volume of digital payments until December 2022 which stood at approximately ₹9,557.4 crore, as per the Digidhan Dashboard. The number is inclusive of mobile banking, internet banking, IMPS, BHIM-UPI and NEFT, among others. The reliance on UPI for dispensing coins is particularly noteworthy and it must be recalled that the payments interface for feature phones was launched in March last year. The apex regulator is also in the midst of a pilot for the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
According to Vipul Kharbanda, non-resident fellow at the Centre for Internet and Society (CIS) the proposal should not be viewed as a “zero-sum game of digital versus cash.” The two can easily supplement each other. “This should not be looked at from a very dogmatic point of view rather a pragmatic one. If digitalisation is not solving a particular problem at this given point of time, then it is very much within RBI’s purview to use other means available to achieve its ultimate objective that is to operate the currency system of the country,” Mr. Kharbanda argues
Question:
According to the passage, the vending machines would dispense coins against debit to the customer’s account using which of the following payment methods?
A. Banknotes
B. Net banking
C. Both 1 & 2
D. UPI
E. Both 1 & 4
Solution
The correct answer is option 4.
Key Points
To answer this question refer to the the first line of the second paragraph of the given passage –
- ‘In simple words, the vending machines would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using United Payments Interface (UPI) instead of physical tendering of banknotes.’
- After reading the above line we can conclude that the vending machines would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using UPI instead of banknotes.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 4 i.e. UPI.
17. Directions: Read the passage carefully to answer the given questions. Each question will have five alternatives as its answer, choose the correct option as your answer.
RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das had stated during the last Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) address that the apex banking regulator, in collaboration with banks, would be launching a pilot project to assess the functioning of a QR-code based coin vending machine.
In simple words, the vending machines would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using United Payments Interface (UPI) instead of physical tendering of banknotes. Customers would be endowed the option of withdrawing coins in required quantities and denominations. The central idea here is to ease the accessibility to coins.
On the supply side of things, T. Rabi Shankar, Deputy Governor at the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had stated that the situation with respect to coins was “peculiar” with the supply being “very high”. “It is taking up a lot of storage space and it is not getting properly distributed. At the same time, there is demand in pockets,” added the Deputy Governor.
The proposed mechanism for coin _______ would be a departure from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges. Further, the proposed machine would eliminate the need for physical tendering of banknotes and their authentication. It was observed that the currency being fed into the machines (for coin exchange) were often found to be fake and could not be checked right at that point of time. Thus, the mandate to eliminate the physical tendering of banknotes. The pilot is initially planned to be rolled out at 19 locations in 12 cities across the country. With particular focus on ease and accessibility, the machines are intended to be installed at public places such as railway stations, shopping mall and marketplaces.
As per the latest RBI bulletin, the total value of circulation of rupee coins stood at ₹28,857 crore as of December 30 last year. The figure is an increase of 7.2% from the year-ago period. Circulation of small coins remained unchanged at ₹743 crore. For perspective, coins in India are issued in denominations of 50 paise, one rupee, two rupees, five rupees, ten rupees and twenty rupees. Coins of up to 50 paise are called ‘small coins’ while those of one rupee and above are called ‘rupee coins’.
The figures above could be compared to the volume of digital payments until December 2022 which stood at approximately ₹9,557.4 crore, as per the Digidhan Dashboard. The number is inclusive of mobile banking, internet banking, IMPS, BHIM-UPI and NEFT, among others. The reliance on UPI for dispensing coins is particularly noteworthy and it must be recalled that the payments interface for feature phones was launched in March last year. The apex regulator is also in the midst of a pilot for the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
According to Vipul Kharbanda, non-resident fellow at the Centre for Internet and Society (CIS) the proposal should not be viewed as a “zero-sum game of digital versus cash.” The two can easily supplement each other. “This should not be looked at from a very dogmatic point of view rather a pragmatic one. If digitalisation is not solving a particular problem at this given point of time, then it is very much within RBI’s purview to use other means available to achieve its ultimate objective that is to operate the currency system of the country,” Mr. Kharbanda argues
Question:
Choose the antonym of the word ‘Conventional‘.
A. traditional
B. extraordinary
C. temporary
D. enduring
E. disquieting
Solution
The correct answer is option 2.
Key Points
To answer the question let’s first look at the meanings of the given word and all the words given in the options –
- Conventional – always behaving in a traditional or normal way (पारंपरिक)
- For Example –
- Our boss is very conventional in her views.
- Traditional – following or belonging to the customs or ways of behaving that have continued in a group of people or society for a long time without changing (परंपरागत)
- For Example –
- The traditional way of life has almost disappeared from our societies.
- For Example –
- She has extraordinary potential when it comes to Maths.
- Temporary – lasting for a short time; not permanent (अस्थायी)
- For Example –
- This medicine will give you temporary relief from the pain.
- Enduring – continuing for a long time; lasting (स्थायी)
- For Example –
- Her most enduring qualities are her grace and elegance.
- Disquieting – inducing feelings of anxiety or worry (बेचैन)
- For Example –
- The news gave disquieting news of the earthquake.
- After looking at the meanings of all the given words we can conclude that ‘Extraordinary’ is the only word that is opposite in meaning to the given word ‘Conventional’.
Therefore, the correct answer would be ‘Extraordinary’.
18. Directions: Read the passage carefully to answer the given questions. Each question will have five alternatives as its answer, choose the correct option as your answer.
RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das had stated during the last Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) address that the apex banking regulator, in collaboration with banks, would be launching a pilot project to assess the functioning of a QR-code based coin vending machine.
In simple words, the vending machines would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using United Payments Interface (UPI) instead of physical tendering of banknotes. Customers would be endowed the option of withdrawing coins in required quantities and denominations. The central idea here is to ease the accessibility to coins.
On the supply side of things, T. Rabi Shankar, Deputy Governor at the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had stated that the situation with respect to coins was “peculiar” with the supply being “very high”. “It is taking up a lot of storage space and it is not getting properly distributed. At the same time, there is demand in pockets,” added the Deputy Governor.
The proposed mechanism for coin _______ would be a departure from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges. Further, the proposed machine would eliminate the need for physical tendering of banknotes and their authentication. It was observed that the currency being fed into the machines (for coin exchange) were often found to be fake and could not be checked right at that point of time. Thus, the mandate to eliminate the physical tendering of banknotes. The pilot is initially planned to be rolled out at 19 locations in 12 cities across the country. With particular focus on ease and accessibility, the machines are intended to be installed at public places such as railway stations, shopping mall and marketplaces.
As per the latest RBI bulletin, the total value of circulation of rupee coins stood at ₹28,857 crore as of December 30 last year. The figure is an increase of 7.2% from the year-ago period. Circulation of small coins remained unchanged at ₹743 crore. For perspective, coins in India are issued in denominations of 50 paise, one rupee, two rupees, five rupees, ten rupees and twenty rupees. Coins of up to 50 paise are called ‘small coins’ while those of one rupee and above are called ‘rupee coins’.
The figures above could be compared to the volume of digital payments until December 2022 which stood at approximately ₹9,557.4 crore, as per the Digidhan Dashboard. The number is inclusive of mobile banking, internet banking, IMPS, BHIM-UPI and NEFT, among others. The reliance on UPI for dispensing coins is particularly noteworthy and it must be recalled that the payments interface for feature phones was launched in March last year. The apex regulator is also in the midst of a pilot for the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
According to Vipul Kharbanda, non-resident fellow at the Centre for Internet and Society (CIS) the proposal should not be viewed as a “zero-sum game of digital versus cash.” The two can easily supplement each other. “This should not be looked at from a very dogmatic point of view rather a pragmatic one. If digitalisation is not solving a particular problem at this given point of time, then it is very much within RBI’s purview to use other means available to achieve its ultimate objective that is to operate the currency system of the country,” Mr. Kharbanda argues
Question:
Choose the synonym of the word ‘Peculiar‘.
A. uncanny
B. sophisticated
C. naive
D. untrustworthy
E. reliable
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
To answer the question let’s first look at the meanings of the given word and all the words given in the options –
- Peculiar – unusual or strange (विचित्र)
- For Example –
- My parents looked at me with a very peculiar expression when I told them the news.
- Uncanny – very strange; that you cannot easily explain (अस्वाभाविक/विचित्र)
- For Example –
- Some people say that dogs have an uncanny way of sensing bad people.
- Sophisticated – having or showing a lot of experience of the world and social situations; knowing about fashion, culture, etc. (परिष्कृत)
- For Example –
- It’s not easy to impress her, she is a highly sophisticated and elegant woman.
- Naive – without enough experience of life and too ready to believe or trust other people (अनाड़ी)
- For Example –
- It’s very naive of you to believe every word he says.
- Untrustworthy – not able to be relied on as honest or truthful (बेईमान)
- For Example –
- I thought that we could be good friends but he turned out to be quite untrustworthy.
- Reliable – suitable or fit to be relied on (भरोसेमंद)
- For Example –
- I want a reliable person to look after my business.
- After looking at the meanings of all the given words we can conclude that ‘Uncanny’ is the only word that is similar in meaning to the given word ‘Peculiar’.
Therefore, the correct answer would be ‘Uncanny‘.
19. Directions: Read the passage carefully to answer the given questions. Each question will have five alternatives as its answer, choose the correct option as your answer.
RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das had stated during the last Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) address that the apex banking regulator, in collaboration with banks, would be launching a pilot project to assess the functioning of a QR-code based coin vending machine.
In simple words, the vending machines would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using United Payments Interface (UPI) instead of physical tendering of banknotes. Customers would be endowed the option of withdrawing coins in required quantities and denominations. The central idea here is to ease the accessibility to coins.
On the supply side of things, T. Rabi Shankar, Deputy Governor at the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had stated that the situation with respect to coins was “peculiar” with the supply being “very high”. “It is taking up a lot of storage space and it is not getting properly distributed. At the same time, there is demand in pockets,” added the Deputy Governor.
The proposed mechanism for coin _______ would be a departure from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges. Further, the proposed machine would eliminate the need for physical tendering of banknotes and their authentication. It was observed that the currency being fed into the machines (for coin exchange) were often found to be fake and could not be checked right at that point of time. Thus, the mandate to eliminate the physical tendering of banknotes. The pilot is initially planned to be rolled out at 19 locations in 12 cities across the country. With particular focus on ease and accessibility, the machines are intended to be installed at public places such as railway stations, shopping mall and marketplaces.
As per the latest RBI bulletin, the total value of circulation of rupee coins stood at ₹28,857 crore as of December 30 last year. The figure is an increase of 7.2% from the year-ago period. Circulation of small coins remained unchanged at ₹743 crore. For perspective, coins in India are issued in denominations of 50 paise, one rupee, two rupees, five rupees, ten rupees and twenty rupees. Coins of up to 50 paise are called ‘small coins’ while those of one rupee and above are called ‘rupee coins’.
The figures above could be compared to the volume of digital payments until December 2022 which stood at approximately ₹9,557.4 crore, as per the Digidhan Dashboard. The number is inclusive of mobile banking, internet banking, IMPS, BHIM-UPI and NEFT, among others. The reliance on UPI for dispensing coins is particularly noteworthy and it must be recalled that the payments interface for feature phones was launched in March last year. The apex regulator is also in the midst of a pilot for the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
According to Vipul Kharbanda, non-resident fellow at the Centre for Internet and Society (CIS) the proposal should not be viewed as a “zero-sum game of digital versus cash.” The two can easily supplement each other. “This should not be looked at from a very dogmatic point of view rather a pragmatic one. If digitalisation is not solving a particular problem at this given point of time, then it is very much within RBI’s purview to use other means available to achieve its ultimate objective that is to operate the currency system of the country,” Mr. Kharbanda argues
Question:
Choose the synonym of the word ‘Accessibility‘.
A. accountability
B. conveyance
C. availability
D. liability
E. immunity
Solution
The correct answer is option 3.
Key Points
To answer the question let’s first look at the meanings of the given word and all the words given in the options –
- Accessibility – fact of being able to be reached or obtained easily (अभिगम्यता)
- For Example –
- The new road is being built to increase accessibility to the town center.
- Accountability – the fact of being responsible for what you do and able to give a satisfactory reason for it (जवाबदेही)
- For Example –
- The end goal is to establish more accountability and improve teaching.
- Conveyance – the process or system of transporting or taking somebody/something from one place to another (परिवहन)
- For Example –
- Our company relies mainly on trains for the conveyance of goods to our customers.
- Availability – the state of being available (उपलब्धता)
- For Example –
- Did you check the availability of this product online?
- Liability – the state of being responsible for something (देयता)
- For Example –
- They have denied any liability for the damage caused by the accident.
- Immunity – the ability to avoid or not be affected by disease, criticism, punishment by law, etc. (प्रतिरक्षा)
- For Example –
- Humans have developed immunity to this virus overtime.
- After looking at the meanings of all the given words we can conclude that ‘Availability’ is the only word that is similar in meaning to the given word ‘Accessibility’.
Therefore, the correct answer would be ‘Availability’.
20. Directions: Read the passage carefully to answer the given questions. Each question will have five alternatives as its answer, choose the correct option as your answer.
RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das had stated during the last Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) address that the apex banking regulator, in collaboration with banks, would be launching a pilot project to assess the functioning of a QR-code based coin vending machine.
In simple words, the vending machines would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using United Payments Interface (UPI) instead of physical tendering of banknotes. Customers would be endowed the option of withdrawing coins in required quantities and denominations. The central idea here is to ease the accessibility to coins.
On the supply side of things, T. Rabi Shankar, Deputy Governor at the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had stated that the situation with respect to coins was “peculiar” with the supply being “very high”. “It is taking up a lot of storage space and it is not getting properly distributed. At the same time, there is demand in pockets,” added the Deputy Governor.
The proposed mechanism for coin _______ would be a departure from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges. Further, the proposed machine would eliminate the need for physical tendering of banknotes and their authentication. It was observed that the currency being fed into the machines (for coin exchange) were often found to be fake and could not be checked right at that point of time. Thus, the mandate to eliminate the physical tendering of banknotes. The pilot is initially planned to be rolled out at 19 locations in 12 cities across the country. With particular focus on ease and accessibility, the machines are intended to be installed at public places such as railway stations, shopping mall and marketplaces.
As per the latest RBI bulletin, the total value of circulation of rupee coins stood at ₹28,857 crore as of December 30 last year. The figure is an increase of 7.2% from the year-ago period. Circulation of small coins remained unchanged at ₹743 crore. For perspective, coins in India are issued in denominations of 50 paise, one rupee, two rupees, five rupees, ten rupees and twenty rupees. Coins of up to 50 paise are called ‘small coins’ while those of one rupee and above are called ‘rupee coins’.
The figures above could be compared to the volume of digital payments until December 2022 which stood at approximately ₹9,557.4 crore, as per the Digidhan Dashboard. The number is inclusive of mobile banking, internet banking, IMPS, BHIM-UPI and NEFT, among others. The reliance on UPI for dispensing coins is particularly noteworthy and it must be recalled that the payments interface for feature phones was launched in March last year. The apex regulator is also in the midst of a pilot for the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
According to Vipul Kharbanda, non-resident fellow at the Centre for Internet and Society (CIS) the proposal should not be viewed as a “zero-sum game of digital versus cash.” The two can easily supplement each other. “This should not be looked at from a very dogmatic point of view rather a pragmatic one. If digitalisation is not solving a particular problem at this given point of time, then it is very much within RBI’s purview to use other means available to achieve its ultimate objective that is to operate the currency system of the country,” Mr. Kharbanda argues
Question:
What of the following words will come in the blank taken from the passage:
The proposed mechanism for coin _______ would be a departure from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges.
