Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.Eight people, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W, are sitting around a circular table facing the centre. P is sitting third to the left of R. S is sitting opposite U. P is an immediate neighbor of S. Q is sitting second to the right of W. W is not an immediate neighbor of S. V is not sitting opposite R.
1.Who is sitting third to the right of W?
A. P
B. U
C. V
D. R
E. T
Solution
People = P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W
1) P is sitting third to the left of R.
(As it is a circular arrangement, we can randomly select a seat for R and then place P accordingly.)

2) S is sitting opposite U.
3) P is an immediate neighbor of S.
(Clearly, we cannot place S to the immediate left of P as R is sitting opposite to that seat. Implies, S is sitting to the immediate right of P and U is sitting second to the right of R.)

4) Q is sitting second to the right of W.
(There are two possibilities to place Q and W. In the first case we can place W to the immediate right of S and Q to the immediate right of R and in the second case we can place W to the immediate right of R and W to the immediate right of U.)
5) W is not an immediate neighbor of S.
(Implies, the first case of the previous statement is not true. Thus, W is sitting to the immediate right of R and Q is sitting to the immediate right of U.)

6) V is not sitting opposite R.
(If V is not sitting opposite R then he must be sitting to the immediate left of R as it is the only seat left. Also, now that only one person is left to be placed i.e. T, we can place T opposite R as it is the only seat left to be filled.)

Clearly, T is sitting third to the right of W.
2. How many people are sitting between V and T if we start counting from V in anti-clockwise direction?
A. More than four
B. Four
C. Three
D. Two
E. Zero
Solution
People = P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W
1) P is sitting third to the left of R.
(As it is a circular arrangement, we can randomly select a seat for R and then place P accordingly.)

2) S is sitting opposite U.
3) P is an immediate neighbor of S.
(Clearly, we cannot place S to the immediate left of P as R is sitting opposite to that seat. Implies, S is sitting to the immediate right of P and U is sitting second to the right of R.)

4) Q is sitting second to the right of W.
(There are two possibilities to place Q and W. In the first case we can place W to the immediate right of S and Q to the immediate right of R and in the second case we can place W to the immediate right of R and W to the immediate right of U.)
5) W is not an immediate neighbor of S.
(Implies, the first case of the previous statement is not true. Thus, W is sitting to the immediate right of R and Q is sitting to the immediate right of U.)

6) V is not sitting opposite R.
(If V is not sitting opposite R then he must be sitting to the immediate left of R as it is the only seat left. Also, now that only one person is left to be placed i.e. T, we can place T opposite R as it is the only seat left to be filled.)

Clearly, four people are sitting between V and T if we start from V and move towards the anti-clockwise direction.
3. Who is sitting opposite P?
A. V
B. Q
C. S
D. W
E. T
Solution
People = P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W
1) P is sitting third to the left of R.
(As it is a circular arrangement, we can randomly select a seat for R and then place P accordingly.)

2) S is sitting opposite U.
3) P is an immediate neighbor of S.
(Clearly, we cannot place S to the immediate left of P as R is sitting opposite to that seat. Implies, S is sitting to the immediate right of P and U is sitting second to the right of R.)

4) Q is sitting second to the right of W.
(There are two possibilities to place Q and W. In the first case we can place W to the immediate right of S and Q to the immediate right of R and in the second case we can place W to the immediate right of R and W to the immediate right of U.)
5) W is not an immediate neighbor of S.
(Implies, the first case of the previous statement is not true. Thus, W is sitting to the immediate right of R and Q is sitting to the immediate right of U.)

6) V is not sitting opposite R.
(If V is not sitting opposite R then he must be sitting to the immediate left of R as it is the only seat left. Also, now that only one person is left to be placed i.e. T, we can place T opposite R as it is the only seat left to be filled.)

Clearly, W is sitting opposite P.
4. Who are the immediate neighbors of U?
A. TQ
B. PS
C. WR
D. VR
E. QW
Solution
People = P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W
1) P is sitting third to the left of R.
(As it is a circular arrangement, we can randomly select a seat for R and then place P accordingly.)

2) S is sitting opposite U.
3) P is an immediate neighbor of S.
(Clearly, we cannot place S to the immediate left of P as R is sitting opposite to that seat. Implies, S is sitting to the immediate right of P and U is sitting second to the right of R.)

4) Q is sitting second to the right of W.
(There are two possibilities to place Q and W. In the first case we can place W to the immediate right of S and Q to the immediate right of R and in the second case we can place W to the immediate right of R and W to the immediate right of U.)
5) W is not an immediate neighbor of S.
(Implies, the first case of the previous statement is not true. Thus, W is sitting to the immediate right of R and Q is sitting to the immediate right of U.)

6) V is not sitting opposite R.
(If V is not sitting opposite R then he must be sitting to the immediate left of R as it is the only seat left. Also, now that only one person is left to be placed i.e. T, we can place T opposite R as it is the only seat left to be filled.)

Clearly, Q and W are the immediate neighbors of U.
5. Who is sitting to the immediate left of P?
A. T
B. U
C. V
D. W
E. S
Solution
People = P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W
1) P is sitting third to the left of R.
(As it is a circular arrangement, we can randomly select a seat for R and then place P accordingly.)

2) S is sitting opposite U.
3) P is an immediate neighbor of S.
(Clearly, we cannot place S to the immediate left of P as R is sitting opposite to that seat. Implies, S is sitting to the immediate right of P and U is sitting second to the right of R.)

4) Q is sitting second to the right of W.
(There are two possibilities to place Q and W. In the first case we can place W to the immediate right of S and Q to the immediate right of R and in the second case we can place W to the immediate right of R and W to the immediate right of U.)
5) W is not an immediate neighbor of S.
(Implies, the first case of the previous statement is not true. Thus, W is sitting to the immediate right of R and Q is sitting to the immediate right of U.)

6) V is not sitting opposite R.
(If V is not sitting opposite R then he must be sitting to the immediate left of R as it is the only seat left. Also, now that only one person is left to be placed i.e. T, we can place T opposite R as it is the only seat left to be filled.)

Clearly, T is sitting to the immediate left of P.
6. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion(s) among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement:
E ≤ K > L > R = X > Q
Conclusions:
I. E > R
II. K > Q
A. Only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Both conclusions I and II follow
D. Either conclusion I or II follows
E. None of the conclusions follows
Solution
Given statement,
E ≤ K > L > R = X > Q
Conclusions:
I. E > R → False (E ≤ K > L > R → a clear relation between E and R cannot be determined).
II. K > Q → True (K > L > R = X > Q → K > Q).
Hence, the correct answer is only conclusion II follows.
7. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among the given two conclusion(s) is /are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
X < Y < Z ≤ F; L ≥ Y ≥ D
Conclusions:
I. Z = D
II. X < L
A. Only conclusion I follow
B. Only conclusion II follow
C. Either conclusion I or II follows
D. Neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. Both conclusion I and II follow
Solution
Given statement: X < Y < Z ≤ F; L ≥ Y ≥ D
Conclusions:
I. Z = D → False (As Z > Y ≥ D; Z > D)
II. X < L → True (As L ≥ Y > X; L > X)
Hence, Only conclusion II follow.
8. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among the given conclusions is/ are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly
Statements: A ≥ X = N > Y; O ≥ A = L; N = Z
Conclusions:
I. O > Z
II. O = Z
A. Only I is true
B. Only II is true
C. Either I or II is true
D. Both I and II is true
E. Neither I nor II is true
Solution
Given statements: A ≥ X = N > Y; O ≥ A = L; N = Z
On combining: O ≥ A ≥ X = N > Y; O ≥ A = L; N = Z; O ≥ A ≥ X = N = Z
Conclusions:
I. O > Z → False (as O ≥ A ≥ X = N = Z, thus clear relation cannot be determined as either O > Z or O = Z)
II. O = Z → False (as O ≥ A ≥ X = N = Z , thus clear relation cannot be determined as either O > Z or O = Z)
Therefore, Conclusion I and Conclusion II forms complementary pair
Hence, Either I or II is true
Key Points
Conditions for Either – or
I. Subject and predicate should be same
II. Both the individual conclusions must be false
Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:There are eight members A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H in the family of three generations. C is the grandmother of F, who is married to D. H has two brothers. B is the father of G and E. F has no siblings. C is married to B. E has a daughter. H is the paternal aunt of F. A is the sister of C.
9. How is A related to B?
A. Daughter
B. Brother-in-law
C. Father
D. Sister
E. None of the above
Solution
The below table represents symbols used to draw a family tree,
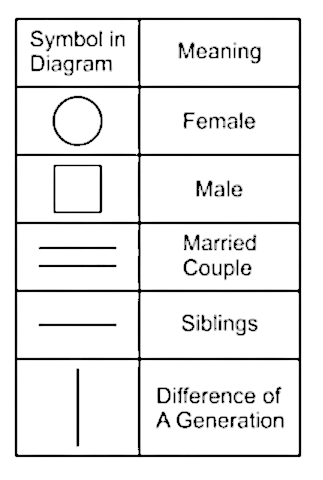
1) B is the father of G and E. E has a daughter.
2) C is married to B. A is the sister of C.
3) C is the grandmother of F, who is married to D.
4) H is the paternal aunt of F. F has no siblings.
5) H has two brothers.
We can draw the following Family Tree from the information given above:

