1. Directions: Read the given instructions and answer the following questions:
Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca are nine persons who work in three different companies namely Apple, Microsoft, and Google such that not less than two persons work in the same company. Grace works in Microsoft where the maximum number of persons works. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google. Michael works with John. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
Question:
Which among the following is true?
A. Apple has the maximum number of persons working in it
B. Arthur works with Billy
C. Tommy works in Microsoft
D. Michael works in Google
E. Alfie and Luca work in different companies
Solution
Persons: Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca
Companies: Apple, Microsoft, and Google
Note: Not less than two persons work in the same company.
1. Grace works in Microsoft. where the maximum number of persons works.
2. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. So, Luca works in Google.
| Companies | Persons |
| Apple | |
| Microsoft | Grace |
| Luca |
3. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur.
4. Michael who works with John.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | JohnMichael | |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | Grace |
| Luca | Luca |
5. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google.
6. John does not work with Arthur.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | TommyArthur | JohnMichael |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | GraceTommyArthur |
| Luca | Luca |
7. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. So, Case 2 is eliminated.
8. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
So, Billy works in Google as maximum number of people works in Microsoft and not as Apple.
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael |
| LucaBilly |
9. The maximum number of persons works in Microsoft. So, Polly works in Microsoft.
Thus, the final arrangement is,
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichaelPolly |
| LucaBilly |
Thus, Alfie and Luca work in different companies is true.
2. Directions: Read the given instructions and answer the following questions:
Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca are nine persons who work in three different companies namely Apple, Microsoft, and Google such that not less than two persons work in the same company. Grace works in Microsoft where the maximum number of persons works. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google. Michael works with John. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
Question:
Which among the following is false about John?
I. He works in Google
II. He works with Grace in the same company
III. He and Alfie works in the same company
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only III
D. Both I and II
E. Both I and III
Solution
Persons: Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca
Companies: Apple, Microsoft, and Google
Note: Not less than two persons work in the same company.
1. Grace works in Microsoft. where the maximum number of persons works.
2. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. So, Luca works in Google.
| Companies | Persons |
| Apple | |
| Microsoft | Grace |
| Luca |
3. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur.
4. Michael who works with John.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | JohnMichael | |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | Grace |
| Luca | Luca |
5. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google.
6. John does not work with Arthur.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | TommyArthur | JohnMichael |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | GraceTommyArthur |
| Luca | Luca |
7. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. So, Case 2 is eliminated.
8. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
So, Billy works in Google as maximum number of people works in Microsoft and not as Apple.
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael |
| LucaBilly |
9. The maximum number of persons works in Microsoft. So, Polly works in Microsoft.
Thus, the final arrangement is,
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichaelPolly |
| LucaBilly |
Thus, Both I and III are false statement.
3. Directions: Read the given instructions and answer the following questions:
Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca are nine persons who work in three different companies namely Apple, Microsoft, and Google such that not less than two persons work in the same company. Grace works in Microsoft where the maximum number of persons works. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google. Michael works with John. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
Question:
Which company has the least number of persons working in it?
A. Apple
B. Microsoft
C. Google
D. Both Apple and Google
E. Both Microsoft and Apple
Solution
Persons: Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca
Companies: Apple, Microsoft, and Google
Note: Not less than two persons work in the same company.
1. Grace works in Microsoft. where the maximum number of persons works.
2. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. So, Luca works in Google.
| Companies | Persons |
| Apple | |
| Microsoft | Grace |
| Luca |
3. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur.
4. Michael who works with John.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | JohnMichael | |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | Grace |
| Luca | Luca |
5. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google.
6. John does not work with Arthur.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | TommyArthur | JohnMichael |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | GraceTommyArthur |
| Luca | Luca |
7. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. So, Case 2 is eliminated.
8. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
So, Billy works in Google as maximum number of people works in Microsoft and not as Apple.
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael |
| LucaBilly |
9. The maximum number of persons works in Microsoft. So, Polly works in Microsoft.
Thus, the final arrangement is,
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichaelPolly |
| LucaBilly |
Thus, Google has the least number of persons working in it.
4. Directions: Read the given instructions and answer the following questions:
Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca are nine persons who work in three different companies namely Apple, Microsoft, and Google such that not less than two persons work in the same company. Grace works in Microsoft where the maximum number of persons works. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google. Michael works with John. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
Question:
In some way Arthur is related to Alfie, John is related to Grace then who among the following is related to Michael?
A. Polly
B. Luca
C. Billy
D. Arthur
E. Tommy
Solution
Persons: Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca
Companies: Apple, Microsoft, and Google
Note: Not less than two persons work in the same company.
1. Grace works in Microsoft. where the maximum number of persons works.
2. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. So, Luca works in Google.
| Companies | Persons |
| Apple | |
| Microsoft | Grace |
| Luca |
3. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur.
4. Michael who works with John.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | JohnMichael | |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | Grace |
| Luca | Luca |
5. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google.
6. John does not work with Arthur.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | TommyArthur | JohnMichael |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | GraceTommyArthur |
| Luca | Luca |
7. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. So, Case 2 is eliminated.
8. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
So, Billy works in Google as maximum number of people works in Microsoft and not as Apple.
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael |
| LucaBilly |
9. The maximum number of persons works in Microsoft. So, Polly works in Microsoft.
Thus, the final arrangement is,
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichaelPolly |
| LucaBilly |
Thus, Polly is related to Michael.
5. Directions: Read the given instructions and answer the following questions:
Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca are nine persons who work in three different companies namely Apple, Microsoft, and Google such that not less than two persons work in the same company. Grace works in Microsoft where the maximum number of persons works. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google. Michael works with John. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
Question:
Who among the following works with Billy?
A. Grace
B. Tommy
C. Polly
D. Luca
E. Arthur
Solution
Persons: Tommy, Arthur, Grace, Polly, John, Alfie, Billy, Michael, and Luca
Companies: Apple, Microsoft, and Google
Note: Not less than two persons work in the same company.
1. Grace works in Microsoft. where the maximum number of persons works.
2. Luca neither works in Apple nor Microsoft. So, Luca works in Google.
| Companies | Persons |
| Apple | |
| Microsoft | Grace |
| Luca |
3. John works in either Microsoft or Apple but not with Arthur.
4. Michael who works with John.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | JohnMichael | |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | Grace |
| Luca | Luca |
5. Tommy works with Arthur but not in the Google.
6. John does not work with Arthur.
| Companies | Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Apple | TommyArthur | JohnMichael |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael | GraceTommyArthur |
| Luca | Luca |
7. Alfie works with Arthur but not with Grace. So, Case 2 is eliminated.
8. Billy does not work in Microsoft.
So, Billy works in Google as maximum number of people works in Microsoft and not as Apple.
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichael |
| LucaBilly |
9. The maximum number of persons works in Microsoft. So, Polly works in Microsoft.
Thus, the final arrangement is,
| Companies | Case 1 |
| Apple | TommyArthurAlfie |
| Microsoft | GraceJohnMichaelPolly |
| LucaBilly |
Thus, Luca works with Billy.
6. Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
T walks 10 km south from his home and turns right and walks 6 km to reach the saloon. Then T turns right and walks 20 km. Again T turns right and walks 12 km to reach his office. Finally, T walks 10 km after turning right to reach the mall.
Question:
If a ice cream shop is 10km south of mall, then it is in which direction with respect to the home?
A. North – East
B. South – West
C. East
D. South – East
E. West
Solution
Given:
1) T walks 10 km south from his home and turns right and walks 6 km to reach the saloon.
2) T turns right and walks 20 km.
3) T turns right and walks 12 km to reach his office.
4) T walks 10 km after turning right to reach the mall.
The diagram according to the above information is:

Hence, the ice cream shop is in the ‘South – East’ direction with respect to the
7. Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
T walks 10 km south from his home and turns right and walks 6 km to reach the saloon. Then T turns right and walks 20 km. Again T turns right and walks 12 km to reach his office. Finally, T walks 10 km after turning right to reach the mall.
Question:
In which direction saloon is located with respect to office?
A. North
B. North – West
C. South – East
D. South – West
E. East
Solution
Given:
1) T walks 10 km south from his home and turns right and walks 6 km to reach the saloon.
2) T turns right and walks 20 km.
3) T turns right and walks 12 km to reach his office.
4) T walks 10 km after turning right to reach the mall.
The diagram according to the above information is:
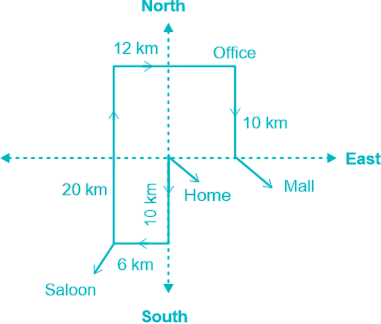
Hence, the saloon is in the ‘South – West’ direction with respect to the office.
8. Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
T walks 10 km south from his home and turns right and walks 6 km to reach the saloon. Then T turns right and walks 20 km. Again T turns right and walks 12 km to reach his office. Finally, T walks 10 km after turning right to reach the mall.
Question:
What is the distance between starting and ending point?
A. 4 km
B. 7 km
C. 6 km
D. 2 km
E. 10 km
Solution
Given:
1) T walks 10 km south from his home and turns right and walks 6 km to reach the saloon.
2) T turns right and walks 20 km.
3) T turns right and walks 12 km to reach his office.
4) T walks 10 km after turning right to reach the mall.
The diagram according to the above information is:
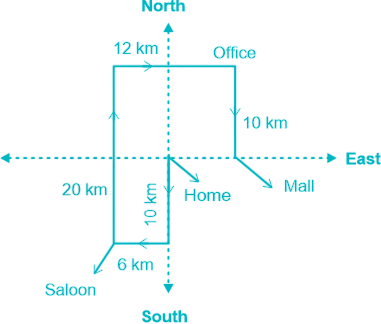
Hence, ‘6 km’ is the distance between the starting and ending points.
9. Direction: In each of the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/ are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: P < Q ≥ R; R < S ≤ T; Q > U ≤ T
Conclusions:
I. P > TII. Q ≥ S
A. Only II is true
B. Only I is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. None is true
E. Either I or II is true
Solution
Given statement: P < Q ≥ R; R < S ≤ T; V > U ≤ T
On combining: P < Q ≥ R < S ≤ T ≥ U < V
Conclusion:
I. P > T → False (as P < Q ≥ R < S ≤ T) thus clear relation between P and T cannot be determined as the symbols are in reverse order.
II. Q ≥ S → False (as Q ≥ R < S) thus clear relation between Q and S cannot be determined as the symbols are in reverse order.Hence, none is true.
10. Direction: In each of the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/ are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: A > B ≤ C; B > D > E; A < F ≤ G
Conclusions:
I. A > EII. F > D
A. Only II is true
B. Only I is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. None is true
E. Either I or II is true
Solution
Given statement: A > B ≤ C; B > D > E; A < F ≤ G
On combining: G ≥ F > A > B > D > E
Conclusion:
I. A > E → True (as A > B > D > E → A > E)
II. F > D → True (as F > A > B > D → F > D)
Hence, both conclusion I and II are true.
11. Direction: In each of the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/ are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement: M > N ≤ O; M < P > Q; O ≤ R < S
Conclusions:
I. S > NII.M > Q
A. Only II is true
B. Only I is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. None is true
E. Either I or II is true
Solution
Given statement: M > N ≤ O; M < P > Q; O ≤ R < S
On combining: Q < P > M > N ≤ O ≤ R < S
Conclusion:
I. S > N → True (as S > R → R ≥ O → O ≥ N → So, S > N)
II. M > Q → False (as Q < P > M) thus clear relation between M and Q cannot be determined as the symbols are in reverse order.
Hence, only I is true.
12. Directions: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below: A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P
Question:
Which of the following is the fifth to the right of the sixth element from the right end of the above arrangement?
A. P
B. Q
C. δ
D. K
E. 5
Solution
Given series:
Left Side A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P Right Side
As, Right – Right = Right
6th from the Right – 5th from the Right = 1st from the Right
Clearly, 1st from the Right is P.
Hence, P is the fifth to the right of the sixth element from the right end of the above arrangement.
13. Directions: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below: A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P
Question:
Which of the following element is exactly in the middle between the fifteenth from the left end and the fifteenth from the right end in the above arrangement?
A. #
B. J
C. 4
D. M
E. None of these
Solution
Given series:
Left Side A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P Right Side
15th from the left → $
15th from right → 3
Terms between $and 3 are M 4 J # U
Therefore, J is exactly in middle of $and 3.
Hence, J is exactly in middle between the fifteenth from the left end and the fifteenth from the right end in the above arrangement.
14. Directions: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below: A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P
Question:
How many such vowels are there in the above arrangement each of which is immediately followed by a symbol but not immediately preceded by a number?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. More than three
Solution
Given series:
Left Side AC B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P Right Side
Vowels which are immediately followed by a symbol but not immediately preceded by a number:
required order is: Not number → Vowel → Symbol
A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P
Hence, there is no vowel which are immediately followed by a symbol but not immediately preceded by a number.
Hence, the correct answer is none.
15. Directions: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below: A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P
Question:
How many such numbers are there between first A and V each of which is both immediately preceded and immediately followed by a consonant?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. More than three
Solution
Given series:
Left Side A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P Right Side
Required order: First A → → Consonant → Number → Consonant → → V
A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P
Hence, there are 2 such numbers.
16. Directions: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below: A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P
Question:
How many such alphabets are there in the above arrangement each of which are immediately preceded by an alphabet and followed by a symbols?
A. None
B. Two
C. One
D. Three
E. More than three
Solution
Given series:
Left Side A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P Right Side
Alphabets which are immediately preceded by an alphabet and followed by a symbol:
Required order is: Alphabet → Alphabet → Symbol
A C B @ K I 9 D L 4 © 5 2 T $ M 4 J # U 3 1 A δ K 5 V W 6 % F Q 7 H P
Hence, there is only one alphabet which is immediately preceded by an alphabet and followed by a symbol: C B @.
17. Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
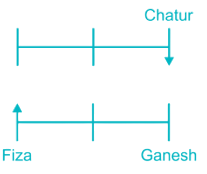
Six persons Amit, Dinesh, Chatur, Fiza, Ganesh and Zeeshan are sitting in two parallel rows viz. row – 1 and row – 2. Amit, Dinesh and Chatur are sitting in row – 1, while Fiza, Ganesh and Zeeshan are sitting in another row. Some of them are facing north and some of them are facing south.
Fiza faces north. The one who sits opposite to Fiza sits second to the right of Chatur. Dinesh faces south and sits opposite to the one, who sits to the immediate right of Ganesh. Ganesh sits second to right of Fiza. Amit faces the opposite direction of Chatur. Ganesh sits immediate right of Zeeshan.
Question:
Who among the following faces Zeeshan?
A. Amit
B. Fiza
C. Ganesh
D. Dinesh
E. None of these
Solution
1) Fiza faces north.
2) The one who sits opposite to Fiza sits second to the right of Chatur.
3) Ganesh sits second right of Fiza.

