Direction: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions.
There are eight persons namely M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, and T living in a building with four floors. Ground floor is numbered as 1 while top floor is numbered as 4. Each floor has two flats such Flat 1 and Flat 2. Flat 1 of all floors stays vertically in the same line and Flat 2 of all floors stays vertically in the same line. Flat 2 of all floors stays east to the flat 1 of all respective floors.
M lives on a Flat 2 of an odd floor. Only one floor lies between M and Q. Q lives east of N. There is one floor between lives between Q and O. R and T lives in a same floor. P lives immediately above N. T lives immediately below Q.
1.Who among the following lives on third floor?
A. S, T
B. Q, P
C. M, N
D. N, Q
E. None of the above
Solution
Person: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, and T
Floor: 1, 2, 3, 4.
1. M lives on a Flat 2 of an odd floor.
2. Only one floor lies between M and Q.
3. Q lives east of N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | M | N | Q | |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | M | |
4. There is one floor between lives between Q and O.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
5. P lives immediately above N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | |||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | |||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
6. R and T lives in a same floor.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | R/T | R/T | P | S |
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | S | R/T | R/T |
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
7. T lives immediately below Q.
| Case 2 | ||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | S |
| 3 | N | Q |
| 2 | R | T |
| 1 | O | M |
Here, N and Q lives on third floor
Hence, the answer is N, Q.
2. How many lives exactly above R?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
E. None of the above
Solution
Person: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, and T
Floor: 1, 2, 3, 4.
1. M lives on a Flat 2 of an odd floor.
2. Only one floor lies between M and Q.
3. Q lives east of N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | M | N | Q | |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | M | |
4. There is one floor between lives between Q and O.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
5. P lives immediately above N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | |||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | |||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
6. R and T lives in a same floor.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | R/T | R/T | P | S |
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | S | R/T | R/T |
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
7. T lives immediately below Q.
| Case 2 | ||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | S |
| 3 | N | Q |
| 2 | R | T |
| 1 | O | M |
Here four persons lives above R but Exactly only 2 persons are living above R. (exactly above R means Living vertically above R which same numbered flat in different floors)
Hence, the answer is Two.
3. Which is the following floor and flat M lives ?
A. Ground floor second flat
B. Ground floor first flat
C. Second floor second flat
D. Third floor First flat
E. None of the above
Solution
Person: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, and T
Floor: 1, 2, 3, 4.
1. M lives on a Flat 2 of an odd floor.
2. Only one floor lies between M and Q.
3. Q lives east of N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | M | N | Q | |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | M | |
4. There is one floor between lives between Q and O.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
5. P lives immediately above N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | |||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | |||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
6. R and T lives in a same floor.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | R/T | R/T | P | S |
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | S | R/T | R/T |
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
7. T lives immediately below Q.
| Case 2 | ||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | S |
| 3 | N | Q |
| 2 | R | T |
| 1 | O | M |
Here M lives in Ground floor and In ground floor M lives in Second flat
Hence, the answer is Ground floor second flat.
4. Four of the following five pair are similar in a certain way in the group, find the one that does not belong to the group?
A. M, O
B. T, R
C. N, Q
D. O, T
E. S, P
Solution
Person: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, and T
Floor: 1, 2, 3, 4.
1. M lives on a Flat 2 of an odd floor.
2. Only one floor lies between M and Q.
3. Q lives east of N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | M | N | Q | |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | M | |
4. There is one floor between lives between Q and O.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
5. P lives immediately above N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | |||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | |||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
6. R and T lives in a same floor.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | R/T | R/T | P | S |
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | S | R/T | R/T |
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
7. T lives immediately below Q.
| Case 2 | ||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | S |
| 3 | N | Q |
| 2 | R | T |
| 1 | O | M |
Here all the pairs are neighbours which means they are living in a same floor but different flats except O, T (they live in different floors)
Hence, the answer is O, T.
5. Who is the neighbour of S?
A. O
B. P
C. M
D. R
E. N
Solution
Person: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, and T
Floor: 1, 2, 3, 4.
1. M lives on a Flat 2 of an odd floor.
2. Only one floor lies between M and Q.
3. Q lives east of N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | M | N | Q | |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | M | |
4. There is one floor between lives between Q and O.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | ||||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | ||||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
5. P lives immediately above N.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | |||
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | |||
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
6. R and T lives in a same floor.
| Case1 | Case 2 | |||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | R/T | R/T | P | S |
| 3 | O | M | N | Q |
| 2 | P | S | R/T | R/T |
| 1 | N | Q | O | M |
7. T lives immediately below Q.
| Case 2 | ||
| Flat 1 | Flat 2 | |
| 4 | P | S |
| 3 | N | Q |
| 2 | R | T |
| 1 | O | M |
Here neighbour of S is P.
Hence, the answer is P.
Comprehension:(Que No. 6 – 8)
Direction : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Point O is 3 km east of point Q. Point T is 4 km to the north of point P. Point V is 6 km to the west of point R which is 9 km north of point Q. Point U is 3 km south of point V and 2 km west of point T.
6. In which direction is point R with respect to point U ?
A. Northwest
B. North
C. Southwest
D. Southeast
E. Northeast
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question,
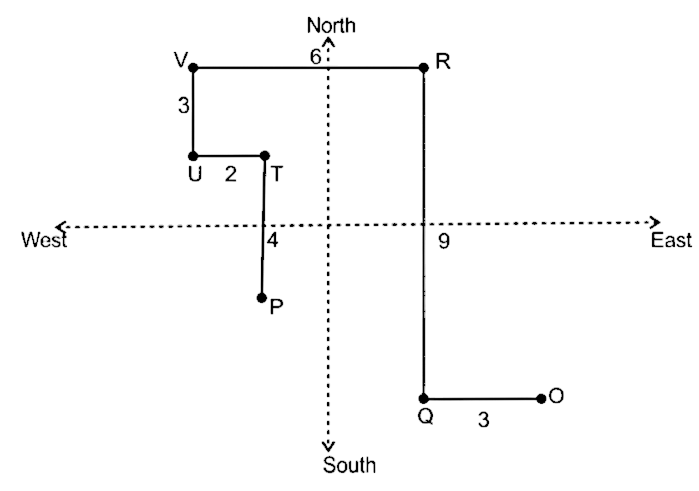
From the above diagram, it is clear point R is in Northeast direction with respect to point U. So, correct answer is ‘Northeast’.
7. Find the odd one out.
A. VP
B. RO
C. VQ
D. TO
E. TP
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question,

All except TP is in Southeast direction with respect to their first point whereas point T is in North direction of point P. Hence, correct answer is TP.
8. If point G is 4 km to west of point Q, then what is the distance between P and G ?
A. 5 km
B. 4 km
C. 3 km
D. 2 km
E. 7 km
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question,

