Direction: Study the following information to answer the given questions: Eight persons M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T are sitting around the circular table facing towards the center. M sits third to the right of N. R sits adjacent to M. O sits second to the right of R. P is not adjacent to R. S sits opposite to P. T is adjacent to neither Q nor N.
1.Who sits immediate left of N?
A. P
B. T
C. R
D. Q
E. S
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T.
1) M sits third to the right of N.
2) R sits adjacent to M.
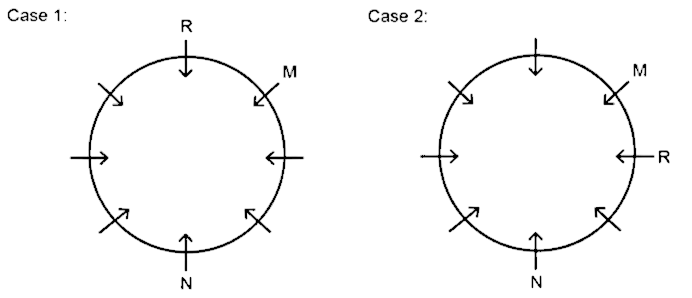
3) O sits second to the right of R.
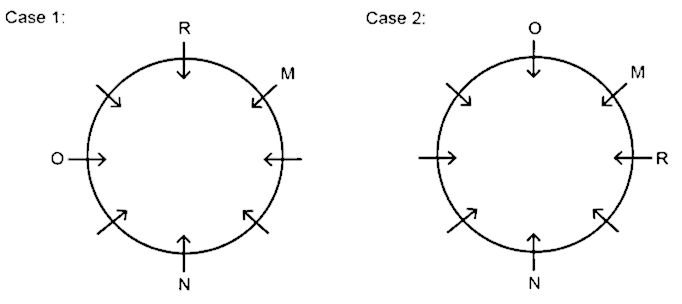
4) S sits opposite to P.
5) P is not adjacent to R.
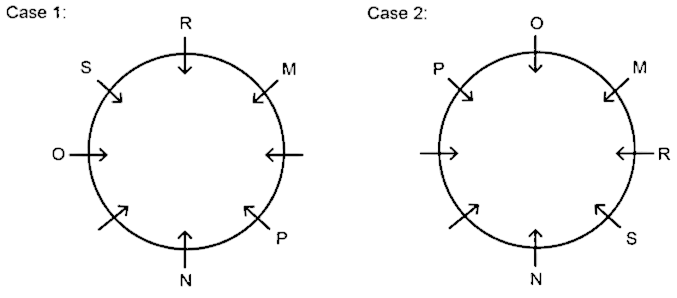
6) T is adjacent to neither Q nor N. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given point.
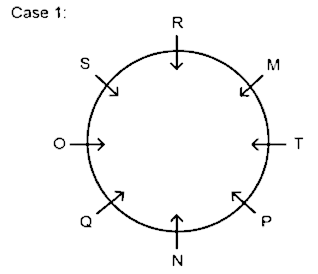
Hence, Q sits immediate left of N.
2. How many persons sit between S and T when counted from the left of S?
A. Three
B. Two
C. Four
D. One
E. Five
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T.
1) M sits third to the right of N.
2) R sits adjacent to M.

3) O sits second to the right of R.

4) S sits opposite to P.
5) P is not adjacent to R.

6) T is adjacent to neither Q nor N. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given point.
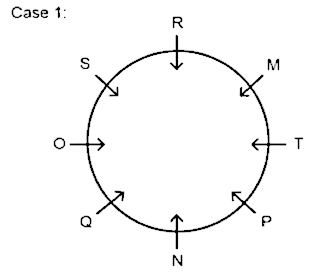
Hence, two persons sit between S and T when counted from the left of S.
3. ______ sits third to the left of O.
A. Q
B. S
C. T
D. P
E. M
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T.
1) M sits third to the right of N.
2) R sits adjacent to M.

3) O sits second to the right of R.

4) S sits opposite to P.
5) P is not adjacent to R.

6) T is adjacent to neither Q nor N. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given point.
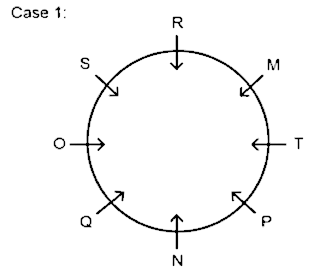
Hence, M sits third to the left of O.
4. Who sits opposite to R?
A. N
B. O
C. Q
D. M
E. T
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T.
1) M sits third to the right of N.
2) R sits adjacent to M.

3) O sits second to the right of R.

4) S sits opposite to P.
5) P is not adjacent to R.

6) T is adjacent to neither Q nor N. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given point.
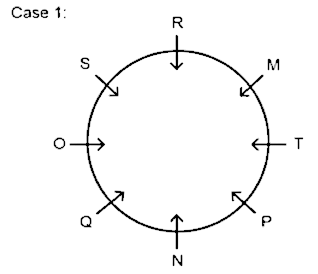
Hence, N sits opposite to R.
5. Which of the following statement is correct?
A. O sits opposite to P
B. M sits immediate right of T
C. Q sits second to the left of M
D. S sits immediate left of Q
E. All are correct
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T.
1) M sits third to the right of N.
2) R sits adjacent to M.

3) O sits second to the right of R.

4) S sits opposite to P.
5) P is not adjacent to R.

6) T is adjacent to neither Q nor N. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given point.
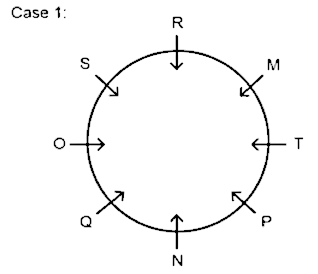
Hence, only statement 2) is correct.
Direction: Study the given information carefully and answer the following questions.Seven trees M, N, O, P, Q, R and S were planted in a garden. Tree O is 8m north of tree S. Tree S is 7m west of tree M. Tree M is 13m east of tree R. Tree R is 15m south of tree N. Tree N is 5m east of tree P. Tree P is 7m east of tree Q.
6. What is the distance between Tree R and Tree S?
A. 14m
B. 8m
C. 7m
D. 13m
E. 6m
Solution
Drawing diagram according to the given information:
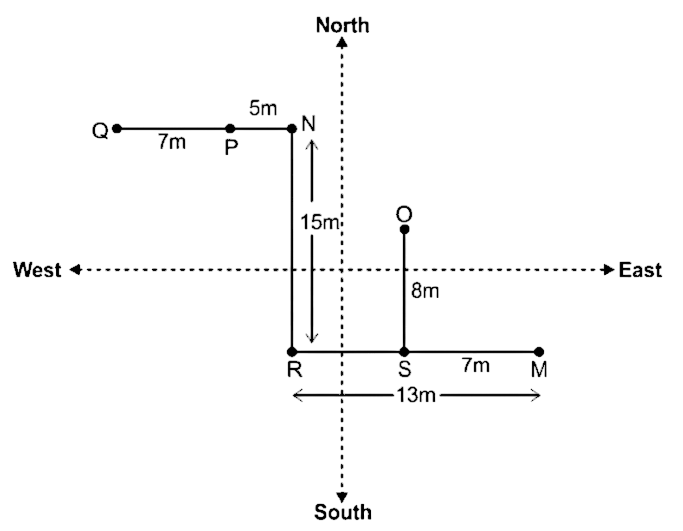
Hence, the distance between tree R and tree S is 6m.
7. Tree M is in which direction with respect to Tree N?
A. East
B. South west
C. North east
D. North west
E. South east
Solution
Drawing diagram according to the given information:

