1. What is ‘Zero Base Budgeting’?
A. No appraisal of new programs
B. Preparation of new budget every time
C. No curtailment in unproductive expenditure
D. Infinite deficit financing
Solution
The correct answer is- each year, budgeting starts from a scratch.
Key Points
- Zero-based budgeting(ZBB):
- Zero-based budgeting (ZBB) is a method of budgeting in which all expenses must be justified for each new period.
- Zero-based budgeting is a technique used by companies, but this type of budgeting can be used by individuals and families.
- Budgets are created around the monetary needs for each upcoming period, like a month.
- Zero-based budgeting helps managers tackle lower costs in a company.
- When an individual or family uses a zero-based budget, they will allocate all income to specific expenditures including retirement and savings, leaving you with zero dollars at the end of each pay period.
Important Points
- Advantages of zero-based budgeting:
- One of the advantages of a zero-based budget is that it’s a great way to track where your money is going, helps you to control your spending, and see the areas where you may be spending too much.
- If you’re new to budgeting, using this method is ideal as it’s easy to customize based on your monthly financial commitments.
- Additionally, to those who suffer from money worries and anxiety due to debt or spending that is out of control, this budgeting system may help to add some clarity to your finances that can’t be achieved by just ‘hoping for the best’ or praying for more money to appear in your bank account.
- It offers a number of advantages including operations, lower costs, budget flexibility, and strategic execution. It brings accuracy and productivity when managers think about how each dollar should spend. Indeed, lower cost, as well as coordination, may prevent misallocation happening when a budget grows.
Hence, the correct answer is- Zero-based budgeting (ZBB) means each year, budgeting starts from scratch.
2. Which of the following statements is correct regarding gender budgeting in India?
A. It ensures that financial outlays are made from a gender perspective.
B. It started in India with the Union Budget 2016–17.
C. It seek to create a separate budget.
D. More than one of the above
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
- Gender Budgeting (GB)
- It is concerned with the gender-sensitive formulation of legislation, programmes and schemes; allocation of resources; implementation and execution; audit and impact assessment of programmes and schemes; and follow-up corrective action to address gender disparities.
- A powerful tool for achieving gender mainstreaming so as to ensure that benefits of development reach women as much as men. Hence, Statement 4 is not correct.
- Does not seek to create a separate budget but seeks affirmative action to address the specific needs of women. Hence, Statement 3 is not correct.
- Monitors expenditure and public service delivery from a gender perspective.
- Entails dissection of the Government budgets to establish its gender differential impacts and to ensure that gender commitments are translated into budgetary commitments.
- According to the Ministry of Women and Child Development, “Gender budgeting is a powerful tool for achieving gender mainstreaming so as to ensure that benefits of development reach women as much as men.”
- Various initiatives with the objective of influencing and effecting gender-oriented budgetary policies, programs to tackle gender imbalances, promote gender equality and development are identified under gender-specific budgeting. Hence, Statement 1 is correct.
- Gender budgeting started in India in 2001. It was furthered by Union Budget 2006–07 which proposed an outlay of Rs. 28,737 crores dedicated to the cause of women. Hence, Statement 2 is not correct.
- The Union Budget 2006-07 also created gender budgeting cells in 32 ministries and departments.
- Gender budgeting in India follows the following measures-
- Specifically targeted expenditure to women and girls;
- Pro-women allocations
- Residual public expenditures that have gender–differential impacts.
3. Which of the following taxes is/are considered to be regressive in nature?
1. Goods and Service Tax
2. Income Tax
3. Cess
4. Value-added Tax
Select the correct answer using the code given below
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 3 and 4 only
C. 1 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Solution
The correct answer is 1, 3 and 4 only.
Key PointsRegressive tax:
- A regressive tax is a tax applied uniformly, taking a larger percentage of income from low-income earners than from high-income earners.
- It is in opposition to a progressive tax, which takes a larger percentage from high-income earners.
