Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Eight persons, L, D, K, M, J, R, X and P join a company on two different dates, on the 13th and the 23rd of four different months, February, April, July and October of a particular year.J joins the company in the month of April. D joins the company on the first allotted date of July. X and R join the company in the same month. K joins in the same month as D. P is the last person to join the company. X doesn’t join in the month of July or October. R joins the company immediately before J. L joins the company in the second allotted date of the month that consists of 30 days. P joins the company immediately after M.
Question:
1. Who was the first person to join the company?
A. R
B. J
C. M
D. X
E. P
Solution
Given: Eight persons join a company on two different dates of four different months of a particular year.
Based on the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. D joins the company on the first allotted date of July. P is the last person to join the company. Combining these two, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | ||
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
2. K joins in the same month as D. J joins the company in the month of April. L joins the company in the second allotted date of the month that consists of 30 days. Combining these statements, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
3. P joins the company immediately after M. From this, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
4. X and R join the company in the same month. X doesn’t join in the month of July or October. R joins the company immediately before J. Combining these statements, we the final table as follows-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | X |
| 23 | R | |
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
From the above final table, we see that X is the first person to join the company.Hence, X joins the company first.
2. L joins the company in the same month as?
A. X
B. K
C. J89% answered correctly
D. R
E. M
Solution
Given: Eight persons join a company on two different dates of four different months of a particular year.
Based on the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. D joins the company on the first allotted date of July. P is the last person to join the company. Combining these two, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | ||
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
2. K joins in the same month as D. J joins the company in the month of April. L joins the company in the second allotted date of the month that consists of 30 days. Combining these statements, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
3. P joins the company immediately after M. From this, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
4. X and R join the company in the same month. X doesn’t join in the month of July or October. R joins the company immediately before J. Combining these statements, we the final table as follows-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | X |
| 23 | R | |
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
From the above final table, we see that J and L join the company in the month of April.
Hence, L joins the company in the same month as J.
3. Who joins the company immediately after L?
A. R
B. X
C. P
D. D
E. J
Solution
Given: Eight persons join a company on two different dates of four different months of a particular year.
Based on the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. D joins the company on the first allotted date of July. P is the last person to join the company. Combining these two, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | ||
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
2. K joins in the same month as D. J joins the company in the month of April. L joins the company in the second allotted date of the month that consists of 30 days. Combining these statements, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
3. P joins the company immediately after M. From this, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
4. X and R join the company in the same month. X doesn’t join in the month of July or October. R joins the company immediately before J. Combining these statements, we the final table as follows-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | X |
| 23 | R | |
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
From the above final table, we see that D joins immediately after L.
Hence, D joins the company immediately after L.
4. K joins the company immediately before?
A. L
B. P
C. J
D. X
E. M
Solution
Given: Eight persons join a company on two different dates of four different months of a particular year.
Based on the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. D joins the company on the first allotted date of July. P is the last person to join the company. Combining these two, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | ||
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
2. K joins in the same month as D. J joins the company in the month of April. L joins the company in the second allotted date of the month that consists of 30 days. Combining these statements, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
3. P joins the company immediately after M. From this, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
4. X and R join the company in the same month. X doesn’t join in the month of July or October. R joins the company immediately before J. Combining these statements, we the final table as follows-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | X |
| 23 | R | |
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
From the above final table, we see that K joins the company immediately before M.
Hence, K joins immediately before M.
5. In the options given below, all the persons share a common relation apart from one. Who is the odd one out?
A. R
B. L
C. K
D. X
E. P
Solution
Given: Eight persons join a company on two different dates of four different months of a particular year.
Based on the given conditions, we get the following possibilities-
1. D joins the company on the first allotted date of July. P is the last person to join the company. Combining these two, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | ||
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
2. K joins in the same month as D. J joins the company in the month of April. L joins the company in the second allotted date of the month that consists of 30 days. Combining these statements, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | |
| 23 | P |
3. P joins the company immediately after M. From this, we get-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | |
| 23 | ||
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
4. X and R join the company in the same month. X doesn’t join in the month of July or October. R joins the company immediately before J. Combining these statements, we the final table as follows-
| MONTH | DATE | PERSON |
| FEBRUARY | 13 | X |
| 23 | R | |
| APRIL | 13 | J |
| 23 | L | |
| JULY | 13 | D |
| 23 | K | |
| OCTOBER | 13 | M |
| 23 | P |
From the above final table, we see that all the options except X join the company on the 23rd of different months.
Hence, person X is the odd one out.
Comprehension:(Que No. 6 – 9)
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language,
‘It is raining heavily’ is coded as ‘at ps qr na’.
‘truck is loaded heavily’ is coded as ‘ac ps rs na’.
‘heavily loaded the truck’ coded as ‘na rs me ac’.
6. How is ‘heavily’ coded in the given language?
A. me
B. ps
C. at
D. na
E. ah
Solution

Hence, ‘na’ is the code for ‘heavily’.
7. How is ‘loaded’ coded in the language?
A. ps
B. at
C. ac
D. rs
E. Either ‘rs’ or ‘ac’
Solution

| Word | loaded | truck |
| Code | rs / ac | rs / ac |
Hence, ‘rs or ac’ is the code for ‘loaded’.
8. What can be the answer for ‘at rs’?
A. Raining heavily
B. Raining loaded
C. the loaded
D. it truck
E. Can not be determined
Solution

‘at’ is the code for :
| Word | it | raining |
| Code | at / qr | at / qr |
‘rs’ is the code for:
| Word | loaded | truck |
| Code | rs / ac | rs / ac |
Hence, the answer is can not be determined.
9. which can be the code for ‘the raining is’ ?
A. ps ac rs
B. at qr me
C. na me ac
D. at ac ah
E. qr ps me72% answered correctly
Solution

The code for ‘raining’ and ‘it’ :
| Word | it | raining |
| Code | at / qr | at / qr |
‘is’ coded as ‘ps’
‘the’ coded as ‘me’.
Hence ‘qr ps me‘ represents the required code.
10. Directions: – Relationship between different elements is shown in the statements below. These Statements are followed by 2 Conclusions. Mark your answer on the basis of given statements and conclusions.
Statements: H < I < J = K, H < M < N
Conclusion:
I) M > J
II) H < K
A. None follows
B. Both follow
C. Only I follows
D. Only II) follows
E. Either I) or II) follows
Solution
I) M > J: False (M > H < I < J : No relationship can be found between M and J, hence false)
II) H < K: True (H < I < J = K: Here, it is clearly visible that H is less than K)
Hence, only II) follows.
11. Directions: – Relationship between different elements is shown in the statements below. These Statements are followed by 2 Conclusions. Mark your answer on the basis of given statements and conclusions.
Statement: K > B < C = D ≤ E, L < B
Conclusions:
I) B ≤ E
II) B < E
A. Only I) follows
B. Only II) follows
C. Either I) or II) follows
D. Both I) and II) follow
E. None follows
Solution
I) B ≤ E: False ( B < C = D ≤ E; B is less than E but it can never be equal to E, hence, false)
II) B < E : True( B < C = D ≤ E; It is clearly visible that B is less than E, hence, true)
Hence, only II) follows.
12. Direction: In each of the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/ are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: X ≥ Y < Z, S > J = X
Conclusion:
I. S > Y
II. J ≥ Z
A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follows
Solution
Given Statements: X ≥ Y < Z, S > J = X
On Combining: S > J = X ≥ Y < Z
Conclusion:
I. S > Y → True (When > sign is given, we have to check that between all the elements > or combination of >, ≥ and = must be present. So, it is true)
II. J ≥ Z → False ( When ≥ sign is given, we have to check that between the elements all the sign are of ≥ type or combination of ≥ or =. So, it is false)
Hence, only I follows.
Directions: Study the following information to answer the given questions.
Eight persons E, F, G, H, I, J, K and L sit in a straight row. Equal number of persons face north and south direction. L sits third to the right of K. Four persons sit between L and H, who sits at one of the extreme ends. J sits to the immediate right of G, who faces same direction as K. One person sits between G and F, who faces south direction. E sits second to the left of I, who faces north direction. Persons, who sit at extreme ends, faces same direction. E and K faces the same direction. H is not a neighbour of I.
13. Who sits 4th to the left of G?
A. E
B. H
C. K50% answered correctly
D. F
E. J
Solution
Eight persons: E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L
Faces both directions North and South
1) L sits third to the right of K.
2) Four persons sit between L and H, who sits at one of the extreme ends.
3) J sits to the immediate right of G, who faces same direction as K.
4) One person sits between G and F, who faces south direction.
5) E sits second to the left of I, who faces north direction.
6) Persons, who sit at extreme ends, faces same direction.
7) E and K faces the same direction.
8) H is not a neighbour of I.