If point G is 4 km to the west of Q, then point G is in South direction of point P and if we add distance between V and U and that of T and P we get 7 km and point Q is in east of point G whereas distance between R and Q is 9 km then we get distance between P and G,
PG = RQ – (VU + TP) = 9 – 7 = 2 km
Hence, the correct answer is 2 km.
9. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion(s) among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statement:
S ≥ U ≥ V = N < G < I
Conclusions:
I. S > N
II. S = N
A. Only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Both conclusions I and II follow
D. Either conclusion I or II follows
E. None follows
Solution
Given Statements: S ≥ U ≥ V = N < G < I
Conclusions:
I. S > N → False ( S ≥ U ≥ V = N ). Thus, it is not definite that S will be greater than N.
II. S = N → False ( S ≥ U ≥ V = N ). Thus, it is not definite that S will be equal to N.
Since, S ≥ N is true. Both the conclusions together form complementary pair. So, either conclusion I or II definitely follows.
Hence, the correct answer is either conclusion I or II follows.
10. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which conclusion among the given two conclusion(s) is /are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
J ≤ Q = K ≥ A ≥ X < F
Conclusions:
I. J < F
II. Q ≥ X
A. Only conclusion I follow
B. Only conclusion II follow
C. Either conclusion I or II follows
D. Neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. Both conclusion I and II follow
Solution
Given statement: J ≤ Q = K ≥ A ≥ X < F
Conclusions:
I. J < F → False (As J ≤ Q = K ≥ A ≥ X < F; no clear relation between J and F.)
II. Q ≥ X → True (Q = K ≥ A ≥ X, makes Q ≥ X)
Hence, only conclusion II follows.
11. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which conclusion among the given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
R < K ≤ L ≤ E; Z = E ≥ S ≥ P
Conclusions:
I. R < S
II. K ≤ Z
A. Both Conclusions I and II are true.
B. Neither Conclusion I nor II is true.
C. Either Conclusion I or II is true.
D. Only Conclusions I is true.
E. Only Conclusions II is true.
Solution
Given statements: R < K ≤ L ≤ E; Z = E ≥ S ≥ P
On combining: R < K ≤ L ≤ Z = E ≥ S ≥ P
Conclusions:
I. R < S → False (as R < K ≤ L ≤ E = Z ≥ S → relation can’t be determined between R and S)
II. K ≤ Z → True (as K ≤ L ≤ E = Z → , therefore, K ≤ Z)
Hence, only conclusion II is true.
Direction : Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Six persons P, Q, R, S, T and U having different weights. They are standing in a row in decreasing order of their weight. Q is heavier than R who is lighter than P. U is not heavier than T. As many person heavier than T as many person lighter than R. The person who is heaviest is 60 Kg whereas the lightest person is 45 Kg. Q is heavier than T but not heaviest among them. R is slightly heavier than U.
12. Who among them is heaviest ?
A. P
B. Q
C. R
D. S
E. T
Solution
Given persons are P, Q, R, S, T and U.
1) Q is heavier than R who is lighter than P which means both Q and P are heavier than R.
2) Q is heavier than T but not heaviest.
3) U is not heavier than T that means T is heavier than U.
Q > T > U
P , Q > R
4) R is slightly heavier than U.
Q > T > R > U
5) As many person heavier than T as many person lighter than R.
6) The heaviest person has 60 Kg weight and lightest weight is 45 Kg. So, the final arrangement is
P > Q > T > R > U > S
60 Kg 45 Kg
Hence, P is heaviest among all.
13. If T’s weight is 55 kg then what would be the possible weight of Q ?
A. 54
B. 50
C. 65
D. 63
E. 58
Solution
Given persons are P, Q, R, S, T and U.
1) Q is heavier than R who is lighter than P which means both Q and P are heavier than R.
2) Q is heavier than T but not heaviest.
3) U is not heavier than T that means T is heavier than U.
Q > T > U
P , Q > R
4) R is slightly heavier than U.
Q > T > R > U
5) As many person heavier than T as many person lighter than R.
6) The heaviest person has 60 Kg weight and lightest weight is 45 Kg. So, the final arrangement is
P > Q > T > R > U > S
60 Kg 45 Kg
According to the given condition if T’s weight is 55 kg then weight of Q lies between 55 kg to 60 kg. Hence, correct answer is 58 kg.
14. Which of the following represents correct arrangement ?
A. Q , T , U , S , P , R
B. P , Q , T , R , U , S
C. S , Q , T , P , R , U
D. R , T , U , P , Q , S
E. P , Q , R , S , T , U
Solution
Given persons are P, Q, R, S, T and U.
1) Q is heavier than R who is lighter than P which means both Q and P are heavier than R.
2) Q is heavier than T but not heaviest.
3) U is not heavier than T that means T is heavier than U.
Q > T > U
P , Q > R
4) R is slightly heavier than U.
Q > T > R > U
5) As many person heavier than T as many person lighter than R.
6) The heaviest person has 60 Kg weight and lightest weight is 45 Kg. So, the final arrangement is
P > Q > T > R > U > S
60 Kg 45 Kg
Hence, the correct answer is P, Q, T, R, U, S.
15. How many persons is / are lighter than Q ?
A. Two
B. Three
C. None
D. Four
E. Five
Solution
Given persons are P, Q, R, S, T and U.
1) Q is heavier than R who is lighter than P which means both Q and P are heavier than R.
2) Q is heavier than T but not heaviest.
3) U is not heavier than T that means T is heavier than U.
Q > T > U
P , Q > R
4) R is slightly heavier than U.
Q > T > R > U
5) As many person heavier than T as many person lighter than R.
6) The heaviest person has 60 Kg weight and lightest weight is 45 Kg. So, the final arrangement is
P > Q > T > R > U > S
60 Kg 45 Kg
Hence, the correct answer is four.
16. As many person heavier than P as many person lighter than whom ?
A. T
B. U
C. Q
D. P
E. S
Solution
Given persons are P, Q, R, S, T and U.
1) Q is heavier than R who is lighter than P which means both Q and P are heavier than R.
2) Q is heavier than T but not heaviest.
3) U is not heavier than T that means T is heavier than U.
Q > T > U
P , Q > R
4) R is slightly heavier than U.
Q > T > R > U
5) As many person heavier than T as many person lighter than R.
6) The heaviest person has 60 Kg weight and lightest weight is 45 Kg. So, the final arrangement is
P > Q > T > R > U > S
60 Kg 45 Kg
Since, P is heaviest among all so no one is heavier than him and S is lightest among all so no one lighter than him. Hence, the correct answer is S.
Directions: Following questions are based on five three letter words are given below:
LIF IMT EAT HON FOR(The new words formed after performing the mentioned operations may or may not necessarily be meaningful English words)
17. If in each of the words, all the alphabets are arranged in English alphabetical order within the word, how many words will remain unchanged?
A. Two
B. Three
C. Four
D. One
E. None of these
Solution
Given words are: LIF IMT EAT HON FOR
On arranging alphabets within the word in English alphabetical order:
FIL IMT AET HNO FORThus, only two words are there that remain unchanged.
18. If H is added at the beginning of all the words that start with vowels, and T is added at the end of the words that start with a consonant, then how many meaningful words can be formed?
A. Two
B. Four
C. Three
D. One
E. None of these
Solution
Given words are: LIF IMT EAT HON FOR
On adding H at the beginning of the word that starts with vowels and adding T at the end of the word that starts with consonant we get:
LIFT HIMT HEAT HONT FORTHence, three meaningful words can be formed.
19. If the positions of the first and last letters of all the words are interchanged, how many meaningful words can be formed?
A. One
B. Three
C. Two
D. Four
E. None of these
Solution
Given words are: LIF IMT EAT HON FOR
On interchanging the position of the first and last letters of all the words we get:
FIL TMI TAE NOH ROFThus, no meaningful words can be formed.
20. If the last letter in each of the words is changed to the previous alphabet in the English alphabetical order, how many words having vowel after arrangement?
A. Two
B. One
C. Four
D. Three
E. More than four
Solution
Given words are: LIF IMT EAT HON FOR
1) On changing the last letter in each of the words to the previous alphabet in the English alphabetical order we get:
LIE IMS EAS HOM FOQ
2) Clearly, five words LIE IMS EAS HOM FOQ have vowels.Hence, more than four words having vowels will be formed.
21. How many letters are there in the English alphabetical series between the third letter of the word which is fifth from the left and the third letter of the word which is third from the right of the given words?
A. One
B. Four
C. Three
D. Two
E. Five
Solution
Given words are:
Left side LIF IMT EAT HON FOR Right side
The last word from the left side is FOR and its third letter is R.
The third word from the right side is EAT and its third letter is T.Letters between R and T as per English alphabetical series are one i.e. S.
22. How many such pairs of letters are there in the word ‘FUNGIBILITY’, each of which has as many letters between them in the word (both forward and backward direction) as they have between them in the English Alphabet?
A. Four
B. Five
C. One
D. Two
E. Three
Solution