- A regressive tax affects people with low incomes more severely than people with high incomes because it is applied uniformly to all situations, regardless of the taxpayer.
- GST is Regressive if GST payments are expressed as a percentage of income.
- A rich person pays less tax as a percentage of his income compared to a poor person. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Cess is regarded as a lazy tax in public finance.
- It may be easy to collect, but it is Regressive and imposes an additional burden on the poorest section of taxpayers.
- Cesses are levied equally on both rich and poor. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Value-added tax (VAT):
- It is a tax on consumption and because lower-income households spend a greater share of their income on consumption than higher-income households do, the burden of a VAT is Regressive. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
- Income tax is Progressive, as poor people need to pay less tax rate as compared to rich people.
- India follows a progressive tax regime.
- A progressive tax system means that high-income earners are taxed more than low-income ones. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
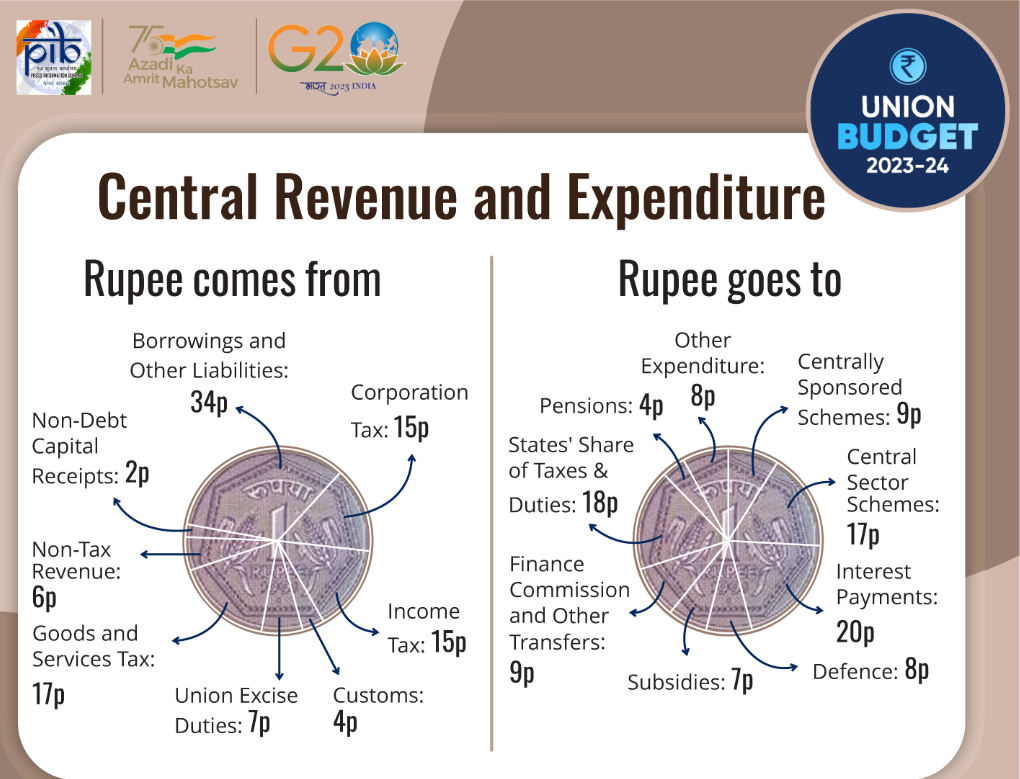
4. According to the Union Budget 2023-2024, in which sector does the Union Government expend the highest money?
A. Subsidies
B. Defence
C. Centrally sponsored schemes
D. Interest payments
Solution
The correct answer is Interest payments.
In News
- The 2023 Union Budget of India was presented by the Minister of Finance of India on February 01, 2023.
Key Points
- Government has pegged the total expenditure in Budget 2023-24 at Rs 45,03,097 crore.