Hence, K sits 4th to the left of G.
14. How many persons sit to the left of F?
A. Two
B. Three43% answered correctly
C. Four
D. Five
E. None
Solution
Eight persons: E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L
Faces both directions North and South
1) L sits third to the right of K.
2) Four persons sit between L and H, who sits at one of the extreme ends.

3) J sits to the immediate right of G, who faces same direction as K.
4) One person sits between G and F, who faces south direction.
5) E sits second to the left of I, who faces north direction.
6) Persons, who sit at extreme ends, faces same direction.
7) E and K faces the same direction.
8) H is not a neighbour of I.

Hence, three persons are sitting to the left of F.
15.K sits second to ___ of ___.
A. Left – F
B. Right – G
C. Left – E
D. Left – H
E. Right – I
Solution
Eight persons: E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L
Faces both directions North and South
1) L sits third to the right of K.
2) Four persons sit between L and H, who sits at one of the extreme ends.

3) J sits to the immediate right of G, who faces same direction as K.
4) One person sits between G and F, who faces south direction.
5) E sits second to the left of I, who faces north direction.
6) Persons, who sit at extreme ends, faces same direction.
7) E and K faces the same direction.
8) H is not a neighbour of I.

Therefore, K sits second to left of H.
16. Which of the following pairs is not correct?
A. South – L
B. North – G
C. South – F
D. North – J
E. South – H
Solution
Eight persons: E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L
Faces both directions North and South
1) L sits third to the right of K.
2) Four persons sit between L and H, who sits at one of the extreme ends.

3) J sits to the immediate right of G, who faces same direction as K.
4) One person sits between G and F, who faces south direction.
5) E sits second to the left of I, who faces north direction.
6) Persons, who sit at extreme ends, faces same direction.
7) E and K faces the same direction.
8) H is not a neighbour of I.

Hence, J faces south direction.
17. Who sits immediate left of H?
A. G
B. J
C. L
D. K
E. E
Solution
Eight persons: E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L
Faces both directions North and South
1) L sits third to the right of K.
2) Four persons sit between L and H, who sits at one of the extreme ends.

3) J sits to the immediate right of G, who faces same direction as K.
4) One person sits between G and F, who faces south direction.
5) E sits second to the left of I, who faces north direction.
6) Persons, who sit at extreme ends, faces same direction.
7) E and K faces the same direction.
8) H is not a neighbour of I.

Hence, E sits immediate left of H.
Direction: Read the instructions carefully and answer the question below.
Each of the six stores – A, B, C, D, E and F sold different number of LED in one day. B sold more LED than E but less than both D and F. A sold less LED than E but more than C. The store which sold second highest number of 29 LED. D does not sell LEDs in a prime number. The Store which sold the minimum LED sold 6 LED.
18. If the number of LED sold by D is 30, then which of the following statement is true?
A. None of the given option is true
B. D and C together definitely sold less than 35 LED
C. Only two stores sold more LED than D
D. D sold maximum number of LED
E. F sold more LED than D
Solution
Six stores- A, B, C, D, E and F
1) B sold more LED than E but Less than both D and F.
(From this statement position of D and F is not clear)
D/F > F/D > B > E
2) A sold less LED than E but more than C.
D/F > F/D > B > E > A > C
3) The store which sold second highest number of 29 LED.
4) D does not sold a LED in a Prime number.
(It means D does not comes on second place because they does not sold a LED in a prime number, So F is in second place and sold 29 LED.
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C
5) The store which sold the minimum LED sold 6 LED
(According to the given information C sold minimum number of LED)
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C(6)
Clearly, D sold maximum number of LED.
19. How many stores sold less LED than A?
A. Two
B. One
C. Three
D. Five
E. None as A sold the lowest number of LED
Solution
Six stores- A, B, C, D, E and F
1) B sold more LED than E but Less than both D and F.
(From this statement position of D and F is not clear)
D/F > F/D > B > E
2) A sold less LED than E but more than C.
D/F > F/D > B > E > A > C
3) The store which sold second highest number of 29 LED.
4) D does not sell a LED in a Prime number.
(It means D does not come in second place because they do not sell a LED in a prime number, So F is in second place and sold 29 LED.
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C
5) The store which sold the minimum LED sold 6 LED
(According to the given information C sold minimum number of LED)
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C(6)
Only, one C is sold less LED than A.
20. How many LED sold by D is one day.
A. 24
B. 27
C. 32
D. 25
E. 23
Solution
Six stores- A, B, C, D, E and F
1) B sold more LED than E but Less than both D and F.
(From this statement position of D and F is not clear)
D/F > F/D > B > E
2) A sold less LED than E but more than C.
D/F > F/D > B > E > A > C
3) The store which sold second highest number of 29 LED.
4) D does not sold a LED in a prime number.
(It means D does not comes on second place because they does not sold a LED in a prime number, So F is in second place and sold 29 LED.
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C
5) The store which sold the minimum LED sold 6 LED
(According to the given information C sold minimum number of LED)
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C(6)
Clearly, D does not sell less LED than F and doesn’t sell in prime number, So D would sell number of LED more than 29. According to the given options, D would sell 32 LED.
Hence, the correct answer is option (3).
21. If E sold 15 LED in one day so how many LED sold by B?
A. 13
B. 20
C. 30
D. 31
E. None of the above
Solution
Six stores- A, B, C, D, E and F
1) B sold more LED than E but Less than both D and F.
(From this statement position of D and F is not clear)
D/F > F/D > B > E
2) A sold less LED than E but more than C.
D/F > F/D > B > E > A > C
3) The store which sold second highest number of 29 LED.
4) D does not sell a LED in a Prime number.
(It means D does not come in second place because they do not sell a LED in a prime number, So F is in second place and sold 29 LED.
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C
5) The store which sold the minimum LED sold 6 LED
(According to the given information C sold a minimum number of LEDs)
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C(6)
According to the question.
If E sold 15 LED then B sold more than E and Less than F, according to this only 20 LED were sold by B.
Hence, 20 will be the correct answer.
22. If the number of LED sold by B is multiple of three, more than 25. How many LED were sold by B?
A. 30
B. 27
C. 33
D. 36
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
Six stores- A, B, C, D, E and F
1) B sold more LED than E but Less than both D and F.
(From this statement position of D and F is not clear)
D/F > F/D > B > E
2) A sold less LED than E but more than C.
D/F > F/D > B > E > A > C
3) The store which sold second highest number of 29 LED.
4) D does not sold a LED in a Prime number.
(It means D does not comes on second place because they does not sold a LED in a prime number, So F is in second place and sold 29 LED.
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C
5) The store which sold the minimum LED sold 6 LED
(According to the given information C sold minimum number of LED)
D > F(29) > B > E > A > C(6)
B sold less than 29 LED and 27 is a multiple of 3 and it is more than 25.
Hence, 27 will be the correct answer.
23. How many such pairs of letters are there in the word ‘GENERALIST’, each of which has as many letters between them in the word (both in the forward and backward direction) as they have between them in the English alphabet?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
E. More than four
Solution

Hence, four pairs are there which has as many letters between them in the word (both forward and backward direction) as they have between them in the English alphabet.
Directions: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions.
There are six members in a family- P, Q, R, S, T, and U. P is the sister of Q. Q is married to R. R is the father of S. T is the son of U. Q is the mother-in-law of U. R has only one son and no daughter.
24. What is the relation of R with respect to U?
A. Maternal Uncle
B. Father
C. Grandfather
D. Father-in-law
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
From the given information,
1) P is the sister of Q, and Q is married to R.
2) R is the father of S. (Implies Q is the mother of S.)
3) R has only one son and no daughter.
4) Q is the mother-in-law of U. (Implies U is the wife of S.)
5) T is the son of U.