A. collection
B. transportation
C. amalgamation
D. introduction
E. dispensation
Solution
The correct answer is option 5.
Key Points
- To answer the question, refer to the first line of the fourth paragraph of the given passage –
- The proposed mechanism for coin _______ would be a departure from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges.
- Above line talks about the mechanism of the QR-code based coin vending machine launched by RBI will will be different from the conventional machines which relied on banknotes for facilitating coin exchanges as it will be using UPI as the mode of payment for providing coins.
- Hence, the most appropriate word to fill the given blank would be ‘dispensation’.
- Dispensation – the action of distributing or supplying something (वितरण)
- For Example –
- The vending machines in our building is used for the dispensation of snacks.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Dispensation’.
Additional Information
Now, let’s understand the meanings of the other given options –
Introduction – the action of introducing something (परिचय)
Collection – the action or process of collecting someone or something (संग्रह)
Transportation – the action of transporting someone or something or the process of being transported (परिवहन)
Amalgamation – the action, process, or result of combining or uniting (समामेलन)
21. In the following sentence, four words or phrases have been printed in bold. One bold part in the sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part and mark its number. If there are no errors in the bold parts, mark (5) i.e. No error as the answer.An acetic life of prayer, fasting and abstinence from wordly pleasures can be lead only by puritans and celibates.
A. Acetic
B. Abstinence
C. Puritans
D. Celibates
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
The incorrect word is ‘Acetic’.
- The correct word should be ‘Ascetic’.
- The word ‘Ascetic‘ refers to a person who practices severe self-discipline and abstention from all forms of indulgence, typically for religious reasons. (संयमी)
- For Example –
- He chose to live an ascetic life of prayer and fasting.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Acetic’.
Additional Information
Let us understand the meanings of the other marked words:
Celibates – people who abstain from marriage and sexual relations, typically for religious reasons (ब्रह्मचारी)
Abstinence – the practice of restraining oneself from indulging in something, typically alcohol or other pleasures (संयम)
Puritans – members of a group of English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to simplify and regulate forms of worship (पवित्रतावादी)
22. In the following sentence, four words or phrases have been printed in bold. One bold part in the sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part and mark its number. If there are no errors in the bold parts, mark (5) i.e. No error as the answer.The opprobrious remarks passed by her friend made her gleam with joy and she was overwhelmed with delight to get such wonderful comments from her colleagues and confederates.
A. Opprobrious
B. Gleam with joy
C. Overwhelmed
D. Confederates
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
The incorrect word is ‘Opprobrious’.
- Opprobrious means expressing scorn or criticism. However, in the context of the sentence, it is incorrectly used to describe remarks that made someone gleam with joy. This is a semantic error as ‘opprobrious’ has a negative connotation.
- The correct word that fits the context would be something like ‘praiseworthy’ or ‘laudatory’ remarks.
Therefore, the correct answer would be ‘Opprobrious’.
Additional Information
Let’s understand the meanings of the other marked words –
Confederates – This word is acceptable in the context and refers to colleagues, allies, or associates.
Gleam with joy – This phrase is correct and means to shine or glow with happiness.
Overwhelmed – It is used correctly in the sentence to convey being emotionally overcome.
23. In the following sentence, four words or phrases have been printed in bold. One bold part in the sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part and mark its number. If there are no errors in the bold parts, mark (5) i.e. No error as the answer.The plaintive accused the new company of ravaging the environment through rigorous dumping of waste materials in the fertile agricultural land and demanded commencement of action against them.
A. Plaintive
B. Ravaging
C. Rigorous
D. Commencement
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
The incorrect word in the sentence is ‘plaintive’.
- Explanation: The word ‘plaintive’ is an adjective that means expressing sorrow or a mournful tone. In the given context, it is incorrect because the sentence refers to an “accused,” which should be a noun like ‘plaintiff’ instead of ‘plaintive’.
- Correct Usage: Replace ‘plaintive’ with ‘plaintiff’, which means a person who brings a case against another in a court of law.
Therefore, the correct word is ‘plaintiff’, and the correct answer is option 1.
Additional Information
Let’s understand the meanings of the other marked words:
- Ravaging: To cause severe damage or destruction. In this context, it is correctly used to describe the damage caused to the environment.
- Rigorous: Extremely thorough or accurate. Although it is correctly used, ‘rigorous dumping’ may not be the best phrase as ‘illegal dumping’ or ‘reckless dumping’ would fit better.
- Commencement: The beginning or start of something. This word is correctly used in the context of demanding the initiation of action.
Thus, the only error in the sentence lies in the use of ‘plaintive’, which should be replaced with ‘plaintiff’.
24. In the following sentence, four words or phrases have been printed in bold. One bold part in the sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part and mark its number. If there are no errors in the bold parts, mark (5) i.e. No error as the answer.My sister and I tried to sneek into the room where the Christmas presents were kept wrapped but we were sent back to the room as the maid caught us.
A. Sneek
B. Presents
C. Wrapped
D. Caught
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
The misspelled word is ‘sneek’.
- The correct spelling would be ‘sneak’.
- The word ‘sneak‘ is a verb which means ‘to move or go in a furtive or stealthy way’. (चुपके से जाना)
- For Example –
- He tried to sneak past the guards unnoticed.
Therefore, the correct answer would be ‘sneek’.
Additional Information
Let’s understand the meanings of the other marked words –
Caught – captured or seized (पकड़ा गया)
Presents – gifts or items given to someone (उपहार)
Wrapped – covered or enclosed in paper or material (लपेटा हुआ)
25. In the following sentence, four words or phrases have been printed in bold. One bold part in the sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part and mark its number. If there are no errors in the bold parts, mark (5) i.e. No error as the answer.Majority of the orchestras use the symbols which along with the drums provide different pitches and frequencies.
A. Majority
B. Symbols
C. Along with
D. Frequencies
E. No Error
Solution
The correct answer is option 2.
Key Points
The incorrect word is ‘symbols’.
- The correct word would be ‘cymbals’.
- The word ‘cymbals‘ refers to percussion instruments made of thin, round plates of metal, used in orchestras to produce sound when struck together.
- Symbols, however, refers to signs or representations, which is not contextually appropriate here.
- For Example – Cymbals are used in orchestras to add rhythm and emphasis to musical compositions.
Therefore, the correct answer would be ‘symbols’.
Additional Information
Let’s understand the meanings of the other marked words:
Frequencies – the rate at which something occurs or repeats over a particular period of time.
Majority – the greater number or part of something.
Along with – in addition to; together with.
26. Directions: In the following question, the sentences of a paragraph are jumbled. They are given as A, B, C, D, and E. Identify the correct order of the sentences to make a meaningful paragraph and answer the following questions.
A: By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
B: Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
C: Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
D: This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
E: Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
Question:
Which of these should be the FIRST sentence in the paragraph?
A. E
B. D
C. C
D. B
E. A
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Option 4‘.
Key Points
- Sentence B introduces stem cells and their unique ability to develop into different cell types.
- Sentence D elaborates on the importance of this characteristic in growth, repair, and regeneration.
- Sentence A explains how stem cells offer therapeutic potential for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries.
- Sentence E connects stem cell therapy to its potential in regenerative medicine.
- Sentence C acknowledges the ethical and regulatory challenges associated with stem cell research.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 4‘.
Correct Sequence:
B – Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
D – This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
A – By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
E – Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
C – Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
Additional Information
Sentence C provides a counterpoint, acknowledging the challenges that come with stem cell research.
Sentence B introduces stem cells and their unique ability, which is elaborated further in sentence D.
Sentence A and E explain how this property of stem cells is applied in medical therapies.
27. Directions: In the following question, the sentences of a paragraph are jumbled. They are given as A, B, C, D, and E. Identify the correct order of the sentences to make a meaningful paragraph and answer the following questions.
A: By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
B: Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
C: Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
D: This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
E: Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
Question:
Which of these should be the SECOND sentence in the paragraph?
A. B
B. A
C. C
D. E
E. D
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Option 5‘.
Key Points
- Sentence B introduces stem cells and their unique ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
- Sentence D elaborates on the importance of this characteristic in growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
- This makes sentence D a logical follow-up to sentence B, as it provides additional information about the significance of stem cells.
- The other sentences either introduce new concepts or provide examples that are better placed later in the paragraph.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 5‘.
Explanation of Sequence:
B – Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
D – This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
A – By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
E – Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
C – Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
Additional Information
The other sentences either discuss applications (A, E) or challenges (C), which would come later in the paragraph.
Sentence B introduces stem cells and their ability to develop into many different cell types. Sentence D elaborates on why this is significant for growth, repair, and regeneration.
This sequence flows logically, with sentence D being the most appropriate follow-up to B.
28. Directions: In the following question, the sentences of a paragraph are jumbled. They are given as A, B, C, D, and E. Identify the correct order of the sentences to make a meaningful paragraph and answer the following questions.
A: By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
B: Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
C: Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
D: This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
E: Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
Question:
Which of these should be the THIRD sentence in the paragraph?
A. A
B. E
C. B
D. D
E. C
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Option 1‘.
Key Points
- Sentence B introduces stem cells and their ability to differentiate into various cell types.
- Sentence D further explains the significance of this characteristic in growth, repair, and regeneration.
- Sentence A follows logically as it details how this ability is used in treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
- Therefore, Sentence A is the third sentence, which builds on the information presented earlier in the paragraph.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 1‘.
Explanation of Sequence:
B – Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
D – This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
A – By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
E – Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
C – Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
Additional Information
The other sentences focus on applications (E) or challenges (C), which are better suited later in the paragraph.
Sentence B introduces stem cells and their ability to differentiate into many different cell types, which is expanded upon in Sentence D.
Sentence A logically follows to describe how this unique property can help treat specific conditions, making it the third sentence in the sequence.
29. Directions: In the following question, the sentences of a paragraph are jumbled. They are given as A, B, C, D, and E. Identify the correct order of the sentences to make a meaningful paragraph and answer the following questions.
A: By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
B: Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
C: Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
D: This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
E: Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
Question:
Which of these should be the FOURTH sentence in the paragraph?
A. B
B. C
C. A
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Option 5‘.
Key Points
- Sentence B introduces stem cells and their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types.
- Sentence D elaborates on the significance of this characteristic in growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
- Sentence A explains how stem cells can help treat conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease, based on their ability to differentiate.
- Sentence E follows, emphasizing how stem cell therapy leverages these properties and represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
- Thus, Sentence E is the logical fourth sentence, providing the conclusion to the previous ideas.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 5‘.
Explanation of Sequence:
B – Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
D – This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
A – By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
E – Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
C – Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
Additional Information
The previous sentences explain stem cell characteristics, their application in treatments, and their importance in medical advancements, all leading up to the statement in Sentence E.
Sentence E provides the conclusion by emphasizing the potential of stem cell therapy in regenerative medicine, making it the fourth sentence in the sequence.
30. Directions: In the following question, the sentences of a paragraph are jumbled. They are given as A, B, C, D, and E. Identify the correct order of the sentences to make a meaningful paragraph and answer the following questions.
A: By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
B: Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
C: Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
D: This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
E: Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
Question:
Which of these should be the FIFTH sentence in the paragraph?
A. A
B. E
C. C
D. D
E. B
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Option 3‘.
Key Points
- Sentence B introduces stem cells and their unique ability to develop into many different cell types.
- Sentence D further explains the importance of this characteristic in growth, repair, and regeneration.
- Sentence A describes how stem cells are used in treating specific conditions, such as spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
- Sentence E emphasizes stem cell therapy as a frontier in regenerative medicine.
- Sentence C appropriately follows, addressing the ethical debates and regulatory challenges surrounding stem cell research, making it the fifth sentence in the paragraph.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘Option 3‘.
Explanation of Sequence:
B – Stem cells are unique because of their ability to develop into many different cell types in the body.
D – This remarkable characteristic makes them crucial for growth, repair, and regeneration within living organisms.
A – By stimulating cells to differentiate into specialized tissues, it offers hope for treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and Parkinson’s disease.
E – Stem cell therapy, leveraging these properties, represents a frontier in regenerative medicine.
C – Despite promising research, stem cell therapy faces ethical debates and regulatory challenges.
Additional Information
After discussing the potential of stem cell research and its applications, Sentence C brings attention to the obstacles it faces.
Sentence C addresses the challenges surrounding stem cell therapy, making it the perfect conclusion to the previous statements.
31. A cruise ship travels from Kochi to Lakshadweep, covering a distance of “y” km downstream in 8 hours. On its return journey upstream, it takes 24 hours to cover the same distance. If the speed of the ship in still water is 40 km/hr, find the value of “y”?
A. 480 km
B. 360 km
C. 400 km
D. 320 km
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Downstream time = 8 hours
Upstream time = 24 hours
Speed of ship in still water = 40 km/h
Let the speed of the current be “c” km/h
Then:
Downstream speed = 40 + c
Upstream speed = 40 – c
Let distance = y km
⇒ y = 8 × (40 + c) … (1)
⇒ y = 24 × (40 – c) … (2)
Equate equations (1) and (2):
⇒ 8 × (40 + c) = 24 × (40 – c)
Expand both sides:
⇒ 320 + 8c = 960 – 24c
Solve for c:
⇒ 8c + 24c = 960 – 320
⇒ 32c = 640 ⇒ c = 20
Put value of c in any equation to find y:
Using equation (1):
⇒ y = 8 × (40 + 20) = 8 × 60 = 480 km
Thus, the correct answer is 480 km.
32. Three partners X, Y, and Z started a business by investing in the ratio of 4:7:6 respectively. After 6 months, Y withdrew part of his investment such that his remaining capital became equal to one-third of the combined initial investments of X and Z. If the total annual profit was Rs. 18,200, what was Y’s share of the profit?
A. Rs. 6,200
B. Rs. 7,800
C. Rs. 8,450
D. Rs. 9,100
E. None of these
Solution
Let initial investments be::
X = 4a
Y = 7a
Z = 6a
Time for each partner:
X and Z kept full investment for 12 months
Y invested 7a for 6 months, then reduced his investment
Y’s remaining capital after 6 months:
Combined capital of X and Z = 4a + 6a = 10a
1/3 of that = (1/3) × 10a = 10a ÷ 3
So, Y invested 10a ÷ 3 for the remaining 6 months
Calculate effective capital × time (investment months):
X: 4a × 12 = 48a
Z: 6a × 12 = 72a
Y: 7a × 6 = 42a, and (10a ÷ 3) × 6 = 60a ÷ 3 = 20a
Total for Y = 42a + 20a = 62a
Total profit ratio:
X : Y : Z = 48a : 62a : 72a
⇒ Divide by 2: 24 : 31 : 36
Total parts = 24 + 31 + 36 = 91
Total Profit = ₹19,500
⇒ Y’s share = (31 ÷ 91) × 18200 = ₹6,200
Thus, the correct answer is Rs. 6,200.
33. A circle of maximum possible area is inscribed in a square. The cost of painting the area inside the circle is ₹6/m², while the cost of painting the area outside the circle (but within the square) is ₹5/m². If the total cost of painting the entire square is ₹370.3, find the side length of the square.