So, A is the sister-in-law of B.Hence, option 5 is correct.
10. Find the odd one out.
A. C
B. A
C. G
D. H
E. F
Solution
The below table represents symbols used to draw a family tree,
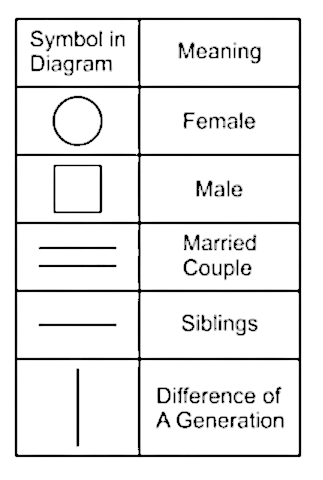
1) B is the father of G and E. E has a daughter.
2) C is married to B. A is the sister of C.
3) C is the grandmother of F, who is married to D.
4) H is the paternal aunt of F. F has no siblings.
5) H has two brothers.
We can draw the following Family Tree from the information given above:

All are females except G.Hence, ‘G’ is the odd one out.
11. How is D related to E?
A. Daughter
B. Son
C. Son-in-law
D. Father-in-law
E. None of the above
Solution
The below table represents symbols used to draw a family tree,
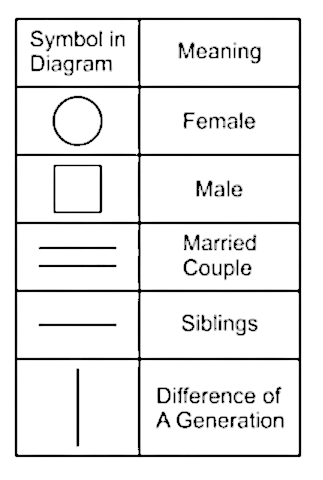
1) B is the father of G and E. E has a daughter.
2) C is married to B. A is the sister of C.
3) C is the grandmother of F, who is married to D.
4) H is the paternal aunt of F. F has no siblings.
5) H has two brothers.
We can draw the following Family Tree from the information given above:

D is the son-in-law of E.Hence, D is the ‘Son-in-law’ of E.
12. If it is possible to make only one meaningful English word with the second, the fifth, the ninth, and the tenth letters of the word STRUGGLING, which of the following will be a third of the word? If no such word can be made give ‘X’ as the answer and if more than one such word can be made give ‘Y’ as the answer.
A. N
B. G
C. T
D. X
E. Y
Solution
| Given Word | STRUGGLING |
| Chosen words | T G N G |
| Possible Word | None |
Clearly, there is no such word that can be made.So, the answer is X.
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H lives in building such that topmost floor is numbered 8 and the ground floor is numbered 1.
No. of floors above B is the same as the no. of floor below D. B lives on an odd floor. G lives below C’s floor. A lives on 6th floor. There is one floor between A and H. D lives on an even floor. A lives 4 floors above D. There are 3 floors between C and G. E lives below the H floor. F lives 4 floor below B.
13. Who lives on floor number 4?
A. C
B. E
C. A
D. B
E. D
Solution
1) A lives on 6th floor.
2) There is one floor between A and H.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | ||
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | H | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 |
3) A lives 4th floor above D so according to this D will live on second floor.
4) B lives on an odd floor.
5) No. of floors above B is the same as the no. of floor below D so according to this B will live on 7th floor.
6) F lives 4th floor below B so F will live on 3rd floor.
7) There are 3 floors between C and G.
8) G lives below C’s floor so C will live on 5th floor and G will live on 1st floor.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | B | B |
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | C | C |
| 4 | E | H |
| 3 | F | F |
| 2 | D | D |
| 1 | G | G |
9) E lives below the H floor so according to this case 2 will get eliminated and case 1 will be right.
| No. of floor | Case 1 |
| 8 | H |
| 7 | B |
| 6 | A |
| 5 | C |
| 4 | E |
| 3 | F |
| 2 | D |
| 1 | G |
So case 1 will be our correct final case.
Clearly, E lives on floor number 4.
14. How many people live between A and G?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
E. More than four
Solution
1) A lives on 6th floor.
2) There is one floor between A and H.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | ||
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | H | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 |
3) A lives 4th floor above D so according to this D will live on second floor.
4) B lives on an odd floor.
5) No. of floors above B is the same as the no. of floor below D so according to this B will live on 7th floor.
6) F lives 4th floor below B so F will live on 3rd floor.
7) There are 3 floors between C and G.
8) G lives below C’s floor so C will live on 5th floor and G will live on 1st floor.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | B | B |
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | C | C |
| 4 | E | H |
| 3 | F | F |
| 2 | D | D |
| 1 | G | G |
9) E lives below the H floor so according to this case 2 will get eliminated and case 1 will be right.
| No. of floor | Case 1 |
| 8 | H |
| 7 | B |
| 6 | A |
| 5 | C |
| 4 | E |
| 3 | F |
| 2 | D |
| 1 | G |
So case 1 will be our correct final case.
Clearly, 4 people live between A and G.
15. Who among the following lives on floor numbered 1?
A. C
B. F
C. H
D. G
E. D
Solution
1) A lives on 6th floor.
2) There is one floor between A and H.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | ||
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | H | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 |
3) A lives 4th floor above D so according to this D will live on second floor.
4) B lives on an odd floor.
5) No. of floors above B is the same as the no. of floor below D so according to this B will live on 7th floor.
6) F lives 4th floor below B so F will live on 3rd floor.
7) There are 3 floors between C and G.
8) G lives below C’s floor so C will live on 5th floor and G will live on 1st floor.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | B | B |
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | C | C |
| 4 | E | H |
| 3 | F | F |
| 2 | D | D |
| 1 | G | G |
9) E lives below the H floor so according to this case 2 will get eliminated and case 1 will be right.
| No. of floor | Case 1 |
| 8 | H |
| 7 | B |
| 6 | A |
| 5 | C |
| 4 | E |
| 3 | F |
| 2 | D |
| 1 | G |
So case 1 will be our correct final case.
Hence, G lives on floor number 1.
16. On which floor F live?
A. First
B. Second
C. Third
D. Fourth
E. None of these
Solution
1) A lives on 6th floor.
2) There is one floor between A and H.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | ||
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | H | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 |
3) A lives 4th floor above D so according to this D will live on second floor.
4) B lives on an odd floor.
5) No. of floors above B is the same as the no. of floor below D so according to this B will live on 7th floor.
6) F lives 4th floor below B so F will live on 3rd floor.
7) There are 3 floors between C and G.
8) G lives below C’s floor so C will live on 5th floor and G will live on 1st floor.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | B | B |
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | C | C |
| 4 | E | H |
| 3 | F | F |
| 2 | D | D |
| 1 | G | G |
9) E lives below the H floor so according to this case 2 will get eliminated and case 1 will be right.
| No. of floor | Case 1 |
| 8 | H |
| 7 | B |
| 6 | A |
| 5 | C |
| 4 | E |
| 3 | F |
| 2 | D |
| 1 | G |
So case 1 will be our correct final case.
Hence, F lives on floor number third.
17. What is the sum of the floor numbers of B and H?
A. 10
B. 12
C. 14
D. 15
E. 9
Solution
1) A lives on 6th floor.
2) There is one floor between A and H.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | ||
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | ||
| 4 | H | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 1 |
3) A lives 4th floor above D so according to this D will live on second floor.
4) B lives on an odd floor.
5) No. of floors above B is the same as the no. of floor below D so according to this B will live on 7th floor.
6) F lives 4th floor below B so F will live on 3rd floor.
7) There are 3 floors between C and G.
8) G lives below C’s floor so C will live on 5th floor and G will live on 1st floor.
| No. of floor | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| 8 | H | |
| 7 | B | B |
| 6 | A | A |
| 5 | C | C |
| 4 | E | H |
| 3 | F | F |
| 2 | D | D |
| 1 | G | G |
9) E lives below the H floor so according to this case 2 will get eliminated and case 1 will be right.
| No. of floor | Case 1 |
| 8 | H |
| 7 | B |
| 6 | A |
| 5 | C |
| 4 | E |
| 3 | F |
| 2 | D |
| 1 | G |
So case 1 will be our correct final case.
The sum of the floor numbers of B and H = (8 + 7) = 15
Hence, the sum of the floor numbers of B and H is 15.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language
‘ga sa ta ha’ means ‘arun watches action movies’,
‘ha ta va ra’ means ‘arun writes action story’,
‘sa fa ha ba’ means ‘action movies have stunts’,
‘va ta ha ca’ means ‘arun narrated action story’.
18. Which of the following means ‘have’ in that code language?
A. sa
B. fa
C. ba
D. Either (1) or (2)
E. Either (2) or (3)
Solution
In the given coding language,