Therefore, R is the father-in-law of U.
25. Who is the nephew of P?
A. U
B. T
C. R
D. S
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
From the given information,
1) P is the sister of Q, and Q is married to R.
2) R is the father of S. (Implies Q is the mother of S.)
3) R has only one son and no daughter.
4) Q is the mother-in-law of U. (Implies U is the wife of S.)
5) T is the son of U.

As P is the sister of Q and, S is the son of Q.
Therefore, S is the nephew of P.
26. If V is married to T, then how is Q related to T?
A. Grandmother
B. Sister-in-law
C. Niece
D. Mother-in-law
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
From the given information,
1) P is the sister of Q, and Q is married to R.
2) R is the father of S. (Implies Q is mother of S.)
3) R has only one son and no daughter.
4) Q is the mother-in-law of U. (Implies U is wife of S.)
5) T is the son of U. (Implies S and Q are father and grandmother of T respectively.)

Therefore, Q is grandmother of T.
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
$ W Z 1 T P 5 6 7 # µ 5 5 4 4 M * N L 9 @ U F Y 7 A 3 & I G % 1 ! H 2 5 V X @ S E
27. How many such symbols are there in the above arrangement each of which are immediately preceded by a number and followed by an alphabet?
A. None
B. Two
C. One
D. Three
E. More than three
Solution
Given series:
Left Side $ W Z 1 T P 5 6 7 # µ 5 5 4 4 M * N L 9 @ U F Y 7 A 3 & I G % 1 ! H 2 5 V X @ S E Right Side
Required Format:
| Number | Symbols | Alphabet |
Symbols which are immediately preceded by a number and followed by an alphabet:
$ W Z 1 T P 5 6 7 # µ 5 5 4 4 M * N L 9 @ U F Y 7 A 3 & I G % 1 ! H 2 5 V X @ S E
Hence, there are 3 symbols which are immediately preceded by number and followed by an alphabet: 9 @ U, 3 & I and 1 ! H.
28. If all the symbols in the above arrangement are dropped, then which of the following will be the twelfth element from the left end?
A. 5
B. M
C. 4
D. L
E. 7
Solution
Given series:
Left Side $ W Z 1 T P 5 6 7 # µ 5 5 4 4 M * N L 9 @ U F Y 7 A 3 & I G % 1 ! H 2 5 V X @ S E Right Side
If all the symbols are dropped:
Left Side W Z 1 T P 5 6 7 5 5 4 4 M N L 9 U F Y 7 A 3 I G 1 H 2 5 V X S E Right Side
So, 12th element from the left end is 4.
29. How many such numbers are there in the above arrangement each of which is immediately followed by a consonant but not immediately preceded by an alphabet?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. More than three
Solution
Given series:
Left Side $ W Z 1 T P 5 6 7 # µ 5 5 4 4 M * N L 9 @ U F Y 7 A 3 & I G % 1 ! H 2 5 V X @ S E Right Side
Required Format:
| Numbers | Consonant |
$ W Z 1 T P 5 6 7 # µ 5 5 4 4 M * N L 9 @ U F Y 7 A 3 & I G % 1 ! H 2 5 V X @ S E
Hence, only two numbers are immediately followed by a consonant but not immediately preceded by an alphabet: 4 4 M, 2 5 V.
30. Four of following five are alike in a certain way based on their positions in the above arrangement and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
A. $ Z T
B. W 1 P
C. * L @
D. U Y 7
E. I % !
Solution
Given series:
Left Side $ W Z 1 T P 5 6 7 # µ 5 5 4 4 M * N L 9 @ U F Y 7 A 3 & I G % 1 ! H 2 5 V X @ S E Right Side
Here the group is formed in which second element is second next to the first, and the third element is also to the second next of the second element.
$(+2) → Z(+2)→ T
W(+2) → 1(+2)→P
*(+2) → L(+2)→@
U(+2) → Y(+1)→7
I(+2) → %(+2)→!
Hence, U Y 7 does not belong to the group.
31. Which of the following is the seventh to the left of the eighteenth element from the left end of the above arrangement?
A. N
B. µ
C. #
D. F
E. 5
Solution
Given series:
Left Side $ W Z 1 T P 5 6 7 # µ 5 5 4 4 M * N L 9 @ U F Y 7 A 3 & I G % 1 ! H 2 5 V X @ S E Right Side
The Eighteenth element from the left end: N
Seventh element to the left of N: µ
(*Trick: i) If both the directions in the question are same then, find the difference between both the positions and count that difference from the same direction end.
ii) If both the directions are different then, then add both the numbers and count that addition from the asked direction end.
For example, here in the above case, both the directions are same, so calculate the difference between them and count that difference from the mentioned direction i.e. left.
∴18 – 7 = 11
Now, count up to 11th position from the left end, we will get our answer i.e. µ.)
Hence, the answer will be µ.
32. Direction: In the following question below, some statements are given followed by some conclusions. Taking the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts, read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows the given statements.
Statements:
I. Some cold are ice.
II. All ice are water.
III. No water is a hot.
Conclusions:
I. Some water are cold.
II. Some ice being hot is a possibility.
A. Only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Both conclusion I and II follow
D. Neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. Either conclusion I or II follows
Solution
The least possible diagram for the given statements is as follows:

Conclusions:
I. Some water are cold → True (As some cold are ice and all ice are water).
II. Some ice being hot is a possibility → False (ice cannot form a relationship with hot because all ice are water and no water is a hot so “no ice is a hot” is definitely true).
Hence, only conclusion I follows.
33. Direction: In the following question below some statements are given followed by some conclusions. Taking the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts, read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows the given statements.
Statements:
I. Some fruits are pears.
II. All pears are beans.
III. All beans are vegetables.
Conclusions:
I. Some beans are fruits.
II. Some vegetables are pears.
A. Only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Both conclusion I and II follow
D. Neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. Either conclusion I or II follows
Solution
The least possible diagram for the given statements is as follows:

Conclusions:
I. Some beans are fruits → True (It is true because some fruits are pears and all pears are beans).
II. Some vegetables are pears → True (As all pears are beans and all beans are vegetables so all pears are vegetables, hence some vegetables are pears).
Hence, both conclusions I and II follow.
34. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding the commonly known facts.
Statement:
All Lions are Tigers.
No Tigers are Wolf.
Some Wolf are Humans.
Conclusions:
I. No Lions are Wolf.
II. Some Humans can be Lions.
A. Only conclusion I follow
B. Only conclusion II follow
C. Either conclusion I or II follows
D. Neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. Both conclusions I and II follow
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram;