4) Dinesh faces south and sits opposite to the one, who sits to the immediate right of Ganesh.
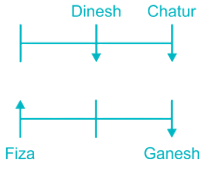
5) Amit faces opposite direction of Chatur.
6) Ganesh sits immediate right of Zeeshan.
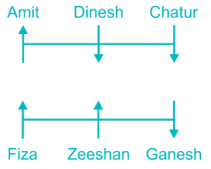
Therefore, Dinesh faces Zeeshan.
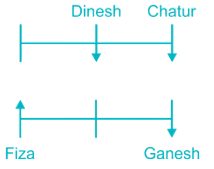
18. Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Six persons Amit, Dinesh, Chatur, Fiza, Ganesh and Zeeshan are sitting in two parallel rows viz. row – 1 and row – 2. Amit, Dinesh and Chatur are sitting in row – 1, while Fiza, Ganesh and Zeeshan are sitting in another row. Some of them are facing north and some of them are facing south.
Fiza faces north. The one who sits opposite to Fiza sits second to the right of Chatur. Dinesh faces south and sits opposite to the one, who sits to the immediate right of Ganesh. Ganesh sits second to right of Fiza. Amit faces the opposite direction of Chatur. Ganesh sits immediate right of Zeeshan.
Question:
Who among the following sits second to the right of Amit?
A. Chatur
B. Fiza
C. Ganesh
D. Dinesh
E. None of these
Solution
1) Fiza faces north.
2) The one who sits opposite to Fiza sits second to the right of Chatur.
3) Ganesh sits second right of Fiza.
4) Dinesh faces south and sits opposite to the one, who sits to the immediate right of Ganesh.
5) Amit faces opposite direction of Chatur.
6) Ganesh sits immediate right of Zeeshan.

Therefore, Chatur sits second to the right of Amit.
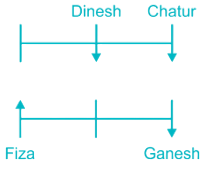
19. Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Six persons Amit, Dinesh, Chatur, Fiza, Ganesh and Zeeshan are sitting in two parallel rows viz. row – 1 and row – 2. Amit, Dinesh and Chatur are sitting in row – 1, while Fiza, Ganesh and Zeeshan are sitting in another row. Some of them are facing north and some of them are facing south.
Fiza faces north. The one who sits opposite to Fiza sits second to the right of Chatur. Dinesh faces south and sits opposite to the one, who sits to the immediate right of Ganesh. Ganesh sits second to right of Fiza. Amit faces the opposite direction of Chatur. Ganesh sits immediate right of Zeeshan.
Question:
How many persons face north direction?
A. One
B. Five
C. Two
D. Three
E. None of these
Solution
1) Fiza faces north.
2) The one who sits opposite to Fiza sits second to the right of Chatur.
3) Ganesh sits second right of Fiza.

4) Dinesh faces south and sits opposite to the one, who sits to the immediate right of Ganesh.
5) Amit faces opposite direction of Chatur.
6) Ganesh sits immediate right of Zeeshan.

So, three persons face north direction.
20. Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the following questions.
Each of the six persons Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti has a different number of chocolates. The numbers of chocolates they have are 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate. Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates. Somya has less chocolate than John
Question:
Which of the following combination is correct?
A. Amit-Ten
B. Chintu-Five
C. John-Two
D. Preeti-Eight
E. Somya-Three
Solution
Six Persons: Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti.
Number of chocolates: 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10
1) The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate.
Rohit chocolates = John’s chocolate* Chintu’s chocolate
We know, 10=5*2 and 6=3*2
So, Rohit could have either 10 chocolates or 6 chocolates. If Rohit has 10 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 5 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. If Rohit has 6 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 3 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. It gives rise to four cases.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu | John | Chintu | John |
| 3 | John | Chintu | ||
| 5 | John | Chintu | ||
| 6 | Rohit | Rohit | ||
| 8 | ||||
| 10 | Rohit | Rohit |
2) Somya has less chocolate than John.
Number of Chocolates John could have is 2, 3, and 5.
If John has two chocolate then the condition that Somya has less chocolate than John could not be followed. So, Cases 2 and 4 are eliminated.
If John has three chocolates then Somya would have 2 chocolates. But, Chintu already has 2 chocolates. So, Case 3 is eliminated.
If John has five chocolates then Somya would have 3 chocolates in Case 1.
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | |
| 8 | |
| 10 | Rohit |
3) Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates.
Amit’s chocolate = John’s chocolate + Somya’s chocolate.
John has 5 chocolates and Somya has 3 chocolates. So, Amit has 8 chocolates (8=5+3)
4) Preeti would have 6 chocolates because that is the left for Preeti.
The final arrangement is:
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | Preeti |
| 8 | Amit |
| 10 | Rohit |
Hence, Somya has three chocolates is the correct combination.
21. Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the following questions.
Each of the six persons Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti has a different number of chocolates. The numbers of chocolates they have are 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate. Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates. Somya has less chocolate than John
Question:
How many persons have more chocolate than Somya?
A. One
B. Four
C. Three
D. None
E. Two
Solution
Six Persons: Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti.
Number of chocolates: 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10
1) The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate.
Rohit chocolates = John’s chocolate* Chintu’s chocolate
We know, 10=5*2 and 6=3*2
So, Rohit could have either 10 chocolates or 6 chocolates. If Rohit has 10 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 5 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. If Rohit has 6 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 3 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. It gives rise to four cases.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu | John | Chintu | John |
| 3 | John | Chintu | ||
| 5 | John | Chintu | ||
| 6 | Rohit | Rohit | ||
| 8 | ||||
| 10 | Rohit | Rohit |
2) Somya has less chocolate than John.
Number of Chocolates John could have is 2, 3, and 5.
If John has two chocolate then the condition that Somya has less chocolate than John could not be followed. So, Cases 2 and 4 are eliminated.
If John has three chocolates then Somya would have 2 chocolates. But, Chintu already has 2 chocolates. So, Case 3 is eliminated.
If John has five chocolates then Somya would have 3 chocolates in Case 1.
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | |
| 8 | |
| 10 | Rohit |
3) Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates.
Amit’s chocolate = John’s chocolate + Somya’s chocolate.
John has 5 chocolates and Somya has 3 chocolates. So, Amit has 8 chocolates (8=5+3)
4) Preeti would have 6 chocolates because that is the left for Preeti.
The final arrangement is:
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | Preeti |
| 8 | Amit |
| 10 | Rohit |
Hence, Four persons have more chocolates than Somya.
22. Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the following questions.
Each of the six persons Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti has a different number of chocolates. The numbers of chocolates they have are 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate. Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates. Somya has less chocolate than John
Question:
What is the difference of the number of chocolates Chintu and Amit have?
A. Six
B. Eight
C. Two
D. Three
E. Ten
Solution
Six Persons: Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti.
Number of chocolates: 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10
1) The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate.
Rohit chocolates = John’s chocolate* Chintu’s chocolate
We know, 10=5*2 and 6=3*2
So, Rohit could have either 10 chocolates or 6 chocolates. If Rohit has 10 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 5 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. If Rohit has 6 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 3 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. It gives rise to four cases.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu | John | Chintu | John |
| 3 | John | Chintu | ||
| 5 | John | Chintu | ||
| 6 | Rohit | Rohit | ||
| 8 | ||||
| 10 | Rohit | Rohit |
2) Somya has less chocolate than John.
Number of Chocolates John could have is 2, 3, and 5.
If John has two chocolate then the condition that Somya has less chocolate than John could not be followed. So, Cases 2 and 4 are eliminated.
If John has three chocolates then Somya would have 2 chocolates. But, Chintu already has 2 chocolates. So, Case 3 is eliminated.
If John has five chocolates then Somya would have 3 chocolates in Case 1.
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | |
| 8 | |
| 10 | Rohit |
3) Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates.
Amit’s chocolate = John’s chocolate + Somya’s chocolate.
John has 5 chocolates and Somya has 3 chocolates. So, Amit has 8 chocolates (8=5+3)
4) Preeti would have 6 chocolates because that is the left for Preeti.
The final arrangement is:
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | Preeti |
| 8 | Amit |
| 10 | Rohit |
Chintu has 2 chocolates and Amit has 8 chocolates. So, the difference between Chintu and Amit chocolate is Six.
23. Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the following questions.
Each of the six persons Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti has a different number of chocolates. The numbers of chocolates they have are 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate. Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates. Somya has less chocolate than John
Question:
How many chocolates Preeti has?
A. Ten
B. Eight
C. two
D. Three
E. Six
Solution
Six Persons: Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti.
Number of chocolates: 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10
1) The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate.
Rohit chocolates = John’s chocolate* Chintu’s chocolate
We know, 10=5*2 and 6=3*2
So, Rohit could have either 10 chocolates or 6 chocolates. If Rohit has 10 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 5 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. If Rohit has 6 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 3 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. It gives rise to four cases.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu | John | Chintu | John |
| 3 | John | Chintu | ||
| 5 | John | Chintu | ||
| 6 | Rohit | Rohit | ||
| 8 | ||||
| 10 | Rohit | Rohit |
2) Somya has less chocolate than John.
Number of Chocolates John could have is 2, 3, and 5.
If John has two chocolate then the condition that Somya has less chocolate than John could not be followed. So, Cases 2 and 4 are eliminated.
If John has three chocolates then Somya would have 2 chocolates. But, Chintu already has 2 chocolates. So, Case 3 is eliminated.
If John has five chocolates then Somya would have 3 chocolates in Case 1.
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | |
| 8 | |
| 10 | Rohit |
3) Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates.
Amit’s chocolate = John’s chocolate + Somya’s chocolate.
John has 5 chocolates and Somya has 3 chocolates. So, Amit has 8 chocolates (8=5+3)
4) Preeti would have 6 chocolates because that is the left for Preeti.
The final arrangement is:
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | Preeti |
| 8 | Amit |
| 10 | Rohit |
Hence, Preeti has Six chocolates.
24. Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the following questions.
Each of the six persons Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti has a different number of chocolates. The numbers of chocolates they have are 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10 but not necessarily in the same order.
The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate. Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates. Somya has less chocolate than John
Question:
Who has the maximum number of chocolates?
A. Amit
B. Preeti
C. Rohit
D. John
E. Chintu
Solution
Six Persons: Somya, Rohit, Chintu, Amit, John, and Preeti.
Number of chocolates: 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10
1) The Number of chocolate Rohit has is the product of John and Chintu’s chocolate.
Rohit chocolates = John’s chocolate* Chintu’s chocolate
We know, 10=5*2 and 6=3*2
So, Rohit could have either 10 chocolates or 6 chocolates. If Rohit has 10 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 5 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. If Rohit has 6 chocolates then John and Chintu could have 3 and 2 chocolates but not necessarily in the same order. It gives rise to four cases.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons | Persons | Persons | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu | John | Chintu | John |
| 3 | John | Chintu | ||
| 5 | John | Chintu | ||
| 6 | Rohit | Rohit | ||
| 8 | ||||
| 10 | Rohit | Rohit |
2) Somya has less chocolate than John.
Number of Chocolates John could have is 2, 3, and 5.
If John has two chocolate then the condition that Somya has less chocolate than John could not be followed. So, Cases 2 and 4 are eliminated.
If John has three chocolates then Somya would have 2 chocolates. But, Chintu already has 2 chocolates. So, Case 3 is eliminated.
If John has five chocolates then Somya would have 3 chocolates in Case 1.
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | |
| 8 | |
| 10 | Rohit |
3) Amit’s chocolate is the sum of John and Somya’s chocolate. Amit does not have the maximum number of chocolates.
Amit’s chocolate = John’s chocolate + Somya’s chocolate.
John has 5 chocolates and Somya has 3 chocolates. So, Amit has 8 chocolates (8=5+3)
4) Preeti would have 6 chocolates because that is the left for Preeti.
The final arrangement is:
| Case 1 | |
| Number of Chocolates | Persons |
| 2 | Chintu |
| 3 | Somya |
| 5 | John |
| 6 | Preeti |
| 8 | Amit |
| 10 | Rohit |
Hence, Rohit has the maximum number of chocolates.
25. Direction: Some statements are given followed by some conclusions. You have to consider the statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. You have to decide which of the given conclusions if any, follow from the given statements.
Statements:
No pant is shirt.
Only a few hats are pants.
All shirts are clothes.
Conclusions:
I. All hats can be pants.
II. Some pants are clothes.
III. All pants are hats is a possibility.
A. Only conclusion III follows
B. Only conclusion I follows
C. Only conclusion II and conclusion III follow
D. Either conclusion I or conclusion III follow
E. All conclusions follow
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as follows-