Hence, tree M is in south east direction with respect to tree N.
8. If tree T is 8m north of tree R, then what will be the distance between treen N and tree T?
A. 9m
B. 15m
C. 12m
D. 7m
E. 8m
Solution
Drawing diagram according to the given information:

Drawing diagram according to the given information:
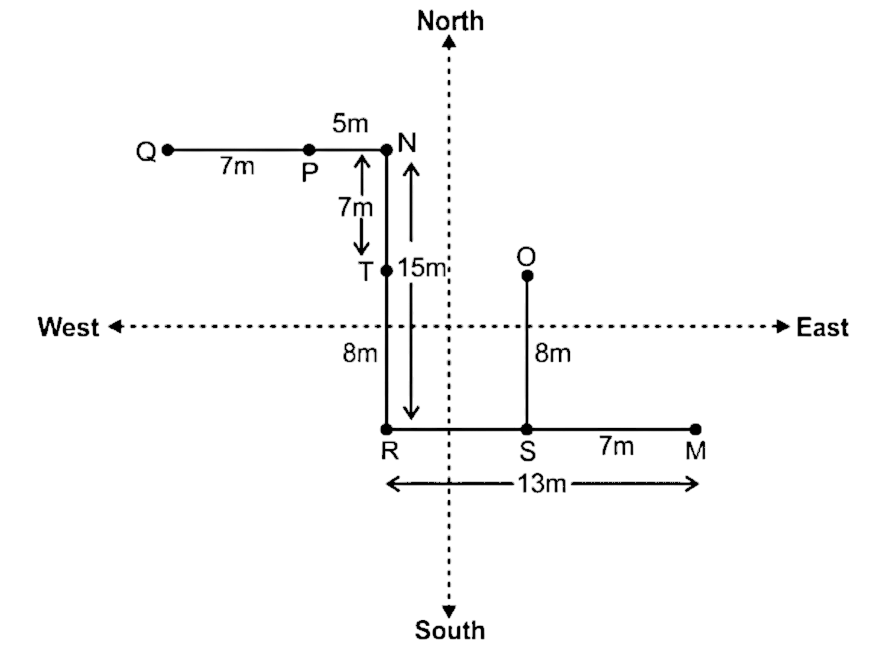
Hence, the distance between tree N and tree T will be 7m.
9. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Some house are home.
Some home are shop.
Some shop are grocery.
Conclusions:
I. All home are shop.
II. Some shop are not home.
A. None follows
B. Either I or II follows
C. Only I follows
D. Only II follows
E. Both I and II follow
Solution
The least possible venn diagram for the given statements is as follows:

Conclusion:
I. All home are shop → False (It is possible but not definite)
II. Some shop are not home → False (It is possible but not definite)
Hence, None follows.
10. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
All car are bike.
All bike are cycle.
Some bike are bus.
Conclusions:
I. All bus being cycle is a possibility.
II. No car is a bus.
A. None follows
B. Either I or II follows
C. Only I follows
D. Only II follows
E. Both I and II follow
Solution
The least possible venn diagram for the given statements is as follows:

Conclusion:
I. All bus being cycle is a possibility → True (Possibility is true as shown below)
II. No car is a bus → False (It is possible but not definite)
Hence, only I follows.
11. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Some movie are film.
Some film are best.
Some best are documentary.
Conclusions:
I. Some documentary are not movie.
II. All film are documentary.
A. None follows
B. Either I or II follows
C. Only I follows
D. Only II follows
E. Both I and II follow
Solution
The least possible venn diagram for the given statements is as follows:

Conclusions:
I. Some documentary are not movie → False (It is possible but not definite)
II. All film are documentary → False (It is possible but not definite)
Hence, none follows
Direction: Study the following information to answer the given questions:
There are 8 floors in a building. Seven persons M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S live on seven different floors of the building. One floor is vacant i. e. no one lives on that floor. The lowermost floor is numbered as 1, the floor above it as 2, and so on. Neither the lowermost nor topmost floor is vacant.Only one person lives below P’s floor. N lives two floors above P’s floor. O lives on floor 6. S lives just above M’s floor. R does not live adjacent to N’s floor. The number of floors below Q’s floor is half of the number of persons living above him.
12. Who lives on topmost floor?
A. M
B. N
C. Q
D. R
E. S
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S.
1) O lives on floor 6.
2) Only one person lives below P’s floor. So, P lives on either floor 2 or floor 3.
3) N lives two floors above P’s floor.
4) Neither the lowermost nor topmost floor is vacant. So, in case 2, floor 2 would be vacant.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 |
5) S lives just above M’s floor.
6) R does not live adjacent to N’s floor. So, R lives on floor 1.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | S | S |
| 7 | M | M |
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | Q |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 | R | R |
7) Number of floors below Q’s floor is half of the number of persons living above him. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given statement. Also, in case 1, floor 5 would be vacant and Q lives on floor 3.
| Floor | Person |
| 8 | S |
| 7 | M |
| 6 | O |
| 5 | Vacant |
| 4 | N |
| 3 | Q |
| 2 | P |
| 1 | R |
Hence, S lives on the topmost floor.
13. How many persons live above N’s floor?
A. Three
B. Four
C. Five
D. Two
E. One
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S.
1) O lives on floor 6.
2) Only one person lives below P’s floor. So, P lives on either floor 2 or floor 3.
3) N lives two floors above P’s floor.
4) Neither the lowermost nor topmost floor is vacant. So, in case 2, floor 2 would be vacant.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 |
5) S lives just above M’s floor.
6) R does not live adjacent to N’s floor. So, R lives on floor 1.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | S | S |
| 7 | M | M |
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | Q |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 | R | R |
7) Number of floors below Q’s floor is half of the number of persons living above him. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given statement. Also, in case 1, floor 5 would be vacant and Q lives on floor 3.
| Floor | Person |
| 8 | S |
| 7 | M |
| 6 | O |
| 5 | Vacant |
| 4 | N |
| 3 | Q |
| 2 | P |
| 1 | R |
Hence, three persons live above N’s floor.
14. Four are the same in a certain way thus forms a group. Which among the following does not belong to the group?
A. N
B. Q
C. O
D. P
E. S
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S.
1) O lives on floor 6.
2) Only one person lives below P’s floor. So, P lives on either floor 2 or floor 3.
3) N lives two floors above P’s floor.
4) Neither the lowermost nor topmost floor is vacant. So, in case 2, floor 2 would be vacant.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 |
5) S lives just above M’s floor.
6) R does not live adjacent to N’s floor. So, R lives on floor 1.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | S | S |
| 7 | M | M |
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | Q |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 | R | R |
7) Number of floors below Q’s floor is half of the number of persons living above him. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given statement. Also, in case 1, floor 5 would be vacant and Q lives on floor 3.
| Floor | Person |
| 8 | S |
| 7 | M |
| 6 | O |
| 5 | Vacant |
| 4 | N |
| 3 | Q |
| 2 | P |
| 1 | R |
All N, O, P and S live on the even-numbered floors except Q.
Hence, Q does not belong to the group.
15. Who lives just above R’s floor?
A. Q
B. P
C. S
D. M
E. O
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S.
1) O lives on floor 6.
2) Only one person lives below P’s floor. So, P lives on either floor 2 or floor 3.
3) N lives two floors above P’s floor.
4) Neither the lowermost nor topmost floor is vacant. So, in case 2, floor 2 would be vacant.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 |
5) S lives just above M’s floor.
6) R does not live adjacent to N’s floor. So, R lives on floor 1.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | S | S |
| 7 | M | M |
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | Q |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 | R | R |
7) Number of floors below Q’s floor is half of the number of persons living above him. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given statement. Also, in case 1, floor 5 would be vacant and Q lives on floor 3.
| Floor | Person |
| 8 | S |
| 7 | M |
| 6 | O |
| 5 | Vacant |
| 4 | N |
| 3 | Q |
| 2 | P |
| 1 | R |
Hence, “P” lives just above R’s floor.
16. Which of the following statement is correct?
A. M lives on floor 5
B. N lives on odd numbered floor
C. P lives just above Q’s floor
D. Floor 5 is a vacant floor
E. All are correct
Solution
Persons: M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S.
1) O lives on floor 6.
2) Only one person lives below P’s floor. So, P lives on either floor 2 or floor 3.
3) N lives two floors above P’s floor.
4) Neither the lowermost nor topmost floor is vacant. So, in case 2, floor 2 would be vacant.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 |
5) S lives just above M’s floor.
6) R does not live adjacent to N’s floor. So, R lives on floor 1.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Floor | Person | Person |
| 8 | S | S |
| 7 | M | M |
| 6 | O | O |
| 5 | N | |
| 4 | N | Q |
| 3 | P | |
| 2 | P | Vacant |
| 1 | R | R |
7) Number of floors below Q’s floor is half of the number of persons living above him. So, case 2 would be invalid as it contradicts the given statement. Also, in case 1, floor 5 would be vacant and Q lives on floor 3.
| Floor | Person |
| 8 | S |
| 7 | M |
| 6 | O |
| 5 | Vacant |
| 4 | N |
| 3 | Q |
| 2 | P |
| 1 | R |
Thus, floor 5 is a vacant floor statement is correct.
Hence, “Option (4)” is the correct answer.
17. How many pairs of digits are there in the given number, that have as many numbers between them as in the series of natural numbers both in the backward and forward direction?
69431852
A. Four
B. One
C. Three
D. Two
E. Seven
Solution
Given number: 69431852