Conclusions:
I. No Lions are Wolf → True (because All Lions are Tigers, No Tigers are Wolf and Some Wolf are Humans.)
II. Some Humans can be Lions → True (As no direct relationship between humans and lions is given, all types of possibilities are true.)
Hence, Both conclusions I and II follow.
Directions:- Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
There are 6 points which are at a distance of each other in different directions. Point A is 5m South of B. point C is 10m west of A. D is 15m north of C. E is 15m east of D. F is 10m south of E.
35. What is the direction of E with respect to B?
A. East
B. North – west
C. North – East
D. South – West
E. South – East
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question:-
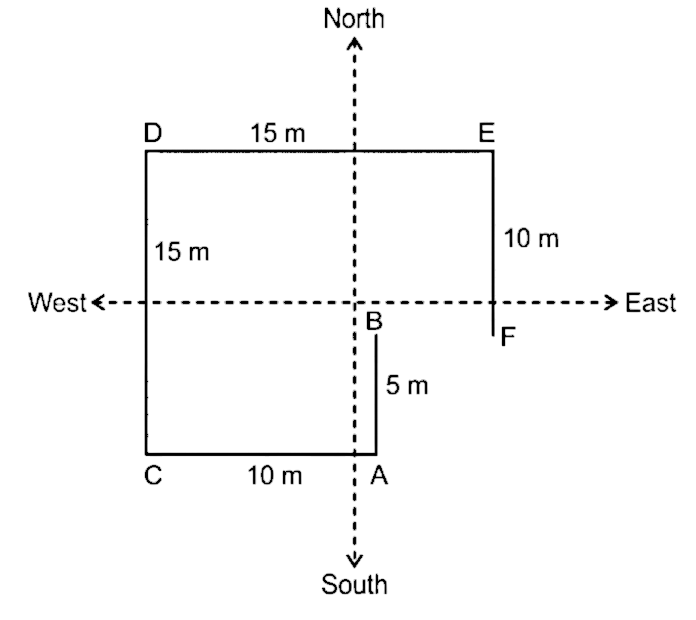
we can clearly see that point E is in North – East Direction from Point B.
Hence, E is in North – East direction from B.
36. What is the distance between Point F and point B?
A. 10m
B. 5m
C. 15m
D. 20m
E. 7m
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question:-

No we have to Find the Distance between F and B.
Distance between point D and point E = 15m
Distance between point C and point A = 10m
Distance between point B and point F = 15m – 10m = 5m
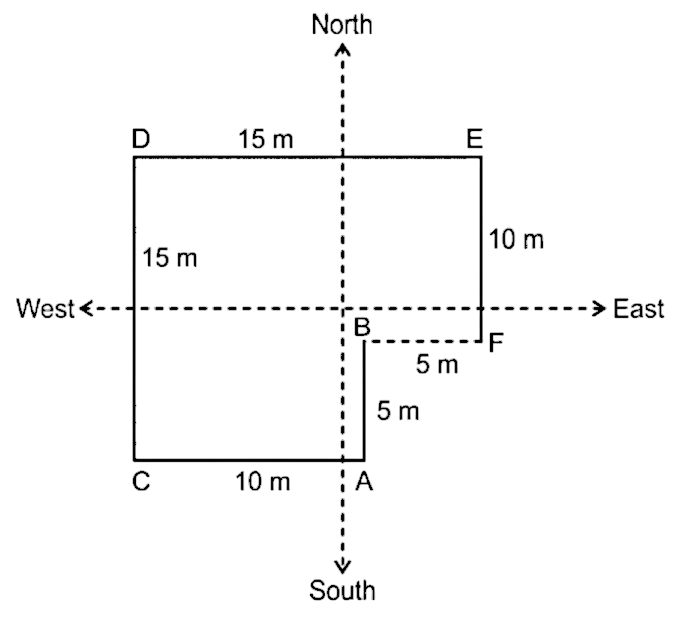
Hence, the distance between Point B and Point F is 5m.
37. If Point F is moving towards South Direction till point G so that Point G is in East direction of Point A then what is the distance between Point G and Point C?
A. 10m
B. 20m
C. 5m
D. 15m
E. 25m
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the Question:-

If Point F is Moving towards South Direction till point G then the Diagram Should look Like given below:-
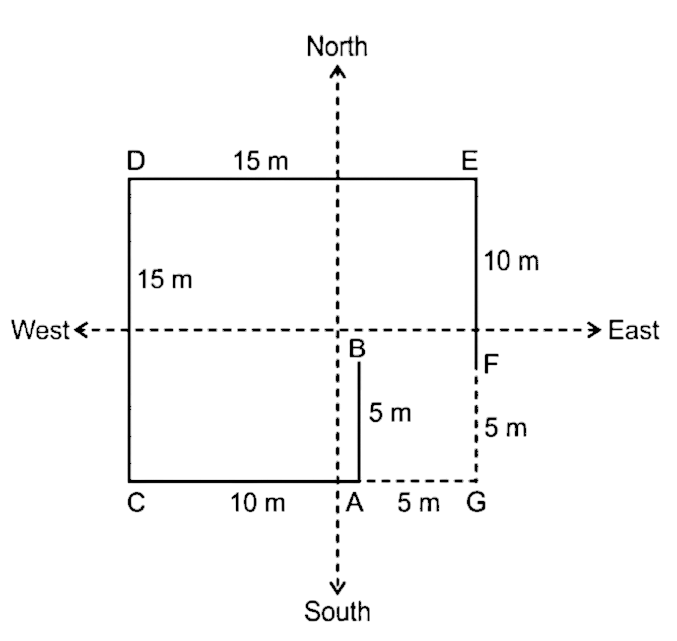
Now we can Clearly see that the Distance between Point C and point G is 15 m.
Hence, the correct answer is 15m.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.Eight people P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W are seated around a circular table facing the center but not necessarily in the same order. P is second to the right of R, who is the neighbor of W, and V. Q is the neighbor of T. W is not the neighbor of P and U. Q is third to the right of U.
38. Who is sitting third to the left of W?
A. S
B. P
C. U
D. Q
E. R
Solution
1) P is second to the right of R, who is the neighbor of W and V.
2) W is not the neighbor of P and U.
3) Q is the neighbor of T.
4) Q is third to the right of U.
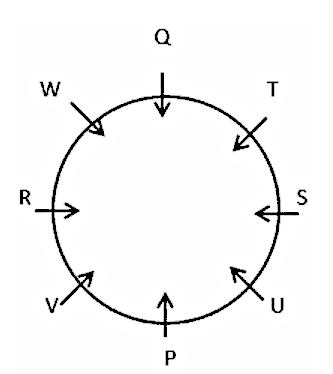
Hence, S is sitting third to the left of W.
39. What is the position of U?
A. immediate left of P
B. immediate right of S
C. immediate left of S
D. third to the left of P
E. None of the above
Solution
1) P is second to the right of R, who is the neighbor of W and V.
2) W is not the neighbor of P and U.

3) Q is the neighbor of T.
4) Q is third to the right of U.

Hence, U is immediate left of S.
40. Who are the immediate neighbors of P?
A. V and R
B. Q and S
C. U and V
D. U and S
E. V and S
Solution
1) P is second to the right of R, who is the neighbor of W and V.
2) W is not the neighbor of P and U.

3) Q is the neighbor of T.
4) Q is third to the right of U.

Hence, U and V are immediate neighbors of P.
Numerical Ability
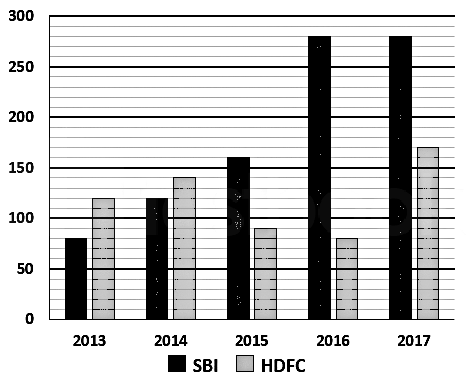
The bar chart given below shows the number of students who were chosen for two different internships, SBI and HDFC Assistant over the years per every 1000 students who appeared in these interviews.
41. If 5 thousand students appeared in 2015, how many more people were selected in SBI over HDFC?
A. 350
B. 325
C. 315
D. 300
E. 425
Solution
Given:
| Year | Number of Student selected in SBI(Per 1000) | Number of Student selected in HDFC(Per 1000) |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 80 | 120 |
| 2014 | 120 | 140 |
| 2015 | 160 | 90 |
| 2016 | 280 | 80 |
| 2017 | 280 | 170 |
Calculation:
Number of student selected for SBI = (5000 × 160)/1000
⇒Number of student selected for SBI = 800
Number of students selected for HDFC = (5000 × 90)/1000
⇒Number of students selected for HDFC = 450
∴Difference = 800 – 450 = 350
∴350 more students were selected in SBI over HDFC
Hint
Values mentioned in bar chart are in the scale 1000 students. Think of it as percentage and solve the question
The bar chart given below shows the number of students who were chosen for two different internships, SBI and HDFC Assistant over the years per every 1000 students who appeared in these interviews.