Hence, one pair are there in the word ‘FUNGIBILITY’, each of which has as many letters between them in the word (both forward and backward direction) as they have between them in the English Alphabet.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language,
‘words are useful all’ is coded as ‘me le sa na’,
‘nice words for girl’ is coded as ‘po ka ge le’,
‘for all girl happy’ is coded as ‘de me ka po’,
‘are meaning happy useful’ is coded as ‘fa de na sa’.
23. what would be the code for “for all”?
A. po le
B. me ge
C. me po
D. ka po
E. me na
Solution
First, let’s decode the words,
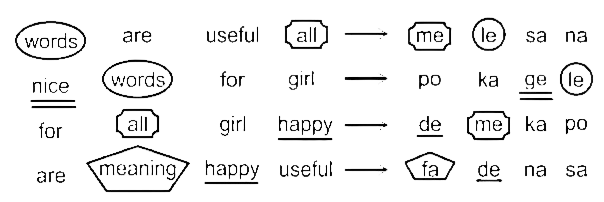
After decoding,
Words → le
All → me
Nice → ge
Happy → de
Meaning → fa
Are → sa/na
Useful → na/sa
For → po/ka
Girl → ka/poHence, the code for “for all” would be “me po”
24. what is the code for ‘ge me de ka’?
A. nice all happy for
B. nice all happy girl
C. for nice useful words
D. Either 1 or 2
E. None of these
Solution
First, let’s decode the words,

After decoding,
Words → le
All → me
Nice → ge
Happy → de
Meaning → fa
Are → sa/na
Useful → na/sa
For → po/ka
Girl → ka/poHence, “Either 1 or 2” is the correct answer.
25. What can be the code for ‘useful for all’ in that code language?
A. na sa me
B. na ka me
C. na po le
D. na le me
E. na po sa
Solution
First, let’s decode the words,

After decoding,
Words → le
All → me
Nice → ge
Happy → de
Meaning → fa
Are → sa/na
Useful → na/sa
For → po/ka
Girl → ka/poHence, “na ka me” is the correct answer.
Direction: Read the following information and answer the given questions.
Seven friends A, B,C, D, E, F and G are sitting around a circular table having eight seats. All of them are facing towards the center. No two friends sitting near each other are in alphabetical order (B does not sit near A and C).D sits second to the right of G. A faces F. E sits second to the left of A. Two friends sit between the vacant seat and C. B does not sit near E.
26. What is the position of B with respect to the vacant seat?
A. Third to the right
B. Third to the left
C. Immediate to the right
D. Immediate to the left
E. Opposite to Vacant seat
Solution
1) D sits second to the right of G. No two friends seating near each other are in alphabetical order
2) A faces F.
3) E sits second to the left of A.
4) Two friends sit between the vacant seat and C.
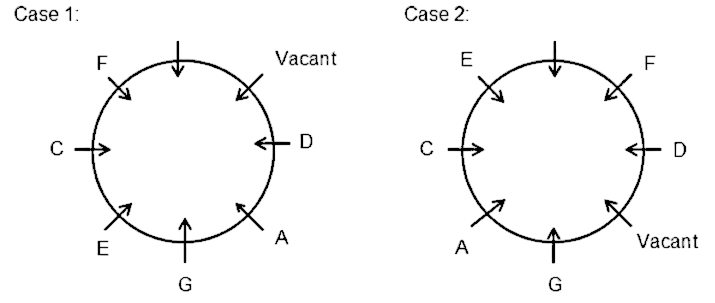
5) B does not sit near E. (This eliminates case 2)
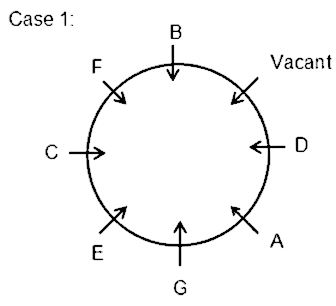
Hence, B sits immediately to the right of the vacant seat.
27. What is the position of F with respect to G?
A. Third to the left
B. Third to the right
C. Second to the left
D. Second to the right
E. Fourth to the right
Solution
1) D sits second to the right of G. No two friends seating near each other are in alphabetical order
2) A faces F.
3) E sits second to the left of A.
4) Two friends sit between the vacant seat and C.

5) B does not sit near E. (This eliminates case 2)

Hence, F sits third to the left of G.
28. How many friends sit between A and F when counted right of A?
A. Four
B. Three
C. Two
D. One
E. None
Solution
1) D sits second to the right of G. No two friends seating near each other are in alphabetical order
2) A faces F.
3) E sits second to the left of A.
4) Two friends sit between the vacant seat and C.

5) B does not sit near E. (This eliminates case 2)

Hence, ‘two’ friends sit between A and F when counted right of A
29. Which of the following statement/statements is/are true about E?
A. E is an immediate neighbor of B
B. E sits third to the right of D
C. E sits immediately to the left of C
D. E sits opposite to Vacant seat
E. All the given statements are true
Solution
1) D sits second to the right of G. No two friends seating near each other are in alphabetical order
2) A faces F.
3) E sits second to the left of A.
4) Two friends sit between the vacant seat and C.

5) B does not sit near E. (This eliminates case 2)

Hence, E sits opposite to vacant seat is a true statement.
30. Four among the five are alike in a certain way. Find the one that does not belong to that group.
A. CE
B. GA
C. BF
D. AD
E. FA
Solution
1) D sits second to the right of G. No two friends seating near each other are in alphabetical order
2) A faces F.
3) E sits second to the left of A.
4) Two friends sit between the vacant seat and C.