Thus, we get three pairs,
Backward → (3, 4), (3, 6), (4, 6)
Hence, three is the correct answer.
Comprehension:(Que No. 18 – 21)
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain language,
“make him your senior partner” is coded as “kpa lpa bpa opa spa”
“harvey make mike smile” is coded as “dpa lpa tpa fpa”
“his partner harvey” is coded as “tpa spa cpa”“your smile matters” is coded as “xpa fpa opa”.
18. What is the code for “matters”?
A. xpa
B. cpa
C. fpa
D. opa
E. cannot be determined
Solution
The words are coded as given below:

Hence, “matters” will be coded as ‘xpa’.
19. What is the code for “mike?
A. kpa
B. dpa
C. fpa
D. tpa
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
The words are coded as given below:

Hence, the code for ‘mike’ is ‘dpa’.
20. What is the code for “senior”?
A. kpa
B. bpa
C. Either (1) or (2)
D. spa
E. cannot be determined
Solution
The words are coded as given below:

Hence, ‘senior’ will be coded as either ‘kpa’ or ‘bpa’.
21. What is the code for “his”?
A. tpa
B. spa
C. fpa
D. cpa
E. none of these
Solution
The words are coded as given below:

Hence, “his” will be coded as ‘cpa’.
Direction: On the basis of the alphabets given below, answer the following questions:
T R G S O I W P A Q D V E U X Z B Y C H F
22. How many such consonants are there in the above series, each of which is immediately preceded by a vowel and followed by a consonant?
A. Three
B. Two
C. One
D. Five
E. Six
Solution
Given series: Left side T R G S O I W P A Q D V E U X Z B Y C H F Right side
Such consonants that are immediately preceded by a vowel and followed by a consonant are:
T R G S O I W P A Q D V E U X Z B Y C H F
Thus, three consonants are immediately preceded by a vowel and followed by a consonant.
Hence, Three is the correct answer.
23. In the above alphabets, if each letter starting from S, is represented by the day of the week starting from Sunday, then what is the position of first occurring Sunday from the right?
A. Sixth
B. Seventh
C. Third
D. Eighth
E. Fourth
Solution
Let Sunday be represented by Su, Monday be Mo, Tuesday be Tu, Wednesday be We, Thursday be Th, Friday be Fr, Saturday be Sa in the following table.
Each letter starting from S is represented by the day of the week starting from Sunday:
| Alphabet | S | O | I | W | P | A | Q | D | V | E | U | X | Z | B | Y | C | H | F |
| Day | Su | Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa | Su | Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa | Su | Mo | Tu | We |
Hence, the position of first occurring Sunday from right is fourth.
23. How many such vowels are there in the above series, each of which is immediately preceded by a vowel and followed by a consonant?
A. Three
B. One
C. Two
D. Five
E. Six
Solution
Given series: Left side T R G S O I W P A Q D V E U X Z B Y C H F Right side
Such vowels that are immediately preceded by a vowel and followed by a consonant are:
T R G S O I W P A Q D V E U X Z B Y C H FHence, two vowels are immediately preceded by a vowel and followed by a consonant.
24. If all the vowels are dropped from the above arrangement, which letter will be the fourth letter to the left of the ninth letter from the left end?
A. P
B. W
C. A
D. I
E. S
Solution
Given series: Left side T R G S O I W P A Q D V E U X Z B Y C H F Right side
If all the vowels are dropped, the new series will be:
Left side T R G S W P Q D V X Z B Y C H F Right side
The ninth letter from the left side is V. T R G S W P Q D V X Z B Y C H F
The fourth letter to the left of V is W. T R G S W P Q D V
Hence, W is the correct answer.
25. If all the vowels are dropped from the above arrangement, which letter will be the fourth letter to the left of the ninth letter from the left end?
A. P
B. W
C. A
D. I
E. S
Solution
Given series: Left side T R G S O I W P A Q D V E U X Z B Y C H F Right side
If all the vowels are dropped, the new series will be:
Left side T R G S W P Q D V X Z B Y C H F Right side
The ninth letter from the left side is V. T R G S W P Q D V X Z B Y C H F
The fourth letter to the left of V is W. T R G S W P Q D V
Hence, W is the correct answer.
26. In the following letter series, which will replace the question mark (?)?PQD, IVQ, SUA, ?, FYW
A. RSO
B. TGS
C. SPE
D. RZP
E. QUX
Solution
Given series: Left side T R G S O I W P A Q D V E U X Z B Y C H F Right side
1) First letters are forming different series:
P – 2 = I
I – 2 = S
S – 2 = R
R – 2 = F
2) Secondletters are forming different series:
Q + 2 = V
V + 2 = U
U + 2 = Z
Z + 2 = Y
3) Third letters are forming different series:
D – 1 = Q
Q – 1 = A
A – 1 = P
P – 1 = WHence, the word formed is RZP.
27. Direction:In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
L > M ≥ O; N = E ≤ M
Conclusions:
I. L > NII. E < L
A. Only II is true
B. Only I is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. Either I or II is true
E. None is true
Solution
Given Statements: L > M ≥ O; N = E ≤ M
On Combining: L > M ≥ E = N; N = E ≤ M ≥ O
Conclusions:
I. L > N → True (As, L > M ≥ E = N → L > N = E or E = N < L)
II. E < L → True (As, L > M ≥ E = N → L > E = N or N = E < L)
Hence, both the conclusions are true
28. Direction:In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
W ≥ Z = B < O; B < F ≤ Q
Conclusions:
I. Q > Z
II. B = Q
A. Only II is true
B. Only I is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. Either I or II is true
E. None is true
Solution
Given Statements: W ≥ Z = B < O; B < F ≤ Q
On Combining: W ≥ Z = B < F ≤ Q; Q ≥ F > Z = B < O
Conclusions:
I. Q > Z → True (As, Q ≥ F > Z = B < O → Q > Z = B)
II. B = Q → False (As, Q ≥ F > Z = B < O → Q > Z = B)
Hence, only conclusion I is true
29. Direction:In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements:
L > J > M; M = H; J < O = P
Conclusions:
I. H < O
II. J ≥ M
A. Only II is true
B. Only I is true
C. Both I and II are true
D. Either I or II is true
E. None is true
Solution
Given Statements: L > J > M; M = H; J < O = P
On Combining: P = O > J > M = H; L > J < O = P
Conclusions:
I. H < O → True (As, P = O > J > M = H → O > H or H < O)
II. J ≥ M → False (As, J > M or M < J)
Hence, only conclusion I is true.
Directions: Study the given information and answer the questions that follows:
There are 6 friends and their names are Aniket, Bankim, Chinmay, Dhruv, Ekansh and Farooq. Each of them have different heights.
Farooq is second tallest among all while Bankim is not the shortest. Chinmay is taller than Dhruv and Aniket but shorter than Farooq. Aniket is taller than only one person who is definitely not Dhruv.
30. Who is the tallest among all six friends?
A. Bankim
B. Aniket
C. Chinmay
D. Dhruv
E. Ekansh
Solution
1. Farooq is second tallest among all.
____> Farooq > ____ > ____ > ____ > ____
2. Aniket is taller than only one person.
____> Farooq > ____ >____ >Aniket ____
3. Chinmay is taller than Dhruv and Aniket but shorter than Farooq.
4. Aniket is taller than only person who is definitely not Dhruv.
____ > Farooq > Chinmay > Dhruv > Aniket > ____
5. Bankim is not the shortest.
Bankim > Farooq > Chinmay > Dhruv > Aniket > Ekansh
Hence, Bankim is the tallest among all.
31. How many people are taller than Aniket?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. None
Solution
1. Farooq is second tallest among all.
____> Farooq > ____ > ____ > ____ > ____
2. Aniket is taller than only one person.
____> Farooq > ____ >____ >Aniket ____
3. Chinmay is taller than Dhruv and Aniket but shorter than Farooq.
4. Aniket is taller than only person who is definitely not Dhruv.
____ > Farooq > Chinmay > Dhruv > Aniket > ____
5. Bankim is not the shortest.
Bankim > Farooq > Chinmay > Dhruv > Aniket > Ekansh
Hence, 4 people are taller than Aniket.
32. Who is/are taller than Dhruv but shorter than Bankim?
A. Aniket
B. Chinmay
C. Farooq
D. Aniket and Chinmay both
E. Chinmay and Farooq both
Solution
1. Farooq is second tallest among all.
____> Farooq > ____ > ____ > ____ > ____
2. Aniket is taller than only one person.
____> Farooq > ____ >____ >Aniket ____
3. Chinmay is taller than Dhruv and Aniket but shorter than Farooq.
4. Aniket is taller than only person who is definitely not Dhruv.
____ > Farooq > Chinmay > Dhruv > Aniket > ____
5. Bankim is not the shortest.
Bankim > Farooq > Chinmay > Dhruv > Aniket > Ekansh
Hence, Chinamy and Farooq both are taller than Dhruv but shorter than Bankim.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
A family consists of seven members and two married couples. Either both the parents of a person are alive or neither of them is alive. B is the father-in-law of O. P is the brother-in-law of O. O and P has same gender. S is the only daughter of V, who is the maternal grandmother of H. P has only one brother. H is the niece of G.
33. How G is related to S?
A. Sister
B. Brother
C. Sister-in-law
D. Brother-in-law
E. Can’t be determined
Solution
As per the given information,
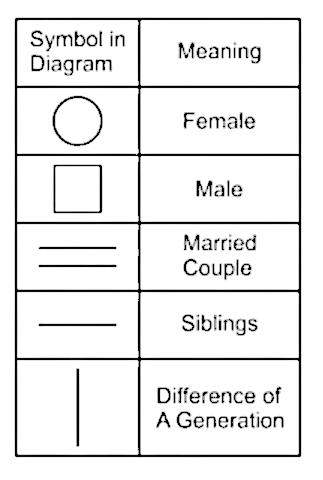
1)B is the father-in-law of O.
2) P is the brother-in-law of O. O and P has same gender.
3) S is the only daughter of V, who is the maternal grandmother of H.
4) P has only one brother. H is the niece of G.