42. If 4 thousand students appeared in 2013, how many less percentage student were selected in SBI over HDFC
A. 25%
B. 35%
C. 45%
D. 60%
E. 33.33%
Solution
Given:
| Year | Number of Student selected in SBI(Per 1000) | Number of Student selected in HDFC(Per 1000) |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 80 | 120 |
| 2014 | 120 | 140 |
| 2015 | 160 | 90 |
| 2016 | 280 | 80 |
| 2017 | 150 | 170 |
Calculation:
Number of student selected for SBI = (4000 × 80)/1000
⇒Number of student selected for SBI = 320
Number of students selected for HDFC = (4000 × 120)/1000
⇒Number of students selected for HDFC= 480
Difference in percentage = (480 – 320) × 100/320
⇒ % difference = (160/480) × 100
⇒ % difference = 33.33%
∴ 33.33% less student were selected in SBI over HDFC
The bar chart given below shows the number of students who were chosen for two different internships, SBI and HDFC Assistant over the years per every 1000 students who appeared in these interviews.

43. If in SBI same number of students appeared in 2015 and 2016, how many percentage more students were selected in 2016 than in 2015 in SBI?
A. 55
B. 60
C. 65
D. 70
E. 75
Solution
Given:
| Year | Number of Student selected in SBI(Per 1000) | Number of Student selected in HDFC(Per 1000) |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 80 | 120 |
| 2014 | 120 | 140 |
| 2015 | 160 | 90 |
| 2016 | 280 | 80 |
| 2017 | 280 | 170 |
Calculations:
Difference in percentage = (280 – 160) × 100/160
⇒Difference in percentage= 12000/160
⇒Difference in percentage= 75%
∴ 75 percentage more students were selected in 2016 than in 2015
The bar chart given below shows the number of students who were chosen for two different internships, SBI and HDFC Assistant over the years per every 1000 students who appeared in these interviews.

44. What would be the ratio of students who got selected in SBI if 2000 students appeared in 2015 and 3000 students applied in 2017?
A. 16: 25
B. 16: 45
C. 8: 21
D. 45: 32
E. 4: 25
Solution
Given:
| Year | Number of Student selected in SBI(Per 1000) | Number of Student selected in HDFC(Per 1000) |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 80 | 120 |
| 2014 | 120 | 140 |
| 2015 | 160 | 90 |
| 2016 | 280 | 80 |
| 2017 | 280 | 170 |
Calculations:
Number of student selected for SBI in 2015 = (2000 × 160)/1000
⇒Number of student selected for SBI in 2015= 320
Number of students selected for SBI in 2017 = (3000 × 280)/1000
⇒Number of students selected for SBI in 2017 = 840
∴Required Ratio = 320: 840
⇒Required Ratio = 8: 21
∴ the ratio of students who got selected in SBI if 2000 students appeared in 2015 and 3000 students appeared in 2017 is 8: 21
Hint
Required Ratio = Number of student selected for SBI in 2015: Number of students selected for SBI in 2017
The bar chart given below shows the number of students who were chosen for two different internships, SBI and HDFC Assistant over the years per every 1000 students who appeared in these interviews.