Conclusions:
I. All hats can be pants → False (As ‘Only a few hats are pants’ so few hats never can be pant)
II. Some pants are clothes → False (It is possible but not definite)
III. All pants are hats is a possibility → True (‘Only a few hats are pants’, that means there are some hats that never can be pant but all pant can be hats. So, the possibility is true as shown below-)

Additional Information:
‘Only a few hats are pants’ → here the first element is hat and the second element is pant. So, that statement means ‘some hats are pants and some parts of hats never can be pants but all pants can be hats’.
So, only a few = some + some not.
Hence, Only III follows.
26. Direction: Some statements are given followed by some conclusions. You have to consider the statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. You have to decide which of the given conclusions if any, follow from the given statements.
Statements:
Some trains are jeeps.
All bicycles are jeeps.
Some planes are trains.
Conclusions:
I. Some bicycle can be plane.
II. Atleast some jeeps are bicycle.
A. Only conclusion II follows
B. Both conclusion I and conclusion II follow
C. Only conclusion I follows
D. Neither conclusion I nor conclusion II follows
E. Either conclusion I or conclusion II follows
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as follows-

Conclusions:
I. Some bicycle can be plane → True (The possibility is true as shown below, as no direct relationship between the two is given).

II. Atleast some jeeps are bicycle → True (As ‘All bicycles are jeeps, So some part of jeep is definitely bicycle).
Hence, Both I and II follow.
27. Direction: Some statements are given followed by some conclusions. You have to consider the statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. You have to decide which of the given conclusions if any, follow from the given statements.
Statements:
Only tigers are lions.
No tiger is cat.
Some cats are dogs.
Conclusions:
I. Some dogs can be tigers.
II. No lion is dog.
A. Both conclusion I and conclusion II follow
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Only conclusion I follows
D. Neither conclusion I nor conclusion II follows
E. None of the above
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as follows-

Conclusions:
I. Some dogs can be tigers → True (The possibility is true as shown below, as the remaining part of dog which is not cat can easily be part of tiger, so the possibility is true).

II. No lion is dog → True (As ‘Only tigers are lions’ so, no other element can be part of lion except tiger.)
Additional Information:
‘Only tigers are lions’ → here the first element is tiger and second element is a lion. So, that statement means ‘All lions are tigers’ and nothing can be lion except tiger but tigers that are not lion can be anything.
Hence, Both Conclusion I and II follows.
28. If it is possible to make only one meaningful English word with the 1st, 5th, 6th, and 8th letters of the word INFORMATION, which of the following will be the fourth letter from the left of that word? If no such word can be formed, give ‘X’ as the answer and if more than one such word can be made give ‘Y’ as the answer.
A. M
B. R
C. I
D. X
E. Y
Solution
| Given Word | I N F O R M A T I O N |
| Chosen letters (1st, 5th, 6th, and 8th letters) | I, R, M, T |
| possible word | TRIM |
| Fourth Letter of the word | M |
Hence, the fourth letter of the word formed by chosen letters is ‘M’.
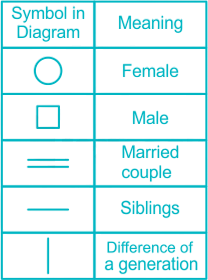
29. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
There are six members A, B, C, D, E and F in the family of three generations. No single person has a child. E’s father’s mother-in-law is F. C is the only son of B. C is bother-in-law of A.The gender of B and E is same.
Question:
F is ______ of D.
A. Brother
B. Grandmother
C. Father
D. Sister
E. Mother
Solution
Below table represents symbols used to draw a family tree,
1) E’s father’s mother-in-law is F.
2) C is the only son of B.
3) C is bother-in-law of A. So, F must be wife of B.
4) The gender of B and E is same. So, B and E are male members of the family.
We can draw the following Family Tree from the information given above:

Hence, F is mother of D.
30. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
There are six members A, B, C, D, E and F in the family of three generations. No single person has a child. E’s father’s mother-in-law is F. C is the only son of B. C is bother-in-law of A.The gender of B and E is same.
Question:
Four are the same in a certain way thus forms a group. Which among the following does not belong to the group?
A. C
B. A
C. E
D. F
E. B
Solution
Below table represents symbols used to draw a family tree,

1) E’s father’s mother-in-law is F.
2) C is the only son of B.
3) C is bother-in-law of A. So, F must be wife of B.
4) The gender of B and E is same. So, B and E are male members of the family.
We can draw the following Family Tree from the information given above:

Hence, ‘F’ does not belong to the group.
31. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
There are six members A, B, C, D, E and F in the family of three generations. No single person has a child. E’s father’s mother-in-law is F. C is the only son of B. C is bother-in-law of A.The gender of B and E is same.
Question:
How is C related to E?
A. Mother
B. Father
C. Nephew
D. Uncle
E. Grandfather
Solution
Below table represents symbols used to draw a family tree,

1) E’s father’s mother-in-law is F.
2) C is the only son of B.
3) C is bother-in-law of A. So, F must be wife of B.
4) The gender of B and E is same. So, B and E are male members of the family.
We can draw the following Family Tree from the information given above:

Hence, C is uncle of E.
32. How many pairs of letters in the word “SUITABLE” have the same number of letters between them in the word (in both forward and backward directions), as they have in the English alphabetical series?
A. 3
B. 2
C. 1
D. 0
E. More than 3
Solution
Given Word: SUITABLE
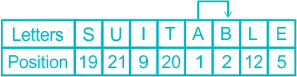
Thus, there is only one such pair → Forward: AB; Backward: 0Hence, ‘1’ is the correct answer.
33. Directions: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.Eight people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H are sitting around a circular table facing the center but not necessarily in the same order. C is sitting second to the right of E. Two people are sitting between B and G. G is an immediate neighbour of C. Either H or D is sitting opposite C. F is sitting second to the left of D. A is not an immediate neighbour of B.
Question:
Who is sitting to the immediate right of F?
A. D
B. B
C. H
D. C
E. A
Solution
People = A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H
1) C is sitting second to the right of E.
(As it is a circular arrangement, we can randomly place E on any of the seats and then we can place C accordingly.)

2) Two people are sitting between B and G.
3) G is an immediate neighbour of C.
(If we place G to the immediate right of C then B would sit on the seat that is opposite to C. If we place G to the immediate left of C then B would sit either second to the left of E or second to the right of C.)
4) Either H or D is sitting opposite C.
(Clearly, as B is not sitting opposite C, implies, G is sitting to the immediate left of C and B is sitting second to the right of C.)

5) F is sitting second to the left of D.
(If we assume that D is sitting opposite C then we would not be able to place F second to the left of D as B is already there. Implies, H is sitting opposite C.)

6) A is not an immediate neighbour of B.
(Implies, A is sitting between H and E as it is the only possibility left. Also, it is clear now that F must be sitting to the immediate left of B and D must be sitting to the immediate right of B (acc. to statement 4.))
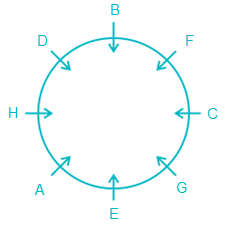
Clearly, B is sitting to the immediate right of F.
34. Directions: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.Eight people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H are sitting around a circular table facing the center but not necessarily in the same order. C is sitting second to the right of E. Two people are sitting between B and G. G is an immediate neighbour of C. Either H or D is sitting opposite C. F is sitting second to the left of D. A is not an immediate neighbour of B.
Question:
Which amongst the following pair represents the immediate neighbours of H?
A. BE
B. GC
C. CA
D. AD
E. EB
Solution
People = A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H
1) C is sitting second to the right of E.
(As it is a circular arrangement, we can randomly place E on any of the seats and then we can place C accordingly.)
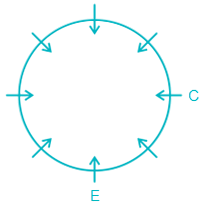
2) Two people are sitting between B and G.
3) G is an immediate neighbour of C.
(If we place G to the immediate right of C then B would sit on the seat that is opposite to C. If we place G to the immediate left of C then B would sit either second to the left of E or second to the right of C.)
4) Either H or D is sitting opposite C.
(Clearly, as B is not sitting opposite C, implies, G is sitting to the immediate left of C and B is sitting second to the right of C.)

5) F is sitting second to the left of D.
(If we assume that D is sitting opposite C then we would not be able to place F second to the left of D as B is already there. Implies, H is sitting opposite C.)
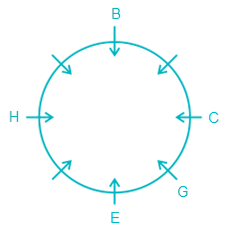
6) A is not an immediate neighbour of B.
(Implies, A is sitting between H and E as it is the only possibility left. Also, it is clear now that F must be sitting to the immediate left of B and D must be sitting to the immediate right of B (acc. to statement 4.))