Hence, G is the brother of S.
34. Which of the following statement is true?
A. B has only one son
B. V is the mother-in-law of P
C. V has three children
D. H is the only son of O
E. None of the above
Solution
As per the given information,
1)B is the father-in-law of O.
2) P is the brother-in-law of O. O and P has same gender.
3) S is the only daughter of V, who is the maternal grandmother of H.
4) P has only one brother. H is the niece of G.

Hence, V has three children is the correct answer.
35. Who among the following is Uncle of H?
A. G
B. P
C. S
D. B
E. Both G and P
Solution
As per the given information,
1)B is the father-in-law of O.
2) P is the brother-in-law of O. O and P has same gender.
3) S is the only daughter of V, who is the maternal grandmother of H.
4) P has only one brother. H is the niece of G.

Hence, Both G and P are the uncles of H.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
In an organisation, there are eight persons Sanju, Jay, Athul, Gopu, Aswin, Raghu, Kripa, and Rahul went to tour on three different tourist spots. The tourist spots are Paris, Kashmir, and New York. At least two persons went to a tourist spot and at most three persons went to a tourist spot.
Athul and Kripa went on tour together to the same place. Rahul doesn’t go to Paris. Gopu doesn’t go to Kashmir. Gopu went on tour with Rahul to the same place. More than two people went on tour to Paris. Jay went on tour with two other people but not in New York. Sanju went on tour with Raghu only.
36. Who among the following went to Paris?
A. Kripa
B. Jay
C. Athul
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
Solution
Given Details
Eight persons Sanju, Jay, Athul, Gopu, Aswin, Raghu, Kripa, and Rahul.
The tourist spots are Paris, Kashmir, and New York.
At least two persons went to a tourist spot and at most three persons went to a tourist spot.
Gopu doesn’t go to Kashmir.
Gopu went on tour with Rahul to the same place.
Rahul doesn’t go to Paris.
From these, we get that Gopu and Rahul went to New York.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Sanju went on tour with Raghu only.
More than two people went on tour to Paris.
From these we get, Sanju and Raghu went tour to Kashmir
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Jay went on tour with two other people but not in New York.
Athul and Kripa went on tour together to the same place.
From these, we get that Jay went with Athul and Kripa to Paris while Aswin went to New York.
Final arrangement.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | Athul, Jay, Kripa |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul, Aswin |
From the final arrangement we get, Athul, Jay, and Kripa went tour to Paris. So the answer is All of the above.
37. Which touring spot was chosen by Gopu for tour?
A. New York
B. Paris
C. Kashmir
D. None
E. All of the above
Solution
Given Details
Eight persons Sanju, Jay, Athul, Gopu, Aswin, Raghu, Kripa, and Rahul.
The tourist spots are Paris, Kashmir, and New York.
At least two persons went to a tourist spot and at most three persons went to a tourist spot.
Gopu doesn’t go to Kashmir.
Gopu went on tour with Rahul to the same place.
Rahul doesn’t go to Paris.
From these, we get that Gopu and Rahul went to New York.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Sanju went on tour with Raghu only.
More than two people went on tour to Paris.
From these we get, Sanju and Raghu went tour to Kashmir
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Jay went on tour with two other people but not in New York.
Athul and Kripa went on tour together to the same place.
From these, we get that Jay went with Athul and Kripa to Paris while Aswin went to New York.
Final arrangement.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | Athul, Jay, Kripa |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul, Aswin |
From the final arrangement we get, Gopu went on tour to New York.
38. To which place did Sanju and Raghu go together?
A. New York
B. Kashmir
C. Paris
D. None of the above
E. All of the above
Solution
Given Details
Eight persons Sanju, Jay, Athul, Gopu, Aswin, Raghu, Kripa, and Rahul.
The tourist spots are Paris, Kashmir, and New York.
At least two persons went to a tourist spot and at most three persons went to a tourist spot.
Gopu doesn’t go to Kashmir.
Gopu went on tour with Rahul to the same place.
Rahul doesn’t go to Paris.
From these, we get that Gopu and Rahul went to New York.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Sanju went on tour with Raghu only.
More than two people went on tour to Paris.
From these we get, Sanju and Raghu went tour to Kashmir
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Jay went on tour with two other people but not in New York.
Athul and Kripa went on tour together to the same place.
From these, we get that Jay went with Athul and Kripa to Paris while Aswin went to New York.
Final arrangement.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | Athul, Jay, Kripa |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul, Aswin |
From the final arrangement we get, Sanju went to Kashmir with Raghu.
39. With whom did Rahul go on tour?
A. Raghu
B. Aswin
C. Athul
D. Jay
E. Kripa
Solution
Given Details
Eight persons Sanju, Jay, Athul, Gopu, Aswin, Raghu, Kripa, and Rahul.
The tourist spots are Paris, Kashmir, and New York.
At least two persons went to a tourist spot and at most three persons went to a tourist spot.
Gopu doesn’t go to Kashmir.
Gopu went on tour with Rahul to the same place.
Rahul doesn’t go to Paris.
From these, we get that Gopu and Rahul went to New York.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Sanju went on tour with Raghu only.
More than two people went on tour to Paris.
From these we get, Sanju and Raghu went tour to Kashmir
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Jay went on tour with two other people but not in New York.
Athul and Kripa went on tour together to the same place.
From these, we get that Jay went with Athul and Kripa to Paris while Aswin went to New York.
Final arrangement.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | Athul, Jay, Kripa |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul, Aswin |
From the final arrangement we get, Rahul went on tour with Aswin.
40. Who among the following went to Kashmir?
A. Sanju
B. Gopu
C. Aswin
D. Jay
E. Kripa
Solution
Given Details
Eight persons Sanju, Jay, Athul, Gopu, Aswin, Raghu, Kripa, and Rahul.
The tourist spots are Paris, Kashmir, and New York.
At least two persons went to a tourist spot and at most three persons went to a tourist spot.
Gopu doesn’t go to Kashmir.
Gopu went on tour with Rahul to the same place.
Rahul doesn’t go to Paris.
From these, we get that Gopu and Rahul went to New York.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Sanju went on tour with Raghu only.
More than two people went on tour to Paris.
From these we get, Sanju and Raghu went tour to Kashmir
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul |
Jay went on tour with two other people but not in New York.
Athul and Kripa went on tour together to the same place.
From these, we get that Jay went with Athul and Kripa to Paris while Aswin went to New York.
Final arrangement.
| Tourist Spot | Names of People |
| Paris | Athul, Jay, Kripa |
| Kashmir | Sanju, Raghu |
| New York | Gopu, Rahul, Aswin |
From the final arrangement we get Sanju went to Kashmir.
Numerical Ability
41.In the following number series, the wrong number is given, find out that number.
123, 121, 111, 99, 83, 63
A. 121
B. 111
C. 99
D. 83
E. 123
Solution
The pattern followed by the series is
123 – 4 = 119
119 – 8 = 111
111 – 12 = 99
99 – 16 = 83
83 – 20 = 63
42. In each of the following number series, the wrong number is given, find out that number.
11, 13, 16, 21, 28, 37
A. 21
B. 13
C. 28
D. 37
E. 16
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
11 + 2 = 13
13 + 3 = 16
16 + 5 = 21
21 + 7 = 28
28 + 11 = 39
∴ The wrong term in the series is 37.
43. In each of the following number series, a wrong number is given. Find out that number.
280, 270, 240, 210, 130, -30
A. 270
B. 240
C. 210
D. 130
E. -30
Solution
The series follows the following pattern
280 – 10 = 270
270 – 20 = 250
250 – 40 = 210
210 – 80 = 130
130 – 160 = – 30
∴ The wrong number in the series is 240
44. In each of the following number series, the wrong number is given, find out that number.
122, 171, 228, 291, 366, 447
A. 228
B. 171
C. 291
D. 447
E. 366
Solution
The series follows the following pattern:
112 + 1 = 122
132 + 2 = 171
152 + 3 = 228
172 + 4 = 293
192 + 5 = 366
212 + 6 = 447
∴ The wrong term in the series is 291.
45. In each of the following number series, the wrong number is given, find out that number.4, 7, 15, 30, 54, 91, 137
A. 54
B. 30
C. 15
D. 7
E. 91
Solution
We can observe the pattern: (Double difference series)