45. If the total numbers of students appeared for SBI in 2016 was 1.5 lakhs then how many of them had cleared the SBI in 2016?
A. 32000
B. 35000
C. 40000
D. 42000
E. 50000
Solution
Given:
| Year | Number of Student selected in SBI(Per 1000) | Number of Student selected in HDFC(Per 1000) |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 80 | 120 |
| 2014 | 120 | 140 |
| 2015 | 160 | 90 |
| 2016 | 280 | 80 |
| 2017 | 280 | 170 |
Calculations:
The total number of students out of 1.5 lakhs who were selected in SBI = (280 × 150000/1000) = 42000
∴Number of students for SBI is 42000
Hint
The data mentioned in graph is per 1000 person hence, treat the values as percentage and find the answer
46. The ratio between compound interest and simple interest is 5 : 4 for 2 years. Find the difference between compound interest and simple interest for 2 years. if one-year simple interest is 200.
A. 200
B. 100
C. 400
D. 500
E. None
Solution
Calculation:
Simple interest for 2 years = 4x
Simple interest for 1 year = 2x = 200
⇒ x = 100
Difference between compound interest and simple interest = 5x – 4x = x
⇒ x = 100
∴ The required result will be 100.
47. Time ratio for upstream to downstream distance is 5 ∶ 3. Downstream speed is 15 km/hr, find the time to travel a distance of 31.5 km in upstream (in hour).
A. 2
B. 2.5
C. 3
D. 4
E. none of these
Solution
Given:-
Time ratio = 5 ∶ 3
Downstream speed, D = 15 km/hr
Formula:-
Speed = Distance/Time
Downstream speed (D) = u + v
Upstream speed (U) = u – v
u and v are speed of boat and stream speed respectively
Calculation:-
Speed ratio = 1/time ratio = 3/5
3/5 = U/15
U = 9
Time = 31.5/9 = 3.5 hours.
Alternate Method
Calculation:
Time ratio of upstream and downstream = 5 : 3
Speed is inversely proportional to time.
Then, Speed Ratio of upstream and downstream = 3 : 5
Let the speed ratio of upstream and downstream be = 3x : 5x
According to the question,
Downstream speed = 5x = 15km/h
⇒ x = 15/5 = 3 km/h
So, upstream speed = (3x) = 3 × 3 = 9 km/h
∴ Time required by upstream = 31.5 / 9 = 3.5 h
48. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 4x – 77 = 0
II. y2 + 23y + 132 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≤ y
D. x ≥ y
E. x = y or the relation between x and y can’t be established.
Solution
Given:
I. x2 – 4x – 77 = 0
II. y2 + 23y + 132 = 0
Calculation:
I. x2 – 4x – 77 = 0
⇒ x2 + 7x – 11x – 77 = 0
⇒ x(x + 7) – 11(x + 7) = 0
⇒ (x – 11)(x + 7) = 0
⇒ x = (-7), 11
II. y2 + 23y + 132 = 0
⇒ y2 + 12y + 11x + 132 = 0
⇒ y(y + 12) + 11(y + 12) = 0
⇒ y = (-12), (-11)
| Value of ‘x’ | Relation | Value of ‘y’ |
| -7 | > | -12 |
| -7 | > | -11 |
| 11 | > | -12 |
| 11 | > | -11 |
When we compared the values of ‘x’ and ‘y’ in the table above, we found that there is ONE relation between X and Y i.e. >. So, a relation between x and y is x > y.
∴ After comparison, all the values of x and y the relation is x > y.
49. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 11x + 28 = 0
II. y2 + 13y + 36 = 0
A. x > y
B. x ≥ y
C. x < y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established
Solution
Calculation:
I. x2 – 11x + 28 = 0
⇒ x2 – 7x – 4x + 28 = 0
⇒ x(x – 7) – 4(x – 7) = 0
⇒ (x – 7) (x – 4) = 0
⇒ x = 7, 4
II. y2 + 13y + 36 = 0
⇒ y2 + 9y + 4y + 36 = 0
⇒ y(y + 9) + 4(y + 9) = 0
⇒ (y + 9) (y + 4) = 0
⇒ y = –9, –4
Comparison between x and y (via tabulation):
| X | Y | Relation |
| 7 | –9 | x > y |
| 7 | –4 | x > y |
| 4 | –9 | x > y |
| 4 | –4 | x > y |
∴ x > y
50. In the following question two equations are given. You have to solve the equations and mark the answer accordingly
l. x2 – 24x + 119 = 0
ll. y2 – 34y + 253 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between them cannot be determined
Solution
Calculation:
From l.
x2 – 24x + 119 = 0
⇒ x2 – 17x – 7x + 119 = 0
⇒ x (x – 17) – 7 (x – 17) = 0
⇒ (x – 7) (x – 17) = 0
⇒ x = 7, 17
From ll.
y2 – 34y + 253 = 0
⇒ y2 – 23y – 11y + 253 = 0
⇒ y (y – 23) – 11 (y – 23) = 0
⇒ (y – 23) (y – 11) = 0
⇒ y = 23, 11
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation between x and y |
| 7 | 23 | x < y |
| 7 | 11 | x < y |
| 17 | 23 | x < y |
| 17 | 11 | x > y |
∴ The relation between x and y cannot determined.
51. In the given question, two questions numbered I and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 3x2 – 4x – 32 = 0
II. 9y2 – 29y + 22 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
Solution
Given:
I. 3×2 – 4x – 32 = 0
II. 9y2 – 29y + 22 = 0
Calculation:
From I,
3×2 – 4x – 32 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 12x + 8x – 32 = 0
⇒ 3x(x – 4) + 8(x – 4) = 0
⇒ (x – 4)(3x + 8) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (x – 4) = 0 or (3x + 8) = 0
⇒ x = 4 or (-8/3)
From II,
9y2 – 29y + 22 = 0
⇒ 9y2 – 18y – 11y + 22 = 0
⇒ 9y(y – 2) – 11(y – 2) = 0
⇒ (y – 2)(9y – 11) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (y – 2) = 0 or (9y – 11) = 0
⇒ y = 2 or (11/9)
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 4 | 2 | x > y |
| 4 | 11/9 | x > y |
| -8/3 | 2 | x < y |
| -8/3 | 11/9 | x < y |
∴ x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
52. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 7x2 + 12x + 5 = 0
II. 3y2 + 7y + 2 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established
Solution
I. 7×2 + 12x + 5 = 0
⇒ 7×2 + 7x + 5x + 5 = 0
⇒ 7x(x + 1) + 5(x + 1) = 0
⇒ (x + 1)(7x + 5) = 0
⇒ x = -1 or -(5/7)
II. 3y2 + 7y + 2 = 0
⇒ 3y2 + 6y + y + 2 = 0
⇒ 3y(y + 2) + 1(y + 2) = 0
⇒ (y + 2)(3y + 1) = 0
⇒ y = -2 or −13−13
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| -1 | -2 | x > y |
| -1 | -1/3 | x < y |
| -5/7 | -2 | x > y |
| -5/7 | -1/3 | x < y |
x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established
53. A can fill the tank in 15 hours and B can fill the tank in 60 hours in how many hours both can fill half of the tank when they work alternatively starting from A.
A. 10
B. 12
C. 15
D. 20
E. None
Solution
Given:
A can fill the tank in = 15 hours
B can fill the tank in = 60 hours
Calculation:
The efficiency of A is = 1/15
The efficiency of B is = 1/60
A and B can fill tank in 2 hours is = 1/15 + 1/60 = 1/12 part of tank
To half fill the tank,
In 12 hours tank will filled is = 6 × (1/12) = 1/2 part of tank
Then the tank will be 1/2 filled in 12 hours
∴ The tank will be 1/2 filled in 12 hours.
54. A is 5 years younger than B; and 3 years ago, the ratio of the ages of A and B was 5 : 6. Find the total of their present ages.
A. 80
B. 75
C. 55
D. 86
E. 61
Solution
Calculation:
Let A’s present age = x
So, B’s present age = x + 5
According the question,
(x – 3)/(x + 5 – 3) = 5/6
(x – 3)/(x + 2) = 5/6
6(x – 3) = 5(x + 2)
⇒ 6x – 18 = 5x + 10
⇒ 6x – 5x = 18 + 10
⇒ x = 28
Hence, A’s present age = 28 years
Also, B’s present age = 28 + 5 = 33 years
∴ The total of their present ages = 28 + 33 = 61 years
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
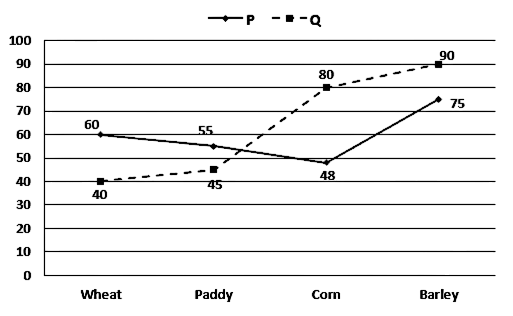
The given line graph shows the per Kg selling price of four different grains of two shops P and Q.
55. Find the sum of per Kg cost price of Wheat of shop P and Q together, if shop P sells per kg wheat at 20% profit and shop Q sells per kg of wheat at 60% profit.
A. 75
B. 80
C. 66
D. 45
E. 50
Solution
Cost price of wheat of shop P = 60 × 100/120 = 50
Cost price of wheat of shop Q = 40 × 100/160 = 25
Total cost price of shop P and Q = 75
Hence, correct answer is option 1.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
The given line graph shows the per Kg selling price of four different grains of two shops P and Q.

56. Selling price of paddy of shop P is what percent of Selling price per kg of paddy of shop Q.
A. 1000/3%
B. 1100/3%
C. 1000/7%
D. 1100/9%
E. 1000/9%
Solution
Required Percentage = 55/45 × 100 = 11/9 × 100 = 1100/9%
Hence, correct answer is option 4.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
The given line graph shows the per Kg selling price of four different grains of two shops P and Q.

57. Find the ratio of average of sp per kg of paddy, barley and corn of shop P to sp per kg of barley of shop P?
A. 111/335
B. 178/225
C. 188/221
D. 167/177
E. 153/189
Solution
Required Average = (55 + 75 + 48)/3 = 178/3
Required ratio = 178/3 × 75 = 178/225
Hence, correct answer is option 2.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
The given line graph shows the per Kg selling price of four different grains of two shops P and Q.

58. Find the sp per kg of wheat of shop R, if the ratio of sp per kg of paddy of shop R to sp per kg of barley of shop P is 24:25. SP per kg of wheat of shop R is 33.33% more than the sp per kg of paddy of shop R.
A. 88
B. 75
C. 96
D. 80
E. 90
Solution
SP per kg of paddy of shop R = 75/25 × 24 = 72
SP per kg of wheat of shop R = 72 × 1/3 + 72 = 96
Hence, correct answer is option 3.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer based on it.
The given line graph shows the per Kg selling price of four different grains of two shops P and Q.