Clearly, A and D are the immediate neighbours of H.
35. Directions: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.Eight people – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H are sitting around a circular table facing the center but not necessarily in the same order. C is sitting second to the right of E. Two people are sitting between B and G. G is an immediate neighbour of C. Either H or D is sitting opposite C. F is sitting second to the left of D. A is not an immediate neighbour of B.
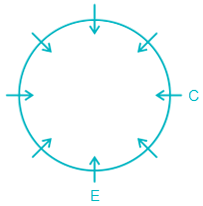
Question:
Who is sitting opposite D?
A. A
B. F
C. G
D. H
E. B
Solution
People = A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H
1) C is sitting second to the right of E.
(As it is a circular arrangement, we can randomly place E on any of the seats and then we can place C accordingly.)
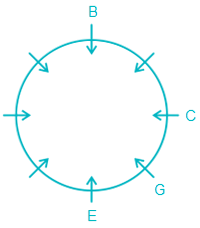
2) Two people are sitting between B and G.
3) G is an immediate neighbour of C.
(If we place G to the immediate right of C then B would sit on the seat that is opposite to C. If we place G to the immediate left of C then B would sit either second to the left of E or second to the right of C.)
4) Either H or D is sitting opposite C.
(Clearly, as B is not sitting opposite C, implies, G is sitting to the immediate left of C and B is sitting second to the right of C.)
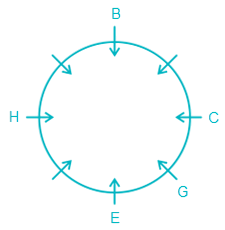
5) F is sitting second to the left of D.
(If we assume that D is sitting opposite C then we would not be able to place F second to the left of D as B is already there. Implies, H is sitting opposite C.)
6) A is not an immediate neighbour of B.
(Implies, A is sitting between H and E as it is the only possibility left. Also, it is clear now that F must be sitting to the immediate left of B and D must be sitting to the immediate right of B (acc. to statement 4.))
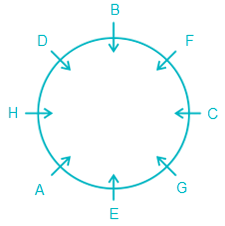
Clearly, G is sitting opposite D.
36. In each of the following number series, the wrong number is given, find out that number.
7, 11, 27, 61, 127, 227
A. 227
B. 127
C. 61
D. 11
E. 27
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
7 + 22 = 11
11 + 42 = 27
27 + 62 = 63
63 + 82 = 127
127 + 102 = 227
∴ The wrong term in the series is 61.
37. In each of the following number series, the wrong number is given, find out that number.
11, 13, 16, 21, 28, 37
A. 21
B. 13
C. 28
D. 37
E. 16
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
11 + 2 = 13
13 + 3 = 16
16 + 5 = 21
21 + 7 = 28
28 + 11 = 39
∴ The wrong term in the series is 37.
38. In each of the following number series, the wrong number is given, find out that number.
2, 10, 32, 71, 134, 227
A. 32
B. 134
C. 227
D. 71
E. 10
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
13 + 1 = 2
23 + 3 = 11
33 + 5 = 32
43 + 7 = 71
53 + 9 = 134
63 + 11 = 227
∴ The wrong term in the series is 10.
39. In each of the following number series, the wrong number is given, find out that number.
3, 9, 22, 50, 104, 215
A. 104
B. 215
C. 22
D. 9
E. 50
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
3 × 2 + 3 = 9
9 × 2 + 4 = 22
22 × 2 + 5 = 49
49 × 2 + 6 = 104
104 × 2 + 7 = 215
∴ wrong number of the series is 50
40. In each of the following number series, the wrong number is given, find out that number.
351, 334, 300, 250, 181, 96
A. 334
B. 300
C. 250
D. 181
E. 96
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
351 – 17 = 334
334 – 34 = 300
300 – 51 = 249
249 – 68 = 181
181 – 85 = 96
∴ The wrong term in the series is 250.
41. Directions: The given table shows the number of students studying in three different class such as X , XI and XII from four different schools
| Name of the school | Number of students studying in class X | Number of students studying in class XI | Number of students studying in class XII |
| A | 250 | 200 | 180 |
| B | 150 | 160 | 220 |
| C | 140 | 120 | 180 |
| D | 160 | 300 | 100 |
Question:
If 20% of the number of students studying from school A in class X is males and 40% of the males studying from school A studying in class XI are males. Find the number of females studying from school A in class X and XI.
A. 420
B. 360
C. 380
D. 320
E. 400
Solution
Solution:
Number of males studying in class X from school A = 250 × (20/100) = 50
Number of females studying in class X from school A = (250 – 50) = 200
Number of males studying in class XI from school A = 200 × 40/100 = 80
Number of females studying in class XI from school A = (200 – 80) = 120
Number of females studying in class X and class XI from school A = (200 + 120) = 320
42. Directions: The given table shows the number of students studying in three different class such as X , XI and XII from four different schools
| Name of the school | Number of students studying in class X | Number of students studying in class XI | Number of students studying in class XII |
| A | 250 | 200 | 180 |
| B | 150 | 160 | 220 |
| C | 140 | 120 | 180 |
| D | 160 | 300 | 100 |
Question:
Find the ratio between the number of students studying in class XI from school B to the number of students studying in class XII from school C.
A. 11: 9
B. 5: 4
C. 8: 9
D. 2: 3
E. 7: 9
Solution
Solution:
Number of students studying in class XI from school B = 160
Number of students studying in class XII from school C = 180
Required ratio = 160: 180 = 8: 9
43. Directions: The given table shows the number of students studying in three different class such as X , XI and XII from four different schools
| Name of the school | Number of students studying in class X | Number of students studying in class XI | Number of students studying in class XII |
| A | 250 | 200 | 180 |
| B | 150 | 160 | 220 |
| C | 140 | 120 | 180 |
| D | 160 | 300 | 100 |
Question:
Find the average number of students studying in class X from all the schools A, B, C and D.
A. 155
B. 245
C. 165
D. 175
E. 215
Solution
Solution:
Number of students studying in class X from school A = 250
Number of students studying in class X from school B = 150
Number of students studying in class X from school C = 140
Number of students studying in class X from school D = 160
Required average = (250 + 150 + 140 + 160)/4 = 175
44. Directions: The given table shows the number of students studying in three different class such as X , XI and XII from four different schools
| Name of the school | Number of students studying in class X | Number of students studying in class XI | Number of students studying in class XII |
| A | 250 | 200 | 180 |
| B | 150 | 160 | 220 |
| C | 140 | 120 | 180 |
| D | 160 | 300 | 100 |
Question:
Find the difference between the number of students studying in class XI from school C and the number of students studying in class XII from school D.
A. 20
B. 25
C. 30
D. 15
E. 35
Solution
Number of students studying in class XI from school C = 120
Number of students studying in class XII from school D = 100
Required difference = (120 – 100) = 20
45. Directions: The given table shows the number of students studying in three different class such as X , XI and XII from four different schools
| Name of the school | Number of students studying in class X | Number of students studying in class XI | Number of students studying in class XII |
| A | 250 | 200 | 180 |
| B | 150 | 160 | 220 |
| C | 140 | 120 | 180 |
| D | 160 | 300 | 100 |
Question:
Number of students studying in class XI from school A is what percentage of total number of students studying in class XII from all the schools A, B, C and D.
A. 24.87%
B. 29.41%
C. 23.76%
D. 21.89%
E. 22.67%
Solution
Solution:
Number of students studying in class XI from school A = 200
Total number of students studying class XII from all the schools A, B, C and D = (180 + 220 + 180 + 100) = 680
Required percentage = 200/(680) × 100 = 29.41%
46. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 3x2 – 10x + 7 = 0
II. y2 + 5y + 6 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
Given:
I. 3×2 – 10x + 7 = 0
II. y2 + 5y + 6 = 0
Concept used:
Using quadratic equation.
Calculation:
From I,
3x2 – 10x + 7 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 3x – 7x + 7 = 0
⇒ (3x – 7)(x – 1) = 0
⇒ x = 7/3, 1
From II,
y2 + 5y + 6 = 0
⇒ y2 + 3y + 2y + 6 = 0
⇒ (y + 2)(y + 3) = 0
⇒ y = -2, -3
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 7/3 | -2 | x > y |
| 7/3 | -2 | x > y |
| 1 | -3 | x > y |
| 1 | -3 | x > y |
∴ x > y
47. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 14x -147 = 0
II. 6y2 – y – 5 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. x2 + 14x – 147 = 0
⇒ x2 + 21x – 7x – 147 = 0
⇒ (x + 21)(x – 7) = 0
⇒ x = -21, 7
II. 6y2 – y – 5 = 0
⇒ 6y2 – 6y + 5y – 5 = 0
⇒ (6y + 5)(y – 1) = 0
⇒ y = -5/6, 1
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| -21 | -5/6 | x < y |
| -21 | 1 | x < y |
| 7 | -5/6 | x > y |
| 7 | 1 | x > y |
Hence, x > y and x < y so the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
48. In the given question, two equations numbered I and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 7x + 12 = 0
II. y2 – 11y + 18 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. x2 + 7x + 12 = 0
⇒ x2 + 4x + 3x + 12 = 0
⇒ x(x + 4) + 3(x + 4) = 0
⇒ (x + 4)(x + 3)= 0
⇒ x = -4, -3
II. y2 – 11y + 18 = 0
⇒ y2 – 9y – 2y + 18 = 0
⇒ y(y – 9) + 2(y – 9) = 0
⇒ (y – 9)(y – 2) = 0
⇒ y = 9, 2
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| -4 | 9 | x < y |
| -4 | 2 | x < y |
| -3 | 9 | x < y |
| -3 | 2 | x < y |
∴ x < y.
49. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and
mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 12x + 32 = 0
II. y2 + 6y + 8 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≤ y
D. x ≥ y
E. x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
Calculation:
From I,
x2 + 12x + 32 = 0
⇒ x2 + 8x + 4x +32 = 0
⇒ x(x+8) + 4(x+8) = 0
⇒ (x+4) (x+8) = 0
Taking,
⇒ x + 4 = 0 or x + 8 = 0
⇒ x = –4 or –8
From II,
y2 + 6y + 8 = 0
⇒ y2 + 4y + 2y + 8 = 0
⇒ y(y+4) + 2(y+4) = 0
⇒ (y+2) (y+4) = 0
Taking,
⇒ y + 2 = 0 or y + 4 = 0
⇒ y = –2 or –4
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Values of x | Values of y | Relation |
| –4 | –2 | x < y |
| –4 | –4 | x = y |
| –8 | –2 | x < y |
| –8 | –4 | x < y |
∴ Relation between x and y is, x ≤ y.
50. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and
mark the appropriate answer.
I.7x2 + 32x – 15 = 0
II. 4y2 – 16y +7 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≤ y
D. x ≥ y
E. x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
Calculation:
From I,
7x2 + 32x – 15 = 0
⇒ 7x2 + 35x – 3x – 15x = 0
⇒ 7x(x+5) – 3(x+5) = 0
⇒ (7x–3) (x+5) = 0
Taking,
⇒ 7x – 3 = 0 or x + 5 = 0
⇒ x = 3/7 or –5
From II,
4y2 – 16y + 7 = 0
⇒ 4y2 – 14y – 2y + 7 = 0
⇒ 2y(2y–1) –7(2y-1) = 0
⇒ (2y–1) (2y–7) = 0
Taking,
⇒ 2y – 1 = 0 or 2y – 7 = 0
⇒ y = 1/2 or y = 7/2
| Values of x | Values of y | Relation |
| 3/7 | 1/2 | x < y |
| –5 | 1/2 | x < y |
| 3/7 | 7/2 | x < y |
| –5 | 7/2 | x < y |
∴ Relation between x and y is, x < y.
51. A person buys rice worth Rs. 6000. He sold 1/3rd part at 20% loss, 2/5th part at 25% profit. To gain an overall profit of 10%, at how much profit percentage should he sell the rest of the rice?
A. 20%
B. 15%
C. 25%
D. 30%
E. 22.22%
Solution
Given:
A person buys rice worth Rs. 6000
He sold 1/3rd part at a 20% loss, 2/5th part at 25% profit
He want to gain 10% overall
Calculation:
Remaining amount = 1 – [(1/3) + (2/5)] = 4/15
Now, for ease of calculation if we take total amount = 15 units
Then, 1/3rd part = 15 × 1/3 = 5 units
And, 2/5th part = 15 × 2/5 = 6 units
So, remaining amount of rice = 15 – (6 + 5) = 4 unit
5 units Sold at 20% loss = 5 × (- 20) = – 100 —————– (i)
6 units sold at 25% profit = 6 × 25 = 150 ———————- (ii)
4 units to be sold at = p —————– (iii)
Total 15 units to be sold at 10% profit = 15 × 10 = 150 (overall profit)
In order to gain overall 150 profit, the remaining rice must be sold at profit
So, (i) + (ii) + (iii) = 150
⇒ – 100 + 150 + p = 150
⇒ p = 100
4 units sold at total of 100
So, each part of that 4 units to be sold at = 100/4 = 25%
∴ The correct answer is option 3
52. Two vessels contain milk and water in the ratio 8 : 7 and 11 : 13 respectively. In what ratio, these vessels are to be mixed to obtain a new mixture containing milk and water in the ratio 1 : 1?
A. 5 : 4
B. 4 : 5
C. 1 : 1
D. 5 : 3
E. 3 : 5
Solution
Given:
| Ratio | Milk : Water |
| Vessel-A | 8 : 7 |
| Vessel-B | 11 : 13 |
| New mixture | 1 : 1 |
Formula used:

Calculation:
Quantity of milk in vessel-A = 8/15
Quantity of milk in vessel-B = 11/24
And, the quantity of milk in new mixture = 1/2