A. 7 m
B. 8 m
C. 9 m
D. 10 m
E. None of these
Solution
Let the side length of the square be s meters.
Area of square = s²
Radius of the inscribed circle = s/2
Area of the circle = π x (s/2)² = (π x s²) ÷ 4
Cost of painting:
Inside circle: ₹6/m²
Outside circle (within square): ₹5/m²
Total cost =
⇒ ₹6 x (π x s² ÷ 4) + ₹5 x (s² – π x s² ÷ 4)
⇒ ₹6 x (πs² ÷ 4) + ₹5 x [s² – (πs² ÷ 4)]
⇒ ₹6 x (πs² ÷ 4) + ₹5 x s² x (1 – π ÷ 4)
Given total cost = ₹370.3
Now substitute π ≈ 3.14:
⇒ 6 x (3.14 x s² ÷ 4) + 5 x s² x (1 – 3.14 ÷ 4) = 370.3
⇒ 6 x (0.785s²) + 5 x s² x (1 – 0.785)
⇒ 4.71s² + 5 x s² x 0.215 = 370.3
⇒ 4.71s² + 1.075s² = 370.3
⇒ 5.785s² = 370.3
⇒ s² = 370.3 ÷ 5.785 ≈ 64
⇒ s = √64 = 8 meters
Thus, the correct answer is 8m.
34. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
Rajat and Suman jointly acquired a 6-acre fruit orchard in the ratio of 4:2 in the year 2020 and began cultivating apples in the year 2021. In that year, Rajat, being the primary investor, gave 60 kg of apples, which was 10% of his total production for that year, to Suman. As a result, Suman’s total apple quantity increased by 30%. In the year 2022, Suman’s total apple production was 50% more than the previous year, so he returned 20% of his total apples produced quantity to Rajat. After receiving from Suman, Rajat’s total apple quantity increased by 15%. In the year 2023, both had produced an equal quantity of apples, and Rajat’s production of apples was increased by 20% over the total quantity of apples he had produced in the previous year.
Question:
What is the percentage change in the total apples produced by both Rajat and Suman combined in 2022 as compared to 2021?
A. 10%
B. 8.33%
C. 12.5%
D. 5%
E. 15%
Solution
General Solution:
Orchard Area Division
Total land = 6 acres
Rajat : Suman = 4 : 2 ⇒ 2 : 1
Apple Production in 2021:
Let Rajat’s production = R₁ kg
He gave 60 kg to Suman, which was 10% of his production
⇒ 10% of R₁ = 60 ⇒ R₁ = 600 kg
Suman got 60 kg which increased his total by 30%
⇒ 60 = 30% of S₁ ⇒ S₁ = 200 kg
2021: Rajat = 600 kg, Suman = 200 kg
2022 Production:
Suman’s 2022 production = 50% more than 2021 = 200 + 50% of 200 = 300 kg
He gives 20% of 300 = 60 kg to Rajat
Let Rajat’s 2022 own production = R₂
Total apples with Rajat = R₂ + 60 = 15% more than R₂
⇒ R₂ + 60 = R₂ + 15% of R₂ = R₂ × 1.15
⇒ R₂ + 60 = 1.15R₂ ⇒ 60 = 0.15R₂ ⇒ R₂ = 400 kg
2022: Rajat = 400 kg, Suman = 300 kg
2023 Production:
Both produced equal quantities
Rajat’s 2023 production is 20% more than previous year = 400 + 20% of 400 = 480 kg
⇒ So, Suman’s 2023 production = 480 kg
2023: Rajat = 480 kg, Suman = 480 kg
Thus:
| Year | Rajat (kg) | Suman (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 600 | 200 |
| 2022 | 400 | 300 |
| 2023 | 480 | 480 |
Calculations:
2021 total = 600 (Rajat) + 200 (Suman) = 800
2022 total = 400 (Rajat) + 300 (Suman) = 700
Change = (700 – 800) ÷ 800 × 100 = -12.5%
Thus, the correct answer is 12.5%.
35. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
Rajat and Suman jointly acquired a 6-acre fruit orchard in the ratio of 4:2 in the year 2020 and began cultivating apples in the year 2021. In that year, Rajat, being the primary investor, gave 60 kg of apples, which was 10% of his total production for that year, to Suman. As a result, Suman’s total apple quantity increased by 30%. In the year 2022, Suman’s total apple production was 50% more than the previous year, so he returned 20% of his total apples produced quantity to Rajat. After receiving from Suman, Rajat’s total apple quantity increased by 15%. In the year 2023, both had produced an equal quantity of apples, and Rajat’s production of apples was increased by 20% over the total quantity of apples he had produced in the previous year.
Question:
If in 2024, both Rajat and Suman decide to increase their production by the average annual percentage increase from 2021 to 2023, what would be the approximate total production in 2024?
A. 1056 kg
B. 1200 kg
C. 1120 kg
D. 1000 kg
E. None of these
Solution
General Solution:
Orchard Area Division
Total land = 6 acres
Rajat : Suman = 4 : 2 ⇒ 2 : 1
Apple Production in 2021:
Let Rajat’s production = R₁ kg
He gave 60 kg to Suman, which was 10% of his production
⇒ 10% of R₁ = 60 ⇒ R₁ = 600 kg
Suman got 60 kg which increased his total by 30%
⇒ 60 = 30% of S₁ ⇒ S₁ = 200 kg
2021: Rajat = 600 kg, Suman = 200 kg
2022 Production:
Suman’s 2022 production = 50% more than 2021 = 200 + 50% of 200 = 300 kg
He gives 20% of 300 = 60 kg to Rajat
Let Rajat’s 2022 own production = R₂
Total apples with Rajat = R₂ + 60 = 15% more than R₂
⇒ R₂ + 60 = R₂ + 15% of R₂ = R₂ × 1.15
⇒ R₂ + 60 = 1.15R₂ ⇒ 60 = 0.15R₂ ⇒ R₂ = 400 kg
2022: Rajat = 400 kg, Suman = 300 kg
2023 Production:
Both produced equal quantities
Rajat’s 2023 production is 20% more than previous year = 400 + 20% of 400 = 480 kg
⇒ So, Suman’s 2023 production = 480 kg
2023: Rajat = 480 kg, Suman = 480 kg
Thus:
| Year | Rajat (kg) | Suman (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 600 | 200 |
| 2022 | 400 | 300 |
| 2023 | 480 | 480 |
Calculations:
2021 total = 600 (Rajat) + 200 (Suman) = 800 kg
2023 total = 480 + 480 = 960 kg
Change over 2 years = 960 − 800 = 160 kg
Average annual % increase = [(Final − Initial)/Initial] ÷ 2 × 100
⇒ (960 − 800)/800 × 100 = 20% over 2 years ⇒ Annual average = 10%
2024 projection = 960 × (1 + 10/100) = 960 × 1.10 = 1056 kg
∴ Approximate total production in 2024 = 1056 kg
36. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
Rajat and Suman jointly acquired a 6-acre fruit orchard in the ratio of 4:2 in the year 2020 and began cultivating apples in the year 2021. In that year, Rajat, being the primary investor, gave 60 kg of apples, which was 10% of his total production for that year, to Suman. As a result, Suman’s total apple quantity increased by 30%. In the year 2022, Suman’s total apple production was 50% more than the previous year, so he returned 20% of his total apples produced quantity to Rajat. After receiving from Suman, Rajat’s total apple quantity increased by 15%. In the year 2023, both had produced an equal quantity of apples, and Rajat’s production of apples was increased by 20% over the total quantity of apples he had produced in the previous year.
Question:
What was the ratio of Rajat’s total apples (own production + received) to Suman’s total apples (after giving) in 2022?
A. 17:9
B. 15:8
C. 19:10
D. 23:12
E. None of these
Solution
General Solution:
Orchard Area Division
Total land = 6 acres
Rajat : Suman = 4 : 2 ⇒ 2 : 1
Apple Production in 2021:
Let Rajat’s production = R₁ kg
He gave 60 kg to Suman, which was 10% of his production
⇒ 10% of R₁ = 60 ⇒ R₁ = 600 kg
Suman got 60 kg which increased his total by 30%
⇒ 60 = 30% of S₁ ⇒ S₁ = 200 kg
2021: Rajat = 600 kg, Suman = 200 kg
2022 Production:
Suman’s 2022 production = 50% more than 2021 = 200 + 50% of 200 = 300 kg
He gives 20% of 300 = 60 kg to Rajat
Let Rajat’s 2022 own production = R₂
Total apples with Rajat = R₂ + 60 = 15% more than R₂
⇒ R₂ + 60 = R₂ + 15% of R₂ = R₂ × 1.15
⇒ R₂ + 60 = 1.15R₂ ⇒ 60 = 0.15R₂ ⇒ R₂ = 400 kg
2022: Rajat = 400 kg, Suman = 300 kg
2023 Production:
Both produced equal quantities
Rajat’s 2023 production is 20% more than previous year = 400 + 20% of 400 = 480 kg
⇒ So, Suman’s 2023 production = 480 kg
2023: Rajat = 480 kg, Suman = 480 kg
Thus:
| Year | Rajat (kg) | Suman (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 600 | 200 |
| 2022 | 400 | 300 |
| 2023 | 480 | 480 |
Calculations:
2022 Apple Quantities:
Rajat’s own production in 2022 = 400 kg
He received 60 kg from Suman
Total apples with Rajat = 400 + 60 = 460 kg
Suman’s production = 300 kg
He gave 20% of 300 = 60 kg to Rajat
Total apples left with Suman = 300 − 60 = 240 kg
Required Ratio:
⇒ Rajat : Suman = 460 : 240 ⇒ 23 : 12
Thus, the correct answer is 23 : 12.
37. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
Rajat and Suman jointly acquired a 6-acre fruit orchard in the ratio of 4:2 in the year 2020 and began cultivating apples in the year 2021. In that year, Rajat, being the primary investor, gave 60 kg of apples, which was 10% of his total production for that year, to Suman. As a result, Suman’s total apple quantity increased by 30%. In the year 2022, Suman’s total apple production was 50% more than the previous year, so he returned 20% of his total apples produced quantity to Rajat. After receiving from Suman, Rajat’s total apple quantity increased by 15%. In the year 2023, both had produced an equal quantity of apples, and Rajat’s production of apples was increased by 20% over the total quantity of apples he had produced in the previous year.
Question:
If the apple price is ₹50 per kg in 2021 and increases by 10% each subsequent year, what is the total revenue earned by Suman over the 3 years (assume that Suman sold his apples after the transactions)?
A. ₹48,530
B. ₹59,810
C. ₹55,240
D. ₹52,450
E. None of these
Solution
General Solution:
Orchard Area Division
Total land = 6 acres
Rajat : Suman = 4 : 2 ⇒ 2 : 1
Apple Production in 2021:
Let Rajat’s production = R₁ kg
He gave 60 kg to Suman, which was 10% of his production
⇒ 10% of R₁ = 60 ⇒ R₁ = 600 kg
Suman got 60 kg which increased his total by 30%
⇒ 60 = 30% of S₁ ⇒ S₁ = 200 kg
2021: Rajat = 600 kg, Suman = 200 kg
2022 Production:
Suman’s 2022 production = 50% more than 2021 = 200 + 50% of 200 = 300 kg
He gives 20% of 300 = 60 kg to Rajat
Let Rajat’s 2022 own production = R₂
Total apples with Rajat = R₂ + 60 = 15% more than R₂
⇒ R₂ + 60 = R₂ + 15% of R₂ = R₂ × 1.15
⇒ R₂ + 60 = 1.15R₂ ⇒ 60 = 0.15R₂ ⇒ R₂ = 400 kg
2022: Rajat = 400 kg, Suman = 300 kg
2023 Production:
Both produced equal quantities
Rajat’s 2023 production is 20% more than previous year = 400 + 20% of 400 = 480 kg
⇒ So, Suman’s 2023 production = 480 kg
2023: Rajat = 480 kg, Suman = 480 kg
Thus:
| Year | Rajat (kg) | Suman (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 600 | 200 |
| 2022 | 400 | 300 |
| 2023 | 480 | 480 |
Calculations:
Apple prices per year:
2021: ₹50 per kg
2022: ₹50 + 10% = ₹55 per kg
2023: ₹55 + 10% = ₹60.5 per kg
Suman’s final apple quantity each year
2021: He had 200 kg + 60 kg from Rajat = 260 kg
2022: Produced 300 kg – gave 60 kg to Rajat = 240 kg
2023: Produced = 480 kg
Calculate Revenue for each year:
2021: 260 kg × ₹50 = ₹13,000
2022: 240 kg × ₹55 = ₹13,200
2023: 480 kg × ₹60.5 = ₹29,040
Total Revenue = 13,000 + 13,200 + 29,040 = ₹55,240
Thus, the correct answer is ₹55,240.
38. Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the questions.
Rajat and Suman jointly acquired a 6-acre fruit orchard in the ratio of 4:2 in the year 2020 and began cultivating apples in the year 2021. In that year, Rajat, being the primary investor, gave 60 kg of apples, which was 10% of his total production for that year, to Suman. As a result, Suman’s total apple quantity increased by 30%. In the year 2022, Suman’s total apple production was 50% more than the previous year, so he returned 20% of his total apples produced quantity to Rajat. After receiving from Suman, Rajat’s total apple quantity increased by 15%. In the year 2023, both had produced an equal quantity of apples, and Rajat’s production of apples was increased by 20% over the total quantity of apples he had produced in the previous year.
Question:
In which year was the percentage difference between Rajat’s and Suman’s apple production the greatest?
A. 2021
B. 2022
C. 2023
D. Both (1) and (2)
E. Equal in all years
Solution
General Solution:
Orchard Area Division
Total land = 6 acres
Rajat : Suman = 4 : 2 ⇒ 2 : 1
Apple Production in 2021:
Let Rajat’s production = R₁ kg
He gave 60 kg to Suman, which was 10% of his production
⇒ 10% of R₁ = 60 ⇒ R₁ = 600 kg
Suman got 60 kg which increased his total by 30%
⇒ 60 = 30% of S₁ ⇒ S₁ = 200 kg
2021: Rajat = 600 kg, Suman = 200 kg
2022 Production:
Suman’s 2022 production = 50% more than 2021 = 200 + 50% of 200 = 300 kg
He gives 20% of 300 = 60 kg to Rajat
Let Rajat’s 2022 own production = R₂
Total apples with Rajat = R₂ + 60 = 15% more than R₂
⇒ R₂ + 60 = R₂ + 15% of R₂ = R₂ × 1.15
⇒ R₂ + 60 = 1.15R₂ ⇒ 60 = 0.15R₂ ⇒ R₂ = 400 kg
2022: Rajat = 400 kg, Suman = 300 kg
2023 Production:
Both produced equal quantities
Rajat’s 2023 production is 20% more than previous year = 400 + 20% of 400 = 480 kg
⇒ So, Suman’s 2023 production = 480 kg
2023: Rajat = 480 kg, Suman = 480 kg
Thus:
| Year | Rajat (kg) | Suman (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 600 | 200 |
| 2022 | 400 | 300 |
| 2023 | 480 | 480 |
Calculations:
Calculate percentage difference = |R – S| ÷ ((R + S)/2) × 100
2021: |600 – 200| ÷ 400 × 100 = 400 ÷ 400 × 100 = 100%
2022: |400 – 300| ÷ 350 × 100 ≈ 28.57%
2023: |480 – 480| ÷ 480 × 100 = 0%
Thus, the correct answer is 2021.