Hence, ‘have’ is coded as ‘fa’ or ‘ba’.
19. Code ‘ca’ is for which of the following word in the given language?
A. arun
B. narrated
C. action
D. story
E. Either (1) or (2)
Solution
In the given coding language,

Hence ‘ca’ is code for ‘narrated’.
20. What would be the code for ‘arun watches real stunts’?
A. ga ta fa za
B. ta za fa sa
C. za ta ga ba
D. ga za ta ha
E. Either (1) or (3)
Solution
In the given coding language,

Code for ‘arun’ is ‘ta’,
Code for ‘watches’ is ‘ga’,
Code for ‘real’ is ‘za’,
Code for ‘stunts’ is either ‘fa’ or ‘ba’.Hence, the possible answer is ‘ga ta fa za’ or ‘za ta ga ba’.
21. In a certain language ‘action movies have horrible stunts’ is coded as ‘fa ba ha sa wa’, then what would be the code for ‘horrible’?
A. ba
B. ha
C. wa
D. sa
E. fa
Solution
In the given coding language,

Code for ‘action movies have stunts’ is ‘ha sa ba fa’,
Hence, the possible code for ‘horrible’ is ‘wa’.
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C
22. How many such symbols are there in the above arrangement each of which are immediately preceded by an alphabet and followed by a number?
A. Two
B. Three
C. None
D. One
E. More than three
Solution
Given series:
Left side F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C Right side
1) Symbols which are immediately preceded by an alphabet and followed by a number:
Required order is, Alphabet → Symbol → Number
F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © CHence, there are 2 symbols which are immediately preceded by an alphabet and followed by a number: F @ 5 and C * 9.
23. If all the numbers in the above arrangement are dropped, then which of the following will be eleventh from right end?
A. U
B. B
C. W
D. A
E. None of these
Solution
Given series:
Left side F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C Right side
1) If all the numbers are dropped:
Left side F @ R $ J P E H % I B # A W U G C * & Z N M © C Right side
2) 11th element from the right end is: WThen, letter / number that is eleventh from right end is ‘W’.
24. Which of the following is 10th to the left of the 18th element from the left end of the above arrangement?
A. J
B. E
C. I
D. P
E. None of these
Solution
Given series:
Left side F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C Right side
As, left – Left = Left
18th from the left – 10th from the left = 8th from the leftClearly, 8th from the left is ‘P’.
25. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way based on their positions in the above arrangement and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
A. 3 J $
B. E % H
C. # 2 W
D. Z © M
E. U * 9
Solution
Given series:
Left side F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C Right side
Here, the group is formed in which second element is third to the right of the first element, and the third element is just before the second element.
3 J $ → F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C
E % H → F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C
# 2 W → F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C
Z © M → F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C
U * 9 → F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © CHence, U * 9 does not belong to the group.
26. How many such consonants are there in the above arrangement each of which is immediately preceded by a number but not immediately followed by a symbol?
A. Two
B. One
C. Three
D. Five
E. None
Solution
Given series:
Left side F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © C Right side
Consonants which are immediately preceded by a number but not immediately followed by a symbol:
Required order is: Number → Consonant → Number / Alphabet
F @ 5 3 R $ J P E 1 H % I 8 4 B 6 # A W 2 U G C * 9 & Z N M © CHence, there is only one consonant which is immediately preceded by a number but not immediately followed by a symbol: ‘4 B 6’
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question that follow.
Eight persons K, L, P, Q, M, N, O, J were born in different months i.e. January, April, July, September on two different dates 10th or 17th. Only One person was born on one date.
L was born in the month of July. Two persons were born between L and P but L is not born on an even date. K born in the month having 30 days with odd date. M was born in an even date of September and two persons were born between M and N. J and O were born in the same month. Q and J were born on the same date.
27. Who among following born on 10th January?
A. K
B. Q
C. N
D. M
E. J
Solution
Persons: K, L, P, Q, M, N, O, J
Months: January, April, July, September
Date: 10th and 17th
1) L was born in the month of July. Two persons born between L and P but L is not born on even date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | ||
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | ||
| July(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | |
| 17 |
2) K born in the month having 30 days with odd date.
| Months | Date | PersonCase 1 | Person Case 2 |
| January(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | |||
| April(30) | 10 | P | P |
| 17 | K | ||
| July(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | L | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | ||
| 17 | K |
3) M was born in even date of September month and two persons born between M and N.
So, case 2 will be eliminated.
4) J and O born in the same month. Q and J were born on the same date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | J |
| 17 | O | |
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | N | |
| July(31) | 10 | Q |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | M |
| 17 | K |
Hence, j born on 10th January.
28. Find the odd one out?
A. O
B. N
C. L
D. Q
E. K
Solution
Persons: K, L, P, Q, M, N, O, J
Months: January, April, July, September
Date: 10th and 17th
1) L was born in the month of July. Two persons born between L and P but L is not born on even date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | ||
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | ||
| July(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | |
| 17 |
2) K born in the month having 30 days with odd date.
| Months | Date | PersonCase 1 | Person Case 2 |
| January(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | |||
| April(30) | 10 | P | P |
| 17 | K | ||
| July(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | L | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | ||
| 17 | K |
3) M was born in even date of September month and two persons born between M and N.
So, case 2 will be eliminated.
4) J and O born in the same month. Q and J were born on the same date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | J |
| 17 | O | |
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | N | |
| July(31) | 10 | Q |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | M |
| 17 | K |
All were born on an odd date except Q.Hence, Q is odd on out.
29. How many persons were born between P and M?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. Five
Solution
Persons: K, L, P, Q, M, N, O, J
Months: January, April, July, September
Date: 10th and 17th
1) L was born in the month of July. Two persons born between L and P but L is not born on even date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | ||
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | ||
| July(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | |
| 17 |
2) K born in the month having 30 days with odd date.
| Months | Date | PersonCase 1 | Person Case 2 |
| January(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | |||
| April(30) | 10 | P | P |
| 17 | K | ||
| July(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | L | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | ||
| 17 | K |
3) M was born in even date of September month and two persons born between M and N.
So, case 2 will be eliminated.
4) J and O born in the same month. Q and J were born on the same date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | J |
| 17 | O | |
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | N | |
| July(31) | 10 | Q |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | M |
| 17 | K |
Hence, there are three persons between the P and M.
30. Who is born in both date of September month?
A. M, K
B. O, M
C. J, O
D. M, L
E. N, Q
Solution
Persons: K, L, P, Q, M, N, O, J
Months: January, April, July, September
Date: 10th and 17th
1) L was born in the month of July. Two persons born between L and P but L is not born on even date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | ||
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | ||
| July(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | |
| 17 |
2) K born in the month having 30 days with odd date.
| Months | Date | PersonCase 1 | Person Case 2 |
| January(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | |||
| April(30) | 10 | P | P |
| 17 | K | ||
| July(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | L | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | ||
| 17 | K |
3) M was born in even date of September month and two persons born between M and N.
So, case 2 will be eliminated.
4) J and O born in the same month. Q and J were born on the same date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | J |
| 17 | O | |
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | N | |
| July(31) | 10 | Q |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | M |
| 17 | K |
Hence, it’s clear that M and K are born in the month of September.
31. Who was born just before person Q?
A. O
B. N
C. L
D. P
E. K
Solution
Persons: K, L, P, Q, M, N, O, J
Months: January, April, July, September
Date: 10th and 17th
1) L was born in the month of July. Two persons born between L and P but L is not born on even date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | ||
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | ||
| July(31) | 10 | |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | |
| 17 |
2) K born in the month having 30 days with odd date.
| Months | Date | PersonCase 1 | Person Case 2 |
| January(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | |||
| April(30) | 10 | P | P |
| 17 | K | ||
| July(31) | 10 | ||
| 17 | L | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | ||
| 17 | K |
3) M was born in even date of September month and two persons born between M and N.
So, case 2 will be eliminated.
4) J and O born in the same month. Q and J were born on the same date.
| Months | Date | Person |
| January(31) | 10 | J |
| 17 | O | |
| April(30) | 10 | P |
| 17 | N | |
| July(31) | 10 | Q |
| 17 | L | |
| September(30) | 10 | M |
| 17 | K |
Hence, N was born just before Q
32. How many such pairs of letters are there in the word EXAMINATION, each of which has as many letters between them in the word, as they have in the English alphabet (considering both ways)?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. More than three
Solution
To know the pair of letters which has as many letters between them in word EXAMINATION as in English alphabets we will write the position number of letters in English alphabets.
| E | X | A | M | I | N | A | T | I | O | N |
| 5 | 24 | 1 | 13 | 9 | 14 | 1 | 20 | 9 | 15 | 14 |
In our word as well as in English alphabets there are 4 alphabets between E and I and no alphabet between O and N.
Hence we have 2 pairs.
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given question:
A certain number of people sitting in a South facing row. Positions of few people are known. Only two persons sit between F and G who is sitting to the left of F. A sits second to the right of R. Only three persons sit between P and R. O sits second to the right of A. There are four persons between O and G. R is 5th from one of the extreme end. G is sitting on 8th position from right end.
33. How many people are sitting in the linear row?
A. 17
B. 18
C. 19
D. More than 19
E. Can’t be determine
Solution
1) R is 5th from one of the extreme end.
2) A sits second to the right of R.
Case I
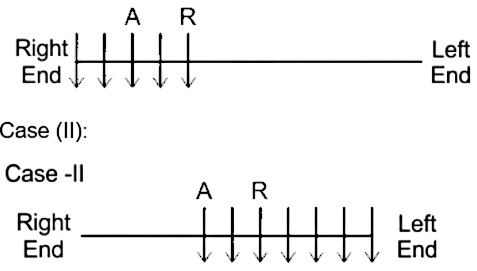
3) O sits second to the right of A.
4) Only three persons sit between P and R.
Using statement 3, Case I will be eliminated.