5) B does not sit near E. (This eliminates case 2)

In given options, people are immediate neighbors of each other except FA.Hence, ‘FA’ does not belong to the group.
31. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
2 # C D 6 % F I M K H 8 © @ T U V 4 € 2 7 8 $ H O K W 5 Y 4 ¥ Y A P @If all the even numbers are dropped, then which of the following element will be 10th from the right end?
A. #
B. O
C. Y
D. 7
E. None of these
Solution
Given series:
Left side 2 # C D 6 % F I M K H 8 © @ T U V 4 € 2 7 8 $ H O K W 5 Y 4 ¥ Y A P @ Right side
1) If all the even numbers are dropped:
# C D % F I M K H © @ T U V € 7 $ H O K W 5 Y ¥ Y A P @
2) 10th element from the right end is O
Then letter/ number that is 10th from the right end is ‘O’.
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Eight persons- M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, and T take an English proficiency test which is held twice a month. They take the test on either the 14th or 27th of four different months – January, April, September, and December of a particular year but not necessarily in the same order.
Q takes the test on an even numbered date of a month which contains an even number of days. O takes the test immediately after T, who takes the test on the 14th of either April or December. Only one person takes the test between N and O. S takes the test on an even-numbered date which comes immediately before the date on which P takes the test. Q doesn’t take the test in the months of April or December. N takes the test in the same month as R but not on the first available date of the year. M takes the test in the same month as Q. P takes the test on the last available date of the year.
32. Who takes the test on the 27th of April?
A. T
B. S
C. Q
D. O
E. N
Solution
Given: Eight persons take an English proficiency test on two different dates in four different months.
From the given conditions, we get the following possibilities:
1. Q takes the test on an even-numbered date of a month having an even number of days. From this, we get the following cases:
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | ||||
2. P takes the test on the last available date of the year. S takes the test on an even-numbered date which comes immediately before the date on which P takes the test. Combining these two statements, we get-
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | S | P | S | P |
3. Q doesn’t take the test in the months of April or December. M takes the test in the same month as Q. Combining these two statements, we see that Case 1 from the above is eliminated and we are left with-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||
| APRIL | ||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
4. O takes the test immediately after T, who takes the test on the 14th of either April or December. Only one person takes the test between N and O. Combining these two statements we get-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | N | |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
5. N takes the test in the same month as R but not on the first available date of the year. From this, we get the final table as follows:
| MONTH | FINAL CASE | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | R | N |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
From the above final table, we see that the test on 27th of April was taken by O.
Hence, O takes the test on the 27th of April.
33. Who takes the test immediately after O?
A. R
B. P
C. Q
D. T
E. S
Solution
Given: Eight persons take an English proficiency test on two different dates in four different months.
From the given conditions, we get the following possibilities:
1. Q takes the test on an even-numbered date of a month having an even number of days. From this, we get the following cases:
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | ||||
2. P takes the test on the last available date of the year. S takes the test on an even-numbered date which comes immediately before the date on which P takes the test. Combining these two statements, we get-
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | S | P | S | P |
3. Q doesn’t take the test in the months of April or December. M takes the test in the same month as Q. Combining these two statements, we see that Case 1 from the above is eliminated and we are left with-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||
| APRIL | ||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
4. O takes the test immediately after T, who takes the test on the 14th of either April or December. Only one person takes the test between N and O. Combining these two statements we get-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | N | |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
5. N takes the test in the same month as R but not on the first available date of the year. From this, we get the final table as follows:
| MONTH | FINAL CASE | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | R | N |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
From the above final table, we see that the person who takes the test immediately after O is Q.
Hence, Q takes the test immediately after O.
34. The number of persons who took the test in between T and S is?
A. Four
B. Six
C. Zero
D. Two
E. Three
Solution
Given: Eight persons take an English proficiency test on two different dates in four different months.
From the given conditions, we get the following possibilities:
1. Q takes the test on an even-numbered date of a month having an even number of days. From this, we get the following cases:
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | ||||
2. P takes the test on the last available date of the year. S takes the test on an even-numbered date which comes immediately before the date on which P takes the test. Combining these two statements, we get-
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | S | P | S | P |
3. Q doesn’t take the test in the months of April or December. M takes the test in the same month as Q. Combining these two statements, we see that Case 1 from the above is eliminated and we are left with-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||
| APRIL | ||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
4. O takes the test immediately after T, who takes the test on the 14th of either April or December. Only one person takes the test between N and O. Combining these two statements we get-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | N | |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
5. N takes the test in the same month as R but not on the first available date of the year. From this, we get the final table as follows:
| MONTH | FINAL CASE | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | R | N |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
From the above final table, we see that three persons take the test between T and S that is O, Q and M.
Hence, the number of people who took the test between T and S is three.
35. The pair which takes the test in the month of September is___
A. R and O
B. Q and N
C. T and S
D. P and M
E. Q and M
Solution
Given: Eight persons take an English proficiency test on two different dates in four different months.
From the given conditions, we get the following possibilities:
1. Q takes the test on an even-numbered date of a month having an even number of days. From this, we get the following cases:
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | ||||
2. P takes the test on the last available date of the year. S takes the test on an even-numbered date which comes immediately before the date on which P takes the test. Combining these two statements, we get-
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | S | P | S | P |
3. Q doesn’t take the test in the months of April or December. M takes the test in the same month as Q. Combining these two statements, we see that Case 1 from the above is eliminated and we are left with-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||
| APRIL | ||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
4. O takes the test immediately after T, who takes the test on the 14th of either April or December. Only one person takes the test between N and O. Combining these two statements we get-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | N | |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
5. N takes the test in the same month as R but not on the first available date of the year. From this, we get the final table as follows:
| MONTH | FINAL CASE | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | R | N |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
From the above final table, we see that Q and M take the test in the month of September.
Hence, the required pair is Q and M.
36. Who among the following is the third last person to take the test?
A. Q
B. S
C. M
D. P
E. T
Solution
Given: Eight persons take an English proficiency test on two different dates in four different months.
From the given conditions, we get the following possibilities:
1. Q takes the test on an even-numbered date of a month having an even number of days. From this, we get the following cases:
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | ||||
2. P takes the test on the last available date of the year. S takes the test on an even-numbered date which comes immediately before the date on which P takes the test. Combining these two statements, we get-
| MONTH | CASE 1 | CASE 2 | ||
| 14TH | 27TH | 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||||
| APRIL | Q | |||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | |||
| DECEMBER | S | P | S | P |
3. Q doesn’t take the test in the months of April or December. M takes the test in the same month as Q. Combining these two statements, we see that Case 1 from the above is eliminated and we are left with-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | ||
| APRIL | ||
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
4. O takes the test immediately after T, who takes the test on the 14th of either April or December. Only one person takes the test between N and O. Combining these two statements we get-
| MONTH | CASE 2 | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | N | |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
5. N takes the test in the same month as R but not on the first available date of the year. From this, we get the final table as follows:
| MONTH | FINAL CASE | |
| 14TH | 27TH | |
| JANUARY | R | N |
| APRIL | T | O |
| SEPTEMBER | Q | M |
| DECEMBER | S | P |
From the above final table, we see that M takes the test on the third last date of the year that is the 27th of September.
Hence, M is the third last person to take the test.
37. If in the word ‘JUPITER’, all the vowels are first arranged alphabetically and then all the consonants are arranged alphabetically and then all the vowels are replaced by the next letters and the consonants are replaced by the previous letters from English alphabet. Which letter will be Fourth from the right end?
A. I
B. O
C. V
D. Q
E. J
Solution
Word is- J U P I T E R
Vowels and then consonants arranged alphabetically- E I U J P R T
Vowels replaced by the next letter and consonants replaced by the previous letter- F J V I O Q SHence, fourth letter from the right end here is I.
Directions: These questions are based on the following information.
There are eight persons in a family of three generations. N is married to the child of K and A is the uncle of C and V. S is the maternal grandfather of V, who is the son of N. T is the paternal grandmother of C. K is married to S and the mother of A. B is the only sister of A and is married to N. There is an equal number of males and females in the family.
38. How is C related to A?
A. Nephew
B. Brother
C. Niece
D. Aunt
E. Daughter
Solution
According to the given information,
1. K is married to S and S is the maternal grandfather of
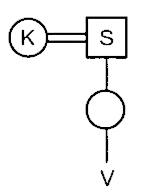
2. B is the only sister of A and is married to N and V is the son of N.