Short trick:
The highest difference is in 2021, i.e, 400.
39. The cost price of two articles P and Q are Rs “y” and Rs ” (2y – 1000) ” respectively. If the shopkeeper sold article P at a profit of 20% and article Q was sold at a profit of 25%. If he allowed a discount of 20% on each of article P and Q. The sum of the marked prices for both articles P and Q is Rs 10000, then find the value of “y”.
A. Rs. 2000
B. Rs. 2250
C. Rs. 2500
D. Rs. 2750
E. Rs. 3000
Solution
Let cost price (CP) of:
Article P = y
Article Q = (2y – 1000)
Marked Price (MP):
P is sold at 20% profit, so SP = y × 1.20
Q is sold at 25% profit, so SP = (2y – 1000) × 1.25
Also, 20% discount on both ⇒ SP = MP × 0.80 ⇒ MP = SP ÷ 0.80
MP of P:
⇒ MPP = (y × 1.20) ÷ 0.80 = y × 1.5
MP of Q:
⇒ MPQ = [(2y – 1000) × 1.25] ÷ 0.80 = (2y – 1000) × 1.5625
Total MP = 10000:
⇒ y × 1.5 + (2y – 1000) × 1.5625 = 10000
⇒ 1.5y + 1.5625 × 2y – 1.5625 × 1000 = 10000
⇒ 1.5y + 3.125y – 1562.5 = 10000
⇒ 4.625y = 10000 + 1562.5 = 11562.5
⇒ y = 11562.5 ÷ 4.625 = 2500
Thus, the correct answer is Rs. 2500.
40. Pipe P and Pipe Q can fill a tank in 18 hours and 12 hours respectively. If the ratio of the combined efficiency of Pipe P and Q to that of Pipe S alone is 5:4, find the time taken by Pipe S alone to fill the same tank.
A. 30 hours
B. 25 hours
C. 20 hours
D. 15 hours
E. None of these
Solution
Find efficiency of Pipe P and Pipe Q:
Efficiency of P = 1/18 (portion of tank filled per hour)
Efficiency of Q = 1/12
Combined efficiency of P and Q = 1/18 + 1/12
⇒ LCM of 18 and 12 = 36
⇒ (2 + 3)/36 = 5/36
Let efficiency of Pipe S = x
Given: (P + Q) : S = 5 : 4
⇒ (5/36) ÷ x = 5 ÷ 4
⇒ (5/36x) = 5/4
⇒ Cross-multiply: 5 × 4 = 5 × 36x
⇒ 20 = 180x
⇒ x = 20 ÷ 180 = 1/9
Time taken by Pipe S = 1 ÷ (1/9) = 9 hours
Thus, the correct answer is None of these.
41. Rahul invested Rs. (y + 2000) in HDFC Bank at 12% p.a. and Rs. “y” in ICICI Bank at 8% p.a. simple interest. After 3 years, he received a total interest of Rs. 3840 from both banks. Find the amount he received from HDFC Bank after 3 years?
A. Rs. 12,880
B. Rs. 14,242
C. Rs. 9,792
D. Rs. 6,161
E. Rs. 5,634
Solution
Let the principal amounts be:
HDFC = (y + 2000), Rate = 12%, Time = 3 years
ICICI = y, Rate = 8%, Time = 3 years
Use the simple interest formula:
⇒ SI = (P × R × T) ÷ 100
HDFC Interest: ⇒ (y + 2000) × 12 × 3 ÷ 100 = (36(y + 2000)) ÷ 100
ICICI Interest: ⇒ y × 8 × 3 ÷ 100 = (24y) ÷ 100
Total Interest = ₹3840
⇒ [(36(y + 2000)) + 24y] ÷ 100 = 3840
⇒ [36y + 72000 + 24y] ÷ 100 = 3840
⇒ (60y + 72000) ÷ 100 = 3840
⇒ 60y + 72000 = 384000
⇒ 60y = 384000 – 72000 = 312000
⇒ y = 312000 ÷ 60 = 5200
HDFC principal = y + 2000 = 5200 + 2000 = ₹7200
Interest from HDFC: ⇒ 7200 × 12 × 3 ÷ 100 = ₹2592
Final Amount from HDFC = Principal + Interest = 7200 + 2592 = ₹9792
Thus, the correct answer is 9792.
42. In a company, the total number of staff is “y”. Among them, 75% of the staff are engineers and the rest are non-engineers. If 40% of the engineers and 30% of the non-engineers received a bonus, and a total of 1560 staff did not receive a bonus, then find the value of “y”?
A. 1258
B. 2496
C. 2266
D. 2340
E. None of these
Solution
Assume total staff = y
Engineers = 75% of y = 0.75y
Non-engineers = 25% of y = 0.25y
Bonus distribution:
Engineers who did NOT get bonus = 60% of engineers = 0.6 × 0.75y = 0.45y
Non-engineers who did NOT get bonus = 70% of non-engineers = 0.7 × 0.25y = 0.175y
Total who did NOT receive bonus = 0.45y + 0.175y = 0.625y
Given that 1560 staff didn’t receive bonus:
⇒ 0.625y = 1560
⇒ y = 1560 ÷ 0.625 = 2496
Thus, the correct answer is 2496.
43. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
12, 30, (?), 132, 182, 306
A. 61
B. 55
C. 60
D. 56
E. 65
Solution
Given Series:
12, 30, (?), 132, 182, 306
The logic followed here is as follows:
⇒ 3 + (3)2 = 12
⇒ 5 + (5)2 = 30
⇒ 7 + (7)2 = 56
⇒ 11 + (11)2 = 132
⇒ 13 + (13)2 = 182
⇒ 17 + (17)2 = 306
Hence, 56 will come in the place of (?).
44. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
133, 124, 129, 136, 145, (?)
A. 156
B. 334
C. 333
D. 313
E. 323
Solution
Given Series:
133, 124, 129, 136, 145, (?)
The logic followed here is as follows:
⇒ 112 + 12 = 133
⇒ 102 + 24 = 124
⇒ 92 + 48 = 129
⇒ 82 + 72 = 136
⇒ 72 + 96 = 145
⇒ 62 + 120 = 156
Hence, 156 will come in the place of (?).
45. What should come in the place of (?) in the given series?
24, 44, 128, 508, (?), 15212
A. 2566
B. 2166
C. 2536
D. 2546
E. 2666
Solution
Given Series:
24, 44, 128, 508, (?), 15212
The logic followed here is as follows:
⇒ 24 x 2 – 4 = 44
⇒ 44 x 3 – 4 = 128
⇒ 128 x 4 – 4 = 508
⇒ 508 x 5 – 4 = 2536
⇒ 2536 x 6 – 4 = 15212
Hence, 2536 will come in the place of (?).
46. What should come in place of (?) in the given series
9, 10, 22, 69, (?), 1405
A. 281
B. 282
C. 283
D. 284
E. 280
Solution
The series follows the following pattern
⇒ 9
⇒ 9 × 1 + 1 = 10
⇒ 10 × 2 + 2 = 22
⇒ 22 × 3 + 3 = 69
⇒ 69 × 4 + 4 = 280
⇒ 280 × 5 + 5 = 1405
Hence, the correct answer will be 280.
47. What will come in the place of question mark in the following number series ?
32.5 , 70 , ? , 160 , 212.5
A. 125.5
B. 112.5
C. 100
D. 102.5
E. 120.5
Solution
Given:
32.5 , 70 , ? , 160 , 212.5
Calculation:
Here the logic follows as,
Hence the third term will be 112.5
∴∴ The correct answer is 112.5.
48. Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The line graph given below shows the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘A’, the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘B’ and the number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ (in ’00) in five different years
Total number of machines manufactured in a year = Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’
.
Question:
What is the difference between the total number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ in 2020 and 2021 together and the total number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ in 2018 and 2019 together?
A. 4000
B. 4100
C. 4200
D. 4300
E. 4400
Solution
Given:
Total number of machines manufactured in a year = Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’
So,
100% = Percentage of Machines manufactured by ‘A’ + Percentage of Machines manufactured by ‘B’ + Percentage of Machines manufactured by ‘C’
or
⇒ Percentage of Machines manufactured by ‘C’ = 100% – (Percentage of Machines manufactured by ‘A’ + Percentage of Machines manufactured by ‘B’)
Example, in 2018,
The percentage of Machines manufactured by ‘A’ = 30%
The percentage of Machines manufactured by ‘B’ = 25%
So,
The percentage of Machines manufactured by ‘C’ = 100% – (30% + 25%) = 45%
So, 45% = 7200
Total Machine Production in 2018 = 100% = 16000
same as,
| Year | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ | A% | B% | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 7200 | 30 | 25 | (7200/45) × 30 = 4800 | (7200/45) × 25 = 4000 |
| 2019 | 7700 | 25 | 20 | (7700/55) × 25 = 3500 | (7700/55) × 20 = 2800 |
| 2020 | 7200 | 28 | 24 | (7200/48) × 28 = 4200 | (7200/48) × 24 = 3600 |
| 2021 | 5400 | 30 | 25 | (5400/45) × 30 = 3600 | (5400/45) × 25 = 3000 |
| 2022 | 6400 | 35 | 25 | (6400/40) × 35 = 5600 | (6400/40) × 25 = 4000 |
The total number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ in 2020 and 2021 together = 7200 + 5400 = 12600
The total number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ in 2018 and 2019 together = 4800 + 3500 = 8300
Required difference = 12600 – 8300 = 4300
Hence, the correct answer is 4300.
49. Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The line graph given below shows the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘A’, the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘B’ and the number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ (in ’00) in five different years
Total number of machines manufactured in a year = Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’
.

Question:
If the number of machines manufactured by company ‘D’ in 2018 is 600 less than that in 2017 and the number of machines manufactured by company ‘D’ in 2018 is 70% more than that by company ‘B’ in the same year then find the average number of total machines manufactured by company ‘D’ in 2017 and 2018 together?
A. 7100
B. 7200
C. 7300
D. 7400
E. 7500
Solution
| Year | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ | A% | B% | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 7200 | 30 | 25 | (7200/45) × 30 = 4800 | (7200/45) × 25 = 4000 |
| 2019 | 7700 | 25 | 20 | (7700/55) × 25 = 3500 | (7700/55) × 20 = 2800 |
| 2020 | 7200 | 28 | 24 | (7200/48) × 28 = 4200 | (7200/48) × 24 = 3600 |
| 2021 | 5400 | 30 | 25 | (5400/45) × 30 = 3600 | (5400/45) × 25 = 3000 |
| 2022 | 6400 | 35 | 25 | (6400/40) × 35 = 5600 | (6400/40) × 25 = 4000 |
The number of machines manufactured by company ‘D’ in 2018 = 1.70 × 4000 = 6800
The number of machines manufactured by company ‘D’ in 2017 = 6800 + 600 = 7400
Required average = (6800 + 7400)/2 = 7100
Hence, the correct answer is 7100.
50. Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The line graph given below shows the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘A’, the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘B’ and the number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ (in ’00) in five different years
Total number of machines manufactured in a year = Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’
.

Question:
If the number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ in 2018 and 2020 is 75% and 60% less than that of company ‘E’ in the same year respectively then find the difference between the number of machines manufactured by company ‘E’ in 2018 and 2020?
A. 6000
B. 7000
C. 8000
D. 9000
E. 10000
Solution
| Year | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ | A% | B% | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 7200 | 30 | 25 | (7200/45) × 30 = 4800 | (7200/45) × 25 = 4000 |
| 2019 | 7700 | 25 | 20 | (7700/55) × 25 = 3500 | (7700/55) × 20 = 2800 |
| 2020 | 7200 | 28 | 24 | (7200/48) × 28 = 4200 | (7200/48) × 24 = 3600 |
| 2021 | 5400 | 30 | 25 | (5400/45) × 30 = 3600 | (5400/45) × 25 = 3000 |
| 2022 | 6400 | 35 | 25 | (6400/40) × 35 = 5600 | (6400/40) × 25 = 4000 |
The number of machines manufactured by company ‘E’ in 2018 = (4000/25) × 100 = 16000
The number of machines manufactured by company ‘E’ in 2020 = (3600/40) × 100 = 9000
Required difference = 16000 – 9000 = 7000
Hence, the correct answer is 7000.
51. Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The line graph given below shows the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘A’, the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘B’ and the number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ (in ’00) in five different years
Total number of machines manufactured in a year = Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’
.

Question:
If the number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ in 2023 and 2024 is 25% and 40% more than that in the previous year respectively then find the sum of the total number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ in 2023 and 2024 together?
A. 16200
B. 16400
C. 16600
D. 16800
E. 17000
Solution
| Year | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ | A% | B% | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 7200 | 30 | 25 | (7200/45) × 30 = 4800 | (7200/45) × 25 = 4000 |
| 2019 | 7700 | 25 | 20 | (7700/55) × 25 = 3500 | (7700/55) × 20 = 2800 |
| 2020 | 7200 | 28 | 24 | (7200/48) × 28 = 4200 | (7200/48) × 24 = 3600 |
| 2021 | 5400 | 30 | 25 | (5400/45) × 30 = 3600 | (5400/45) × 25 = 3000 |
| 2022 | 6400 | 35 | 25 | (6400/40) × 35 = 5600 | (6400/40) × 25 = 4000 |
The number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ in 2023 = 5600 × 1.25 = 7000
The number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ in 2024 = 7000 × 1.40 = 9800
Required total = 7000 + 9800 = 16800
Hence, the correct answer is 16800.
52. Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The line graph given below shows the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘A’, the percentage of the machines manufactured by company ‘B’ and the number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ (in ’00) in five different years
Total number of machines manufactured in a year = Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ + Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’
.

Question:
The total number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ in 2019 and 2020 together is approximately what percentage more/less than the total number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ in 2018 and 2021 together?
A. 73%
B. 74%
C. 75%
D. 76%
E. 77%
Solution
| Year | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ | A% | B% | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ | Number of machines manufactured by company ‘B’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 7200 | 30 | 25 | (7200/45) × 30 = 4800 | (7200/45) × 25 = 4000 |
| 2019 | 7700 | 25 | 20 | (7700/55) × 25 = 3500 | (7700/55) × 20 = 2800 |
| 2020 | 7200 | 28 | 24 | (7200/48) × 28 = 4200 | (7200/48) × 24 = 3600 |
| 2021 | 5400 | 30 | 25 | (5400/45) × 30 = 3600 | (5400/45) × 25 = 3000 |
| 2022 | 6400 | 35 | 25 | (6400/40) × 35 = 5600 | (6400/40) × 25 = 4000 |
The total number of machines manufactured by company ‘C’ in 2019 and 2020 together = 7700 + 7200 = 14900
The total number of machines manufactured by company ‘A’ in 2018 and 2021 together = 4800 + 3600 = 8400
Required% = [(14900 – 8400)/8400] × 100 = 77.38% = 77% approx
Hence, the correct answer is 77%.
53. Directions: Below question is followed by two statements labeled I and II. Decide if these statements are sufficient to conclusively answer the question. Choose the appropriate answer from the options given below:
What is the difference between the amounts invested in Scheme X and Scheme Y?
Statement I:
Rahul invests a total of ₹10,000 in Scheme X (for 2 years) and Scheme Y (for 3 years). Scheme Y offers 12% simple interest per annum.