5) G is sitting on 8th position from right end.
6) There are four persons between O and G.
CAse II(a)
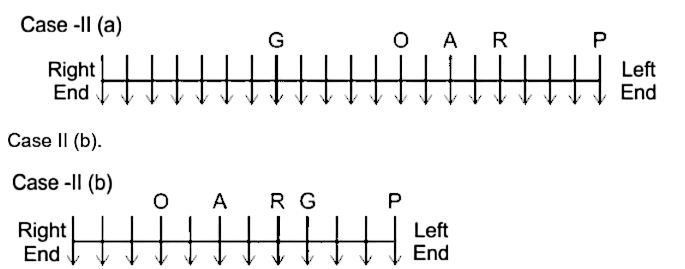
7) Only two persons sit between F and G who is sitting left of F. This eliminates case II(b)

Total 21 persons are sitting in the row.Hence, the correct answer is 21 i.e. more than 19.
34.How many people sits between A and F?
A. 9
B. 10
C. 8
D. 7
E. None of these
Solution
1) R is 5th from one of the extreme end.
2) A sits second to the right of R.
Case I

3) O sits second to the right of A.
4) Only three persons sit between P and R.
Using statement 3, Case I will be eliminated.

5) G is sitting on 8th position from right end.
6) There are four persons between O and G.
CAse II(a)
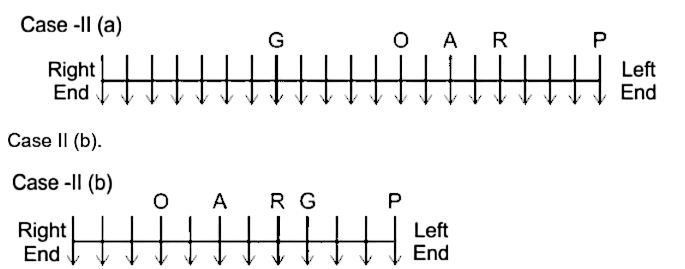
7) Only two persons sit between F and G who is sitting left of F. This eliminates case II(b)

Total 21 persons are sitting in the row.Hence, the correct answer is 9.
35. What is the position of R with respect to G?
A. 9th from left
B. 7th from right
C. 13th from right
D. 7th from left
E. None of these
Solution
1) R is 5th from one of the extreme end.
2) A sits second to the right of R.
Case I

3) O sits second to the right of A.
4) Only three persons sit between P and R.
Using statement 3, Case I will be eliminated.

5) G is sitting on 8th position from right end.
6) There are four persons between O and G.
CAse II(a)
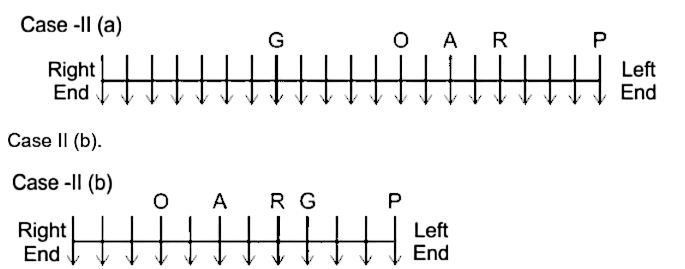
7) Only two persons sit between F and G who is sitting left of F. This eliminates case II(b)

Total 21 persons are sitting in the row.
R is sitting 9th to the left of G.Hence, the correct answer is ‘9th from left’.
36. What is the position of O?
A. 9th from left
B. 7th from right
C. 13th from right
D. Either 1 or 3
E. None of these
Solution
1) R is 5th from one of the extreme end.
2) A sits second to the right of R.
Case I

3) O sits second to the right of A.
4) Only three persons sit between P and R.
Using statement 3, Case I will be eliminated.