59.Find the cost price of corn of shop Q. If marked price of corn per kg shop Q is 20% above the cost price. Seller Q gives 20% discount of corn per kg.
A. 55
B. 83.33
C. 48
D. 28.55
E. 50
Solution
Mark price of corn per kg of shop Q = 80 × 100/80 = 100
Cost price of corn per kg of shop Q = 100 × 100/120 = 83.33
Hence, correct answer is option 2.
60. The weights of Zinc, Copper, and Iron in an alloy are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 4. In the alloy weighing 72 kg the difference between the weights of Iron and Zinc is ?
A. 4 kg
B. 5 kg
C. 6 kg
D. 7 kg
E. 8 kg
Solution
Given:
Zinc : Copper : Iron = 3 : 5 : 4
Weight of alloy = 72 kg
Calculation:
Total weight = 3 + 5 + 4 = 12 ratio
so, 12 ratio = 72 kg
1 ratio = 6 kg
Difference in weight = 4 – 3 = 1 ratio = 6 kg
∴ The difference is 6 kg
61. A man goes to his office at 5/6 of his original speed and gets late by 2 hrs. Find the speed (in m/s) when he covered 150 km in usual time to reach the office?
A. 15 m/s
B. 18 m/s
C. 50/8 m/s
D. 75/4 m/s
E. 75/18 m/s
Solution
Given:
Let the actual speed be 5x and usual speed 6x
Reach the office late by 2 hrs
Formula:
Distance = Speed × time
Time = Distance/speed
Calculation:
In 1st condition, distance is same
Let the usual time be t
⇒ 6x × t = 5x × (t + 2)
⇒ t = 10 hrs
His usual time to reach the office = 10 hrs
Speed to cover the distance 150 km in 10 hrs
⇒ Speed = 150/10 = 15 km/hr
⇒ 15 km/hr = 15 × (5/18) = 75/18 m/s
∴ Speed when he covered 150 km in usual time used to reach the office = 75/18 m/s
Alternate Method
Actual Speed : Usual Speed = 5 : 6
Time = 6 : 5
As speed is inversely proportional to time when distance is same
According to question
⇒ 1x = 2
⇒ 5x = 10 hrs
Speed when he cover 150 km in usual time used to reach the office = 150/10
⇒ Speed = 15 km
⇒ 15 km/hr = 15 × (5/18) m/s = 75/18 m/s
∴ Speed when he covered 150 km in usual time used to reach the office = 75/18 m/s
62. The sum of the radius and height of a cylinder is 21 cm. The total surface area of the cylinder is 1188 sq.cm. What is the volume of the cylinder?
A. 902π cu.cm
B. 928π cu.cm
C. 943π cu.cm
D. 972π cu.cm
E. 875π cu.cm
Solution
Given:
r + h = 21 cm
T.S.A = 1188 sq.cm
Formula used:
T.S.A of cylinder = 2πr(h + r)
Volume of cylinder = πr2h
Calculation:
r + h = 21
2πr(r + h) = 1188
⇒ 2 × 22/7 × r × 21 = 1188
⇒ r = 1188/(2 × 22 × 3) = 9 cm
so, h= 21 – 9 = 12 cm
∴ Volume = π × 9 × 9 × 12 = 972π cu.cm
∴ The volume is 972π cu.cm
63. What approximate value will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
[(24.94)2 + 13.97% of 600.11 = (?)3 – 20
A. 9
B. 3
C. 27
D. 81
E. None of these
Solution
Solution:
Rules of Approximation:
1. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal less than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal. The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
2. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal more than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal and raise the remaining number by ‘1’.The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
(25)2 + 14% of 600 = (?)3 – 20
⇒ 625 + 14% of 600 = (?)3 – 20
⇒ 625 + 84 = (?)3 – 20
⇒ 625 + 84 + 20 = (?)3
⇒ (?)3 = 729
∴ ? = 9
64. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
24.99 × 3.01 + 72.1 ÷ 7.99 – 6.9 = ?
A. 77
B. 74
C. 82
D. 70
E. 79
Solution
Rules of Approximation:
1. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal less than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal. The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
2. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal more than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal and raise the remaining number by ‘1’.The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
Concept:
In this type of question, we are expected to calculate the approximate value (not the exact value), so we can replace the given numbers by their nearest perfect places which makes the calculation easy.
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculations:
24.99 × 3.01 + 72.1 ÷ 7.99 – 6.9 = ?
Taking approximate value, we get
25 × 3 + 72 ÷ 8 – 7 = ?
⇒ 75 + 9 – 7 = ?
⇒ ? = 77
∴ The value of ? is 77.
65. What approximate value will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
99.97 ÷ 4.95 + (34.21 + √24.84) = ?
A. 65
B. 75
C. 53
D. 59
E. None of these
Solution
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below:

Calculation:
99.97 ÷ 4.95 + (34.21 + √24.84) = ?
On taking the approximate values, we get:
⇒ 100 ÷ 5 + (34 + √25) = ?
⇒ 20 + (34 + 5) = ?
⇒ 20 + 39 = ?
⇒ ? = 59
∴ The value of ? is 59
66. What approximate value will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
(15 × 4.012) ÷ 11.94 + 24.92 × 4 = ?
A. 120
B. 130
C. 125
D. 105
E. None
Solution
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below:

Calculation:
(15 × 4.012) ÷ 11.94 + 24.92 × 4 = ?
On taking the approximate values, we get:
⇒ (15 × 4) ÷ 12 + 25 × 4 = ?
⇒ 60 ÷ 12 + 25 × 4 = ?
⇒ 5 + 25 × 4 = ?
⇒ 5 + 100 = ?
⇒ ? = 105
∴ The value of ? is 105
67. What approximate value will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
16.96 + 29.89 + 150 = ? – 7.98
A. 195
B. 215
C. 200
D. 205
E. None
Solution
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below:

Calculation:
16.96 + 29.89 + 150 = ? – 7.98
On taking the approximate values, we get:
⇒ 17 + 30 + 150 = ? – 8
⇒ 197 = ? – 8
⇒ ? = 197 + 8 = 205
∴ The value of ? is 205
68. What approximate value should come in place of ‘?’ in the following equation:
[(33.01)2 + 30.98] ÷ 7.96 = (?)2 – (2)2
A. 11
B. 13
C. 14
D. 12
E. None of these
Solution
Solution:
Rules of Approximation:
1. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal less than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal. The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
2. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal more than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal and raise the remaining number by ‘1’.The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
[(33)2 + 31] ÷ 8 = (?)2 – (2)2
⇒ [1089 + 31] ÷ 8 = (?)2 – 4
⇒ 1120 ÷ 8 = (?)2 – 4
⇒ 140 = (?)2 – 4
⇒ (?)2 = 140 + 4
⇒ (?)2 = 144
∴ ? = 12
69. What approximate will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?16.8975 × 14.789 + 8.89 × 5 = ?2 – 100
A. 25
B. 15
C. 41
D. 29
E. 20
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step-1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step-2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step-3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step-4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
CALCULATION:
17 × 15 + 9 × 5 = ?2 – 100
⇒ 255 + 45 = ?2 – 100
⇒ 300 = ?2 – 100
⇒ 300 + 100 = ?2
⇒ 400 = ?2
∴ ? = 20
70. What is the average of 10 numbers where first number is five and following number is 3 more than the preceding number?
A. 17.2
B. 16.8
C. 16.5
D. 18.5
E. 20.5
Solution
First number = 5
Each number is 3 more than the preceding number
∴ Numbers are = 5, 8, 11 ,14, 17, 20, 23, 26, 29, 32
∴ Sum of n terms (Sn) = n/2[2a + (n– 1)d]
where, n → Number of term
a → First term
d → Difference between the terms
⇒ Sum of the 10 numbers (S10) = 10/2[2 × 5 + (10 – 1)3]
⇒ S10 = 5 (10 + 27) = 185
∴ Average of this numbers = 185/10 = 18.5
Alternate Method
Average of number = (First term + Last term)/2
⇒ Average = (5 + 32)/2 = 18.5
71. A shopkeeper has 1400 kg of wheat, one type of wheat he sells at 28% profit and the other type he sells at 35% profit. In the whole transaction, he gains 30%. Find the quantity sold at 28% profit?
A. 1000
B. 400
C. 700
D. 600
E. 800
Solution
Given:
The total quantity of wheat = 1400 kg
Profit percentage after selling one type = 28%
Profit percentage after selling second type = 35%
Profit percentage on the whole transaction = 30%
Calculation:
Let x be the first type of wheat
Let (1400 – x) be the second type of wheat
(28/100)x + (35/100) × (1400 – x) = (30/100) × 1400
⇒ (28/100)x + (35/100) × 1400 – (35/100)x = 420
⇒ (7/100)x = 490 – 420
⇒ x = (70 × 100)/7 = 1000
∴ The quantity sold at 28% is 1000 kg.
Alternate Method