Statement II:
Scheme X offers 8% compound interest annually. The total interest earned from both schemes after their respective periods is ₹2,390.
A. The data in Statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question, while the data in Statement II alone is not sufficient.
B. The data in Statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question, while the data in Statement I alone is not sufficient.
C. The data either in Statement I alone or in Statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question.
D. The data given in both Statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
E. The data given in both Statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
Solution
Let: x = amount invested in Scheme X 10000 – x = amount invested in Scheme Y
From Statement I alone: We only know x + (10000 – x) = 10000, and Scheme Y’s rate and period, but no interest amounts ⇒ cannot find x.
From Statement II alone: We know Scheme X rate (8% compounded annually for 2 years) and Scheme Y rate (12% simple for 3 years), and total interest = ₹2390, but we don’t know the total principal (10000) ⇒ cannot determine x.
Using I and II together:
Interest from X = x × [(1.08)² – 1] = 0.1664x
Interest from Y = (10000 – x) × (12% × 3) = 0.36 (10000 – x) = 3600 – 0.36x
Total interest = 0.1664x + (3600 – 0.36x) = 3600 – 0.1936x = 2390 ⇒ 3600 – 2390 = 0.1936x ⇒ 1210 = 0.1936x ⇒ x = 6250
⇒ Amount in Y = 10000 – 6250 = 3750
⇒ Difference = 6250 – 3750 = ₹2500
Thus, the data given in both Statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
54. Directions: Below question is followed by two statements labeled I and II. Decide if these statements are sufficient to conclusively answer the question. Choose the appropriate answer from the options given below:
The total number of employees in Companies X and Y is equal. Find the number of female employees in X and Y combined?
Statements:
I: The male-to-female ratio in X is 4:3 and in Y is 5:2. The ratio of junior to senior male employees in X is 3:5.
II: The ratio of junior to senior female employees in Y is 1:2. The sum of senior male employees in X and senior female employees in Y is 690.
A. Statement I alone is sufficient, but Statement II alone is not sufficient
B. Statement II alone is sufficient, but Statement I alone is not sufficient
C. Either statement alone is sufficient
D. Both statements together are necessary
E. Both statements together are not sufficient
Solution
Let that total number be T.
Statement I:
Male : Female in X = 4 : 3 → So in X, male = 4x and female = 3x ⇒ total in X = 7x
Male : Female in Y = 5 : 2 → So in Y, male = 5y and female = 2y ⇒ total in Y = 7y
Now, we are given that total employees in X = total employees in Y
⇒ 7x = 7y ⇒ x = y
Now:
Female in X = 3x
Female in Y = 2x (since y = x)
Total females = 3x + 2x = 5x
But x is unknown.
Even the ratio of junior to senior male employees in X (3:5) is irrelevant here unless we know a value.
So, Statement I alone is NOT sufficient.
Statement II:
Ratio of junior to senior female in Y = 1:2
Let junior female = a, senior female = 2a ⇒ total female in Y = a + 2a = 3a
Senior male in X + senior female in Y = 690
We don’t know total male in X or how many are senior → cannot extract female number in X.
Also, we cannot connect this info to total employees (T) or get specific values.
So, Statement II alone is NOT sufficient.
Now combine both statements:
From Statement I:
Female in X = 3x
Female in Y = 2x
Total females = 5x
From Statement II:
Senior male in X + senior female in Y = 690
→ From Statement I, male in X = 4x
→ Ratio of junior to senior male = 3:5
⇒ So, senior male in X = 5 parts out of (3+5) = 5/8 of 4x
⇒ Senior male in X = (5/8) × 4x = (20x)/8 = 2.5x
Female in Y = 2x
→ From Statement II, ratio of junior:senior = 1:2 ⇒ senior = 2 parts out of 3 ⇒ 2/3 of 2x = (4x)/3
Now:
2.5x + (4x)/3 = 690
(7.5x + 4x)/3 = 690
(11.5x)/3 = 690
11.5x = 2070
x = 180
Now we can compute:
Female in X = 3x = 540
Female in Y = 2x = 360
Total females = 900
Thus, Both statements together are necessary.
55. Directions: Below question is followed by two statements labeled I and II. Decide if these statements are sufficient to conclusively answer the question. Choose the appropriate answer from the options given below:
There are four consecutive even integers. Find the average of these integers?
Statement I: The largest number is 6 more than the smallest number.
Statement II: The second smallest number is 20% less than the third number.
A. The data in statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement II alone is not sufficient
B. The data in statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement I alone is not sufficient
C. The data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question
D. The data given in both statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question
E. The data given in both statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question
Solution
Let the four consecutive even integers be:
x, (x + 2), (x + 4), (x + 6)
The average of these numbers =
⇒ [x + (x + 2) + (x + 4) + (x + 6)] ÷ 4 = (4x + 12) ÷ 4 = x + 3
Statement I: The largest number is 6 more than the smallest number.
⇒ (x + 6) = x + 6 ⇒ Always true for consecutive even numbers.
This confirms the numbers are in the pattern we assumed, but does not give the value of x.
Thus, Not sufficient to find the average.
Statement II: The second smallest number is 20% less than the third number.
Second smallest = (x + 2)
Third number = (x + 4)
⇒ (x + 2) = (x + 4) – 20% of (x + 4)
⇒ x + 2 = 0.8(x + 4)
⇒ x + 2 = 0.8x + 3.2
⇒ x – 0.8x = 3.2 – 2 ⇒ 0.2x = 1.2 ⇒ x = 6
Now we can find all the numbers:
⇒ x = 6 ⇒ Numbers: 6, 8, 10, 12
⇒ Average = (6 + 8 + 10 + 12) ÷ 4 = 36 ÷ 4 = 9
Thus, Sufficient to find the average.
Therefore, the data in statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement I alone is not sufficient.
56. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
2/3 of 48% of 600 – 2/3 of 33% of 700 = 2 × ?
A. 17
B. 21
C. 12
D. 13
E. 19
Solution
Given:
2/3 of 48% of 600 – 2/3 of 33% of 700 = 2 × ?
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
Calculation:
Let us solve step by step
⇒ 2/3 of 48% of 600 – 2/3 of 33% of 700 = 2 × ?
⇒ 32% of 600 – 22% of 700 = 2 × ?
⇒ (32/100) of 600 – (22/100) of 700 = 2 × ?
⇒ 192 – 154 = 2 × ?
⇒ ? = 38/2
⇒ ? = 19
∴ 19 will come in the place of ?.
57. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
34 + 24 ÷ [170 – {26 × 6 + (32 – 5 × 6)}] = ?
A. 36
B. 40
C. 32
D. 46
E. 26
Solution
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:
Calculation:
34 + 24 ÷ [170 – {26 × 6 + (32 – 5 × 6)}] = ?
⇒ 34 + 24 ÷ [170 – {26 × 6 + (32 – 30)}] = ?
⇒ 34 + 24 ÷ [170 – {156 + 2}] = ?
⇒ 34 + 24 ÷ [170 – 158] = ?
⇒ 34 + 24 ÷ 12 = ?
⇒ 34 + 2 = ?
⇒ 36 = ?
∴ The value of ? is 36
58. What will come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
33.33% of 168 + 137.5% of 216 – 8.33% of ? = 182182
A. 344
B. 349
C. 325
D. 348
E. 341
Solution
Given:
33.33% of 168 + 137.5% of 216 – 8.33% of ? = 182182
Concept used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
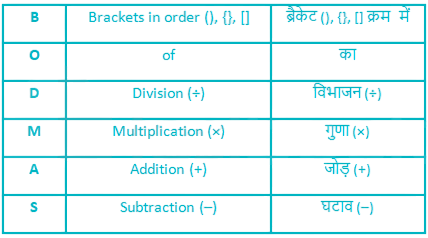
33.33% = 1/3
137.5% = 11/8
8.33% = 1/12
Calculation:
33.33% of 168 + 137.5% of 216 – 8.33% of ? = 182182
⇒ 1/3 × 168 + 11/8 × 216 – 1/12 × ? = 324
⇒ 56 + 297 – 1/12 × ? = 324
⇒ 353 – 1/12 × ? = 324
⇒ – 1/12 × ? = 324 – 353
⇒ – 1/12 × ? = – 29
⇒ 1/12 × ? = 29
⇒ ? = 29 × 12
⇒ ? = 348
∴ The value of ? is 348.
59. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
(16.67% of 4446 × 1292) ÷ (37.5% of 2584) = ?3 – 343
A. 15
B. 11
C. 24
D. 14
E. 16
Solution
Concept:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,
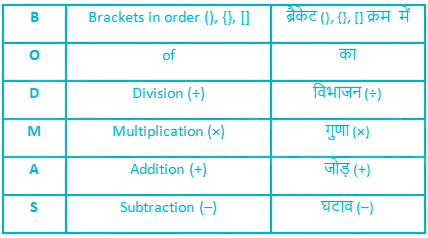
Calculations:
The given expression is:
(16.67% of 4446 × 1292) ÷ (37.5% of 2584) = ?3 – 343
⇒ (4446 × 1/6 × 1292) ÷ (2584 × 3/8) = ?3 – 343
⇒ 741 × 1292 ÷ (323 × 3) = ?3 – 343
⇒ 247 × 4 + 343 = ?3
⇒ 988 + 343 = ?3
⇒ ?3 = 1331
⇒ ? = 11
∴ The correct answer is 11.
60. What will come in place of the question mark?
40 × 25 + 1000 ÷ 5 – {2 × (25 ÷ ?)} = 1100
A. 0.2
B. 0.55
C. 0.45
D. 0.5
E. 0.6
Solution
Concept used:
We have to follow the BODMAS rule.
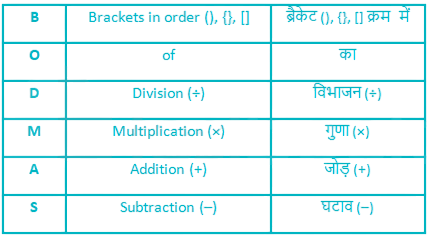
Calculation:
⇒ 1000 + 200 – {2 × (25 ÷ ?)} = 1100
⇒ 1200 – {2 × (25 ÷ ?)} = 1100
⇒ 1200 – 1100 = {2 × (25 ÷ ?)}
⇒ 100 = 2 × (25 ÷ ?)
⇒ 50 = 25 ÷ ?
⇒ ? = 0.5
∴ The required value of ? is 0.5
61. Comprehension:(Que No. 31 – 35)
Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The given pie chart shows the distribution (either in percentage or actual value) of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by a vehicle company in five different months out of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in the given five months together.
Note: Total number of helmets sold in a given month = Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold + Number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold
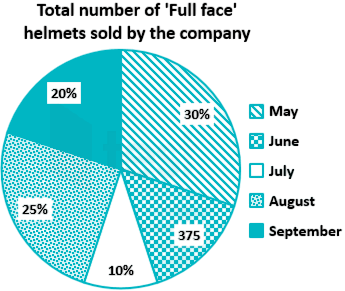
Question:
Total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in May and July together is how much percent of the number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in September?
A. 100%
B. 125%
C. 150%
D. 175%
E. 200%
Solution
Let the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 100%
ATQ, 30% + 375 + 10% + 25% + 20% = 100%
⇒ 15% = 375
⇒ 1% = 25
The total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 2500
Putting all the given information in a table form we get
| Month | Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold |
|---|---|
| May | 30 × 25 = 750 |
| June | 375 |
| July | 10 × 25 = 250 |
| August | 25 × 25 = 625 |
| September | 20 × 25 = 500 |
Total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in May and July together = 750 + 250 = 1000
Required% = (1000/500) × 100 = 200%
Hence, the correct answer is 200%.
62. Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The given pie chart shows the distribution (either in percentage or actual value) of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by a vehicle company in five different months out of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in the given five months together.
Note: Total number of helmets sold in a given month = Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold + Number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold
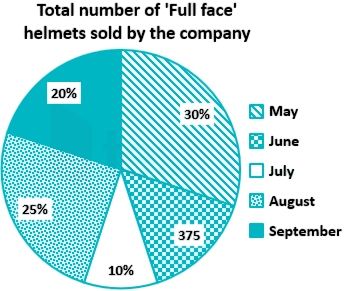
Question:
The number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold in June is 80% more than the number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in the same month. Find the total number of helmets sold in June.
A. 950
B. 1050
C. 1150
D. 1250
E. 1350
Solution
Let the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 100%
ATQ, 30% + 375 + 10% + 25% + 20% = 100%
⇒ 15% = 375
⇒ 1% = 25
The total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 2500
Putting all the given information in a table form we get
| Month | Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold |
|---|---|
| May | 30 × 25 = 750 |
| June | 375 |
| July | 10 × 25 = 250 |
| August | 25 × 25 = 625 |
| September | 20 × 25 = 500 |
Number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold in June = 375 × 1.80 = 675
Total number of helmets sold in June = 375 + 675 = 1050
Hence, the correct answer is 1050.
63. Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The given pie chart shows the distribution (either in percentage or actual value) of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by a vehicle company in five different months out of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in the given five months together.
Note: Total number of helmets sold in a given month = Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold + Number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold
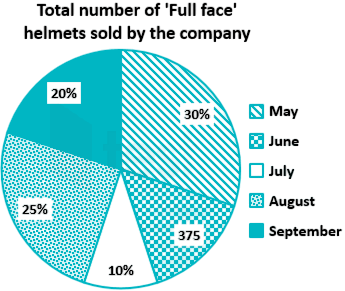
Question:
If the ratio of the number of ‘Full face’ and ‘Half face’ helmets sold in August is 25 : 22 respectively, then the number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold in August is how many more than the number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in September?
A. 50
B. 75
C. 100
D. 125
E. 150
Solution
Let the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 100%
ATQ, 30% + 375 + 10% + 25% + 20% = 100%
⇒ 15% = 375
⇒ 1% = 25
The total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 2500
Putting all the given information in a table form we get
| Month | Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold |
|---|---|
| May | 30 × 25 = 750 |
| June | 375 |
| July | 10 × 25 = 250 |
| August | 25 × 25 = 625 |
| September | 20 × 25 = 500 |
Number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold in August = (22/25) × 625 = 550
Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in September = 500
Required difference = 550 – 500 = 50
Hence, the correct answer is 50.
64. Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The given pie chart shows the distribution (either in percentage or actual value) of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by a vehicle company in five different months out of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in the given five months together.
Note: Total number of helmets sold in a given month = Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold + Number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold
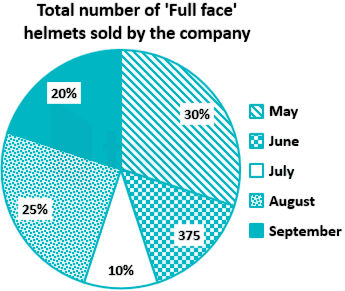
Question:
The number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold in May is 120 less than the number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in the same month while the number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold in July is 150 more than that of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in the same month. Find the average number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold in May and July together?