5) G is sitting on 8th position from right end.
6) There are four persons between O and G.
CAse II(a)
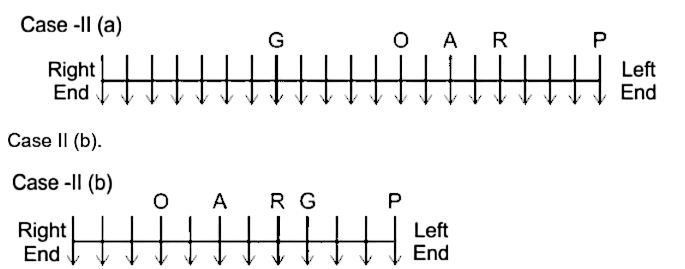
7) Only two persons sit between F and G who is sitting left of F. This eliminates case II(b)

Total 21 persons are sitting in the row.
O is sitting 9th from left end and 13th from the right end.Hence, the correct answer is ‘Either 1 or 3’.
37. If W is sitting to the immediate left of R, how many persons are there in between W and P?
A. Three
B. Two
C. Four
D. Five
E. None of these
Solution
1) R is 5th from one of the extreme end.
2) A sits second to the right of R.
Case I

3) O sits second to the right of A.
4) Only three persons sit between P and R.
Using statement 3, Case I will be eliminated.

5) G is sitting on 8th position from right end.
6) There are four persons between O and G.
CAse II(a)
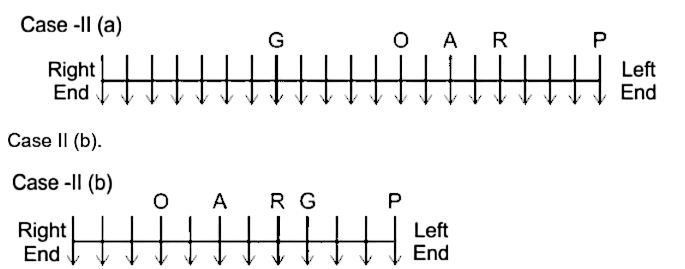
7) Only two persons sit between F and G who is sitting left of F. This eliminates case II(b)

Total 21 persons are sitting in the row.
If W is sitting to the immediate left of R, total 2 persons are there in between W and P.Hence, the correct answer is two.
Direction: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.Point V is 3m in the west of point X. Point Y is 6m in the west of point Z. Point W is 9m in the east of point T. Point U is 4m in the north of point V. Point Z is 5m in the south of point X. Point Y is 3m in the north of point T.
38. In which direction is point Y with respect to point X?
A. South – East
B. North
C. West
D. South – West
E. North – West
Solution
According to the given information, we get the following figure,
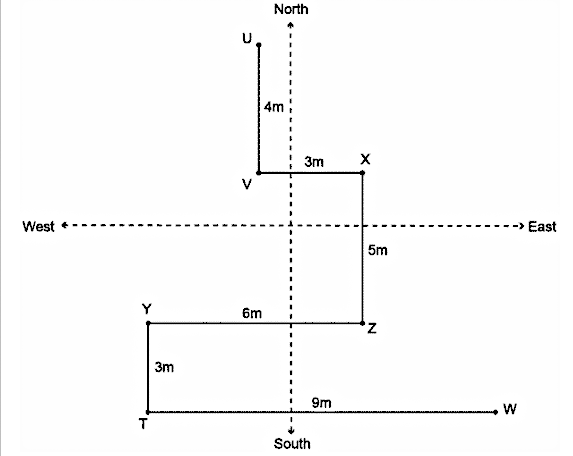
Hence, point Y is in south – west of point X.
39. If a person travel from W to U via points T, Y, Z, X and V then what distance will he/she cover?
A. 40m
B. 17m
C. 31m
D. 30m
E. 25m
Solution

Total distance between point W and U = WT + TY + YZ + ZX + XV + VU = 9m + 3m + 6m + 5m + 3m + 4m = 30mHence, ‘30m’ is the correct answer.
40. In which direction is point V with respect to point Z?
A. South – East
B. North
C. West
D. South – West
E. North – West
Solution
According to the given information, we get the following figure,

Hence, point V is in North – west of point Z.
Numerical Ability
Direction∶ Read the following graph carefully and answer the following questions∶

Stock remaining = Production – Sales
41. Find the average sales of all items.
A. 5340 litres
B. 5440 litres
C. 5020 litres
D. 5640 litres
E. 5120 litres
Solution
Calculation∶
Total sales of five items = (60 + 35 + 40 + 65 + 82) × 100
⇒ 28200 litres
Required average = 28200 / 5
⇒ 5640 litres
∴ The required average is 5640 litres
Direction∶ Read the following graph carefully and answer the following questions∶

Stock remaining = Production – Sales
42. Find the difference between the number of production and sales of all five items.
A. 5100 litres
B. 5840 litres
C. 6400 litres
D. 5400 litres
E. 5800 litres
Solution
Total production of five items = (80 + 50 + 55 + 70 + 85) × 100
⇒ 34000 litres
Total sales of five items = (60 + 35 + 40 + 65 + 82) × 100
⇒ 28200 litres
Required difference = (34000 – 28200) litres
⇒ 5800 litres
∴ The difference between productions and sales is 5800 litres
Direction∶ Read the following graph carefully and answer the following questions∶

Stock remaining = Production – Sales
43. Find approximately, the production of Milk is how much percent more than the sales of Milk?
A. 37%
B. 30%
C. 36%
D. 33%
E. 35%
Solution
Total production of milk = 8000 litres
Total sales of milk = 6000 litres
Required percentage = [(8000 – 6000) / 6000] × 100
⇒ 33.33% ≈ 33%
∴ The required percentage is 33%
Direction∶ Read the following graph carefully and answer the following questions∶

Stock remaining = Production – Sales
44. Find approximately, the total stock remaining is what percent of the total production of five items?
A. 12%
B. 14%
C. 15%
D. 17%
E. 19%
Solution
Calculation∶
Total production of five items = (80 + 50 + 55 + 70 + 85) × 100
⇒ 34000 litres
Total sales of five items = (60 + 35 + 40 + 65 + 82) × 100
⇒ 28200 litres
Total stock remaining = 34000 – 28200 = 5800 litres
Required percentage = (5800 / 34000) × 100
⇒ 17.05% ≈ 17%
Direction∶ Read the following graph carefully and answer the following questions∶