3. A is the uncle of C and V and T is the paternal grandmother of C.
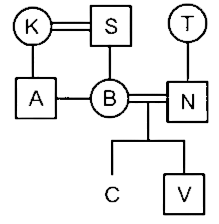
4. There is an equal number of males and females in the family. So, C is female.

Hence, C is the niece of A.
39. How is N’s wife related to T?
A. Daughter
B. Sister
C. Aunt
D. Daughter-in-law
E. Mother
Solution
According to the given information,
1. K is married to S and S is the maternal grandfather of

2. B is the only sister of A and is married to N and V is the son of N.

3. A is the uncle of C and V and T is the paternal grandmother of C.

4. There is an equal number of males and females in the family. So, C is female.

Hence, N’s wife, B is the daughter-in-law of T.
40. How is A related to S?
A. Son
B. Brother
C. Son-in-law
D. Father
E. Grandson
Solution
According to the given information,
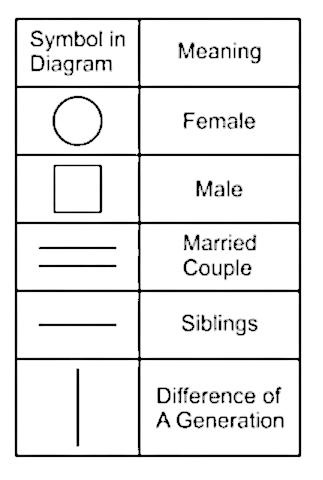
1. K is married to S and S is the maternal grandfather of

2. B is the only sister of A and is married to N and V is the son of N.

3. A is the uncle of C and V and T is the paternal grandmother of C.

4. There is an equal number of males and females in the family. So, C is female.

Hence, A is the son of S.
Numerical Ability
41.What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
21, 29, 45, 77, 141, ?
A. 215
B. 235
C. 297
D. 269
E. 257
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
21 + 8 = 29
29 + 16 = 45
45 + 32 = 77
77 + 64 = 141
141 + 128 = 269
42. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
12.5, 15, 19.5, 26, 34.5, ?
A. 42
B. 44
C. 46
D. 41
E. 45
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
12.5 + 2.5 = 15
15 + 4.5 = 19.5
19.5 + 6.5 = 26
26 + 8.5 = 34.5
34.5 + 10.5 = 45
43. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
21, 30, 57, 102, ?, 246
A. 172
B. 158
C. 165
D. 156
E. 148
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
21 + 9 = 30
30 + 27 = 57
57 + 45 = 102
102 + 63 = 165
165 + 81 = 246
44. What number should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
10, 11, 24, 75, ?, 1525
A. 244
B. 344
C. 304
D. 324
E. 294
Solution
GIVEN :
10, 11, 24, 75, ?, 1525
CALCULATION :
The series follows the following pattern:
10 × 1 + 1 = 11
11 × 2 + 2 = 24
24 × 3 + 3 = 75
75 × 4 + 4 = 304
304 × 5 + 5 = 1525
45. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
24, 25, 29, 38, 54, ?
A. 77
B. 69
C. 89
D. 79
E. 87
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
24 + 12 = 25
25 + 22 = 29
29 + 32 = 38
38 + 42 = 54
54 + 52 = 79
Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions:
The following bar graph shows the marks obtained by Raj, Ram, and Radha in five subjects.

46. Find the difference between the total marks obtained by Radha and Raj in five subjects.
A. 25
B. 22
C. 30
D. 20
E. 28
Solution
Calculation:
Total marks obtained by Raj in five subjects = 80 + 70 + 75 + 60 + 65 = 350
Total marks obtained by Radha in five subjects = 70 + 60 + 90 + 85 + 70 = 375
Required difference = 375 – 350
⇒ 25
∴ Required difference is 25
Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions:
The following bar graph shows the marks obtained by Raj, Ram, and Radha in five subjects.

47. Find the ratio between the total marks obtained by three in English and Social Science.
A. 11 : 12
B. 20 : 13
C. 13 : 17
D. 17 : 19
E. 16 : 13
Solution
Calculation:
Total marks obtained in English by all three = 80 + 90 + 70 = 240
Total marks obtained in Social Science by all three = 65 + 60 + 70 = 195
Required ratio = 240 : 195
⇒ 16 : 13
∴ Required ratio is 16 : 13
Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions:
The following bar graph shows the marks obtained by Raj, Ram, and Radha in five subjects.

48. Find the average marks obtained by all three in Hindi.
A. 70
B. 85
C. 80
D. 60
E. 65
Solution
Calculation:
Total marks obtained in Hindi by all three = 70 + 80 + 60 = 210
Required average = 210/3
⇒ 70
∴The average marks obtained by three in Hindi is 70
Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions:
The following bar graph shows the marks obtained by Raj, Ram, and Radha in five subjects.

49. The marks obtained in Marathi by Ram is approximately what percent of the total marks obtained by all three in Marathi?
A. 40%
B. 32%
C. 30%
D. 33%
E. 39%
Solution
Calculation:
Total marks obtained in Marathi by all three = 75 + 70 + 90 = 235
Marks obtained by Ram in Marathi = 70
Required percentage = (70/235) × 100
⇒ 29.78% ≈ 30%
∴ Required percentage is 30%
Directions: Study the following data and answer the following questions:
The following bar graph shows the marks obtained by Raj, Ram, and Radha in five subjects.