A. 515
B. 525
C. 535
D. 545
E. 555
Solution
Let the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 100%
ATQ, 30% + 375 + 10% + 25% + 20% = 100%
⇒ 15% = 375
⇒ 1% = 25
The total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 2500
Putting all the given information in a table form we get
| Month | Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold |
|---|---|
| May | 30 × 25 = 750 |
| June | 375 |
| July | 10 × 25 = 250 |
| August | 25 × 25 = 625 |
| September | 20 × 25 = 500 |
Number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold in May = 750 – 120 = 630
Number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold in July = 250 + 150 = 400
Required average = (630 + 400)/2 = 515
Hence, the correct answer is 515.
65. Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The given pie chart shows the distribution (either in percentage or actual value) of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by a vehicle company in five different months out of the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in the given five months together.
Note: Total number of helmets sold in a given month = Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold + Number of ‘Half face’ helmets sold
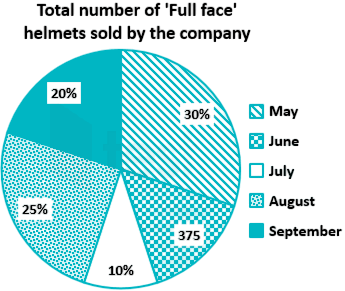
Question:
In October, the number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold is 35% more than the number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in September. Find the number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in October?
A. 550
B. 600
C. 625
D. 675
E. 700
Solution
Let the total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 100%
ATQ, 30% + 375 + 10% + 25% + 20% = 100%
⇒ 15% = 375
⇒ 1% = 25
The total number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold by the company in all given five months together = 2500
Putting all the given information in a table form we get
| Month | Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold |
|---|---|
| May | 30 × 25 = 750 |
| June | 375 |
| July | 10 × 25 = 250 |
| August | 25 × 25 = 625 |
| September | 20 × 25 = 500 |
Number of ‘Full face’ helmets sold in October = 500 × 1.35 = 675
Hence, the correct answer is 675.
66. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Nine people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, sit in a row facing different directions but not necessarily in the same order. Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South. The people sitting at the end facing South. A sits in the middle of the row facing North. Two people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row. Four people sit between E and D, who faces South. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C. F sits beside A, facing the same direction. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions. B does not sit beside D. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
Question:
How many people sit between C and D?
A. 1 person – A
B. 2 people – E and C
C. 3 people – E, F, and A
D. 2 people – F and A
E. 1 person – F
Solution
Given:
9 people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South.
The people sitting at the corners sit facing South.
1. A sits in the middle of the row facing North.
2. 2 people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row.
3. 4 people sit between E and D, who faces South.
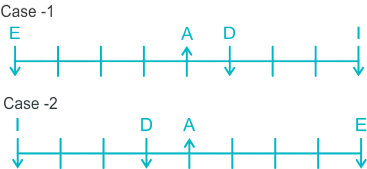
4. F sits beside A, facing the same direction.
5. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
6. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E.
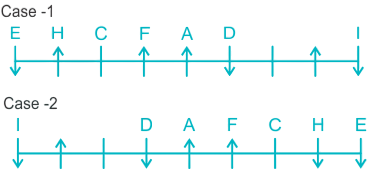
7. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C.
8. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions.
9. B does not sit beside D.

(Case 2 will not be possible as it will contradict point 7)
Final Arrangement:
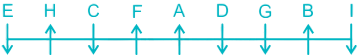
Hence, 2 people – F and A, sit between C and D.
67. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Nine people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, sit in a row facing different directions but not necessarily in the same order. Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South. The people sitting at the end facing South. A sits in the middle of the row facing North. Two people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row. Four people sit between E and D, who faces South. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C. F sits beside A, facing the same direction. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions. B does not sit beside D. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
Question:
Who sits second to the right of the one who sits third to the left of the one sitting beside I?
A. B
B. H
C. G
D. F
E. A
Solution
Given:
9 people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South.
The people sitting at the corners sit facing South.
1. A sits in the middle of the row facing North.
2. 2 people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row.
3. 4 people sit between E and D, who faces South.
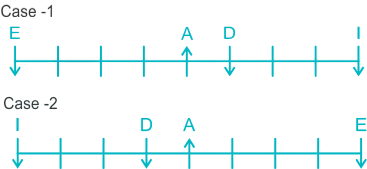
4. F sits beside A, facing the same direction.
5. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
6. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E.
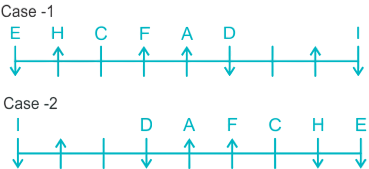
7. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C.
8. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions.
9. B does not sit beside D.

(Case 2 will not be possible as it will contradict point 7)
Final Arrangement:
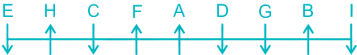
B sits beside I.
A sits third to the left of B.
Hence, G sits second to the right of A.
68. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Nine people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, sit in a row facing different directions but not necessarily in the same order. Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South. The people sitting at the end facing South. A sits in the middle of the row facing North. Two people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row. Four people sit between E and D, who faces South. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C. F sits beside A, facing the same direction. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions. B does not sit beside D. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
Question:
How many people sit facing South?
A. 5 people
B. 4 people
C. 3 people
D. 2 people
E. 1 person
Solution
Given:
9 people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South.
The people sitting at the corners sit facing South.
1. A sits in the middle of the row facing North.
2. 2 people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row.
3. 4 people sit between E and D, who faces South.
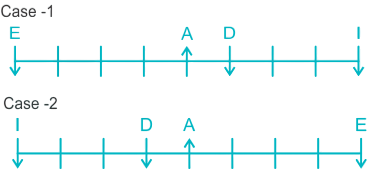
4. F sits beside A, facing the same direction.
5. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
6. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E.
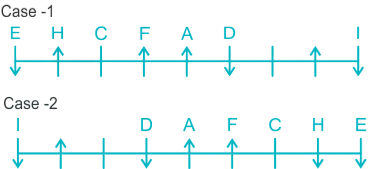
7. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C.
8. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions.
9. B does not sit beside D.

(Case 2 will not be possible as it will contradict point 7)
Final Arrangement:
Hence, 5 people sit facing South.
69. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Nine people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, sit in a row facing different directions but not necessarily in the same order. Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South. The people sitting at the end facing South. A sits in the middle of the row facing North. Two people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row. Four people sit between E and D, who faces South. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C. F sits beside A, facing the same direction. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions. B does not sit beside D. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
Question:
Who sits at the right end of the row?
A. H
B. I
C. E
D. F
E. G
Solution
Given:
9 people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South.
The people sitting at the corners sit facing South.
1. A sits in the middle of the row facing North.
2. 2 people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row.
3. 4 people sit between E and D, who faces South.
4. F sits beside A, facing the same direction.
5. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
6. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E.
7. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C.
8. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions.
9. B does not sit beside D.

(Case 2 will not be possible as it will contradict point 7)
Final Arrangement:
Hence, I sits at the right end of the row.
70. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Nine people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I, sit in a row facing different directions but not necessarily in the same order. Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South. The people sitting at the end facing South. A sits in the middle of the row facing North. Two people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row. Four people sit between E and D, who faces South. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C. F sits beside A, facing the same direction. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions. B does not sit beside D. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
Question:
Who sits fourth from the left end of the row?
A. B
B. C
C. D
D. E
E. F
Solution
Given:
9 people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Some people sit facing North, while the others sit facing South.
The people sitting at the corners sit facing South.
1. A sits in the middle of the row facing North.
2. 2 people sit between D and I, who sits at the end of the row.
3. 4 people sit between E and D, who faces South.
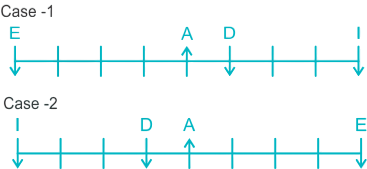
4. F sits beside A, facing the same direction.
5. The one who sits beside I faces the opposite direction as I.
6. C sits to the immediate right of H, who sits beside E.
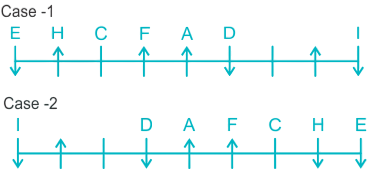
7. The neighbors of C sit facing the opposite direction as C.
8. G and B sit beside each other, facing opposite directions.
9. B does not sit beside D.

(Case 2 will not be possible as it will contradict point 7)
Final Arrangement:
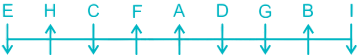
Hence, F sits fourth from the left end of the row.
71. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statement to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement: N < O > B = E > F; C = S > A ≤ P; N = M > R < Q ≤ P
Question:
Conclusions:
I. A > N
II. B ≥ R
A. Either I or II follows
B. Neither I nor II follows
C. Both I and II follow
D. Only I follow
E. Only II follow
Solution
Given statement: N < O > B = E > F; C = S > A ≤ P; N = M > R < Q ≤ P
On combining: C = S > A ≤ P ≥ Q > R < M = N < O > B = E > F
Conclusions:
I. A > N → False (As we cannot find the relationship between A and N in the combining statement)
II. B ≥ R → False (As we cannot find the relationship between A and N in the combining statement)
Hence, Neither I nor II follows.
72. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statement to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement: N < O > B = E > F; C = S > A ≤ P; N = M > R < Q ≤ P
Question:
Conclusions:
I. C > A
II. A = Q
A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Both I and II follow
D. Either I or II follow
E. Neither I nor II follow
Solution
Given statement: N < O > B = E > F; C = S > A ≤ P; N = M > R < Q ≤ P
On combining: C = S > A ≤ P ≥ Q > R < M = N < O > B = E > F
Conclusions:
I. C > A → True (As S > A and C = S, so we can say that C > A hence true)
II. A = Q → False (Here, A ≤ P ≥ Q, we cannot consider ‘=’ sign, as A is < / = P, and P is > / = Q, so we cannot consider only ‘=’ sig, hence false).
Hence, Only I follows.
73. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statement to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement: N < O > B = E > F; C = S > A ≤ P; N = M > R < Q ≤ P
Question:
Conclusions:
I. P ≥ R
II. R < P
A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Both I and II follow
D. Neither I nor II follow
E. Either I or II follow
Solution
Given statement: N < O > B = E > F; C = S > A ≤ P; N = M > R < Q ≤ P
On combining: C = S > A ≤ P ≥ Q > R < M = N < O > B = E > F
Conclusions:
I. P ≥ R → False (As we can see clearly in the combining statement the relation between P and R: P ≥ Q > R so, P > R hence, false)
II. R < P → True (As we can see clearly in the combining statement the relation between P and R: P ≥ Q > R so, P > R hence, true)
Hence, Only II follows.
74. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Eight boxes numbered 1 to 8 are placed one above the other such that box 1 is placed at the bottom and box 8 is at the top. Each of the boxes contains books of different subjects viz Science, History, Hindi, Geography, Physics, Biology, English, and Chemistry not necessarily in the same order. Three books are kept between the Science book and History book. The Chemistry book is kept immediately below the Science book. Two books are kept between Chemistry book and English book. There are as many books between Hindi book and Geography book as between Chemistry book and History book. The physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. The Science book is not kept above the History book. The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book.
Question:
Which of the following statement is true as per the given arrangement?
A. Only two books are kept between History book and Science book.
B. Biology book is kept just above the Science book.
C. All of the given statements are true
D. Physics book is kept at even number position
E. None of the given statements are true.
Solution
1) Three books are kept between the Science book and the History book.
2) Chemistry book is kept immediately below the Science book
3) The Science book is not kept above the History book
| Box | Case I | Case II | Case III |
| 8 | History | ||
| 7 | History | ||
| 6 | History | ||
| 5 | |||
| 4 | Science | ||
| 3 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 2 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 1 | Chemistry |
4) Two books are kept between the Chemistry book and the English book.
5) There are as many books between the Hindi book and Geography book as there are between the Chemistry book and the History book.
6) The Physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. (Case II gets canceled because this statement would not be satisfied)
As there is no position left for the Geography book and for the Physics books to be placed adjacent to each other in this case.
| Box | Case I | Case III |
| 8 | History | Geography |
| 7 | Hindi | Physics |
| 6 | English | History |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | Science | English |
| 3 | Chemistry | Hindi |
| 2 | Geography | Science |
| 1 | Physics | Chemistry |
7) The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book. (Case 3 gets canceled, as in this case, the Biology book will be placed immediately below History which violates the statement given).
So, the final arrangement will be
| Box | Case I |
| 8 | History |
| 7 | Hindi |
| 6 | English |
| 5 | Biology |
| 4 | Science |
| 3 | Chemistry |
| 2 | Geography |
| 1 | Physics |
Hence, the Biology book is kept just above the Science book
75. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Eight boxes numbered 1 to 8 are placed one above the other such that box 1 is placed at the bottom and box 8 is at the top. Each of the boxes contains books of different subjects viz Science, History, Hindi, Geography, Physics, Biology, English, and Chemistry not necessarily in the same order. Three books are kept between the Science book and History book. The Chemistry book is kept immediately below the Science book. Two books are kept between Chemistry book and English book. There are as many books between Hindi book and Geography book as between Chemistry book and History book. The physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. The Science book is not kept above the History book. The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book.
Question:
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way, find out the one which does not belong to that group
A. Hindi
B. Biology
C. Chemistry
D. History
E. Physics
Solution
1) Three books are kept between the Science book and the History book.
2) Chemistry book is kept immediately below the Science book
3) The Science book is not kept above the History book
| Box | Case I | Case II | Case III |
| 8 | History | ||
| 7 | History | ||
| 6 | History | ||
| 5 | |||
| 4 | Science | ||
| 3 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 2 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 1 | Chemistry |
4) Two books are kept between the Chemistry book and the English book.
5) There are as many books between the Hindi book and Geography book as there are between the Chemistry book and the History book.
6) The Physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. (Case II gets canceled because this statement would not be satisfied)
As there is no position left for the Geography book and for the Physics books to be placed adjacent to each other in this case.
| Box | Case I | Case III |
| 8 | History | Geography |
| 7 | Hindi | Physics |
| 6 | English | History |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | Science | English |
| 3 | Chemistry | Hindi |
| 2 | Geography | Science |
| 1 | Physics | Chemistry |
7) The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book. (Case 3 gets canceled, as in this case, the Biology book will be placed immediately below History which violates the statement given).
So, the final arrangement will be
| Box | Case I |
| 8 | History |
| 7 | Hindi |
| 6 | English |
| 5 | Biology |
| 4 | Science |
| 3 | Chemistry |
| 2 | Geography |
| 1 | Physics |
Hence, the History book is kept at an even-numbered position while other books are kept at an odd number position.
76. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Eight boxes numbered 1 to 8 are placed one above the other such that box 1 is placed at the bottom and box 8 is at the top. Each of the boxes contains books of different subjects viz Science, History, Hindi, Geography, Physics, Biology, English, and Chemistry not necessarily in the same order. Three books are kept between the Science book and History book. The Chemistry book is kept immediately below the Science book. Two books are kept between Chemistry book and English book. There are as many books between Hindi book and Geography book as between Chemistry book and History book. The physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. The Science book is not kept above the History book. The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book.
Question:
How many books are kept between Hindi book and Science book?
A. Four
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. None
Solution
1) Three books are kept between the Science book and the History book.
2) Chemistry book is kept immediately below the Science book
3) The Science book is not kept above the History book
| Box | Case I | Case II | Case III |
| 8 | History | ||
| 7 | History | ||
| 6 | History | ||
| 5 | |||
| 4 | Science | ||
| 3 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 2 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 1 | Chemistry |
4) Two books are kept between the Chemistry book and the English book.