LCM of 24 and 30 = 120
Required ratio = [(1/24) × 120] : [(1/30) × 120]
⇒ 5 : 4
∴ Vessel A and Vessel B are to be mixed in 5 : 4 ratio.
Alternate Method
Let the amount of milk and water in the first vessel be 8x and 7x respectively.
Let the amount of milk and water in the second vessel be 11y and 13y respectively.
Quantity in first vessel = 8x + 7x = 15x
Quantity in second vessel = 11y + 13 y = 24y
To make total quantity same = 15x = 24y
⇒ x : y = 8 : 5
So, Total quantity = 15x = 24y ⇒ 15 × 8 = 24 × 5 = 120 units
Amount of milk in first vessel = 8x ⇒ 64 units
Amount of water in first vessel = 7x ⇒ 56 units
Amount of milk in first vessel = 11y ⇒ 55 units
Amount of water in first vessel = 13y ⇒ 65 units
Let we have taken “a” units of the first vessel and “b” units of the second vessel.
So, Amount taken of milk from the first vessel = 64a
Amount taken of water from the first vessel = 56a
Amount taken of milk from second vessel = 55b
Amount taken of water from second vessel = 65b
Milk in final mixture : Water in final mixture = 1 : 1
⇒ (64a + 55b)/(56a + 65b) = 1/1
⇒ 8a = 10b
⇒ a : b = 5 : 4
∴ Vessel A and Vessel B are to be mixed in 5 : 4 ratio.
Mistake Points
Before directly adding the milk to milk and water to water first make sure total quantity in both the vessel are same.
53. Direction: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions accordingly.In a hospital, there are 4 wards. In ward A, 56 patients are admitted, and the ratio of male to female is 3 ∶ 4. In ward B, 60 patients are admitted and the ratio of male to female is 3 ∶ 1. In ward – C, 52 patients are admitted and the ratio of male to female is 8 ∶ 5. In ward – D, 44 patients are admitted and the ratio of male to female is 6 ∶ 5.
Question:
Find the total number of females patients admitted in ward – A and Ward – C together.
A. 32
B. 42
C. 68
D. 52
E. 48
Solution
Number of females in ward-A = 4/7 × 56 = 32
Number of females in ward-C = 5/13 × 52 = 20∴ Total number = 32 + 20 = 52
54. Direction: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions accordingly.In a hospital, there are 4 wards. In ward A, 56 patients are admitted, and the ratio of male to female is 3 ∶ 4. In ward B, 60 patients are admitted and the ratio of male to female is 3 ∶ 1. In ward – C, 52 patients are admitted and the ratio of male to female is 8 ∶ 5. In ward – D, 44 patients are admitted and the ratio of male to female is 6 ∶ 5.
Question:
The total number of male patients in ward B and ward D together are approximately what percent of the total number of patients in the same wards together?
A. 66%
B. 56%
C. 72%
D. 52%
E. None of these
Solution
Number of males in ward – B = 3/4 × 60 = 45
Number of males in ward – D = 6/11 × 44 = 24
Total number of males in ward – B and ward – D = 45 + 24 = 69
Total number of people admitted in wards B and D = 60 + 44 = 104∴ Required percentage = 69/104 × 100 = 66.35% ≈ 66%
55. Direction: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions accordingly.In a hospital, there are 4 wards. In ward A, 56 patients are admitted, and the ratio of male to female is 3 ∶ 4. In ward B, 60 patients are admitted and the ratio of male to female is 3 ∶ 1. In ward – C, 52 patients are admitted and the ratio of male to female is 8 ∶ 5. In ward – D, 44 patients are admitted and the ratio of male to female is 6 ∶ 5.
Question:
Find the average number of patients in all the wards.
A. 50
B. 52
C. 53
D. 55
E. 54
Solution
Total number of patients in all the wards = 56 + 60 + 52 + 44 = 212∴ Required average = 212/4 = 53
56. If a number is increased by 30% and the resulting number is decreased by 30%, then the net percentage change in the original number is:
A. No change
B. Decreased by 9%
C. Increased by 9%
D. Decreased by 6%
E. Increased by 6%
Solution
Let the original number be 100
Increase it by 30%:
⇒ 100 + 30% of 100 = 100 + 30 = 130
Decrease the result by 30%:
⇒ 30% of 130 = 0.3 × 130 = 39
⇒ New number = 130 − 39 = 91
Compare with original number:
Original = 100, Final = 91
⇒ Change = 100 − 91 = 9
⇒ Percentage change = (9 ÷ 100) × 100 = 9%
So, it is decreased by 9%
Thus, the correct answer is (b) Decreased by 9%.
57. C can complete 4/7 of a work in 14 days. C and D together complete 2/7 of the same work in 4 2/3 days. Find the time taken by D to complete the entire work alone.
A. 28 days
B. 32 days
C. 49 days
D.. 35 days
E. 23 days
Solution
C can complete 4/7 of the work in 14 days.
Work done by C in 1 day = (4/7) / 14 = 4/98 = 2/49
C and D together complete 2/7 of the work in 4 2/3 days (14/3) days:
Work done by C and D in 1 day = (2/7) / (14/3) = 2/7 × 3/14 = 6/98 = 3/49
D’s 1-day work = 3/49 − 2/49 = 1/49
If D does 1/49 of the work in 1 day, the time taken to complete the entire work is:
Time taken by D = 1 / (1/49) = 49 days.
Thus, D will take 49 days to complete the work alone.
58. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
?2 + 9.092 = 7.983 + 18.99 – 2.992
A. 21
B. 23
C. 31
D. 29
E. 19
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
?2 + 9.092 = 7.983 + 18.99 – 2.992
⇒ ?2 + 92 = 83 + 19 – 32
⇒ ?2 + 81 = 522
⇒ ?2 = 441
⇒ ? = 21
59. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
(6.972 + 1.01) × [2.982 + 3.03] ÷ 5.96 = ?
A. 50
B. 150
C. 200
D. 80
E. 100
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
(6.972 + 1.01) × [2.982 + 3.03] ÷ 5.96 = ?
⇒ (72 + 1) × [32 + 3] ÷ 6 = ?
⇒ 50 × [12 × 1] ÷ 6 = ?
⇒ 50 × 12 ÷ 6 = ?
⇒ 50 × 2 = ?
⇒ ? = 100
60. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
13.98 + 27.992 ÷ 6.99 + 3.942 = ?
A. 124
B. 136
C. 142
D. 152
E. 156
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.

Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
13.98 + 27.992 ÷ 6.99 + 3.942 = ?
⇒ 14 + 282 ÷ 7 + 42 = ?
⇒ 14 + 784/7 + 16 = ?
⇒ 14 + 112 + 16 = ?
∴ ? = 142
61. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
(√288.99 × 13.99) ÷ 6.98 + √675.99 = ?
A. 70
B. 50
C. 40
D. 60
E. 80
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
(√288.99 × 13.99) ÷ 6.98 + √675.99 = ?
⇒ (√289 × 14) ÷ 7 + √676 = ?
⇒ (17 × 14) ÷ 7 + 26 = ?
⇒ 238 ÷ 7 + 26 = ?
⇒ 34 + 26 = ?
∴ ? = 60
62. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
{44.98 – (10.99 × 5.96 – 5.98 × 2.023)} = ?3
A. 3
B. 2
C. 4
D. 6
E. 5
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
{44.98 – (10.99 × 5.96 – 5.98 × 2.023)} = ?3
⇒ {45 – (11 × 6 – 6 × 23)} = ?3
⇒ {45 – (66 – 6 × 8)} = ?3
⇒ {45 – (66 – 48)} = ?3
⇒ {45 – 18} = ?3
∴ ? = 3
63. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
91.99 – [70.97 + {4.04 – (4.95 – 1.99))}] = ?
A. 10
B. 15
C. 25
D. 20
E. 30
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
91.99 – [70.97 + {4.04 – (4.95 – 1.99))}] = ?
⇒ 92 – [71 + {4 – (5 – 2)}] = ?
⇒ 92 – [71 + {4 – 3}] = ?
⇒ 92 – [71 + 1] = ?
⇒ 92 – 72 = ?
⇒ 20 = ?
64. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
12.972 × (13.03/2.98) = (12.98)? ÷ 3.03
A. 1
B. 5
C. 3
D. 7
E. 4
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
12.972 × (13.03/2.98) = (12.98)? ÷ 3.03
⇒ 132 × 13/3 = (13)? ÷ 3
⇒ 133/3 = (13)? ÷ 3
∴ ? = 3
65. What approximate value will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following questions? (You are not expected to calculate the exact value)
8.07 × 11.02 + √120.91 + 33.03 = ?
A. 121
B. 122
C. 124
D. 126
E. 128
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this expression, as per the order given below,
Step-1-Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first,
Step-2-Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3-Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4-Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
8.07 × 11.02 + √120.91 + 33.03 = ?
⇒ 8 × 11 + √121 + 33 = ?
⇒ 88 + 11 + 27 = ?
⇒ 126 = ?
66. What approximate value will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following questions? (You are not expected to calculate the exact value)
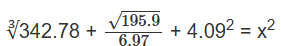
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
E. 6
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this expression, as per the order given below,
Step-1-Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first,
Step-2-Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3-Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4-Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.