∴ 91 is the wrong term and must be replaced with 89.
There are two areas in Jaipur – Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar. The total population of Vaishali Nagar is 300 more than the total population of Mansarovar. 40% of total population of Mansarovar is doctors and 60% of total population of Vaishali Nagar is doctors. The ratio of male to female doctors in Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar is 4 ∶ 5 and 7 ∶ 5 respectively and the total population of Mansarovar is 900.
46. What is the product of average of total male doctors from both areas and the average of female doctors from both area?
A. 85000
B. 82500
C. 70000
D. 72500
E. None of these
Solution
Given that:
Total population of Mansarovar = 900
Total doctors in Mansarovar = 40% of 900 = 360
Ratio of male and female doctors in Mansarovar = 4 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 4/9 = 160
Female doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 5/9 = 200
Now, total population of Vaishali Nagar =(900 + 300) = 1200
Total doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 60% of 1200 = 720
Ratio of male and female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 7 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 7/12 = 420
Female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 5/12 = 300
| Number of doctor | Male doctor | Female doctor | Total | |
| Mansarovar | 360 | 160 | 200 | 900 |
| Vaishali Nagar | 720 | 420 | 300 | 1200 |
Formula:
Average = sum of total doctors in areas/no. of areas
Calculation:
Average of male doctors = (160 + 420)/2 = 580/2 = 290
Average of Female doctors = (200 + 300)/2 = 250
Required product = 290 × 250 = 72500
∴ Product is 72500.
There are two areas in Jaipur – Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar. The total population of Vaishali Nagar is 300 more than the total population of Mansarovar. 40% of total population of Mansarovar is doctors and 60% of total population of Vaishali Nagar is doctors. The ratio of male to female doctors in Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar is 4 ∶ 5 and 7 ∶ 5 respectively and the total population of Mansarovar is 900.
47. 30% of the number of Male doctors in Mansarovar are what percent of the 120% of the number of female doctors in Vaishali Nagar?
A. 10%
B. 11%
C. 13.33%
D. 16%
E. None of these
Solution
Given that:
Total population of Mansarovar = 900
Total doctors in Mansarovar = 40% of 900 = 360
Ratio of male and female doctors in Mansarovar = 4 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 4/9 = 160
Female doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 5/.9 = 200
Now, total population of Vaishali Nagar =(900 + 300) = 1200
Total doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 60% of 1200 = 720
Ratio of male and female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 7 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 7/12 = 420
Female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 5/12 = 300
| Number of doctor | Total Doctors | Male doctor | Female Doctors | |
| Mansarovar | 360 | 160 | 200 | 900 |
| Vaishali Nagar | 720 | 420 | 300 | 1200 |
According to the question,
30% of the number of Male doctors in Mansarovar =160 × 30/100 = 48
120% of the number of Female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 300 × 120/100 = 360
Required% = (48/360) × 100
⇒ 13.33%
∴ required percent is 13.33%.
There are two areas in Jaipur – Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar. The total population of Vaishali Nagar is 300 more than the total population of Mansarovar. 40% of total population of Mansarovar is doctors and 60% of total population of Vaishali Nagar is doctors. The ratio of male to female doctors in Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar is 4 ∶ 5 and 7 ∶ 5 respectively and the total population of Mansarovar is 900.
48. Total Male doctors from both areas are how much more or less than total population of Mansarovar?
A. 500
B. 620
C. 400
D. 320
E. None of these
Solution
Given that:
Total population of Mansarovar = 900
Total doctors in Mansarovar = 40% of 900 = 360
Ratio of male and female doctors in Mansarovar = 4 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 4/9 = 160
Female doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 5/.9 = 200
Now, total population of Vaishali Nagar =(900 + 300) = 1200
Total doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 60% of 1200 = 720
Ratio of male and female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 7 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 7/12 = 420
Female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 5/12 = 300
| Total doctor | Male doctor | Female doctor | ||
| Mansarovar | 360 | 160 | 200 | 900 |
| Vaishali Nagar | 720 | 420 | 300 | 1200 |
Formula:
Required difference = (total population of Mansarovar – total Male doctors of both areas)
Calculation:
Male doctors in both areas = 160 + 420 = 580
Population of Mansarovar = 900
Difference = 900 – 580 = 320
∴ Total Male doctors form both areas are 320 less than total population of Mansarovar.