50. The marks obtained in five subjects for Raj is approximately what percent less than the marks obtained by Ram?
A. 8%
B. 10%
C. 5%
D. 11%
E. 15%
Solution
Calculation:
Total marks obtained in five subjects by Raj = 80 + 70 + 75 + 60 + 65 = 350
Total marks obtained in five subjects by Ram = 90 + 80 + 70 + 80 + 60 = 380
Required percentage = [(380 – 350)/380] × 100
⇒ [30/380] × 100
⇒ 7.89% ≈ 8%
∴ Required percentage is 8%
51. Two positive integers are in the ratio of 5 : 9. If the product of these numbers is 180 then, find the greater number.
A. 18
B. 9
C. 10
D. 11
E. 12
Solution
Given:
Ratio of two number = 5 : 9
Calculations:
Let the ratio be x
According to question,
⇒ 5x × 9x = 180
⇒ 45x2 = 180
⇒ x2 = 4
⇒ x = 2
Two numbers are : 10, 18
∴ Greater number is 18.
52. If the principal of ₹ 10,000 amounts to ₹ 16,900 in 2 years, calculate the rate of interest if interest is compounded annually.
A. 15%
B. 20%
C. 30%
D. 40%
E. 50%
Solution
GIVEN:
Principal = ₹ 10,000
Time = 2 years
Amount after interest = ₹ 16,900
FORMULA USED:
Amount = Principal × (1 + r/100)t
CALCULATION:
Amount = 10,000 × (1 + r/100)2 = 10,000 × {(100 + r)/100)2
→→ 16,900 = 10,000 × {(100 + r)/100)2
→→ 1.69 = {(100 + r)/100)2
→→ r = 30% p.a.
∴ Rate of interest = 30% p.a.
Alternate Method
When the sum is compounded for 2 years.
Amount ∶ Sum = √16900 ∶ √10000
⇒ Amount ∶ Sum = 13 ∶ 10
Rate of interest = [(13 – 10)/10] × 100
⇒ Rate of interest = 30%
53. P can do a piece of work in ‘x’ days; Q can do the same work in 4x days. To finish the work together they take 16 days. What is the value of x?
A. 25
B. 20
C. 15
D. 30
E. 45
Solution
Given:
P can do a piece of work in ‘x’ days;
Q can do the same work in 4x days;
To finish the work together they take 16 days
Formula Used:
If a person takes “a” days to complete a work,
Part of the work completed by him in 1 day = 1/a
Calculation:
A’s 1 day’s work = 1/x
B’s 1 day’s work = 1/4x
(A + B)’s 1 day’s work = (1/x) + (1/4x) = 5/4x
Hence, we get:
⇒ 5/4x = 1/16
⇒ x = 20
∴ The value of x is 20.
54. In a hostel, food available for 300 students for 50 days. After 10 days 100 more students join the hostel for how many more days will the food last
A. 30 days
B. 45 days
C. 40 days
D. 38 days
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Food is available for 300 students for 50 days.
Calculation:
Man days for which food is available = 300 × 50
⇒ 15000
Available food is enough for 1 student for 15000 days
Food used by 300 students in 10 days = 300 × 10
1 man-day of food = 3000
Man days of food left = 15000 – 3000 = 12000 man-days of food
Total number of students now = 300 + 100 = 400
The remaining food can be used for 400 students for = 12000/400
⇒ 30 days
∴ The food remains last in 30 days
55. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 2x2 – 5x + 2 = 0
II. 6y2 – 5y + 1 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I.2x2 – 5x + 2 = 0
⇒2x2 – x – 4x + 2 = 0
⇒ (x – 2) (2x – 1) = 0
⇒ x =2, 1/2
II. 6y2 – 5y + 1 = 0
⇒ 6y2 – 2y – 3y + 1 = 0
⇒ (2y – 1) (3y – 1) = 0
⇒ y = 1/2, 1/3
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 2 | 1/2 | x > y |
| 2 | 1/3 | x > y |
| 1/2 | 1/2 | x = y |
| 1/2 | 1/3 | x > y |
Hence, x ≥ y.
56. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 2x2 –18= 0
II. y2 – 12y + 32 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. 2x2 –18= 0
⇒ x2 –9= 0
⇒ x = ± 3
⇒ x = –3, 3
II. y2– 12y + 32 = 0
⇒ y2 – 4y – 8y + 32 = 0
⇒ (y – 4) (y – 8) = 0
⇒ y = 4, 8
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| –3 | 4 | x < y |
| –3 | 8 | x < y |
| 3 | 4 | x < y |
| 3 | 8 | x < y |
Hence, x < y.
57. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 16x + 48 = 0
II. y2 – 10y + 21 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. x2 – 16x + 48 = 0
⇒ x2 – 12x – 4x + 48 = 0
⇒ x (x – 12) – 4(x – 12) = 0
⇒ x(x – 12) – 4(x – 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 12) (x – 4) = 0
⇒ x = 12, 4
II. y2 – 10y + 21 = 0
⇒ y2 – 7y – 3y + 21 = 0
⇒ y(y – 7) – 3(y – 7) = 0
⇒ (y – 7) (y – 3) = 0
⇒ y = 7, 3
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 12 | 7 | x > y |
| 12 | 3 | x > y |
| 4 | 7 | x < y |
| 4 | 3 | x > y |
∴ The relationship between x and y cannot be established.
58. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 20x + 64 = 0
II. y2 + 27y + 110 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. x2 + 20x + 64 = 0
⇒ x2 + 4x + 16x + 64 = 0
⇒ x (x + 4) + 16 (x + 4) = 0
⇒ (x + 16) (x + 4) = 0
⇒ x = -16, -4
II. y2 + 27y + 110 = 0
⇒ y2 + 5y + 22y + 110 = 0
⇒ y (y + 5) + 22 (y + 5) = 0
⇒ (y + 5) (y + 22) = 0
⇒ y = -5, -22
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| -16 | -22 | x > y |
| -16 | -5 | x < y |
| -4 | -22 | x > y |
| -4 | -5 | x > y |
Hence, Relationship between x and y cannot be established
59. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 3x – 40 = 0
II. y2 – 2y – 15 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
i. x2 – 3x – 40 = 0
⇒ x2 – 8x + 5x – 40 = 0
⇒ (x -8) (x + 5) = 0
⇒ x = -5, 8
ii. y2 – 2y – 15 = 0
⇒ y2 + 3y – 5y – 15 = 0
⇒ (y + 3) (y – 5) = 0
⇒ y = -3, 5
| Value of X | Value of Y | Relation |
| 8 | -3 | x > y |
| 8 | 5 | x > y |
| -5 | -3 | x < y |
| -5 | 5 | x < y |
Hence, relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the following questions.
The pie-chart below shows the percentage of the number of different android phones sold in the year.

60. How many Realme phones were sold in the year?
A. 5,400
B. 7,200
C. 1080
D. 1,800
E. 10,800
Solution
Given:
Total number of phones sold = 36,000
Percentage of Realme phones sold = 30%
Concept used:
Number of Realme phones sold = Total sales × percentage of Realme sold
Calculation:
Total number of phones sold = 36,000
Number of Realme phones sold = 30% × 36,000
⇒ 10,800
∴ The number of Realme phones sold is 10,800.
Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the following questions.
The pie-chart below shows the percentage of the number of different android phones sold in the year.

61. The sales of Samsung is how much more than that of iPhone?
A. 7,200
B. 1,800
C. 1,440
D. 5,400
E. 6,400
Solution
Given:
Total number of phones sold = 36,000
Percentage of Samsung phones = 20%
Percentage of iPhones = 5%
Concept used:
Number of Samsung sold more that iPhone = number of Samsung phones – number of iPhones
Calculation:
Number of Redmi phones = 36,000 × 20%
⇒ 7,200
Number of iPhones sold = 36,000 × 5%
⇒ 1,800
Number of Samsung phones sold more than iPhones = 7,200 – 1,800
⇒ 5,400
∴ The 5,400 number of Samsung were sold more than the iPhone.
Alternate Method
Percentage difference in the sale of Samsung and iPhone = 20% – 5%
⇒ Percentage difference in the sale of Samsung and iPhone = 15%
Number of Samsung phones sold more than iPhone = 15% × 36,000
⇒ The number of Samsung phones sold more than iPhone = 5,400.
∴ The 5,400 number of Samsung were sold more than the iPhone.
Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the following questions.
The pie-chart below shows the percentage of the number of different android phones sold in the year.