67. What approximate value will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following questions? (You are not expected to calculate the exact value)
420.03 – 21.07 × 24.98 + ? = 160.23
A. 234
B. 265
C. 287
D. 326
E. 364
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this expression, as per the order given below,
Step-1-Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first,
Step-2-Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3-Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4-Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
420.03 – 21.07 × 24.98 + ? = 160.23
⇒ 420 – 21 × 25 + ? = 160
⇒ 420 – 525 + ? = 160
⇒ ? = 160 + 525 – 420
⇒ ? = 265
68. Rs. [x + 240] invest in simple interest at the rate of interest of 25% for 2 years. If the simple interest is Rs. 940, find the value of x?
A. 1860
B. 1160
C. 1640
D. 1540
E. 1760
Solution
Given:
Principal = x + 240
Rate = 25%
Time = 2 years
SI = ₹940
Formula used:
SI = (P × R × T) ÷ 100
Calculations:
940 = (x + 240) × 25 × 2 ÷ 100
⇒ 940 = (x + 240) × 0.5
⇒ x + 240 = 940 ÷ 0.5 = 1880
⇒ x = 1880 – 240 = ₹1640
∴ The value of x is ₹1640.
69. The respective ratio between the speed of a bike, car, and a cycle is 5 : 9 : 4. The average speed of the bike, car, and cycle is 36 km/h together. Find the average speed of the bike and the car together.
A. 40 km/h
B. 42 km/h
C. 45 km/h
D. 43 km/h
E. 44 km/h
Solution
Given:
The ratio of the speed of a bike, car, and cycle is 5 : 9 : 4
The average speed of bike, car and cycle is 36 km/h
Calculation:
Let the speed of the bike be 5x km/h.
Let the speed of the car be 9x km/h.
Let the speed of the cycle be 4x km/h.
⇒ Total speed = (36 × 3) Km/h
⇒ 108 Km/h
Required equation,
⇒ 5x + 9x + 4x = 108
⇒ 18x = 108
⇒ x = 6 km/h
Speed of bike = 5 × 6
⇒ 30 Km/h
Speed of car = 9 × 6
⇒ 54 Km/h
Their average speed = (30 + 54)/2
⇒ 84/2 km/h
⇒ 42 km/h
∴ The average speed of the bike and the car together is 42 km/h.
Shortcut Trick
After finding the value of x
Directly calculate the average by
⇒ 5x + 9x
⇒ 14x
⇒ 14 × 6
⇒ 84km/h
Their average speed = (30 + 54)/2
⇒ 84/2 km/h
⇒ 42 km/h
∴ The average speed of the bike and the car together is 42 km/h.
70. Ratio of length and breadth of rectangle is 5:3. Perimeter of rectangle is 80 m. Find the area of square whose side is 7/5th of the length of rectangle?
A. 2025
B. 1325
C. 1225
D. 1445
E. 1525
Solution
Calculation
Let length = 5x, breadth = 3x, Perimeter is 80 m
So, 2(5x + 3x) =80
⇒ 16x = 80
⇒ x = 5
⇒ Length = 25 m
Side of square = [7/5] × 25 = 35 m
Area of square = 352 = 1225m2
71. In the following sentence, four words or phrases have been printed in bold. One bold part in the sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part and mark its number. If there are no errors in the bold parts, mark (5) i.e. No error as the answer.
The British had to exceed to India’s demand for freedom.
A. British
B. Exceed
C. Demand
D. Freedom
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is option 2.
Key Points
The incorrect word is ‘Exceed’.
- The word ‘Exceed’ has been incorrectly used in the sentence.
- The correct word should be ‘Accede‘ instead of ‘Exceed’.
- The word ‘Accede‘ means to agree to a demand, request, or treaty. (सहमति देना)
Corrected Sentence: The British had to accede to India’s demand for freedom.
Additional Information
Let’s understand the difference between ‘Exceed’ and ‘Accede’:
- Exceed – to go beyond a limit or boundary (ज्यादा होना/अतिक्रमण करना).
- Accede – to agree to a demand, request, or treaty (सहमति देना).
For Example:
Accede: The government acceded to the protesters’ demands.
Exceed: The speed limit was exceeded by the driver.
72. In the following sentence, four words or phrases have been printed in bold. One bold part in the sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part and mark its number. If there are no errors in the bold parts, mark (5) i.e. No error as the answer.
My mom taught me to sow and knit when I was 10 years old.
A. Taught
B. Sow
C. When
D. Old.
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is option 2.
Key Points
The incorrect word in the sentence is ‘sow’.
- The correct word should be ‘sew’.
- ‘Sew’ means to join or attach pieces of fabric by stitching with a needle and thread. (सिलाई करना)
- For Example – My mom taught me to sew dresses when I was younger.
Therefore, the correct answer is ‘sow’.
Additional Information
Explanation of other marked words –
- Taught – Refers to the past tense of ‘teach’, meaning to instruct someone in a skill or subject. (सिखाया)
- When – Indicates the time at which something happened. (जब)
- Old – Refers to the age of a person or object. (पुराना)
Since the other bold words are correct, the incorrect word is ‘sow’.
73. In the following sentence, four words or phrases have been printed in bold. One bold part in the sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part and mark its number. If there are no errors in the bold parts, mark (5) i.e. No error as the answer.Last night the ambassador was summoned to the foreign office to discuss the cricis.
A. ambassador
B. summoned
C. foreign
D. cricis
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is option 4.
Key Points
The misspelled word is ‘cricis’.
- The correct spelling would be ‘crisis’.
- The word ‘crisis‘ is a noun which means ‘a time of intense difficulty or danger’. (संकट)
- For Example –
- The company is facing a financial crisis.
Therefore, the correct answer would be ‘cricis’.
Additional Information
Let’s understand the meanings of the other marked words –
Foreign – belonging to or originating from a different country (विदेशी)
Ambassador – an accredited diplomat sent by a country as its official representative to a foreign country (राजदूत)
Summoned – urgently call someone to be present (आह्वान करना)
74. In the following sentence, four words or phrases have been printed in bold. One bold part in the sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part and mark its number. If there are no errors in the bold parts, mark (5) i.e. No error as the answer.It never seizes to amaze me how he can talk for so long without ever saying anything interesting.
A. seizes
B. amaze
C. talk
D. interesting
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is option 1.
Key Points
The incorrect word in the given sentence is ‘seizes’.
- The correct word would be ‘ceases’.
- The word ‘ceases‘ is a verb which means ‘to stop or come to an end’. (रुकना या समाप्त होना)
- For Example –
- The noise ceases as soon as the children leave the room.
Therefore, the correct answer would be ‘ceases’.
Additional Information
Let’s understand the meanings of the other marked words –
Interesting – arousing curiosity or holding attention (दिलचस्प)
Amaze – to cause someone to feel astonished or impressed (आश्चर्यचकित करना)
Talk – to speak in order to give information or express ideas or feelings (बोलना)
75. Directions: In the following question, two columns are given, containing three phrases each. A phrase from the first column may or may not connect with a phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. There are five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which the phrases can be joined to form a correct sentence. If none of the phrases make a correct sentence, mark ‘None of these’ as your answer.
| Column I | Column II |
| (A) At langar, not only everyone is made welcome to eat, | (D) But also everyone is made welcome to work! |
| (B) An institutional solution would have three parts, | (E) but also for all ministries is that we need to get out of our silos. |
| (C) Science and Technology is not only a continuing priority for this government | (F) relating to the appointment of the organization’s chief, lines of accountability, and professionalism. |
A. C-E
B. A-D and B-F
C. B-E
D. A-F and B-E
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is Option 2 i.e. ‘Sentences A-D and Sentences B-F’ form a pair.
Key Points
- Sentence A in column I connects to Sentence D in column II and Sentence B in column I connects to Sentence F in column II.
- In sentence A, there is a usage of ‘not only’ which forms a pair with ‘but also’ if we look at the sentence D in column II it makes a contextually correct sentence and also it makes pair of ‘not only and but also’
- In sentence B, there is a usage of three parts which is only written in sentence F. Hence, it makes a meaningful sentence.
So the correct sentences are:
B-F : At langar, not only everyone is made welcome to eat, but also everyone is made welcome to work!
A-D : An institutional solution would have three parts, relating to the appointment of the organization’s chief, lines of accountability, and professionalism.
76. In the following question, two columns are given, containing three phrases each. A phrase from the first column may or may not connect with a phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. There are five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which the phrases can be joined to form a correct sentence. If none of the phrases make a correct sentence, mark ‘None of these’ as your answer.
| Column (1) | Column (2) |
| (A) Charles Darwin’s masterwork, the 1859 “Origin of Species,” offered ample evidence | (D) in science and is the unifying theory of biological science. |
| (B) The theory that modern humans originated in many places simultaneously, in contrast | (E) are as old as the earliest Homo fossils found in Africa; and that Homo erectus might have originated in Asia |
| (C) Evolution is among the most substantiated concepts | (F) for evolution having occurred, as well as the first strong explanation for its mechanism, natural selection. |
A. A-F and C-D
B. A-D and C-F
C. C-E and B-D
D. A-D and B-E
E. None of these
Solution
The correct answer is A-F and C-D
Key Points
Evolution is among the most substantiated concepts in science and is the unifying theory of biological science.
Fragment A in column 1 connects to fragment F in column 2 both contextually and grammatically as they combine together to make a meaningful sentence.
Charles Darwin’s masterwork, the 1859 “Origin of Species,” offered ample evidence for evolution having occurred, as well as the first strong explanation for its mechanism, natural selection.
A can not be connected with ‘D’ as ‘ample evidence’ is plural and needs a plural verb.
A can not be connected with ‘E’ as it will make the sentence grammatically incorrect (tense mismatch)
Fragment C in column 1 connects to fragment D in column 2 both contextually and grammatically as they combine together to make a meaningful sentence.
77. Which of the phrases given below the sentence should replace the word/phrase that is given in bold in the sentence to make it grammatically correct? If the sentence is correct as it is given and no correction is required, mark ‘No correction required’ as the answer.
John Snow has returned to Castle Black one month ago.
A. returned
B. have returned
C. has been returned
D. Both 1 and 3
E. No correction required
Solution
The correct answer is returned.
Key Points
Point of time (ago) in the past indicates that the action took place at a point in the past. Thus, the action is mentioned in the simple past.
- Present perfect + Point of time= Simple past
- For example: I returned to Mumbai two days ago.
- The point of time in the past is expressed by since, ever since, last, yesterday, ago, before, etc.
- Therefore, the correct answer is: John Snow returned to Castle Black one month ago.
Additional Information
Present Indefinite + Time Expression= Present Perfect
Since is used to express a point of time.
For example: John Snow has been residing in Castle Black for two months.
For is used to express a period of time.
Another example: John Snow has been residing in Castle Black since 1663.
78. Which of the phrases given below the sentence should replace the word/phrase that is given in bold in the sentence to make it grammatically correct? If the sentence is correct as it is given and no correction is required, mark ‘No correction required’ as the answer.
Carlie was annoyed at his brother for not contributing to any household chores.
A. annoyed with
B. annoyed after
C. annoyed by
D. annoyed of
E. No correction required
Solution
The correct answer is annoyed with.
Key Points
Annoyed: feeling or showing anger; irritation
- Annoyed with: angry with a person
- For example: I am annoyed with my brother.
- Annoyed at: angry because of a certain act
- For example: I am annoyed at the mischievous nature of my brother.
- Therefore, the correct answer is: Carlie was annoyed with his brother for not contributing to any household chores.
Additional Information
Certain words that agree with the preposition with:
| Word | Meaning |
| Abound with | full of |
| Acquaint with | familiar with |
| Seething with | discontent |
| Perish with | suffer from |
| Laugh with | enjoy with others |
79. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
We admire better hygiene and better traffic discipline abroad but would breach the same back home. We condemn our system for churning out unemployed youth, but don’t like working hard to acquire knowledge. Students demanded their right to cheat in an examination; it is the same set of discards that later become a burden as they fail to acquire a skill for gainful employment. Rights are forcefully demanded, but duties generally detested.
As citizens of a functioning democracy, we welcome populist policies and government bounties. The State is expected to provide free electricity, free Wi-fi, free water, free books, free housing, free transport, free health facilities, free education. This will not raise many cavils if they are provided to the deserving sections of society. The problem arises when undeserving elements try to corner these benefits through devious means. The benefits that are provided by the government are seldom used in a responsible manner. Water and electricity are wasted, public utilities vandalized. We want the State’s delivery mechanism to be prompt and efficient, but we seldom reciprocate. We forget that it is the people who make the country and not the other way round. We resent nepotism and favouritism in government service delivery, but would not mind peddling influence to seek undue favours.
The plan to develop smart cities would turn out to be still-born if we don’t have smart citizens who would be willing to make sacrifices for a dignified living. We under-report our income and underpay our taxes, but we resent the government’s plea on inadequate resources to provide for basic amenities. There are enough laws and rules, but enforcement is seldom effective. While you pay a hefty $ 1000 fine for littering in a developed country or for a traffic violation, in India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling). Sometimes, the systemic imperfections impede the enforcement of the rule of law as the law-abiding citizens do not always get their rightful dues. Today, hundreds of thousands of applications for a fire licence or a building plan are allegedly pending in government offices for years, unless you pass on the speed money to those in the gravy train.
Information technology needs to be suitably harnessed for most of these services. E-governance is definitely the way to the future. As a country, we shall continue to grovel in the dust until the citizens are aware of their responsibilities. One only hopes that we shall soon wake up by acting as responsible citizens of a great nation.
Question:
According to the passage, the word ‘vandalized‘ means –
A. restored (something damaged, faulty, or worn) to a good condition
B. the action or process of reconstructing or being reconstructed
C. returned to health
D. deliberately destroyed or damaged (public or private property)
E. separated into pieces as a result of a blow, shock, or strain.
Solution
The correct answer is option 4 i.e. deliberately destroyed or damaged (public or private property).
Key Points
The passage is on the need to develop and plan ‘smart cities’ and how responsible citizens are necessary for this.
- The sentence that contains the word ‘vandalized‘ is as follows: “Water and electricity are wasted, public utilities vandalized.“
- In this case, it would mean that public utilities have been ‘intentionally destroyed/vandalized‘.
- An example of the same is: “The walls have been horribly vandalized with spray paint.”
Therefore, option 4 is the correct answer.
80. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
We admire better hygiene and better traffic discipline abroad but would breach the same back home. We condemn our system for churning out unemployed youth, but don’t like working hard to acquire knowledge. Students demanded their right to cheat in an examination; it is the same set of discards that later become a burden as they fail to acquire a skill for gainful employment. Rights are forcefully demanded, but duties generally detested.
As citizens of a functioning democracy, we welcome populist policies and government bounties. The State is expected to provide free electricity, free Wi-fi, free water, free books, free housing, free transport, free health facilities, free education. This will not raise many cavils if they are provided to the deserving sections of society. The problem arises when undeserving elements try to corner these benefits through devious means. The benefits that are provided by the government are seldom used in a responsible manner. Water and electricity are wasted, public utilities vandalized. We want the State’s delivery mechanism to be prompt and efficient, but we seldom reciprocate. We forget that it is the people who make the country and not the other way round. We resent nepotism and favouritism in government service delivery, but would not mind peddling influence to seek undue favours.
The plan to develop smart cities would turn out to be still-born if we don’t have smart citizens who would be willing to make sacrifices for a dignified living. We under-report our income and underpay our taxes, but we resent the government’s plea on inadequate resources to provide for basic amenities. There are enough laws and rules, but enforcement is seldom effective. While you pay a hefty $ 1000 fine for littering in a developed country or for a traffic violation, in India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling). Sometimes, the systemic imperfections impede the enforcement of the rule of law as the law-abiding citizens do not always get their rightful dues. Today, hundreds of thousands of applications for a fire licence or a building plan are allegedly pending in government offices for years, unless you pass on the speed money to those in the gravy train.