5) There are as many books between the Hindi book and Geography book as there are between the Chemistry book and the History book.
6) The Physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. (Case II gets canceled because this statement would not be satisfied)
As there is no position left for the Geography book and for the Physics books to be placed adjacent to each other in this case.
| Box | Case I | Case III |
| 8 | History | Geography |
| 7 | Hindi | Physics |
| 6 | English | History |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | Science | English |
| 3 | Chemistry | Hindi |
| 2 | Geography | Science |
| 1 | Physics | Chemistry |
7) The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book. (Case 3 gets canceled, as in this case, the Biology book will be placed immediately below History which violates the statement given).
So, the final arrangement will be
| Box | Case I |
| 8 | History |
| 7 | Hindi |
| 6 | English |
| 5 | Biology |
| 4 | Science |
| 3 | Chemistry |
| 2 | Geography |
| 1 | Physics |
Hence, Two books are kept between Hindi book and Science book.
77. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Eight boxes numbered 1 to 8 are placed one above the other such that box 1 is placed at the bottom and box 8 is at the top. Each of the boxes contains books of different subjects viz Science, History, Hindi, Geography, Physics, Biology, English, and Chemistry not necessarily in the same order. Three books are kept between the Science book and History book. The Chemistry book is kept immediately below the Science book. Two books are kept between Chemistry book and English book. There are as many books between Hindi book and Geography book as between Chemistry book and History book. The physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. The Science book is not kept above the History book. The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book.
Question:
Which of the following books is kept at the top?
A. Hindi
B. English
C. Physics
D. Geography
E. None of these
Solution
1) Three books are kept between the Science book and the History book.
2) Chemistry book is kept immediately below the Science book
3) The Science book is not kept above the History book
| Box | Case I | Case II | Case III |
| 8 | History | ||
| 7 | History | ||
| 6 | History | ||
| 5 | |||
| 4 | Science | ||
| 3 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 2 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 1 | Chemistry |
4) Two books are kept between the Chemistry book and the English book.
5) There are as many books between the Hindi book and Geography book as there are between the Chemistry book and the History book.
6) The Physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. (Case II gets canceled because this statement would not be satisfied)
As there is no position left for the Geography book and for the Physics books to be placed adjacent to each other in this case.
| Box | Case I | Case III |
| 8 | History | Geography |
| 7 | Hindi | Physics |
| 6 | English | History |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | Science | English |
| 3 | Chemistry | Hindi |
| 2 | Geography | Science |
| 1 | Physics | Chemistry |
7) The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book. (Case 3 gets canceled, as in this case, the Biology book will be placed immediately below History which violates the statement given).
So, the final arrangement will be
| Box | Case I |
| 8 | History |
| 7 | Hindi |
| 6 | English |
| 5 | Biology |
| 4 | Science |
| 3 | Chemistry |
| 2 | Geography |
| 1 | Physics |
Hence, History book is kept at top
78. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Eight boxes numbered 1 to 8 are placed one above the other such that box 1 is placed at the bottom and box 8 is at the top. Each of the boxes contains books of different subjects viz Science, History, Hindi, Geography, Physics, Biology, English, and Chemistry not necessarily in the same order. Three books are kept between the Science book and History book. The Chemistry book is kept immediately below the Science book. Two books are kept between Chemistry book and English book. There are as many books between Hindi book and Geography book as between Chemistry book and History book. The physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. The Science book is not kept above the History book. The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book.
Question:
How many books are kept above the Geography book?
A. Three
B. Two
C. Four
D. Six
E. None of these
Solution
1) Three books are kept between the Science book and the History book.
2) Chemistry book is kept immediately below Science book
3) The Science book is not kept above the History book
| Box | Case I | Case II | Case III |
| 8 | History | ||
| 7 | History | ||
| 6 | History | ||
| 5 | |||
| 4 | Science | ||
| 3 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 2 | Chemistry | Science | |
| 1 | Chemistry |
4) Two books are kept between the Chemistry book and the English book.
5) There are as many books between the Hindi book and Geography book as there are between the Chemistry book and the History book.
6) The Physics book is kept immediately below the Geography book. (Case II gets canceled because this statement would not be satisfied)
As there is no position left for the Geography book and for the Physics books to be placed adjacent to each other in this case.
| Box | Case I | Case III |
| 8 | History | Geography |
| 7 | Hindi | Physics |
| 6 | English | History |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | Science | English |
| 3 | Chemistry | Hindi |
| 2 | Geography | Science |
| 1 | Physics | Chemistry |
7) The Biology book is not kept immediately below the History book. (Case 3 gets canceled, as in this case, the Biology book will be placed immediately below History which violates the statement given).
So, the final arrangement will be
| Box | Case I |
| 8 | History |
| 7 | Hindi |
| 6 | English |
| 5 | Biology |
| 4 | Science |
| 3 | Chemistry |
| 2 | Geography |
| 1 | Physics |
Hence, Six books are kept above the Geography book
79. How many such pairs of letters are there in the word ‘LINGUIST’, each of which has as many letters between them in the word (both forward and backward direction) as they have between them in the English Alphabet?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
E. Five
Solution
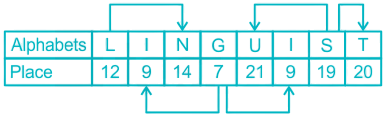
Pairs:- (LN), (GI), (GI), (SU), and (ST)
Hence, five pairs are there in the word ‘LINGUIST’, each of which has as many letters between them in the word (both forward and backward direction) as they have between them in the English Alphabet.
80. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z live in a five-storey building. The ground floor is numbered 1. Each floor consists of two flats i.e. flat M and flat N. Flat M of floor 2 is exactly above the flat M of floor 1 and exactly below the flat M of floor 3 and so on. Flat M is in the west of flat N.
O lives in flat M. A lives to the South of U. Z lives on an even-numbered floor. S is not in the north of R. One floor is between Q and U. Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. Two floors are between S and O. Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. R lives to the Southwest of Q.
Question:
Which of the following pair lives in the same flat?
A. ZQ
B. UY
C. AB
D. OS
E. RU
Solution
Given:
Ten persons – A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z
Five Floors – (Ground floor) 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 (Topmost Floor)
Two Flats – M and N (Flat M is in the west of flat N)
Now,
1) S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. S and W can live on the 1st, 3rd, or 5th floor.
2) Two floors are between S and O. O lives in flat M. It means S & W do not live on the 3rd floor.
The possibilities are –
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
Case II –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | O | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 | S / W | W / S |
3) Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. It means Y lives just above O in the same flat.
4) Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. It means Q lives in Flat N above the floor of Y. This is not possible in case II so it gets eliminated.
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
5) One floor is between Q and U. It means U lives in Flat N on the second floor.
6) A lives to the South of U. It means A also lives in flat N on the first floor.
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | A |
7) R lives to the Southwest of Q. It means R lives in Flat M of the first floor.
8) Z lives on an even-numbered floor. It means Z lives on the 4th floor in Flat M.
9) S is not in the north of R. It means W is in the north of R and S lives in Flat N.
The remaining person B lives in Flat N of the 3rd floor.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | W | S |
| 4 | Z | Q |
| 3 | Y | B |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | R | A |
Among the given option, AB lives in the same flat.
Hence, the correct answer is AB.
81. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z live in a five-storey building. The ground floor is numbered 1. Each floor consists of two flats i.e. flat M and flat N. Flat M of floor 2 is exactly above the flat M of floor 1 and exactly below the flat M of floor 3 and so on. Flat M is in the west of flat N.
O lives in flat M. A lives to the South of U. Z lives on an even-numbered floor. S is not in the north of R. One floor is between Q and U. Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. Two floors are between S and O. Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. R lives to the Southwest of Q.
Question:
How many total number of persons live between R and Q ?
A. Two
B. Four
C. Six
D. None
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Ten persons – A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z
Five Floors – (Ground floor) 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 (Topmost Floor)
Two Flats – M and N (Flat M is in the west of flat N)
Now,
1) S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. S and W can live on the 1st, 3rd, or 5th floor.
2) Two floors are between S and O. O lives in flat M. It means S & W do not live on the 3rd floor.
The possibilities are –
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
Case II –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | O | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 | S / W | W / S |
3) Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. It means Y lives just above O in the same flat.
4) Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. It means Q lives in Flat N above the floor of Y. This is not possible in case II so it gets eliminated.
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
5) One floor is between Q and U. It means U lives in Flat N on the second floor.
6) A lives to the South of U. It means A also lives in flat N on the first floor.
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | A |
7) R lives to the Southwest of Q. It means R lives in Flat M of the first floor.
8) Z lives on an even-numbered floor. It means Z lives on the 4th floor in Flat M.
9) S is not in the north of R. It means W is in the north of R and S lives in Flat N.
The remaining person B lives in Flat N of the 3rd floor.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | W | S |
| 4 | Z | Q |
| 3 | Y | B |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | R | A |
Four persons live between R and Q.
Hence, the correct answer is Four.
82. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z live in a five-storey building. The ground floor is numbered 1. Each floor consists of two flats i.e. flat M and flat N. Flat M of floor 2 is exactly above the flat M of floor 1 and exactly below the flat M of floor 3 and so on. Flat M is in the west of flat N.
O lives in flat M. A lives to the South of U. Z lives on an even-numbered floor. S is not in the north of R. One floor is between Q and U. Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. Two floors are between S and O. Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. R lives to the Southwest of Q.
Question:
Who lives on the third floor?
A. S
B. W
C. U
D. A
E. B
Solution
Given:
Ten persons – A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z
Five Floors – (Ground floor) 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 (Topmost Floor)
Two Flats – M and N (Flat M is in the west of flat N)
Now,
1) S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. S and W can live on the 1st, 3rd, or 5th floor.
2) Two floors are between S and O. O lives in flat M. It means S & W do not live on the 3rd floor.
The possibilities are –
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
Case II –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | O | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 | S / W | W / S |
3) Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. It means Y lives just above O in the same flat.
4) Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. It means Q lives in Flat N above the floor of Y. This is not possible in case II so it gets eliminated.
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
5) One floor is between Q and U. It means U lives in Flat N on the second floor.
6) A lives to the South of U. It means A also lives in flat N on the first floor.
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | A |
7) R lives to the Southwest of Q. It means R lives in Flat M of the first floor.
8) Z lives on an even-numbered floor. It means Z lives on the 4th floor in Flat M.
9) S is not in the north of R. It means W is in the north of R and S lives in Flat N.
The remaining person B lives in Flat N of the 3rd floor.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | W | S |
| 4 | Z | Q |
| 3 | Y | B |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | R | A |
Among the given options, B lives on the third floor.
Hence, the correct answer is B.
83. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z live in a five-storey building. The ground floor is numbered 1. Each floor consists of two flats i.e. flat M and flat N. Flat M of floor 2 is exactly above the flat M of floor 1 and exactly below the flat M of floor 3 and so on. Flat M is in the west of flat N.
O lives in flat M. A lives to the South of U. Z lives on an even-numbered floor. S is not in the north of R. One floor is between Q and U. Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. Two floors are between S and O. Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. R lives to the Southwest of Q.
Question:
Find the odd one out:
A. Z
B. Y
C. Q
D. O
E. U
Solution
Given:
Ten persons – A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z
Five Floors – (Ground floor) 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 (Topmost Floor)
Two Flats – M and N (Flat M is in the west of flat N)
Now,
1) S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. S and W can live on the 1st, 3rd, or 5th floor.
2) Two floors are between S and O. O lives in flat M. It means S & W do not live on the 3rd floor.
The possibilities are –
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
Case II –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | O | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 | S / W | W / S |
3) Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. It means Y lives just above O in the same flat.
4) Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. It means Q lives in Flat N above the floor of Y. This is not possible in case II so it gets eliminated.
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
5) One floor is between Q and U. It means U lives in Flat N on the second floor.
6) A lives to the South of U. It means A also lives in flat N on the first floor.
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | A |
7) R lives to the Southwest of Q. It means R lives in Flat M of the first floor.
8) Z lives on an even-numbered floor. It means Z lives on the 4th floor in Flat M.
9) S is not in the north of R. It means W is in the north of R and S lives in Flat N.
The remaining person B lives in Flat N of the 3rd floor.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | W | S |
| 4 | Z | Q |
| 3 | Y | B |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | R | A |
Among the given options, only Y lives on an odd numbered floor.
Hence, the correct answer is Y.
84. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z live in a five-storey building. The ground floor is numbered 1. Each floor consists of two flats i.e. flat M and flat N. Flat M of floor 2 is exactly above the flat M of floor 1 and exactly below the flat M of floor 3 and so on. Flat M is in the west of flat N.
O lives in flat M. A lives to the South of U. Z lives on an even-numbered floor. S is not in the north of R. One floor is between Q and U. Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. Two floors are between S and O. Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. R lives to the Southwest of Q.
Question:
Who among the following lives in Flat N?
A. R
B. Y
C. Z
D. S
E. O
Solution
Given:
Ten persons – A, B, O, Q, R, S, U, W, Y, and Z
Five Floors – (Ground floor) 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 (Topmost Floor)
Two Flats – M and N (Flat M is in the west of flat N)
Now,
1) S lives with W on an odd-numbered floor. S and W can live on the 1st, 3rd, or 5th floor.
2) Two floors are between S and O. O lives in flat M. It means S & W do not live on the 3rd floor.
The possibilities are –
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
Case II –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | O | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 | S / W | W / S |
3) Y lives in the Northwest of the person who lives on the same floor as O, where O and Y lives on the adjacent floor. It means Y lives just above O in the same flat.
4) Q lives above the floor on which Y lives but not in the same flat. It means Q lives in Flat N above the floor of Y. This is not possible in case II so it gets eliminated.
Case I –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | |
| 1 |
5) One floor is between Q and U. It means U lives in Flat N on the second floor.
6) A lives to the South of U. It means A also lives in flat N on the first floor.
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | S / W | W / S |
| 4 | Q | |
| 3 | Y | |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | A |
7) R lives to the Southwest of Q. It means R lives in Flat M of the first floor.
8) Z lives on an even-numbered floor. It means Z lives on the 4th floor in Flat M.
9) S is not in the north of R. It means W is in the north of R and S lives in Flat N.
The remaining person B lives in Flat N of the 3rd floor.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
| Floors | Flat M | Flat N |
| 5 | W | S |
| 4 | Z | Q |
| 3 | Y | B |
| 2 | O | U |
| 1 | R | A |
Among the given options, S lives in Flat N.
Hence, the correct answer is S.
85. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Nine persons viz. A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I are working in an organization in nine different positions i.e., General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon but not necessarily in the same order. The order of seniority is the same as given above such that the General Manager (GM) is the seniormost person and the Peon is the juniormost person.
There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position. F is senior to B. I is immediate senior to E. G is the Chief Manager. At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E. There is no post between the posts of H and D. B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager. A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
Question:
Who is the Branch Manager?
A. E
B. F
C. I
D. A
E. G
Solution
Nine persons: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Nine positions: General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon.
1) There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position.
2) F is senior to B.
3) B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager.
4) G is the Chief Manager.
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | |
| CM | G |
| SM | |
| BM | |
| AM | |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon |
5) There is no post between the posts of H and D.
6) I is immediate senior to E.