There are two areas in Jaipur – Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar. The total population of Vaishali Nagar is 300 more than the total population of Mansarovar. 40% of total population of Mansarovar is doctors and 60% of total population of Vaishali Nagar is doctors. The ratio of male to female doctors in Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar is 4 ∶ 5 and 7 ∶ 5 respectively and the total population of Mansarovar is 900.
49. What is the ratio of Male doctors from Mansarovar to Female doctors from Vaishali Nagar?
A. 3 : 2
B. 15 : 8
C. 2 : 3
D. 8 : 15
E. None of these
Solution
Given that:
Total population of Mansarovar = 900
Total doctors in Mansarovar = 40% of 900 = 360
Ratio of male and female doctors in Mansarovar = 4 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 4/9 = 160
Female doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 5/.9 = 200
Now, total population of Vaishali Nagar =(900 + 300) = 1200
Total doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 60% of 1200 = 720
Ratio of male and female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 7 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 7/12 = 420
Female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 5/12 = 300
| Number of doctor | Male doctor | Female doctor | Total | |
| Mansarovar | 160 | 200 | 360 | 900 |
| Vaishali Nagar | 420 | 300 | 720 | 1200 |
Formula:
Required ratio = Male doctors of Mansarovar ∶ Female doctors of Vaishali Nagar
Calculation:
Required ratio = 160 ∶ 300
⇒ 8 ∶ 15
∴ The ratio of Male doctors of Mansarovar to Female doctors of Vaishali Nagar is 8 ∶ 15.
There are two areas in Jaipur – Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar. The total population of Vaishali Nagar is 300 more than the total population of Mansarovar. 40% of total population of Mansarovar is doctors and 60% of total population of Vaishali Nagar is doctors. The ratio of male to female doctors in Mansarovar and Vaishali Nagar is 4 ∶ 5 and 7 ∶ 5 respectively and the total population of Mansarovar is 900. 10
50. Total number of Female doctors from both areas is what percent more or less than total population of Vaishali Nagar?
A. 55.33%
B. 56%
C. 58.33%
D. 50%
E. None of these
Solution
Given that:
Total population of Mansarovar = 900
Total doctors in Mansarovar = 40% of 900 = 360
Ratio of male and female doctors in Mansarovar = 4 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 4/9 = 160
Female doctors in Mansarovar = 360 × 5/9 = 200
Now, total population of Vaishali Nagar =(900 + 300) = 1200
Total doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 60% of 1200 = 720
Ratio of male and female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 7 ∶ 5
So, the Male doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 7/12 = 420
Female doctors in Vaishali Nagar = 720 × 5/12 = 300
| Number of doctor | Total doctor | Male doctor | Female Doctor | |
| Mansarovar | 360 | 160 | 200 | 900 |
| Vaishali Nagar | 720 | 420 | 300 | 1200 |
Formula:
Required% = [(difference of total Female doctors of of both areas and total population of Vaishali Nagar)/total population of Vaishali Nagar ] × 100
Calculation:
Total Female doctors of both areas = 200 + 300 = 500
Total population of Vaishali Nagar = 1200
Required% = [(1200 – 500)/1200]× 100
⇒ 700/12 = 58.33%
∴ the required answer is 58.33%
51. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + x – 6 = 0
II. y2 – 11y + 18 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. x2 + x – 6 = 0
⇒ x2 + 3x – 2x – 6 = 0
⇒ x(x + 3) – 2(x + 3) = 0
⇒ (x + 3) (x – 2) = 0
⇒ x = –3, 2
II. y2 – 11y + 18 = 0
⇒ y2 – 2y – 9y + 18 = 0
⇒ y(y – 2) – 9(y – 2) = 0
⇒ (y – 2) (y – 9) = 0
⇒ y = 2, 9
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| –3 | 2 | x < y |
| –3 | 9 | x < y |
| 2 | 2 | x = y |
| 2 | 9 | x < y |
∴ x ≤ y
52. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 8x2 + 10x + 3 = 0
II. 2y2 + 17y + 21 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. 8x2 + 10x + 3 = 0
⇒ 8x2 + 6x + 4x + 3 = 0
⇒ (2x + 1) (4x + 3) = 0
⇒ x = -1/2, -3/4
II. 2y2 + 17y + 21 = 0
⇒ 2y2 + 14y + 3y + 21= 0
⇒ (2y + 3) (y + 7) = 0
⇒ y = -3/2, -7
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| -1/2 | -3/2 | x > y |
| -1/2 | -7 | x > y |
| -3/4 | -3/2 | x > y |
| -3/4 | -7 | x > y |
∴ x > y.
53. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 11x + 28 = 0
II. y2 + 10y + 21 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
Calculations:
I. x2 + 11x + 28 = 0
⇒ x2 + 7x + 4x + 28 = 0
⇒ x(x + 7) + 4(x + 7) = 0
⇒ (x + 4) (x + 7) = 0
⇒ x = –4, –7
II. y2 + 10y + 21 = 0
⇒ y2 + 7y + 3y + 21 = 0
⇒ y(y + 7) + 3(y + 7) = 0
⇒ (y + 7) (y + 3) = 0
⇒ y = –3, –7
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| –4 | –3 | x < y |
| –4 | –7 | x > y |
| –7 | –3 | x < y |
| –7 | –7 | x = y |
Comparison between x and y (via Line graph):

∴ x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
54. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 18x + 72 = 0
II. y2 + 12y + 36 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or the relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. x2 + 18x + 72 = 0
⇒ x2 + 6x + 12x + 72 = 0
⇒ x(x + 6) + 12 (x + 6) = 0
⇒ (x + 6) (x + 12) = 0
⇒ x = – 6, – 12
II. y2 + 12y + 36 = 0
⇒ y2 + 6y + 6y + 36 = 0
⇒ y (y + 6) + 6 (y + 6) = 0
⇒ (y + 6) (y + 6) = 0
⇒ y = – 6, – 6
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| -6 | -6 | x = y |
| -6 | -6 | x = y |
| -12 | -6 | x < y |
| -12 | -6 | x < y |
Comparison between x and y (via Line graph):