Stock remaining = Production – Sales
45. Find the ratio between the sales of Curd and Ghee.
A. 8 ∶ 13
B. 5 ∶ 13
C. 5 ∶ 8
D. 13 ∶ 8
E. 8 ∶ 5
Solution
Calculation∶
Sales of Curd = 4000 litres
Sales of Ghee = 6500 litres
Required ratio = 4000 ∶ 6500
⇒ 8 ∶ 13
∴ The required ratio is 8 ∶ 13
46. In the given question, two equations numbered I and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 16x + 48 = 0
II. y2 + 9y – 36 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x = y or the relationship cannot be established
D. x ≥ y
E. x ≤ y
Solution
Solution:
I. x2 – 16x + 48 = 0
Or, x2 – 12x -4x + 48 = 0
Or, (x – 4)(x – 12) = 0,
x = 12, 4
II. y2 + 9y – 36 = 0
Or, y2 + 12y – 3y – 36 = 0
Or, (y + 12)(y – 3) = 0,
y = -12, y = 3
So, x > y
47. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
4x2 – 7x – 2 = 0
3y2 + y – 2 = 0
A. if x > y
B. if x < y
C. if x ≥ y
D. if x ≤ y
E. if x = y or relationship can’t be established
Solution
Equation I
4x2 – 7x – 2 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – 8x + x – 2 = 0
⇒ 4x (x – 2) + 1 (x – 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 2) (4x + 1) = 0
⇒ x = 2, – 0.25
Equation ii
3y2 + y – 2 = 0
⇒ 3y2 + 3y – 2y – 2 = 0
⇒ 3y (y + 1) – 2(y + 1) = 0
⇒ (y + 1) (3y – 1) = 0
⇒ y = – 1, 0.67
Hence, relation between x and y cannot be established
48. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 = 16
II. y = √16
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. x2 = 16
⇒ x = ± 4
⇒ x = 4, -4
II. y = √16
⇒ y = 4
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 4 | 4 | x = y |
| -4 | 4 | x < y |
Hence, x ≤ y.
Mistake Point
x2 = 16 gives x = +4 and -4 while √16 gives only +4.
49. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 2x2 + 5x – 3 = 0
II. y2 – 14y + 24 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
i. 2x2 + 5x – 3 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 6x – x – 3 = 0
⇒ (2x – 1) (x + 3) = 0
⇒ x = 1 / 2, -3
ii. y2 – 14y + 24 = 0
⇒ y2 – 12y – 2y + 24 = 0
⇒ (y – 12) (y – 2) = 0
⇒ y = 12, 2
| Value of X | Value of Y | Relation |
| 1 / 2 | 12 | x < y |
| 1 / 2 | 2 | x < y |
| -3 | 12 | x < y |
| -3 | 2 | x < y |
Hence, x < y.
50. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 11x + 28 = 0
II. y2 – 17y + 70 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. x2 – 11x + 28 = 0
⇒ x2 – 4x – 7x + 28 = 0
⇒ (x – 4) (x – 7) = 0
⇒ x = 4, 7
II. y2 – 17y + 70 = 0
⇒ y2 – 7y – 10y + 70 = 0
⇒ (y – 7) (y – 10) = 0
⇒ y = 7, 10
| Value of X | Value of Y | Relation |
| 4 | 7 | x < y |
| 4 | 10 | x < y |
| 7 | 7 | x = y |
| 7 | 10 | x < y |
Hence, x ≤ y.
51. Dumbledore enterprises sold a master piece for $45000 then he gains an amount equal to loss when he sold the master piece for $23000. Find the cost price of the master piece.
A. 38000
B. 45000
C. 34000
D. 50000
E. 60000
Solution
Given
When, Master piece is sold for $45000 then he gains
When, Master piece is sold for $23000 then he get loss
Gain = loss
Concept used
SP – CP = Profit
CP – SP = Loss
Calculation
Let the cost price (c.p) = $ x
When , he gets loss
C.p = x – 23000 …….(1)
When , he gets profit/ gain
C.p = 45000 – x ……(2)
From (1) and (2)
x – 23000 = 45000 – x
⇒ 2x = 68000
⇒ x = 34000
∴ Cost price of the article is $34000
52. A tap can fill the cistern in 6 hrs and second one can empty the cistern in 8 hrs. If the cistern is empty, find the time taken by both the taps to fill the tank when opened simultaneously.
A. 20 hrs
B. 14 hrs
C. 10 hrs
D. 24 hrs
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
The first tap can fill the cistern in 6 hrs
The second tap can empty the tank in 8 hrs
Concept used:
Time ∝ 1/Efficiency
Calculation:
Taking the L.C.M of 6 and 8
L.C.M of 6 and 8 = 24
⇒ Efficiency of first tap = 24/6 = 4
⇒ Efficiency of second tap = 24/8 = 3
1-hour work when both taps are opened = 4 – 3 = 1
Both taps will fill the tank in 24/1 = 24 hrs
∴ The required time is 24 hours.
Directions: Read the information given below and answer the following questions.
The table shows numbers of bikes sold in the year 2019 and 2020 by showroom A, B, C, D and E.
| Showroom | Year 2019 | Year 2020 |
| A | 2500 | 2200 |
| B | 1000 | 1500 |
| C | 2000 | 2200 |
| D | 3000 | 3200 |
| E | 3500 | 3400 |
53. What is the average sales of bikes of all the showrooms in 2020?
A. 12500
B. 2500
C. 2600
D. 1500
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Sales of showroom A in 2020 = 2200
Sales of showroom B in 2020 = 1500
Sales of showroom C in 2020 = 2200
Sales of showroom D in 2020 = 3200
Sales of showroom E in 2020 = 3400
Formula used:
Average = (Sum of values)/(Number of values)
Calculations:
Average = (2200 + 1500 + 2200 + 3200 + 3400)/5
⇒ 12500/5
⇒ 2500
∴ Average sales of bikes of all the showrooms in 2020 is 2500
Directions: Read the information given below and answer the following questions.
The table shows numbers of bikes sold in the year 2019 and 2020 by showroom A, B, C, D and E.
| Showroom | Year 2019 | Year 2020 |
| A | 2500 | 2200 |
| B | 1000 | 1500 |
| C | 2000 | 2200 |
| D | 3000 | 3200 |
| E | 3500 | 3400 |
54. What is the ratio of sales of showroom A and D together in 2019 to sales of showroom C and E together in 2020?
A. 56 : 55
B. 55 : 56
C. 1 : 1
D. 2 : 3
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Sales of showroom A in 2019 = 2500
Sales of showroom D in 2019 = 3000
Sales of showroom C in 2020 = 2200
Sales of showroom E in 2020 = 3400
Calculations:
Total sales of showroom A and D in 2019 = 2500 + 3000
⇒ 5500
Total sales of showroom C and E in 2020 = 2200 + 3400
⇒ 5600
Ratio = 5500 : 5600
⇒ 55 : 56
Directions: Read the information given below and answer the following questions.
The table shows numbers of bikes sold in the year 2019 and 2020 by showroom A, B, C, D and E.
| Showroom | Year 2019 | Year 2020 |
| A | 2500 | 2200 |
| B | 1000 | 1500 |
| C | 2000 | 2200 |
| D | 3000 | 3200 |
| E | 3500 | 3400 |
55. What is the difference of sales of all the showroom in 2019 and sales of all the showrooms in 2020?
A. 500
B. 600
C. 700
D. 800
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Sales of showroom A in 2019 = 2500
Sales of showroom B in 2019 = 1000
Sales of showroom C in 2019 = 2000
Sales of showroom D in 2019 = 3000
Sales of showroom E in 2019 = 3500
Sales of showroom A in 2020 = 2200
Sales of showroom B in 2020 = 1500
Sales of showroom C in 2020 = 2200
Sales of showroom D in 2020 = 3200
Sales of showroom E in 2020 = 3400
Calculations:
Total sales of bikes in 2019 = 2500 + 1000 + 2000 + 3000 + 3500
⇒ 12000
Total sales of bikes in 2020 = 2200 + 1500 + 2200 + 3200 + 3400
⇒ 12500
Difference = 12500 – 12000
⇒ 500
∴ The difference of sales of all the showroom in 2019 and sales of all the showrooms in 2020 is 500
Directions: Read the information given below and answer the following questions.
The table shows numbers of bikes sold in the year 2019 and 2020 by showroom A, B, C, D and E.
| Showroom | Year 2019 | Year 2020 |
| A | 2500 | 2200 |
| B | 1000 | 1500 |
| C | 2000 | 2200 |
| D | 3000 | 3200 |
| E | 3500 | 3400 |
56. If sales of bikes of showroom C is increased by 12.5% in 2021 from 2020, then sales in 2021 is how much percent more than sales of bikes of C showroom in 2019?
A. 12.75%
B. 32.75%
C. 23.75%
D. 12.5%
E. 19.19%
Solution
Given:
Sales of bikes of showroom C in 2020 = 2200
Increased in sales = 12.5%
Sales of bikes of showroom C in 2019 = 2000
Calculations:
Sales of bikes of showroom C in 2021 = 2200 + (2200 × 12.5%)
⇒ 2200 + 275
⇒ 2475
Percentage difference = {(2475 – 2000)/2000} × 100
⇒ (475/2000) × 100
⇒ 23.75%
∴ Sales in 2021 is 23.75% more than sales of bikes of C showroom in 2019
Directions: Read the information given below and answer the following questions.
The table shows numbers of bikes sold in the year 2019 and 2020 by showroom A, B, C, D and E.
| Showroom | Year 2019 | Year 2020 |
| A | 2500 | 2200 |
| B | 1000 | 1500 |
| C | 2000 | 2200 |
| D | 3000 | 3200 |
| E | 3500 | 3400 |
57. If sales of bikes of showroom E increased by 1/17 in 2021 from 2020, then what is the ratio of sales of showroom B in 2019 to the sales of bikes of E showroom in 2021?
A. 18 : 5
B. 5 : 18
C. 7 : 18
D. 18 : 7
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Sales of bikes of showroom E in 2020 = 3400
Increased in sales = 1/17
Sales of showroom B in 2019 = 1000
Calculations:
Sales of showroom E in 2021 = 3400 + {3400 × 1/17)}
⇒ 3400 + 200
⇒ 3600
Ratio of sales of showroom B in 2019 to the sales of showroom E in 2021 = 1000 : 3600
⇒ 5 : 18
∴ The ratio of sales of showroom B in 2019 to the sales of bikes of E showroom in 2021 is 5 : 18
58. Monthly income of A is 5000 and his saving is 40% of his income then find his annual expenditure on school fees. He spent 25% of overall expenditure on school fees.
A. 8000
B. 9000
C. 2000
D. 4000
E. None
Solution
Given:
Monthly income of A = 5000
Saving of A = (40/100) × 5000
Calculation:
He spent on school fees in a month = 5000 × (60/100) × (25/100)
⇒ 750
For 12 month = 750 × 12
⇒ 9000
∴ The required result is 9000.
59. What is the difference between the compound interest compounded annually and half yearly on Rs. 10,000 for a year at 10% per annum?
A. Rs. 30
B. Rs. 25
C. Rs. 60
D. Rs. 50
E. Rs. 18
Solution
Formula used∶
CI(annual) = [P(1 + R /100)n – P]
CI (half yearly) = [P(1 + R / 200)2n – P]
Calculations∶
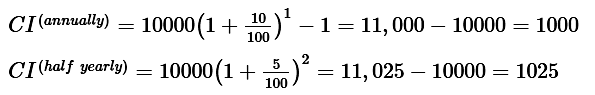
Difference = 1025 – 1000 = 25
∴ the correct answer is 25
60. A car travels first 160 km at 64 km/hr and the next 160 km at 80 km/hr. What is the average speed for the first 320 km of the tour?
A. 71.11 km/hr
B. 72.22 km/hr
C. 70.11 km/hr
D. 61.88 km/hr
E. 95.36 km/hr
Solution
Given:
Speed of car in first 160 km = 64 km/hr
Speed of car in next 160 km = 80 km/hr
Formula Used:
Average Speed = Total distance travelled / Total time taken
Calculation:
Time taken to travel first 160 km = 160/64 hr
Time taken to travel next 160 km = 160/80 hr
Total distance travelled = 160 + 160 = 320 km
Total time taken = (160/64) + (160/80)
⇒ 2.5 + 2 = 4.5 hr
∴ Average speed for the first 320 km of the tour = 320/4.5 km/hr
= 71.11 km/hr
Average Speed = (2xy)/(x + y)
⇒ (2 × 64 × 80) / (64 + 80) = 71.11 km/hr
∴ Average speed for the first 320 km of the tour = 71.11 km/hr
61. What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
(144 ÷ 12) × 5 + 72 – (64 ÷ 8) = ?
A. 124
B. 135
C. 146
D. 117
E. 108
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
(144 ÷ 12) × 5 + 72 – (64 ÷ 8) = ?
12 × 5 + 72 – 8 = ?
60 + 72 – 8 = ?
132 – 8 = ?
∴ 124 will come in place of the question mark
62. What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
8/5×75+20−(18/3)=?
A. 125
B. 134
C. 146
D. 153
E. 109
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
8/5×75+20−(18/3)=?
120 + 20 – 6 = ?
140 – 6 = ?
∴ 134 will come in place of the question mark
63. What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
√625 × 2 – 30% of 100 + 7 = ?
A. 27
B. 35
C. 46
D. 19
E. 56
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
√625 × 2 – 30% of 100 + 7 = ?
25 × 2 – 30 + 7 = ?
50 – 30 + 7 = ?
∴ 27 will come in place of the question mark
64. What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
182 – (225 ÷ 5) + 12 = ?
A. 273
B. 284
C. 265
D. 256
E. 291
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
182 – (225 ÷ 5) + 12 = ?
324 – 45 + 12 = ?
279 + 12 = ?
∴ 291 will come in place of the question mark
65. What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
(35% of 400)+(3/4 of 320)=?
A. 340
B. 357
C. 368
D. 380
E. 398
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
(35% of 400)+(3/4 of 320)=?
140 + 240 = ?
∴ 380 will come in place of the question mark
66. What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
25% of 480 × 2 – 36 ÷ 6 + 5 = ?
A. 231
B. 224
C. 217
D. 239
E. 245
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
25% of 480 × 2 – 36 ÷ 6 + 5 = ?
120 × 2 – 6 + 5 = ?
240 – 6 + 5 = ?
∴ 239 will come in place of the question mark
67. Find the value of x.
x2 = 72.8 × 5 − 852 ÷ 4 + √2025
A. 12
B. 13
C. 14
D. 16
E. 15
Solution
Solution:
x2 = 72.8 × 5 − 852 ÷ 4 + √2025
x2 = 364 − 213 + 45
x2 = 196
x = 14
68. Find the value of x.
√1521 + √1089 – x = 3√4096 + √1024
A. 32
B. 28
C. 30
D. 24
E. 26
Solution
Solution:
√1521 + √1089 – x = 3√4096 + √1024
39 + 33 – x = 16 + 32
72 – x = 48
x = 24
69. A boat can go 18 km downstream and 21 km upstream in 9 hours. Also, it can go 27km downstream and 15km upstream in 8 hours. What is the speed of boat downstream in km/hr ?
A. 18 km/hr
B. 3 km/hr
C. 6 km/hr
D. 9 km/hr
E. 12 km/hr
Solution
Given:
A boat can go 18 km downstream and 21 km upstream in 9 hours
Also, it can go 27km downstream and 15km upstream in 8 hours
Formula used:
Distance = Speed × Time
Downstream speed = Speed of the boat + Speed of the stream
Upstream speed = Speed of the boat – Speed of the stream
Calculation:
Let speeds of boat and stream be B and S respectively,
According to the question,
18/B+S+21/B−S=9 ——(1)
27/B+S+15/B−S=8 ——-(2)
Subtracting (1)× 3 and (2) × 2,
We get,
54/B+S+63/B−S−54/B+S−30/B−S=27−16
63/B−S−30/B−S=11
33/B−S=11
B – S = 33/11
Upstream = 3 km/hr
Sub (B – S) in (1),
18/B+S+21/3=9
18/B+S+7=9
18/B+S=2
B + S = 18/2
Downstream = 9 km/hr
Answer is 9 km/hr.
70. The marked price of an article is Rs. 15,000. After allowing a discount of 18%, the profit earned is Rs. 300. Marked price is how much percent more than the cost price of the article?
A. 50%
B. 35%
C. 30%
D. 25%
E. 20%
Solution
Given:
The marked price of an article is Rs. 15,000
Discount allowed = 18%
and Profit earned = Rs. 300
Formula used:
(1) Profit = Selling Price – Cost Price
(2) Selling Price = Marked Price × [1 – (Discount%)/100]
(3) Percent = [(Favourable value)/(Base Value)] × 100
Calculation:
Let the cost price of the article be Rs. x
then, Selling Price of the article = Marked Price × [1 – (Discount%)/100]
⇒ Rs. 15,000 × [1 – (18/100)]/100
⇒ Rs. 15,000 × (82/100)
⇒ Rs. 12,300
Profit = Selling Price – Cost Price
⇒ Rs. 300 = Rs. 12,300 – x
⇒ x = Rs. 12,000
Now, the difference between Marked Price and Cost Price = Rs. 15,000 – Rs. 12,000
⇒ Rs. 3,000
Required Percent = (Rs. 3,000/Rs. 12,000) × 100
⇒ (3/12) × 100
⇒ 25%
∴ The marked price is 25% more than the cost price of the article.
Direction: Read the following line graph carefully and answer the following questions
Following graph shows the production of cars in different years (in lakhs)