62. If all brands have to give tax of 5%, what amount will be collected as tax from Samsung provided each phone cost Rs.20,000.
A. 36 lakh
B. 54 lakh
C. 64 lakh
D. 72 lakh
E. 81 lakh
Solution
Given:
Total number of phones sold = 36,000
Percentage of Samsung mobiles sold = 20%
Tax collected on each phone = 5%
Cost of each Samsung mobile = Rs. 20,000.
Concept used:
The total amount obtained as tax from Samsung = number of Samsung sold × cost of each phone × tax obtained on each phone
Calculation:
Number of Samsung mobile sold = 20% × 36,000
⇒ 7,200
Cost of 7,200 Samsung mobiles sold = 7,200 × 20,000
⇒ Rs.14.4 Cr
Tax obtained on Samsung phones = 14.4 Cr × 5%
⇒ 72 lakhs
∴ The total tax obtained from the sale of Samsung is 72 lakhs.
Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the following questions.
The pie-chart below shows the percentage of the number of different android phones sold in the year.

63. If half of the Nokia users decided to switch to Realme, find total number of Realme users.
A. 5,400
B. 8,400
C. 14,400
D. 20,400
E. 24,400
Solution
Given:
Total number of phones sold = 36,000
Percentage of Nokia mobiles sold = 20%
Percentage of Nokia users who switched to Realme = 50% of 20% Nokia users
Percentage of Realme mobiles sold = 30%
Concept used:
Total number of Realme users = number of Nokia users who switched to Realme + Number of Realme users
Calculation:
Number of Realme users = 30% × 36,000
⇒ Number of Realme users = 10,800
Percentage of Nokia users who switched to Realme = 10%
Number of Nokia users who switched to Realme = 10% × 36,000
⇒ Number of Nokia users who switched to Realme = 3,600
Total number of Realme users = 10,800 + 3,600
∴ Total number of Realme users is 14,400.
Alternate Method
Percentage of Nokia users who switched to Realme = 10%
Total percentage of people using Realme = 30% + 10%
⇒ Total percentage of people using Realme = 40%
Total number of Realme users = 40% × 36,000
⇒ Total number of Realme users = 14,400.
∴ The number of Realme users is 14,400.
Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the following questions.
The pie-chart below shows the percentage of the number of different android phones sold in the year.

64. Find the difference between the number of Samsung and Nokia mobiles sold together and the number of Realme and Redmi mobiles sold together.
A. 7,200
B. 1,800
C. 5,400
D. 6,400
E. 8,100
Solution
Given:
Total number of phones sold = 36,000
Percentage of Samsung mobiles sold = 20%
Percentage of Nokia mobiles sold = 20%
Percentage of Realme mobiles sold = 30%
Percentage of Redmi mobiles sold = 25%
Concept used:
Difference between number of Samsung and Nokia mobiles sold to that of Realme and Redmi sold = Number of (Redmi + Realme) – Number of(Samsung + Nokia)
Calculation:
Number of Samsung mobiles sold = 7,200
Number of Nokia mobiles sold = 7,200
Number of (Samsung + Nokia) = 14,400
Number of Realme mobiles sold = 10,800
Number of Redmi mobiles sold = 9,000
Number of (Redmi + Realme) = 19,800
Difference = 19,800 – 14,400
⇒ 5,400
∴ The difference in sale is 5,400
Alternate Method
Total percentage of Nokia and Samsung = 20% + 20%
⇒ Total percentage of Nokia and Samsung = 40%
Total percentage of Realme and Redmi = 30% + 25%
⇒ Total percentage of Realme and Redmi = 55%
Difference in percentage = 55% – 40%
⇒ Difference in percentage 15%
Difference in sale = 36,000 × 15%
⇒ Difference in sale = 5,400.
∴ The difference in sale is 5,400
65. Present age of Arush is 3/8 of his mother. After 5 years age of mother will be 5 years more than twice the age of Arush. Find the age of Arush.
A. 12 years
B. 15 years
C. 20 years
D. 18 years
E. 16 years
Solution
Given:
Present age of Arush = (3/8) × (age of his mother)
Calculations:
Let the present age of Arush and his mother be A and M respectively.
According to question,
⇒ A = 3/8 M
⇒ M = 8/3 A —-(1)
After 5 years age of mother will be 5 years more than twice the age of Arush,
So, Age of Arush after 5 years will be (A+5) and age of Mother will be (M + 5)
⇒ M + 5 = 5 + 2(A + 5)
⇒ M = 2A + 10
Put M = 8/3 A from equation(1)
⇒ 8/3 A – 2A = 10
⇒ A = 15 years
∴ The age of Arush is 15 years.
66. Manoj reaches his office 6 minutes late, walking at a speed of 5 km/hr and he reaches there 2 minutes early when walking at 6 km/hr then find the distance of his office from home.
A. 4 km
B. 5 km
C. 6 km
D. 7 km
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
When speed is 5 km/hr reaches 6 min late
And when speed is 6 km/hr reaches 2 min early
Formula:
Speed = distance/time
Calculations:
Let distance = d km
now, when speed 5 km/hr he reaches 6 minutes late
Time = (T + 6/60) hour
When speed 6 km/hr reaches 2 minutes before
Time = (T – 2/60) hour
Time difference = (T + 6/60) – (T – 2/60)
⇒ T + 6/60 – T + 2/60
⇒ 8/60 hour
⇒ d/5 – d/6 = 8/60
⇒ d/30 = 8/60
⇒ d = 4 km
∴ Distance between home and office is 4 km.
67. What is the ratio between volume and surface area of the cube, if the radius of sphere inscribed in the cube is 7 cm?
A. 3 : 7
B. 7 : 3
C. 7 : 5
D. 4 : 3
E. 5 : 7
Solution
Solution:
Given:
Radius of inscribed sphere = 7 cm
Concept:
Volume of cube = a3
Surface area of cube = 6a2
Calculation:
Side length of cube = 2 × radius of inscribed sphere
⇒ a = 2 × 7 = 14 cm
Volume of cube = (14)3
Surface area of cube = 6 (14)2
Ratio of volume and surface area = (14)3 : 6 (14)2
⇒ Volume: surface area = 14 : 6 = 7 : 3
∴ Ratio of volume and surface area of the sphere is 7 : 3
68. Two Bags are selected from 12 Bags. How many ways are to achieve this?
A. 120
B. 122
C. 66
D. 140
E. 142
Solution
Concept used:
n! = n × (n-1)
Number of ways=12 * 11/2 = 66
69. What approximate will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
? ÷ 3.02 + 46.02 × 4.99 – 12.02 = 317.05
A. 300
B. 297
C. 99
D. 350
E. 347
Solution
Rules of Approximation:
1. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal less than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal. The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
2. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal more than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal and raise the remaining number by ‘1’.The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
? ÷ 3.02 + 46.02 × 4.99 – 12.02 = 317.05
⇒ ? ÷ 3 + 46 × 5 – 12 = 317
⇒ ? ÷ 3 + 230 – 12 = 317
⇒ ?/3 = 317 – 230 + 12
⇒ ?/3 = 329 – 230
⇒ ?/3 = 99
⇒ ? = 99 × 3
⇒ ? = 297
∴ The value of ? is 297
70. What approximate value should come in place of ‘?’ in the following equation:
242 + (32 × 2) = ?2 + (3 × 4)2 + 32
A. 21
B. 441
C. 22
D. 20
E. None of these
Solution
Solution:
Rules of Approximation:
1. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal less than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal. The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
2. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal more than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal and raise the remaining number by ‘1’.The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
242 + (32 × 2) = ?2 + (3 × 4)2 + 32
⇒ 242 + (9 × 2) = ?2 + 122 + 32
⇒ 242 + 18 = ?2 + 122 + 32
⇒ 576 + 18 = ?2 + 144 + 9
⇒ 594 = ?2 + 153
⇒ 594 – 153 = ?2
⇒ 441 = ?2
∴ ? = 21
71. What approximate value will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?24.9 × 2.76 – (50.01% of 41.85 ÷ 6.85) = ?
A. 81
B. 72
C. 55
D. 48
E. 60
Solution
Rules of Approximation:
1. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal less than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal. The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
2. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal more than 5, then just drop the digits to the right of the decimal and raise the remaining number by ‘1’.The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
Concept:
In this type of question, we are expected to calculate approximate value (not exact value), so we can replace the given numbers by their nearest perfect places which makes the calculation easy.
24.9 × 2.76 – (50.01% of 41.85 ÷ 6.85) = ?
Taking approximate value, we get
25 × 3 – (50% of 42 ÷ 7) = ?
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