Information technology needs to be suitably harnessed for most of these services. E-governance is definitely the way to the future. As a country, we shall continue to grovel in the dust until the citizens are aware of their responsibilities. One only hopes that we shall soon wake up by acting as responsible citizens of a great nation.
Question:
According to the passage, the word ‘detested‘ means –
A. disliked intensely
B. an intense feeling of deep affection
C. religious worship or observance
D. affection or liking for someone or something
E. regarded with respect or warm approval
Solution
The correct answer is option 1 i.e. disliked intensely.
Key Points
The passage is on the need to develop and plan ‘smart cities’ and how responsible citizens are necessary for this.
- The sentence that contains the word ‘detested‘ is as follows: “Rights are forcefully demanded, but duties generally detested.”
- In this case, it would mean that rights are expected to be given, however, the duties that come with the responsibilities are ‘disliked/detested.’
- An example of the same is: “Much as they detested having to make the phone call, both knew it was necessary.”
Therefore, option 1 is the correct answer.
81. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
We admire better hygiene and better traffic discipline abroad but would breach the same back home. We condemn our system for churning out unemployed youth, but don’t like working hard to acquire knowledge. Students demanded their right to cheat in an examination; it is the same set of discards that later become a burden as they fail to acquire a skill for gainful employment. Rights are forcefully demanded, but duties generally detested.
As citizens of a functioning democracy, we welcome populist policies and government bounties. The State is expected to provide free electricity, free Wi-fi, free water, free books, free housing, free transport, free health facilities, free education. This will not raise many cavils if they are provided to the deserving sections of society. The problem arises when undeserving elements try to corner these benefits through devious means. The benefits that are provided by the government are seldom used in a responsible manner. Water and electricity are wasted, public utilities vandalized. We want the State’s delivery mechanism to be prompt and efficient, but we seldom reciprocate. We forget that it is the people who make the country and not the other way round. We resent nepotism and favouritism in government service delivery, but would not mind peddling influence to seek undue favours.
The plan to develop smart cities would turn out to be still-born if we don’t have smart citizens who would be willing to make sacrifices for a dignified living. We under-report our income and underpay our taxes, but we resent the government’s plea on inadequate resources to provide for basic amenities. There are enough laws and rules, but enforcement is seldom effective. While you pay a hefty $ 1000 fine for littering in a developed country or for a traffic violation, in India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling). Sometimes, the systemic imperfections impede the enforcement of the rule of law as the law-abiding citizens do not always get their rightful dues. Today, hundreds of thousands of applications for a fire licence or a building plan are allegedly pending in government offices for years, unless you pass on the speed money to those in the gravy train.
Information technology needs to be suitably harnessed for most of these services. E-governance is definitely the way to the future. As a country, we shall continue to grovel in the dust until the citizens are aware of their responsibilities. One only hopes that we shall soon wake up by acting as responsible citizens of a great nation.
Question:
According to the passage, the word ‘discipline‘ means-
A. a course along which someone or something moves.
B. the breakdown of peaceful and law-abiding public behavior
C. the practice of training people to obey rules or a code of behaviour
D. lack of proper planning and control.
E. lack of knowledge or information.
Solution
The correct answer is option 3 i.e. the practice of training people to obey rules or a code of behaviour.
Key Points
The passage is on the need to develop and plan ‘smart cities’ and how responsible citizens are necessary for this.
- The sentence that contains the word ‘discipline‘ is as follows: “We admire better hygiene and better traffic discipline abroad, but would breach the same back home.”
- In this case, a ‘better traffic discipline’ means that the people aboard follow traffic rules and guidelines properly unlike the people of India.
- An example of the same is: “We need to maintain discipline in the classrooms.”
Therefore, option 3 is the correct answer.
82. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
We admire better hygiene and better traffic discipline abroad but would breach the same back home. We condemn our system for churning out unemployed youth, but don’t like working hard to acquire knowledge. Students demanded their right to cheat in an examination; it is the same set of discards that later become a burden as they fail to acquire a skill for gainful employment. Rights are forcefully demanded, but duties generally detested.
As citizens of a functioning democracy, we welcome populist policies and government bounties. The State is expected to provide free electricity, free Wi-fi, free water, free books, free housing, free transport, free health facilities, free education. This will not raise many cavils if they are provided to the deserving sections of society. The problem arises when undeserving elements try to corner these benefits through devious means. The benefits that are provided by the government are seldom used in a responsible manner. Water and electricity are wasted, public utilities vandalized. We want the State’s delivery mechanism to be prompt and efficient, but we seldom reciprocate. We forget that it is the people who make the country and not the other way round. We resent nepotism and favouritism in government service delivery, but would not mind peddling influence to seek undue favours.
The plan to develop smart cities would turn out to be still-born if we don’t have smart citizens who would be willing to make sacrifices for a dignified living. We under-report our income and underpay our taxes, but we resent the government’s plea on inadequate resources to provide for basic amenities. There are enough laws and rules, but enforcement is seldom effective. While you pay a hefty $ 1000 fine for littering in a developed country or for a traffic violation, in India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling). Sometimes, the systemic imperfections impede the enforcement of the rule of law as the law-abiding citizens do not always get their rightful dues. Today, hundreds of thousands of applications for a fire licence or a building plan are allegedly pending in government offices for years, unless you pass on the speed money to those in the gravy train.
Information technology needs to be suitably harnessed for most of these services. E-governance is definitely the way to the future. As a country, we shall continue to grovel in the dust until the citizens are aware of their responsibilities. One only hopes that we shall soon wake up by acting as responsible citizens of a great nation.
Question:
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. In India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling).
B. E-governance is definitely a thing of the past.
C. The State is not expected to provide free electricity, free Wi-fi, free water or free books.
D. A hefty fine $100 is taken for littering in a developed country or for a traffic violation.
E. Today, hundreds of thousands of applications for a fire licence or a building plan are being resolved.
Solution
The correct answer is option 1 i.e. In India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling).
Key Points
The passage is on the need to develop and plan ‘smart cities’ and how responsible citizens are necessary for this.
- The following is stated in the passage: “…in India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling).”
Mistake Points
- The other options are not appropriate as they have been altered or changed in meaning.
- Therefore, it is important to compare the options with the statements in the passage to verify their validity.
Therefore, option 1 is the correct answer.
83. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
We admire better hygiene and better traffic discipline abroad but would breach the same back home. We condemn our system for churning out unemployed youth, but don’t like working hard to acquire knowledge. Students demanded their right to cheat in an examination; it is the same set of discards that later become a burden as they fail to acquire a skill for gainful employment. Rights are forcefully demanded, but duties generally detested.
As citizens of a functioning democracy, we welcome populist policies and government bounties. The State is expected to provide free electricity, free Wi-fi, free water, free books, free housing, free transport, free health facilities, free education. This will not raise many cavils if they are provided to the deserving sections of society. The problem arises when undeserving elements try to corner these benefits through devious means. The benefits that are provided by the government are seldom used in a responsible manner. Water and electricity are wasted, public utilities vandalized. We want the State’s delivery mechanism to be prompt and efficient, but we seldom reciprocate. We forget that it is the people who make the country and not the other way round. We resent nepotism and favouritism in government service delivery, but would not mind peddling influence to seek undue favours.
The plan to develop smart cities would turn out to be still-born if we don’t have smart citizens who would be willing to make sacrifices for a dignified living. We under-report our income and underpay our taxes, but we resent the government’s plea on inadequate resources to provide for basic amenities. There are enough laws and rules, but enforcement is seldom effective. While you pay a hefty $ 1000 fine for littering in a developed country or for a traffic violation, in India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling). Sometimes, the systemic imperfections impede the enforcement of the rule of law as the law-abiding citizens do not always get their rightful dues. Today, hundreds of thousands of applications for a fire licence or a building plan are allegedly pending in government offices for years, unless you pass on the speed money to those in the gravy train.
Information technology needs to be suitably harnessed for most of these services. E-governance is definitely the way to the future. As a country, we shall continue to grovel in the dust until the citizens are aware of their responsibilities. One only hopes that we shall soon wake up by acting as responsible citizens of a great nation.
Question:
Which of the following is expected to be provided by the State?
1. Free housing
2. Free Wi-Fi
3. Free transport
A. Only 1
B. only 2
C. only 3
D. all except 2
E. all of the above
Solution
The correct answer is option 5 i.e. all of the above.
Key Points
- The passage is on the need to develop and plan ‘smart cities’ and how responsible citizens are necessary for this.
- The following is stated in the passage: “The State is expected to provide free electricity, free Wi-fi, free water, free books, free housing, free transport, free health facilities, free education.”
Therefore, option 5 is the correct answer.
84. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
We admire better hygiene and better traffic discipline abroad but would breach the same back home. We condemn our system for churning out unemployed youth, but don’t like working hard to acquire knowledge. Students demanded their right to cheat in an examination; it is the same set of discards that later become a burden as they fail to acquire a skill for gainful employment. Rights are forcefully demanded, but duties generally detested.
As citizens of a functioning democracy, we welcome populist policies and government bounties. The State is expected to provide free electricity, free Wi-fi, free water, free books, free housing, free transport, free health facilities, free education. This will not raise many cavils if they are provided to the deserving sections of society. The problem arises when undeserving elements try to corner these benefits through devious means. The benefits that are provided by the government are seldom used in a responsible manner. Water and electricity are wasted, public utilities vandalized. We want the State’s delivery mechanism to be prompt and efficient, but we seldom reciprocate. We forget that it is the people who make the country and not the other way round. We resent nepotism and favouritism in government service delivery, but would not mind peddling influence to seek undue favours.
The plan to develop smart cities would turn out to be still-born if we don’t have smart citizens who would be willing to make sacrifices for a dignified living. We under-report our income and underpay our taxes, but we resent the government’s plea on inadequate resources to provide for basic amenities. There are enough laws and rules, but enforcement is seldom effective. While you pay a hefty $ 1000 fine for littering in a developed country or for a traffic violation, in India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling). Sometimes, the systemic imperfections impede the enforcement of the rule of law as the law-abiding citizens do not always get their rightful dues. Today, hundreds of thousands of applications for a fire licence or a building plan are allegedly pending in government offices for years, unless you pass on the speed money to those in the gravy train.
Information technology needs to be suitably harnessed for most of these services. E-governance is definitely the way to the future. As a country, we shall continue to grovel in the dust until the citizens are aware of their responsibilities. One only hopes that we shall soon wake up by acting as responsible citizens of a great nation.
Question:
Which of the following is the most appropriate meaning of ‘cavil‘ as used in the passage?
A. A trivial and annoying objection
B. To lower the dignity
C. To act in an objectionable manner
D. Possessing qualities that given great satisfaction
E. Exercising power
Solution
The correct answer is option 1 i.e. A trivial and annoying objection.
Key Points
The passage is on the need to develop and plan ‘smart cities’ and how responsible citizens are necessary for this.
- The sentence that contains this word is- “This will not raise many cavils if they are provided to the deserving sections of society.”
- Here, ‘cavil’ means a small but annoying objection.
Therefore, option 1 is the correct answer.
85. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
We admire better hygiene and better traffic discipline abroad but would breach the same back home. We condemn our system for churning out unemployed youth, but don’t like working hard to acquire knowledge. Students demanded their right to cheat in an examination; it is the same set of discards that later become a burden as they fail to acquire a skill for gainful employment. Rights are forcefully demanded, but duties generally detested.
As citizens of a functioning democracy, we welcome populist policies and government bounties. The State is expected to provide free electricity, free Wi-fi, free water, free books, free housing, free transport, free health facilities, free education. This will not raise many cavils if they are provided to the deserving sections of society. The problem arises when undeserving elements try to corner these benefits through devious means. The benefits that are provided by the government are seldom used in a responsible manner. Water and electricity are wasted, public utilities vandalized. We want the State’s delivery mechanism to be prompt and efficient, but we seldom reciprocate. We forget that it is the people who make the country and not the other way round. We resent nepotism and favouritism in government service delivery, but would not mind peddling influence to seek undue favours.
The plan to develop smart cities would turn out to be still-born if we don’t have smart citizens who would be willing to make sacrifices for a dignified living. We under-report our income and underpay our taxes, but we resent the government’s plea on inadequate resources to provide for basic amenities. There are enough laws and rules, but enforcement is seldom effective. While you pay a hefty $ 1000 fine for littering in a developed country or for a traffic violation, in India you can get away without penalty through various “desi jugad” (influence-peddling). Sometimes, the systemic imperfections impede the enforcement of the rule of law as the law-abiding citizens do not always get their rightful dues. Today, hundreds of thousands of applications for a fire licence or a building plan are allegedly pending in government offices for years, unless you pass on the speed money to those in the gravy train.
Information technology needs to be suitably harnessed for most of these services. E-governance is definitely the way to the future. As a country, we shall continue to grovel in the dust until the citizens are aware of their responsibilities. One only hopes that we shall soon wake up by acting as responsible citizens of a great nation.
Question:
Which of the following is/are valid suggestion(s) given by the author?
1. Responsibility should be shared among the citizen.
2. E–governance should be encouraged.
3. Information technology needs to be suitably harnessed for most services.
A. only 1
B. only 2
C. only 3
D. all of the above
E. none of these
Solution
The correct answer is option 4 i.e. all of the above.
Key Points
The passage is on the need to develop and plan ‘smart cities’ and how responsible citizens are necessary for this.
- The sentences in the passage clearly mention all three points as suggestions. They are:
- E-governance is definitely the way to the future.
- As a country, we shall continue to grovel in the dust until the citizens are aware of their responsibilities.
- Information technology needs to be suitably harnessed for most of these services.
Therefore, option 4 is the correct answer.
86. Direction: Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If a sentence is free from error, select ‘No Error’.