71. What is the difference between the production of Car A and Car B in all the years together?
A. 2,00,000
B. 3,00,000
C. 1,00,000
D. 50,000
E. 80,000
Solution
Production of Car A in year 2014 = 4.5 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2015 = 5.8 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2016 = 4.2 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2017 = 5.6 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2018 = 7.2 lakh
∴ Total production of Car A in all the years = 4.5 + 5.8 + 4.2 + 5.6 + 7.2 = 27.3 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2014 = 3.6 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2015 = 5 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2016 = 5.2 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2017 = 6.8 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2018 = 5.7 lakh
∴ Total production of Car B in all the years = 3.6 + 5 + 5.2 + 6.8 + 5.7 = 26.3 lakh
Difference between the production of Car A and Car B in all the years together
⇒ Difference = 27.3 – 26.3 = 1 lakh = 1,00,000
To find the difference between the production of Car A and Car B in all the years together, we will take individual difference per year.
Let assume number of Car A is greater than car B.
Required Difference = (4.5 – 3.6) + (5.8 – 5) +(4.2 – 5.2) + (5.6 – 6.8) + (7.2 – 5.7)
Required Difference = (0.9) + (0.8) +( – 1) + (– 1.2) + (1.5)
Required Difference = (0.9) + (0.8) +( – 1) + (– 1.2) + (1.5)
Required Difference = (0.9) – 0.2 + 0.3
Required Difference = 0.9 + 0.1
Required Difference = 1 Lakh = 1,00,000
Direction: Read the following line graph carefully and answer the following questions
Following graph shows the production of cars in different years (in lakhs)