⇒ 25 × 3 – (21 ÷ 7) = ?
⇒ 25 × 3 – 3 = ?
⇒ 75 – 3 = ?
∴ ? = 72
72. Find the approximate value of “?” in the following equation: –
69.2 + 46.7 – ? ÷ 12.05 × 4.97 = 86.02
A. 80
B. 75
C. 70
D. 72.5
E. 82.5
Solution
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Given:
The equation: –
69.2 + 46.7 – ? ÷ 12.05 × 4.97 = 86.02
As we have to calculate the approximate value we will take the nearest value of the integers.
Calculation:
The given equation is: –
69 + 47 – ? ÷ 12 × 5= 86
⇒ – ? ÷ 12 × 5 = 86 – 69 – 47
⇒ (-?/12) × 5 = 86 – 116
⇒ (-?/12) × 5 = – 30
⇒ -?/12 = 30/5
⇒ -? = (-30/5) × 12
⇒ ? = 6 × 12
⇒ ? = 72
∴ The required approximate value of “?” in the given equation is 72.5 as it is nearest to 72.
73. Calculate the approximate value of “?” in the following equation: -√16.21 + 12.01 × 3.16 – 14.31/7.11 = ?
A. 31
B. 38
C. 35
D. 40
E. 32
Solution
Rules of Approximation:
1. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal less than 5. Then just drop the digits to the right of the decimals. The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
2. If a number has digits to the right of the decimal more than 5. Then just drop the digits to the right of the decimals and raise the remaining number by ‘1’.The number so obtained will be the approximated value.
Concept Used:
We have to follow the BODMAS rule

Calculation:
Considering the given equation
√16.21 + 12.01 × 3.16 – 14.31/7.11 = ?
⇒ √16 + 12 × 3 – 2 = ?
⇒ √16 + 36 – 2 = ?
⇒ 4 + 36 – 2 = ?
⇒ 40 – 2 = ?
⇒ ? = 38
∴ ? = 38
74. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
16.97 × 23.99 ÷ 1.993 + 1.922 × 6.97 = ?
A. 86
B. 58
C. 67
D. 103
E. 79
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
16.97 × 23.99 ÷ 1.993 + 1.922 × 6.97 = ?
⇒ 17 × 24 ÷ 23 + 22 × 7 = ?
⇒ 17 × 24 ÷ 23 + 28 = ?
⇒ 408 ÷ 8 + 28 = ?
⇒ 51 + 28 = ?
∴ ? = 79
75. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
4.95 × 20.91 + 34.95 – 22.93 × 4.99 = √?
A. 5
B. 25
C. 125
D. 625
E. 1225
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
4.95 × 20.91 + 34.95 – 22.93 × 4.99 = √?
⇒ 5 × 21 + 35 – 23 × 5 = √?
⇒ 105 + 35 – 23 × 5 = √?
⇒ 140 – 115 = √?
⇒ 25 = √?
∴ ? = 625
76. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
12.93 × 67.98 + 4.953 × 7.07 = ? – 40.99
A. 1800
B. 1600
C. 1700
D. 2000
E. 2200
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
12.93 × 67.98 + 4.953 × 7.07 = ? – 40.99
⇒ 13 × 68 + 53 × 7 = ? – 41
⇒ 13 × 68 + 125 × 7 = ? – 41
⇒ 884 + 875 = ? – 41
⇒ 1759 = ? – 41
⇒ ? = 1759 + 41 = 1800
77. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
(25.96 – 12.93 × 2.02) ÷ 1.98 + 1.01 = ?
A. -3
B. -1
C. 1
D. 7
E. 3
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
(25.96 – 12.93 × 2.02) ÷ 1.98 + 1.01 = ?
⇒ (26 – 13 × 2) ÷ 2 + 1 = ?
⇒ (26 – 26) ÷ 2 + 1 = ?
⇒ 0 ÷ 2 + 1 = ?
⇒ 0 + 1 = ?
⇒ 1 = ?
78. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
(√360.99 × 23.94) ÷ 11.92 + √483.94 = ?
A. 70
B. 60
C. 90
D. 110
E. 80
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
(√360.99 × 23.94) ÷ 11.92 + √483.94 = ?
⇒ (√361 × 24) ÷ 12 + √484 = ?
⇒ (19 × 24) ÷ 12 + 22 = ?
⇒ 456 ÷ 12 + 22 = ?
⇒ 38 + 22 = ?
∴ ? = 60
79. Speed of the stream is 15 kmph and speed of the boat downstream in 45 kmph. Find the ratio of upstream speed and downstream speed of a boat.
A. 1 : 3
B. 1 : 5
C. 2 : 1
D. 3 : 5
E. 1 : 2
Solution
FORMULA USED:
If speed of stream = B km/hour and speed of boat in still water = A km/hour
Downstream speed = (A + B) km/hour
Upstream speed = (A – B) km/hour
CALCULATION:
Speed of the stream, B = 15 kmph
Speed of the downstream = A + B = 45 kmph
Speed of the boat in still water, A = 45 – 15 = 30 kmph
Speed upstream = A – B = 30 – 15 = 15 kmph
∴ Required ratio = 15 : 45 = 1 : 3
80. Selling price of a dress Is Rs 7,500 After allowing two successive discount of 75% and 70%. Find the marked price.
A. Rs. 100000
B. Rs. 75000
C. Rs. 200000
D. Rs. 90000
E. Rs. 50000
Solution
Given:
SP is Rs 7,500; two successive discount are 75% and 70%.
Formula used:
SP = MP [(100 – D1)/100] [(100 –D2)/100]
Calculation:
⇒ 7,500 = MP [(100 – 75)/100] [(100 – 70)/100]
⇒ 7,500 = MP (25/100) (30/100) ⇒ (7,500 × 100 × 100)/25 × 30 = MP
∴ Rs 1,00,000 = MP