7) At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
8) A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | A |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
We cannot place A in Case I and Case II.
So, C is AGM.
The final arrangement is——-
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | C |
| CM | G |
| SM | A |
| BM | I |
| AM | E |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon | D |
Hence, I is the Branch Manager.
86. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Nine persons viz. A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I are working in an organization in nine different positions i.e., General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon but not necessarily in the same order. The order of seniority is the same as given above such that the General Manager (GM) is the seniormost person and the Peon is the juniormost person.
There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position. F is senior to B. I is immediate senior to E. G is the Chief Manager. At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E. There is no post between the posts of H and D. B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager. A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
Question:
In a certain way, ‘F’ is related to ‘C’ and ‘G’ is related to ‘I’, then in the same way ‘A’ is related to whom?
A. F
B. G
C. I
D. E
E. H
Solution
Nine persons: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Nine positions: General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon.
1) There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position.
2) F is senior to B.
3) B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager.
4) G is the Chief Manager.
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | |
| CM | G |
| SM | |
| BM | |
| AM | |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon |
5) There is no post between the posts of H and D.
6) I is immediate senior to E.
7) At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
8) A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | A |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
We cannot place A in Case I and Case II.
So, C is AGM.
The final arrangement is——-
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | C |
| CM | G |
| SM | A |
| BM | I |
| AM | E |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon | D |
There is one position between the positions of ‘F’ and ‘C’.
There is one position between the positions of ‘G’ and ‘I’.
Similarly, there is one position between the positions of ‘A’ and ‘E’.
Hence, A is related to E.
87. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Nine persons viz. A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I are working in an organization in nine different positions i.e., General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon but not necessarily in the same order. The order of seniority is the same as given above such that the General Manager (GM) is the seniormost person and the Peon is the juniormost person.
There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position. F is senior to B. I is immediate senior to E. G is the Chief Manager. At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E. There is no post between the posts of H and D. B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager. A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
Question:
Who is two positions senior to D?
A. F
B. C
C. A
D. I
E. E
Solution
Nine persons: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Nine positions: General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon.
1) There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position.
2) F is senior to B.
3) B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager.
4) G is the Chief Manager.
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | |
| CM | G |
| SM | |
| BM | |
| AM | |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon |
5) There is no post between the posts of H and D.
6) I is immediate senior to E.
7) At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
8) A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | A |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
We cannot place A in Case I and Case II.
So, C is AGM.
The final arrangement is——-
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | C |
| CM | G |
| SM | A |
| BM | I |
| AM | E |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon | D |
Hence, E is two positions senior to D.
88. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Nine persons viz. A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I are working in an organization in nine different positions i.e., General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon but not necessarily in the same order. The order of seniority is the same as given above such that the General Manager (GM) is the seniormost person and the Peon is the juniormost person.
There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position. F is senior to B. I is immediate senior to E. G is the Chief Manager. At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E. There is no post between the posts of H and D. B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager. A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
Question:
Who is the Senior Manager?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
Nine persons: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Nine positions: General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon.
1) There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position.
2) F is senior to B.
3) B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager.
4) G is the Chief Manager.
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | |
| CM | G |
| SM | |
| BM | |
| AM | |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon |
5) There is no post between the posts of H and D.
6) I is immediate senior to E.
7) At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
8) A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | A |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
We cannot place A in Case I and Case II.
So, C is AGM.
The final arrangement is——-
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | C |
| CM | G |
| SM | A |
| BM | I |
| AM | E |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon | D |
Hence, A is the Senior manager.
89. Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Nine persons viz. A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I are working in an organization in nine different positions i.e., General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon but not necessarily in the same order. The order of seniority is the same as given above such that the General Manager (GM) is the seniormost person and the Peon is the juniormost person.
There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position. F is senior to B. I is immediate senior to E. G is the Chief Manager. At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E. There is no post between the posts of H and D. B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager. A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
Question:
What is the position of C?
A. Senior Manager
B. Assistant manager
C. Assistant General manager
D. Clerk
E. Peon
Solution
Nine persons: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I
Nine positions: General Manager (GM), Deputy General Manager (DGM), Assistant General Manager (AGM), Chief Manager (CM), Senior Manager (SM), Branch Manager (BM), Assistant Manager (AM), Clerk and Peon.
1) There are five posts between B and H, and neither of them works at the top position.
2) F is senior to B.
3) B is senior to the person, who is Assistant General Manager.
4) G is the Chief Manager.
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | |
| CM | G |
| SM | |
| BM | |
| AM | |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon |
5) There is no post between the posts of H and D.
6) I is immediate senior to E.
7) At most two posts are there between the posts of G and E.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
8) A is senior to I, but not the Assistant General Manager.
| Case I | Case II | Case III | |
| Designations | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| GM | F | F | F |
| DGM | B | B | B |
| AGM | |||
| CM | G | G | G |
| SM | I | I | A |
| BM | E | E | I |
| AM | D | E | |
| Clerk | H | H | H |
| Peon | D | D |
We cannot place A in Case I and Case II.
So, C is AGM.
The final arrangement is——-
| Designations | Persons |
| GM | F |
| DGM | B |
| AGM | C |
| CM | G |
| SM | A |
| BM | I |
| AM | E |
| Clerk | H |
| Peon | D |
Hence, C is the Assistant General Manager.
90. Directions: In the question below are given statement followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statement:
Only a few Parrots are Tit
Some parrots are Owls
No Tit is Stork
Conclusion:
I: Some Parrot are not stork
II: All Tit is Parrots is a possibility
A. Only conclusion II follows.
B. Both conclusion I and II follows
C. Neither conclusion I nor II follows.
D. Only conclusion I follows.
E. Either I or II follows
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram according to the above statement is:
Conclusion:
I. Some Parrot are not stork → True( Part of parrots that are tit will be not be stork hence given statement is true)
II. All Tit is Parrots is a possibility →True (All Tit can be parrots but all parrot can never be Tit, Only a few parrot are tit means some parrot are tit and some parrot are no tit. Here all tit can be parrot but all parrot cannot be tit. )
Hence, Both conclusion I and II follows is a correct answer.
91. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Some Museums are Banks.
Some Banks are not College.
No Museum is House.
Conclusions:
I. Some Banks can be College.
II. Some Banks can be Houses.
III. All Museums are not Colleges.
A. All follow
B. Only I and II follow
C. None follows.
D. Only II and III follow
E. Only II follows
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as follows –
Conclusions:
I. Some Banks can be College. → True (Some Banks are not College but it is possible that Some Banks are College (the remaining portion). So, it follows.)
II. Some Banks can be Houses. → True (As there is no direct relation between Bank and House it is possible that Some Bank is House. So, it follows.)
III. All Museums are not Colleges. → False (There is no direct or negative relation given between Museum and College. So, it is possible that All Museum is College. Hence, it doesn’t follow.)
Hence, the correct answer is Only I and II follow.
92. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
All Xenon is Krypton.
Only a few Krypton is Radon.
No Radon is Argon.
Conclusions:
I. Some Argon are Xenon.
II. All Radon can be Xenon.
A. Only II follows
B. Either I or II follows
C. Only I follows
D. Both I and II follow
E. Neither I nor II follows
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as follows –
Conclusions:
I. Some Argon are Xenon. → False (It is possible but not definite as there is no direct relation given between Argon and Xenon. Hence, it doesn’t follow.)
II. All Radon can be Xenon. → True (Only a few Krypton is Radon means Some Krypton is Radon and Some Krypton are not Radon. But it is possible that All Radon are Xenon as there is no direct or negative relation given between them. Hence, it follows.)
Hence, the correct answer is Only II follows.
93. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
Eight people are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing inside the centre while some are facing outside the centre. D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. Both H and E sit immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B. H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing the same direction but opposite to D. Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre.
Question:
How many people are sitting between G and F, when counted from the right of F?
A. One
B. Four
C. Two
D. Three
E. None
Solution
From the given instructions:
1) D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. So, here we have two cases,
2) A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. So, here we have one more case in Case 2 as Case 2(a),
3) Both H and E sits immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C.
Here, Case 2 gets cancelled because there is no space to place H and E immediately left to each other.
4) H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing same direction but opposite to D. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B.
5) Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre. So, here Case 1 gets cancelled because five people are facing inside and three people are facing outside.
So, Final Arrangement:
Four people are sitting between G and F, when counted from the right of F.
94. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
Eight people are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing inside the centre while some are facing outside the centre. D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. Both H and E sit immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B. H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing the same direction but opposite to D. Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre.
Question:
Who sits adjacent to B?
A. E
B. H
C. A
D. C
E. D
Solution
From the given instructions:
1) D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. So, here we have two cases,
2) A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. So, here we have one more case in Case 2 as Case 2(a),
3) Both H and E sits immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C.
Here, Case 2 gets cancelled because there is no space to place H and E immediately left to each other.
4) H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing same direction but opposite to D. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B.
5) Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre. So, here Case 1 gets cancelled because five people are facing inside and three people are facing outside.
So, Final Arrangement:
D sits adjacent to B.
95. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
Eight people are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing inside the centre while some are facing outside the centre. D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. Both H and E sit immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B. H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing the same direction but opposite to D. Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre.
Question:
Who sits second to the right of A?
A. D
B. H
C. G
D. C
E. F
Solution
From the given instructions:
1) D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. So, here we have two cases,
2) A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. So, here we have one more case in Case 2 as Case 2(a),
3) Both H and E sits immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C.
Here, Case 2 gets cancelled because there is no space to place H and E immediately left to each other.
4) H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing same direction but opposite to D. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B.
5) Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre. So, here Case 1 gets cancelled because five people are facing inside and three people are facing outside.
So, Final Arrangement:
H sits second to the right of A.
96. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
Eight people are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing inside the centre while some are facing outside the centre. D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. Both H and E sit immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B. H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing the same direction but opposite to D. Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre.
Question:
Which of the following statement/s are true according to the final arrangement?
l. E sits second to the left of G.
II. Two people are sitting between A and E, when counted from the left of A.
III. B sits immediate to the left of D.
A. Only I and II
B. Only II and III
C. Only I and III
D. All are true
E. None is true
Solution
From the given instructions:
1) D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. So, here we have two cases,
2) A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. So, here we have one more case in Case 2 as Case 2(a),
3) Both H and E sits immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C.
Here, Case 2 gets cancelled because there is no space to place H and E immediately left to each other.
4) H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing same direction but opposite to D. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B.
5) Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre. So, here Case 1 gets cancelled because five people are facing inside and three people are facing outside.
So, Final Arrangement:
Statement II is not true as there are four people sitting between A and E, when counted from the left of A.
So, Only I and III are true.
97. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
Eight people are sitting around a circular table. Some of them are facing inside the centre while some are facing outside the centre. D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. Both H and E sit immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B. H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing the same direction but opposite to D. Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre.
Question:
How many people are sitting between B and G, when counted from the right of G?
A. Two
B. One
C. None
D. Three
E. None of these
Solution
From the given instructions:
1) D sits third to the right of G, who faces inside the centre. A sits second to the right of D. So, here we have two cases,

2) A sits third to the left of B. F sits second to the left of D. So, here we have one more case in Case 2 as Case 2(a),
3) Both H and E sits immediate to the left of each other. Only two people sit between F and C.
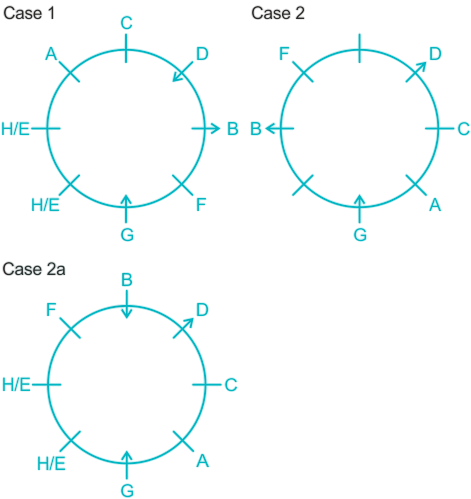
Here, Case 2 gets cancelled because there is no space to place H and E immediately left to each other.
4) H sits second to the left of F. H and C facing same direction but opposite to D. A faces same direction as E but opposite to B.
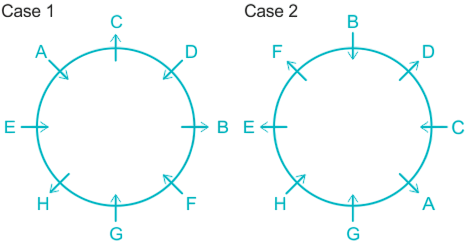
5) Equal number of people facing inside and outside the centre. So, here Case 1 gets cancelled because five people are facing inside and three people are facing outside.
So, Final Arrangement:
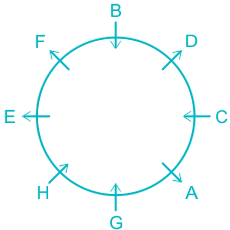
Three people are sitting between B and G, when counted from the right of G.
98. Direction: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Point X is 3 m north of point G. Point W is 2 m north of point S. Point T and B is 6 m south of point V and A respectively. V is 2 m west of point S. Point S is 3 m west of the point G. Point A is 5 m east of the point G.
Question:
What is the direction of point W with respect to the point G?
A. West
B. Northwest
C. Southeast
D. East
E. South
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question,
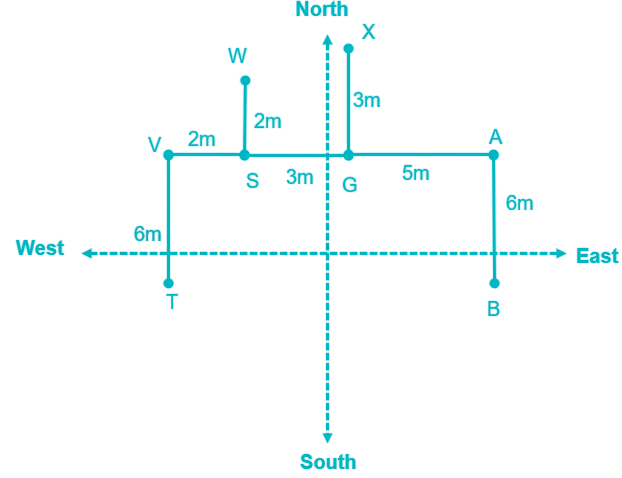
Hence, the direction of the W with respect to the G is northwest.
99. Direction: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Point X is 3 m north of point G. Point W is 2 m north of point S. Point T and B is 6 m south of point V and A respectively. V is 2 m west of point S. Point S is 3 m west of the point G. Point A is 5 m east of the point G.
Question:
What is the shortest distance between the point T and B?
A. 6m
B. 22m
C. 10m
D. 8m
E. 20m
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question,
The distance between the point T and point B is,
→ VA = TB = VS + SG + GA = 2 + 3 + 5 = 10 m
Hence, 10 m is the correct answer.
100. Direction: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Point H is 6m south of point V. Point V is 15m west of point W. Point M is 3m south of the point N and Point C is 3m south of point S. Point S is the 2m northeast of the point H and Point N is 2m northwest of the point Z. Point W is the 6m north of the point Z.
Question:
What is the direction of the point Z with respect to the point H?
A. East
B. West
C. South
D. North
E. Cannot be determine
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question,
Hence, point Z is the east direction with respect to point H.