72. The production of Car B in year 2014, 2015 and 2016 together is what percentage greater than or less than production of Car A in 2017 and 2018 together (approx. value)?
A. 27%
B. 8%
C. 19%
D. 46%
E. 30%
Solution
Production of Car B in year in 2014 = 3.6 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2015 = 5 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2016 = 5.2 lakh
∴ Total Production of Car B = 3.6 + 5 + 5.2 = 13.8 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2017 = 5.6 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2018 = 7.2 lakh
∴ Total production of Car A = 5.6 + 7.2 = 12.8 lakh
Percentage difference between production of Car B and Car A = {(Difference between production of Car B and Car A)/Production of Car A} × 100
⇒ Percentage difference = {(13.8 – 12.8)/12.8} × 100 = 100/12.8 = 7.8% ≈ 8%
Calculation note :
As we know that 1/12.5 = 8% So, when we increase denominator the value will slighty decrease and there is only one option near 7.8% i.e 8%.
Direction: Read the following line graph carefully and answer the following questions
Following graph shows the production of cars in different years (in lakhs)

73. What is the ratio of production of Car A in 2014, 2015 and 2016 and Car B in 2016, 2017, 2018 together?
A. 23 ∶ 25
B. 145 ∶ 177
C. 177 ∶ 145
D. 25 ∶ 23
E. 130 ∶ 156
Solution
Production of Car A in year 2014 = 4.5 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2015 = 5.8 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2016 = 4.2 lakh
⇒ Total production of Car A for these 3 yrs = 4.5 + 5.8 + 4.2 = 14.5 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2016 = 5.2 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2017 = 6.8 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2018 = 5.7 lakh
⇒ Total production of Car B for these 3 yrs = 5.2 + 6.8 + 5.7 = 17.7 lakh
∴ Ratio of production of Car A and Car B = 14.5 ∶ 17.7 = 145 ∶ 177
Important Point
You can solve this question by calculation the production of either Car A or Car B.
If you calculate for car A,
Production of Car A in year 2014 = 4.5 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2015 = 5.8 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2016 = 4.2 lakh
⇒ Total production of Car A for these 3 yrs = 4.5 + 5.8 + 4.2 = 14.5 lakh
Answer is option number 2.
Similarly,If you calculate for car B,
Production of Car B in year in 2016 = 5.2 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2017 = 6.8 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2018 = 5.7 lakh
⇒ Total production of Car B for these 3 yrs = 5.2 + 6.8 + 5.7 = 17.7 lakh
Answer is option number 2.
Because no values on either side is multiple of value of either side.
Example: On considering Left Side, 145 is neither the multiple nor the factor of any given number on left side.
Similarly for 177 on Rght side.
Direction: Read the following line graph carefully and answer the following questions
Following graph shows the production of cars in different years (in lakhs)

74. What was the increase of production of Car A from 2014 to 2018?
A. 50%
B. 40%
C. 70%
D. 60%
E. 45%
Solution
Production of Car A in year 2014 = 4.5 lakh
Production of Car A in year 2018 = 7.2 lakh
⇒ Required difference = 7.2 – 4.5 = 2.7 lakh
∴ Percentage increase = (2.7/4.5) × 100 = (3/5) × 100 = 60%
Direction: Read the following line graph carefully and answer the following questions
Following graph shows the production of cars in different years (in lakhs)

75. What is the Average production of Car B over the given years?
A. 5
B. 5.56
C. 4
D. 5.26
E. 6
Solution
Production of Car B in year in 2014 = 3.6 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2015 = 5 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2016 = 5.2 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2017 = 6.8 lakh
Production of Car B in year in 2018 = 5.7 lakh
⇒ Total production of Car B in all the years = 3.6 + 5 + 5.2 + 6.8 + 5.7 = 26.3 lakh
Average production of Car B = (26.3/5) = 5.26
∴ Average production of Car B = 5.26
76. In a defective dice throw, it is thrice as likely to get a six as any other number. Find the probability that upon throwing the dice twice no six is obtained.
A. 49/64
B. 25/64
C. 9/64
D. 16/36
E. None of these
Solution
Concept:-
In case of defective dice or deck or coin, total number of cases need not necessarily be same as in usual case.
Calculation:-
Number of cases possible = 8 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 6) (6 is thrice as likely to occur)
Probability of not getting a six = 5/8
Probability of not getting a six when dice is thrown twice = 5/8 × 5/8 = 25/64
77. P and Q together can complete a work in 36 days. With the help of R, they can complete it in 24 days. Find the number of days in which R can complete 75% of the work.
A. 24
B. 34
C. 44
D. 54
E. 64
Solution
Given:
Number of days in which P and Q can complete the work = 36 days
Number of days in which P, Q, and R can complete the work = 24 days
Concept used:
Total work = Efficiency × Time period
Calculation:
Taking the L.C.M of 36 & 24
L.C.M of 36 & 24 = 72
One day work of P and Q = 72/36 = 2
One day work of P, Q, and R = 72/24 = 3
One day work of R = 3 – 2 = 1
Number of days R takes to complete 75% of work = (75/100) × (72/1) = 54 days
∴ The number of days in which R can complete 75% of the work is 54 days.
78. A mixture of milk and water in a jar contains 35 L milk and 15 L water. If K L milk and K L water are mixed in same mixture to form a mixture of which 60% is 36 L, then what is the value of K?
A. 4 L
B. 5 L
C. 6 L
D. 7 L
E. None
Solution
Calculation:
⇒ From the given data
⇒ 60% × (35 + 15 + K + K) = 36
⇒ 50 + 2K = 60
⇒ K = 5 L
∴ The required result will be 5 L.
79. A train 280 m long is moving at a speed of 120 km/hr. What is the time taken by the train to cross a platform 320 m long?
A. 20 sec
B. 19 sec
C. 22 sec
D. 17 sec
E. None of these
Solution
Speed = 120 km/hr
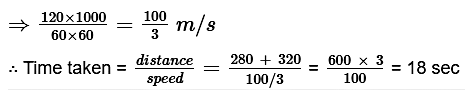
80. The diameters of two cylinders, whose volumes are equal, are in the ratio 3 ∶ 2. Their heights will be in the ratio-
A. 4 ∶ 9
B. 5 ∶ 6
C. 5 ∶ 8
D. 8 ∶ 9
E. 9 : 4
Solution
Let the diameter and height of cylinder 1 and 2 be denoted by d1, h1, d2 and h2 respectively.
Also,
⇒ Volume of cylinder = π × radius2 × height = π × (diameter/2) 2 × height
According to the question,
⇒ Volume of cylinder 1 = volume of cylinder 2
⇒ (πd12h1) /4 = (πd22h2) /4
⇒ (d1/d2)2 = h2/h1
⇒ h2/h1 = (3/2)2
⇒ h2/h1 = 9/4
⇒ h1 ∶ h2 = 4 ∶ 9
∴ Their heights will be in the ratio 4 ∶ 9