⇒ The total quantity of wheat in terms of ratio = 5 + 2 = 7
⇒ 7 → 1400
⇒ 5 → (1400/7) × 5 = 1000
∴ The quantity sold at 28% is 1000 kg.
72. If three unbiased coins are to be tossed simultaneously what are the chances of getting atleast one Head.
A. 5/8
B. 1/2
C. 7/8
D. 4/5
E. 3/8
Solution
Given
Three coins are tossed simultaneously.
Concept used
P(E) = Favourable outcomes/ Total outcomes
Calculation
Sample space = {HHH, HHT ,HTH, THH, TTT, TTH, THT, HTT}
n(sample space) = 8
Atleast one head = {HHH, HHT, HTH, THH, TTH, THT, HTT}
n(Atleast one head) = 7
P( Atleast one head) = 7/8
∴ 7/8 is the required probability
Study the following Pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
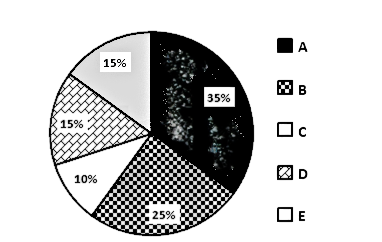
Pie-chart given below shows investment (in terms of percentage) out of the total investment of five different persons.
Total Investment = Rs.1,50,000
73. If B and E started a business together. B left the business 9 months after starting of business but E continued for the entire year. Find the difference profits shares of B and E. If their total profit at the end of the year is Rs 18000?
A. Rs 1200
B. Rs 1800
C. Rs 1500
D. Rs 2000
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Investment of B = 25% of 150000
Investment of E = 15% of 150000
Time period of B = 9 months
Time period of E = 12 months
Formula used:
Profit = Investment × time
Calculation:
Investment ratio of B and E is = 25% of 150000 : 15% of 150000 = 5 : 3
Time period ratio of B and E = 9 : 12 = 3 : 4
Profit ratio of B and E = 5 × 3 : 3 × 4 = 5 : 4
Then 9x = 18000
⇒ x = 18000/9 = 2000
So, Difference in B and E = 5x – 4x = x = Rs 2000
∴ The required answer is Rs 2000
Study the following Pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
Pie-chart given below shows investment (in terms of percentage) out of the total investment of five different persons.
Total Investment = Rs.1,50,000

74. By what percent is the average investment of A, B and E together more or less than investment of C and D together?
A. 100%
B. 75%
C. 50%
D. 25%
E. 0%
Solution
Given:
Investment of A = 35% of 150000 = Rs 52500
Investment of B = 25% of 150000 = Rs 37500
nvestment of C = 10% of 150000 = Rs 15000
Investment of D = 15% of 150000 = Rs 22500
Investment of E = 15% of 150000 = Rs 22500
Formula used:
Average = Sum of observations/Number of observations
Calculation:
Sum of investment of A,B and E is = 52500 + 37500 + 22500 = 112500
Required Average = 112500/3 = 37500
Sum of investment of C and D together = 15000 + 22500 = 37500
Required percentage = (Average of A, B and E – Sum of C and D) × 100 /(Sum of C and D) = (37500 – 37500) × 100 / 37500
Required percentage = 0%
∴ The two quantities are the same, or we can say, there is 0% increase or decrease in quantities compared.
Investment of C and D is asked in the question and not their average. If the question is not read carefully, you might take the average of C and D which will result in the required percentage to be 50%, which is wrong.
Study the following Pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
Pie-chart given below shows investment (in terms of percentage) out of the total investment of five different persons.
Total Investment = Rs.1,50,000

75. A, C and F started a business together. F invested Rs 3000 more than the amount invested by C. F left the business after 8 months of starting of business. After 2 more months C left the business. If the total profit at the end of the year is Rs 15400. The share of F is?
A. Rs 2400
B. Rs 2500
C. Rs 3600
D. Rs 4500
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Investment of A = 35% of 150000 = Rs 52500
Investment of C = 10% of 150000 = Rs 15000
Investment of F = 15000+3000 = Rs 18000
Time period of A =12 months
Time period of C = 10 months
Time period of F = 8 months
Formula used:
Profit = Investment × time
Calculation:
Investment ratio of A,C and F = 52500 : 15000 : 18000 = 35 : 10 : 12
Time period ratio of A,C and F = 12 : 10 : 8 = 6 : 5 : 4
Profit ratio of A,C and F = 35 × 6 : 10 × 5: 12 × 4 = 105 : 25 : 24
Then 154x = 15400
⇒ x =15400/154 = 100
Then the share of F = 100 × 24 = Rs 2400
∴ The required answer is Rs 2400
Study the following Pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
Pie-chart given below shows investment (in terms of percentage) out of the total investment of five different persons.
Total Investment = Rs.1,50,000

76. If B invests two times its given investment, then the investment of D and E together makes what per cent of B’s investment?
A. 150/3%
B. 650/3%
C. 60%
D. 200/3%
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Investment of B = 25% of 150000 = Rs 37500
Investment of D = 15% of 150000 = Rs 22500
Investment of E = 15% of 150000 = Rs 22500
Formula used:
Percentage = B investment/(D + E investment)
Calculation:
New investment of B = 2 × 37500 = 75000
Sum of Investment of D and E together = 22500 + 22500 = Rs 45000
Required % = (45000/75000) × 100 = 60%
∴ The required answer is 60%
Study the following Pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
Pie-chart given below shows investment (in terms of percentage) out of the total investment of five different persons.
Total Investment = Rs.1,50,000

77. What is the ratio of A and C investment together to B and D investment together is?
A. 10 : 11
B. 11 : 10
C. 8 : 9
D. 9 : 8
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Investment of A = 35% of 150000 = Rs 52500
Investment of C = 10% of 150000 = Rs 15000
Investment of B = 25% of 150000 = Rs 37500
Investment of D = 15% of 150000 = Rs 22500
Formula used:
Required ratio = Sum of Investment of A and C : Sum of Investment of B and D
Calculation:
Sum of Investment of A and C together= 52500 + 15000 = Rs 67500
Sum of Investment of B and D together= 37500 + 22500 = Rs 60000
Required ratio = 67500 : 60000 = 9 : 8
.∴ The required answer is 9 : 8
78. P, Q and R are engaged to do a project and earn Rs. 1600. P and R completes (15/16)th of a work together. Find the amount that will be paid to Q.
A. Rs. 1400
B. Rs. 1200
C. Rs. 500
D. Rs. 100
E. Rs. 600
Solution
Given:
Earning of P, Q and R = Rs. 1600
P and R completes (15/16)th of the work.
Calculation:
⇒ Remaining work is done by Q = (1/16)th of the work
⇒ Amount paid to Q = (1/16) × 1600
⇒ Rs.100
∴ Required amount that will be paid to Q = Rs.100
79. A dishonest shopkeeper uses false weights while buying and selling goods and cheats 20% each on selling and buying. What is his total gain percent?
A. 50%
B. 40%
C. 35%
D. 44%
E. 20%
Solution
Given:
Cheats while buying = 20%
Cheats while selling = 20%
Formula used:
Profit = total selling price – total cost price
Calculation:
Let the shopkeeper buy 500 gm goods.
Now, he uses false weights and cheats 20% on buying
So, his actual purchase = 500 – [500 × (20/100)] = 400 gm
Now, he uses false weights and cheats 20% on selling
So, his actual sale = 500 + [500 × (20/100)] = 600 gm
Gain = 600 – 400 = 200 gm
So, gain percent = (200/400) × 100 = 50%
∴ His total gain is 50%.
80. A’s income is 20000 less than B’s income. If both of them spend 4/5 of their incomes, then find B’s income. The total savings of A and B is Rs. 26000.
A. Rs. 55000
B. Rs. 70000
C. Rs. 65000
D. Rs. 75000
E. Rs. 50,000
Solution
Given:
A’s income = B’s income – 20000
Expenses = 4/5th of income
(A + B)’s savings = Rs. 26000
Calculation:
Let B’s income be Rs. x
∴ A’s income = x – 20000
A.T.Q
1/5 of x + 1/5 of (x – 20000) = 26000
⇒ x + x – 20000 = 130000
⇒ x = Rs. 75000
∴ The answer is Rs. 75000