He is very stubborn (A)/ since childhood but him (B)/ is still very respectful (C)/ towards elders and relatives. (D)/ No error (E)/
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option (2) i.e. B.
Explanation:
- The error lies in the wrong usage of the pronoun ‘him’ in Part B.
- “him” will be replaced with “he”, subjective case of the pronoun.
- But is used as a conjunction as well as preposition.
- But when used as conjunction gives the sense of connecting two sentence giving reasoning.
- But when used as preposition gives the sense of except,excluding something.
- In this sentence ‘but’ is used as conjunction.
- Whenever any conjunction is used in a sentence , we will always use subjective case after it.
- Conjunction +Subjective caseObjective caseAnd,but,for,nor,or,so,yet
- Correct Sentence: “He is very stubborn since childhood but he is still very respectful towards elders and relatives”
Additional Information
PersonNumberSubject.Object.Poss. Adj.Poss. Pro.1stSingularIMeMyMine”PluralWeUsOurOurs2ndSingularYouYouYourYours”PluralYouYouYourYours3rdSingularHeHimHisHis””SheHerHerHers””ItItIts-“PluralTheyThemTheirTheirs
87. Direction: Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If a sentence is free from error, select ‘No Error’.
No other teacher (A)/ of his age in the (B)/ schools here in Patna is (C)/ as brilliant as him. (D)/ No error (E)/
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option (4) i.e. D.
Explanation:
- The error lies in the wrong usage of the pronoun ‘him’ in Part D.
- ‘him’ should be replaced by ‘he’ because after ‘as’, the pronoun used should be in the same case as that of the pronoun /Noun used before ‘as’.
For example- You as big as him.
- In the given sentence, ‘teacher’ – the noun before ‘as’ is in the subjective case; hence, the pronoun after ‘as’ needs to be in the subjective case.
- Therefore, ‘he’ should be used instead of ‘him’.
Correct sentence : “No other teacher of his age in the schools here in Patna is as brilliant as he. ”
88. A sentence is divided into four segments marked A, B, C, D. Select the segment of the sentence that contains a grammatical error and mark the segment. If there is no error, mark ‘No error’ as your answer
A tenth (A)/ chapter of (B) the book (C)/ is very interesting (D)/ No error (E)
A. D
B. A
C. C
D. B
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 2) i.e. A
- ‘The’ article is used with ordinals and while expressing the numbers.
- ‘A’ tenth chapter is an incorrect usage of the article.
- Although the noun ‘chapters’ is countable but the specific chapter ‘tenth’ mentioned nulls its use of indefinite articles.
It is to be noted that an article is used prior to a common singular number, which makes it function more appropriate in a sentence.
The correct sentence is : The tenth chapter of the book is very interesting.
89. A sentence is divided into four segments marked A, B, C, D. Select the segment of the sentence that contains a grammatical error and mark the segment. If there is no error, mark ‘No error’ as your answer.
A Dr. Khanna (A)/ whom you met (B)/ last night, (C)/ is my uncle (D)/ No error (E)
A. A
B. B
C. D
D. C
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 1) i.e. A
Key Points
- The proper noun when qualified by an adjective, is described with ‘The’.Dr Khanna is a particular person referred here, he is not a thing.
- ‘The’ specifies the particular doctor being mentioned relating to the other part of the sentence.
- The indefinite article do not justify the introduction of the sentence.
The correct sentence: The Dr. Khanna whom you met last night, is my uncle.
90. Pick out the most appropriate word from the given words to fill in the blank to make the sentence meaningfully correct.
Neem powder contains a unique ______ of organic and beneficial compounds, so products derived from it are very popular in herbal remedies.
A. Flavouring
B. Composition
C. Discontent
D. Notorious
E. Inferior
Solution
The correct answer is composition.
Key Points
- Let us look at the meaning of the other words:
- ‘Flavouring’ means a substance used to give a different, stronger /more agreeable taste to food / drink
- ‘Composition’ means the nature of something’s ingredient / way in which a whole or mixture is made
- ‘Discontent’ means dissatisfaction with one’s circumstances; lack of contentment
- ‘Notorious’ means famous or well known, typically for some bad quality or deed.
- ‘Inferior’ means lower in rank, status, or quality.
- The correct word that should fill the bank would be composition.
- Example statements:
- ‘We cannot determine the chemical composition of soil simply by touching it.’
- Since it is clear through the statement that the word ‘composition’ is more suitable than the other options.
- Hence the correct answer is option 2.
Correct sentence: “Neem powder contains a unique composition of organic and beneficial compounds, so products derived from it are very popular in herbal remedies.“
91. Pick out the most appropriate word from the given words to fill in the blank to make the sentence meaningfully correct.
The town has grown rapidly since the _______ of the railway system, and has a large trade in petroleum from Baku.
A. Termination
B. Completion
C. Stoppage
D. Interruption
E. Obtrusion
Solution
The correct answer is completion.
Let us look at the meaning of other words:
‘Termination’ means the action of terminating something or the fact of being terminated.
‘Completion’ means the action or process of completing or finishing something.
‘Stoppage’ means an instance of movement, activity, or supply stopping or being stopped.
‘Interruption’ means the action of interrupting or being interrupted.
‘Obtrusion’ means the action of imposing on someone in an unwelcome or intrusive way.
For example,
‘Mr. Gupta’s work on the new golf course is nearing completion’
‘In Britain, it seems to have been positively unknown until quoted some years after its completion by a catalouge compiler on account of some peculiarities of nomenclature which it presented’
Since it is clear through the statement that the word ‘Completion’ is more suitable than the other options.
Hence the correct answer is option 2.
92. Direction: Fill in the blank with an appropriate word from the given options.
Rahul gave a __________ account of the event.
A. Rapid
B. Presumably
C. Vivid
D. Underlying
E. None of the above
Solution
Here, understanding the context is essential in determining the correct usage of the given options. The correct word will be in its adjective form to make the sentence complete.
Key Points
- Rapid means happening in a short time or at a great rate.
- Presumably means by assuming reasonably.
- Vivid means producing powerful feelings or strong, clear images in the mind.
- Underlying means to lie or be situated under.
- In the above sentence, the correct answer will be vivid as it makes the context relevant.
- Rahul gave a vivid account of the event.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 3
93. The given question has one blank indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the word for the given options that could fit in the blank correctly.
There is a global drive to ______ the growth and development of nations through innovation and technology.
A. break
B. accelerate
C. speed
D. expand
E. none of these
Solution
The correct answer is accelerate.
Key Points
Let’s look at the meaning of the correct answer.
- A global drive for growth and development of nations through innovation and technology should be accelerated.
- Accelerate – Increase the speed of something
- Example: Our country should accelerate economic growth.
- From the given meaning we can conclude that the correct answer is accelerate.
Thus the correct sentence is: “There is a global drive to accelerate the growth and development of nations through innovation and technology”.
Additional Information
Let’s discuss the meaning of other options:
expand – make larger or more extensive.
break – an interruption of continuity or uniformity.
speed – the rate at which someone or something moves
94. Direction: Evaluate the following word, accompanied by three sentences containing it. Determine the sentence(s) that accurately convey the meaning of the given word.
CONDUCT
A. Her conduct at the event was impeccable, showcasing her professionalism and courtesy.
B. The fallen tree branch conducted the path, making it difficult to continue hiking.
C. The teacher will conduct a science experiment to demonstrate the principles of chemical reactions.
A. Only B
B. Both A & B
C. Only A
D. All A, B & C
E. Both A & C
Solution
The correct answer is option 5.
\key
Therefore, the correct answer is “Both A & C.”
To answer this question, let’s first understand the meaning of the given word –
Conduct – (Noun) – the manner in which a person behaves, especially in a particular place or situation (आचरण)
For Example –
The scientist’s conduct during the experiment was meticulous and precise.
Conduct – (Verb) – organize and carry out (संचालित करना)
For Example –
The scientist will conduct experiments to test their hypothesis.
After understanding the meaning of the given word, we can conclude that ‘conduct’ is used correctly in both sentences A (as a noun) and C (as a verb), while sentence B is incorrect.
Sentence B – The fallen tree branch conducted the path, making it difficult to continue hiking.
This sentence is incorrect because “conduct” is used incorrectly here. “Conduct” means to guide or lead, but in this context, the fallen tree branch is not guiding the path. It should be replaced with something “obstruct” to indicate that the fallen branch is blocking or hindering the path.
95. Direction: Evaluate the following word, accompanied by three sentences containing it. Determine the sentence(s) that accurately convey the meaning of the given word.
CENSURE
A. The committee chose to censure the member who violated the organization’s code of conduct.
B. The newspaper editorial contained a scathing censure of the government’s handling of the crisis.
C. The motion censure activated the lights as I entered the room.
A. Only A
B. Only C
C. All A, B & C
D. Both A & B
E. Only B
Solution
The correct answer is option 4.
\key
Therefore, the correct answer is “Both A & B.”
To answer this question, let’s first understand the meaning of the given word –
Censure – (Verb) – express severe disapproval of (someone or something), especially in a formal statement (निंदा करना)
For Example –
The supervisor decided to censure the employee for repeatedly coming in late to work.
Censure – (Noun) – the formal expression of severe disapproval (निंदा)
For Example –
The politician faced severe censure from his colleagues after his controversial remarks.
After understanding the meaning of the given word, we can conclude that ‘censure’ is used correctly in both sentences A (as a verb) and B (as a noun), while sentence C is incorrect.
Sentence C – The motion censure activated the lights as I entered the room.
The word “censure” means to criticize or express disapproval, while in the sentence, it seems like it’s being used to talk about activating lights. “Sensor” should be used instead to describe a device that detects motion and turns on the lights.
96. Rearrange the following five sentences (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph then answer the questions given below them.
A. There were so many anxieties in the early days of the pandemic when the spread of the contagion was still poorly understood.
B. This dividend is attributed to the young, and values energy over experience.
C. One example of the unpredictability is how it has taken the lives of many young people while sparing many among the elderly, who were believed to be at maximum risk.
D. But the coronavirus is unpredictable, it does not seem to respect logic.
E. Among those anxieties was the very real apprehension about its effect on the elderly, most of whom are compromised by age-related disorders.
Question:
Which of these is the FIRST sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 1 i.e. A.
Explanation-
- The first sentence is A as it introduces the subject i.e. the understanding of the effect of the contagion.
- The second sentence is E as it refers to ‘the anxieties’ that are mentioned in sentence A.
- The third sentence should be D as it starts with ‘but’ and adds more information by telling that the virus is unpredictable.
- The fourth sentence should be C as it proves how the virus is unpredictable as mentioned in D.
- The last sentence is B as it gives a conclusion by mentioning the reason behind the demographic dividend.
- Thus, the correct sequence is AEDCB.
- The first sentence is A.
97. Rearrange the following five sentences (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph then answer the questions given below them.
A. There were so many anxieties in the early days of the pandemic when the spread of the contagion was still poorly understood.
B. This dividend is attributed to the young, and values energy over experience.
C. One example of the unpredictability is how it has taken the lives of many young people while sparing many among the elderly, who were believed to be at maximum risk.
D. But the coronavirus is unpredictable, it does not seem to respect logic.
E. Among those anxieties was the very real apprehension about its effect on the elderly, most of whom are compromised by age-related disorders.
Question:
Which of these is the SECOND sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 5 i.e. E.
Explanation-
- The first sentence is A as it introduces the subject i.e. the understanding of the effect of the contagion.
- The second sentence is E as it refers to ‘the anxieties’ that are mentioned in sentence A.
- The third sentence should be D as it starts with ‘but’ and adds more information by telling that the virus is unpredictable.
- The fourth sentence should be C as it proves how the virus is unpredictable as mentioned in D.
- The last sentence is B as it gives a conclusion by mentioning the reason behind the demographic dividend.
- Thus, the correct sequence is AEDCB.
- The second sentence is E.
98. Rearrange the following five sentences (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph then answer the questions given below them.
A. There were so many anxieties in the early days of the pandemic when the spread of the contagion was still poorly understood.
B. This dividend is attributed to the young, and values energy over experience.
C. One example of the unpredictability is how it has taken the lives of many young people while sparing many among the elderly, who were believed to be at maximum risk.
D. But the coronavirus is unpredictable, it does not seem to respect logic.
E. Among those anxieties was the very real apprehension about its effect on the elderly, most of whom are compromised by age-related disorders.
Question:
Which of these pairs form consecutive sentences after rearrangement?
A. A-B
B. D-B
C. E-C
D. A-D
E. E-D
Solution
The correct answer is option 5 i.e. E-D.
Explanation-
- The first sentence is A as it introduces the subject i.e. the understanding of the effect of the contagion.
- The second sentence is E as it refers to ‘the anxieties’ that are mentioned in sentence A.
- The third sentence should be D as it starts with ‘but’ and adds more information by telling that the virus is unpredictable.
- The fourth sentence should be C as it proves how the virus is unpredictable as mentioned in D.
- The last sentence is B as it gives a conclusion by mentioning the reason behind the demographic dividend.
- Thus, the correct sequence is AEDCB.
- The only pair which forms 2 consecutive sentences and is mentioned in the options is E-D i.e. the second and third sentence.
99. Rearrange the following five sentences (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph then answer the questions given below them.
A. There were so many anxieties in the early days of the pandemic when the spread of the contagion was still poorly understood.
B. This dividend is attributed to the young, and values energy over experience.
C. One example of the unpredictability is how it has taken the lives of many young people while sparing many among the elderly, who were believed to be at maximum risk.
D. But the coronavirus is unpredictable, it does not seem to respect logic.
E. Among those anxieties was the very real apprehension about its effect on the elderly, most of whom are compromised by age-related disorders.
Question:
Which of these is the FOURTH sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 3 i.e. C.
Explanation-
- The first sentence is A as it introduces the subject i.e. the understanding of the effect of the contagion.
- The second sentence is E as it refers to ‘the anxieties’ that are mentioned in sentence A.
- The third sentence should be D as it starts with ‘but’ and adds more information by telling that the virus is unpredictable.
- The fourth sentence should be C as it proves how the virus is unpredictable as mentioned in D.
- The last sentence is B as it gives a conclusion by mentioning the reason behind the demographic dividend.
- Thus, the correct sequence is AEDCB.
- The fourth sentence is C.
100. Rearrange the following five sentences (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph then answer the questions given below them.
A. There were so many anxieties in the early days of the pandemic when the spread of the contagion was still poorly understood.
B. This dividend is attributed to the young, and values energy over experience.
C. One example of the unpredictability is how it has taken the lives of many young people while sparing many among the elderly, who were believed to be at maximum risk.
D. But the coronavirus is unpredictable, it does not seem to respect logic.
E. Among those anxieties was the very real apprehension about its effect on the elderly, most of whom are compromised by age-related disorders.
Question:
Which of these is the FIFTH sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is option 2 i.e. B.
Explanation-
- The first sentence is A as it introduces the subject i.e. the understanding of the effect of the contagion.
- The second sentence is E as it refers to ‘the anxieties’ that are mentioned in sentence A.
- The third sentence should be D as it starts with ‘but’ and adds more information by telling that the virus is unpredictable.
- The fourth sentence should be C as it proves how the virus is unpredictable as mentioned in D.
- The last sentence is B as it gives a conclusion by mentioning the reason behind the demographic dividend.
- Thus, the correct sequence is AEDCB.
- The fifth sentence is B.