- Interest payments will see highest share of expense i.e. 20%.
- States’ share of taxes & duties, Central Sector Scheme will be second and third in sequence of share of expenses.
5. What was the total allocation for the Ministry of Railway in the Union Budget 2023-24?
A. Rs. 2.40 lakh crore
B. Rs. 2.50 lakh crore
C. Rs. 2.60 lakh crore
D. Rs. 2.70 lakh crore
Solution
The correct answer is Rs. 2.40 lakh crore.
Key Points
- The total allocation for the Ministry of Railways in the Union Budget 2023-24 was Rs. 2.40 lakh crore.
- This is the highest ever allocation to the railways and continues on the trend followed last year with a gross budgetary support of Rs. 1.37 lakh crore in fiscal 2022-23.
- Here is a more detailed breakdown of the allocation:
- Capital expenditure: Rs. 2.01 lakh crore
- Revenue expenditure: Rs. 39,000 crore
- Subsidies: Rs. 1,500 crore
- The capital expenditure will be used for projects such as:
- Doubling and electrification of railway tracks
- Construction of new railway lines
- Upgrading of railway stations
- Purchase of new rolling stock
- The revenue expenditure will be used for:
- Salaries and pensions of railway employees
- Maintenance of railway infrastructure
- Provision of passenger amenities
- The subsidies will be used to provide concessions to passengers on certain trains.
- The allocation for the railways in the Union Budget 2023-24 is a significant increase from the previous year.
6. With reference to Economic Survey 2022-23, consider the following statements:
1. Insurance penetration in India has been steadily increasing, with life insurance penetration being above the emerging markets and global averages
2. The Pension Sector has witnessed a robust increase in subscribers and assets under management (AuM).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
Solution
The correct answer is Both 1 and 2
Key Points
Economic Survey 2022-23:
- The increasing outreach of the banking sector and capital markets is reflected in the insurance and pension sectors.
- Insurance penetration in India has been steadily increasing, with life insurance penetration being above the emerging markets and global averages. Hence statement 1 is correct
- Important government interventions and a conducive regulatory environment have supported the growth of the insurance market, which has seen increasing partnerships, product innovations, and vibrant distribution channels.
- India is poised to emerge as one of the fastest-growing insurance markets in the coming decade.
- The pension sector too has been taking rapid strides since the introduction of the National Pension Scheme (NPS), more recently, the Atal Pension Yojana (APY).
- The sector has witnessed a robust increase in the number of subscribers and assets under management (AuM). Hence statement 2 is correct
- The expansion of the sector has been aided by government measures such as relaxation in CCS (Pension) Rules, integration of electronic Pension Payment Order (e-PPO) with DigiLocker, and relaxation in the timeline for submitting Digital Life Certificate.
7. Which of the following are the fiscal policy measures taken by the government to control inflation?
A. Reduction in public expenditure and public borrowing.
B. Decreasing taxes on private businesses
C. Increasing interest rates in the economy.
D. Increase public expenditure and public borrowing.
Solution
The correct answer is Reduction in public expenditure and public borrowing.
Key Points
- Fiscal policy:
- It is the economic policy of the government that is concerned with (a) taxation (b) public expenditure and (c) public borrowing.
- The government uses fiscal policy to control the rising prices ordeal with the situation of deflation.
- At the time of inflation, the government increases taxes for dropping private spending. If direct taxes on profits increase, the total disposable income would reduce. As a result, the total spending of individuals decreases, which, in turn, reduces the money supply in the market. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
- Along with taxation policy, the government must reduce public expenditure and public borrowing to control excess demand. Reduction in public expenditure and public borrowing reduces the supply of money thereby reducing inflation. Hence statement 1 is correct and Statement 4 is not correct.
- Increasing interest rates in the economy to control inflation is a monetary policy tool and it is done by the Monetary Policy Committee of RBI. Hence statement 3 is not correct.
8. Match the following.
| List I | List II | ||
| A. | Direct tax | 1. | Excise duty |
| B. | Indirect tax | 2. | Interest receipt |
| C. | Non-tax receipts | 3. | Income tax |
A. A – 1, B – 2, C – 3
B. A – 2, B – 3, C – 1
C. A – 3, B – 1, C – 2
D. A – 3, B – 2, C – 1
Solution
The correct answer is option 3.
Important Points
| Direct tax | It is a tax in which the impact and incidence is on same person.It is borne by the person on whom it is levied.The burden of direct tax can not shifted to other person.The main example of direct tax is income tax.Income tax is levied on the income of individual, which can not be shifted to other person. |
| Indirect tax | It is tax in which impact and incidence of tax is on other people.These are those taxes which have their impact or burden on one person but the final payment or incidence will be on other person.The burden of tax can be shifted.It includes excise duty, custom duty, GST, etc.Excise duty is imposed by the central government on the goods produced with in the country except certain goods. |
| Non tax receipts | These are those receipts which is earned from sources other than taxes by the government.These are revenue receipts that are not generated by taxing the public.It includes fees, fines, interests received by government, escheats, administrative fees.Interest receipts: These are those interests received by the government through the loans provided by it to state governments, UTs, general public. |
- Hence, the main example of Direct tax is Income tax(A-3); the example of Indirect tax is excise duty(B-1); and the example of non tax receipts is interest receipts(C-2).
9. Fiscal deficit less interest payments is _______.
A. revenue deficit
B. budget deficit
C. fiscal surplus
D. primary deficit
Solution
The correct answer is Primary Deficit.
Key Points
- A fiscal deficit of fewer interest payments is Primary Deficit.
Primary Deficit:
- It is measured by subtracting the interest payments from the fiscal deficit.
- Primary Deficit = Fiscal Deficit – Interest Payments.
- A primary deficit is a measure of the current year’s fiscal operation after excluding the liability of interest payments created due to borrowings of the past.
- Primary deficit is considered a tool in the process of bringing in more transparency in the government’s expenditure pattern.
Additional Information
Revenue Deficit:
- Difference between total revenue expenditure and total revenue receipts.
Budget Deficit:
- Difference between total expenditure and total receipts.
Monetized Deficit:
- Increase in the net RBI credit to the Union Government.
Fiscal policy:
- It refers to the use of government spending and tax policies to influence economic conditions, especially macroeconomic conditions, including aggregate demand for goods and services, employment, inflation, and economic growth.
- A budget surplus occurs when receipts exceed expenditures.
- The term often refers to a government’s financial state, as individuals have “savings” rather than a “budget surplus”.
10. Consider the following:
1. Disinvestment proceeds
2. Foreign government grants
3. Loans received from international organizations
4. Loan recoveries from States and Union Territories
Which of the above constitute capital receipts of the Government of India?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Solution
The correct answer is 1, 3 and 4 only.
Key PointsCapital Budget:
- The Capital Budget is an account of the assets as well as liabilities of the central government, which takes into consideration changes in capital.
- It consists of capital receipts and capital expenditure of the government.
- This shows the capital requirements of the government and the pattern of their financing.
- The main items of Capital Receipts are:
- loans raised by the government from the public which are called market borrowings
- borrowing by the government from the Reserve Bank and commercial banks through the sale of treasury bills
- loans received from foreign governments and international organisations. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- recoveries of loans granted by the central government. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
- small savings (Post-Office Savings Accounts, National Savings Certificates, etc), provident funds
- net receipts obtained from the sale of shares/Disinvestment in Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs). Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Capital Expenditure:
- This includes expenditure on the acquisition of land, building, machinery, equipment, investment in shares, and loans and advances by the central government to state and union territory governments, PSUs and other parties.
- Foreign government grants are accounted under Revenue receipts of the Government of India. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