Hence, x ≤ y
55. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 13x + 30 = 0
II. y2+ 5y + 4 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established.
Solution
I. x2 – 13x + 30 = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x – 10x + 30 = 0
⇒ (x – 3) (x – 10) = 0
⇒ x = 3, 10
II. y2+ 5y + 4 = 0
⇒ y2 + y + 4y + 4 = 0
⇒ (y + 4) (y + 1) = 0
⇒ y = –4, –1
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 3 | –4 | x > y |
| 3 | –1 | x > y |
| 10 | –4 | x > y |
| 10 | –1 | x > y |
Hence, x > y.
Shortcut Trick
When two equations are in the form as below
a1x2 – b1x + c1 = 0
a2y2 + b2y + c2 = 0
Answer will be always x > y.
56. There are two positive numbers in the ratio 2 : 7. If the larger number exceeds the smaller number by 15, then find the smaller number.
A. 5
B. 4
C. 6
D. 7
E. 3
Solution
Given:
The difference between the numbers is 15
The ratio of two numbers is 2 : 7
Calculation:
Let the numbers be 2x and 7x
According to the question,
7x – 2x = 15
⇒ 5x = 15
⇒ x = 3
⇒ Smaller number = 2x = 2 × 3 = 6
∴ The smaller number is 6.
57. In what ratio must milk costing Rs. 6.50 per litre be mixed with water costing Rs. 14 per litre, so that the mixture be worth Rs. 12 per litre?
A. 4 : 7
B. 7 : 4
C. 4 : 11
D. 11 : 4
E. 1 : 1
Solution
Given:
The cost of milk per litre = Rs. 6.50
The cost of water per litre = Rs. 14
The cost of mixture per litre = Rs. 12
Concept:
Alligation method,

The required ratio = (Y – M) : (M – X)
Calculation:
By alligation method,

Required ratio = 2 : 5.50
⇒ 2 : (11/2)
⇒ 4 : 11
∴ The required ratio will be 4 : 11.
58. A boat travels 88 kms downstream and 65 km upstream in 9 hours while it travels 121 km downstream and 97.5 km upstream in 13 hours. Find the speed of stream(in km/hr).
A. 1.5
B. 2.5
C. 3.5
D. 4.5
E. 5.5
Solution
Given:-
Time for 88 kms downstream and 65 km upstream = 9 hours
Time for 121 kms downstream and 97.5 km upstream = 13 hours
Formula:-
Speed = Distance/Time
Downstream speed = u + v
Upstream speed = u – v
Boat speed = ½ (D + U)
Stream speed = ½ (D – U)
U and v are boat and stream speeds and D and U downstream and upstream speeds.
Calculation:-
88/(u + v) + 65/(u – v) = 9
121/(u + v) + 97.5/(u – v) = 13
Let 1/(u + v) = x and 1/(u – v) = y
88x + 65y = 9
121x + 97.5y = 13
Solving both, x = 1/22 and y = 1/13
Or U = 13 and D = 22
V = ½ (22 – 13) = 4.5 km/hr
59. The area of a square is 441 sq cm and its side is half of the radius of a circle. Find the circumference of the circle.
A. 264 cm
B. 484 cm
C. 286 cm
D. 584 cm
E. 224 cm
Solution
Given:
Area of a square = 441 sq cm
Side of the square = (1/2) of the radius of the circle
Formula used:
Area of a square = (Side)2
Circumference of a circle = 2πr
Calculation:
Let a be the side of a square.

441 = (a)2
⇒ a = 21
Radius of the circle = 2 × 21 = 42
⇒ Circumference of the circle = 2 × (22/7) × 42
⇒ Circumference of the circle = 264
∴ The circumference of the circle is 264 cm.
60. A can finish a work in 6 days. B can finish a work in 10 days. What is the ratio of the amounts that A and B would be paid for the same amount of work if they finish it individually.
A. 3 : 4
B. 4 : 5
C. 5 : 3
D. 2 : 1
E. 3 : 2
Solution
Ratio of A and B one day’s work = 1/6 : 1/10 = 5 : 3.Hence, ratio of amounts they will be paid for the same amount of work = 5 : 3.
61. What will come in the place of the question mark ? in the following question ?
12% of 220 – 11% of 240 + 462 = ?2
A. 56
B. 66
C. 34
D. 46
E. 52
Solution
Solution :
Concept used :
Follow the BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the question is given below:
Step 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘ Brackets ‘ must be solved first and in the bracket,
Step 2: Any mathematical ‘ of ‘ or ‘exponent’ must be solved next,
Step 3: Next, The part of the equation that contains ‘Division’ and ‘multiplication’ are calculated,
Step 4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contains ‘Addition ‘ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated
Given :
⇒ 12% of 220 – 11% of 240 + 462 = ?2
⇒ 12 × 220 / 100 – 11 × 240 / 100 + 462 = ?2
⇒ 1.2 × 22 – 11 × 2.4 + 462 = ?2
⇒ 26.4 – 26.4 + 462 = ?2
⇒ 462 = ?2
⇒ ? = 46
Hence 46 is the correct answer.
62. Fill in the question mark (?) in the equation:
? = 18% of 850 + 22% of 700
A. 307
B. 317
C. 327
D. 337
E. 347
Solution
Concept Used:
Apply the BODMAS rule.
Calculation:
? = 18% of 850 + 22% of 700
? = (18/100) × 850 + (22/100) × 700
? = 153 + 154
∴ ? = 307
63. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
125 × 20% – 130 × 30% + ? = 515 + 52
A. 382
B. 581
C. 591
D. 335
E. 585
Solution
Given:
125 × 20% – 130 × 30% + ? = 515 + 52
Concept used:
Follow the ‘BODMAS’ Rule
B ⇒ Bracket, O ⇒ of, D ⇒ Division, M ⇒ Multiplication, A ⇒ Add, S ⇒ Subtraction
Calculation:
⇒ 125 × 20% – 130 × 30% + ? = 515 + 52
⇒ 25 – 39 + ? = 567
⇒ -14 + ? = 567
⇒ ? = 581
∴ The value of ? is 581.
64. What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
152 – 45 × 2 + 8 × 4 = ?
A. 125
B. 167
C. 143
D. 165
E. 109
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
152 – 45 × 2 + 8 × 4 = ?
⇒ 225 – 90 + 32 = ?
⇒ 257 – 90 = ?
⇒ 167 = ?
∴ The correct answer is 167.
65. What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
(3/5×125)÷(9/3)+12=?
A. 48
B. 37
C. 53
D. 26
E. 62
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
(35×125)÷(93)+12=?(35×125)÷(93)+12=?
75 ÷ 3 + 12 = ?
25 + 12 = ?
∴ 37 will come in place of the question mark
66. What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
96 ÷ 8 × 6 – 14 + 72 ÷ 9 = ?
A. 45
B. 32
C. 66
D. 57
E. 78
Solution
Concept Used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below,

Calculation:
96 ÷ 8 × 6 – 14 + 72 ÷ 9 = ?
12 × 6 – 14 + 8 = ?
72 – 14 + 8 = ?
58 + 8 = ?
∴ 66 will come in place of the question mark
67. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
40% of 75 + 32% of 350 + 36 ÷ 18 = ?
A. 244
B. 104
C. 204
D. 144
E. 124
Solution
Given:
40% of 75 + 32% of 350 + 36 ÷ 18 = ?
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the given table below:

Calculation:
40% of 75 + 32% of 350 + 36 ÷ 18 = ?
⇒ (40/100) × 75 + (32/100) × 350 + 2 = ?
⇒ (2/5) × 75 + (8/25) × 350 + 2 = ?
⇒ 30 + 112 + 2 = ?
⇒ ? = 144
∴ 144 should come in place of the question mark (?).
68. A transistor was sold at a profit of 20%. If it would have been sold for Rs. 80 less, the profit would have been 15%. What was the cost price of the transistor?
A. Rs. 1,360
B. Rs. 1,600
C. Rs. 1,840
D. Rs. 1,920
E. Rs. 2,000
Solution
Calculation:
Let the cost price be x
1st condition,
S.P. = C.P. × 120% = 1.2x
2nd condition,
S.P. = C.P. × 115% = 1.15x
According to the condition,
⇒ 1.2x – 1.15x = 80
⇒ 0.05x = 80
⇒ x = 80/0.05
⇒ x = 8000/5
∴ x = Rs. 1600
69. If a sum of money yields Rs. 900 as simple interest at 10% p.a. after 3 years. Then, the same sum of money will yield how much compound interest at 20% p.a. in the same time?
A. Rs. 1956
B. Rs. 1834
C. Rs. 2184
D. Rs. 1856
E. Rs. 2298
Solution
Given:
SI = Rs. 900, rate = 10%, time = 3 years
For CI, rate = 20%, time = 3 years
Formula:
SI = P × R × T/100
CI = P[(1 + R/100)n – 1]
Calculation:
Let the principal be P
900 = 3 × 10 × P/100
⇒ P = Rs. 3000
Now, compound interest after 3 years will be,
∴ CI = 3000[(1 + 20/100)3 – 1]
= 3000 × (91/125) = Rs. 2184
70. Average of x numbers is y3 and the average of y numbers is x3. So find the average of all the numbers taken together ?
A. ![]()
B. 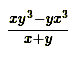
C. 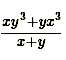
D. 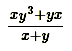
E. 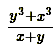
Solution
Given:
Average of x numbers is y3
the average of y numbers is x3
Formula used:
Average = Total Sum/Number Of Terms
Calculation:
Total sum of x numbers = x × y3
= xy3
Total sum of y numbers = y × x3
= yx3
Average of all the numbers = 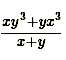
Answer is 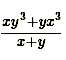
Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total number of candidates who qualified for SBI PO in 6 different years and the ratio of boys to girls in them.
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2014 | 1500 | 3 : 2 |
| 2015 | 1800 | 7 : 2 |
| 2016 | 2200 | 5 : 6 |
| 2017 | 2600 | 8 : 5 |
| 2018 | 3000 | 8 : 7 |
| 2019 | 3200 | 5 : 3 |
71. What is the ratio of the total number of girls to the total number of boys who qualified for the SBI PO exam in the years 2015, 2017 and 2019 together?
A. 12 : 25
B. 13 : 25
C. 25 : 13
D. 25 : 12
E. 11 : 25
Solution
Given:
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2015 | 1800 | 7 : 2 |
| 2017 | 2600 | 8 : 5 |
| 2019 | 3200 | 5 : 3 |
Calculation:
The number of girls who qualified for the SBI PO exam in the year 2015 = {2/(2 + 7)} × 1800
⇒ (2/9) × 1800
⇒ 400
The number of boys who qualified for the SBI PO exam in the year 2015 = 1800 – 400
⇒ 1400
Similarly,
| Year | Number of girls | Number of boys |
| 2015 | (2/9) × 1800 = 400 | 1800 – 400 = 1400 |
| 2017 | (5/13) × 2600 = 1000 | 2600 – 1000 = 1600 |
| 2019 | (3/8) × 3200 = 1200 | 3200 – 1200 = 2000 |
The total number of girls who qualified for the SBI PO exam in the years 2015, 2017 and 2019 together = 400 + 1000 + 1200
⇒ 2600
The total number of boys who qualified for the SBI PO exam in the years 2015, 2017 and 2019 together = 1400 + 1600 + 2000
⇒ 5000
The required ratio = 2600/5000
⇒ 13 : 25
∴ The ratio of the total number of girls to the total number of boys who qualified for the SBI PO exam in the years 2015, 2017 and 2019 together will be 13 : 25.
Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total number of candidates who qualified for SBI PO in 6 different years and the ratio of boys to girls in them.
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2014 | 1500 | 3 : 2 |
| 2015 | 1800 | 7 : 2 |
| 2016 | 2200 | 5 : 6 |
| 2017 | 2600 | 8 : 5 |
| 2018 | 3000 | 8 : 7 |
| 2019 | 3200 | 5 : 3 |
72. The number of boy candidates who qualified in the Year 2015 approximately what percent of the total number of candidates who qualified for the exam in the year 2016?
A. 50%
B. 63.64%
C. 68%
D. 73.74%
E. 70%
Solution
Given:
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2015 | 1800 | 7 : 2 |
| 2016 | 2200 | 5 : 6 |
Calculation:
The number of boy candidates who qualified in the year 2015 = {7/(2 + 7)} × 1800
⇒ (7/9) × 1800
⇒ 1400
The total number of candidates who qualified for the exam in the year 2016 = 2200
The required percentage = (1400/2200) × 100
⇒ 700/11
⇒ 63.64%
∴ The number of boy candidates who qualified in the Year 2015 will be approximately 63.64% of the total number of candidates who qualified for the exam in the year 2016.
Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total number of candidates who qualified for SBI PO in 6 different years and the ratio of boys to girls in them.
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2014 | 1500 | 3 : 2 |
| 2015 | 1800 | 7 : 2 |
| 2016 | 2200 | 5 : 6 |
| 2017 | 2600 | 8 : 5 |
| 2018 | 3000 | 8 : 7 |
| 2019 | 3200 | 5 : 3 |
73. What is the average number of girl candidates who qualified for the exam in the Year 2014, 2015 and 2018 together?
A. 700
B. 800
C. 900
D. 880
E. 780
Solution
Given:
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2014 | 1500 | 3 : 2 |
| 2015 | 1800 | 7 : 2 |
| 2018 | 3000 | 8 : 7 |
Formula Used:
Average = (Sum of all observations)/(Number of observations)
Calculation:
The number of girl candidates who qualified for the exam in 2014 = {2/(2 + 3)} × 1500
⇒ (2/5) × 1500
⇒ 600
The number of girl candidates who qualified for the exam in 2015 = {2/(2 + 7)} × 1800
⇒ (2/9) × 1800
⇒ 400
The number of girl candidates who qualified for the exam in 2018 = {7/(7 + 8)} × 3000
⇒ (7/15) × 3000
⇒ 1400
Total number of girl candidates who qualified for the exam in the Year 2014, 2015 and 2018 together = 600 + 400 + 1400
⇒ 2400
The required average = 2400/3
⇒ 800
∴ The average number of girl candidates who qualified for the exam in the Year 2014, 2015 and 2018 together will be 800.
Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total number of candidates who qualified for SBI PO in 6 different years and the ratio of boys to girls in them.
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2014 | 1500 | 3 : 2 |
| 2015 | 1800 | 7 : 2 |
| 2016 | 2200 | 5 : 6 |
| 2017 | 2600 | 8 : 5 |
| 2018 | 3000 | 8 : 7 |
| 2019 | 3200 | 5 : 3 |
74. What is the difference between the number of boy candidates qualified in the year 2015 and 2019 together and the number of girl candidates who qualified in the year 2016 and 2017 together?
A. 1000
B. 1100
C. 800
D. 2200
E. 1200
Solution
Given:
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2015 | 1800 | 7 : 2 |
| 2016 | 2200 | 5 : 6 |
| 2017 | 2600 | 8 : 5 |
| 2019 | 3200 | 5 : 3 |
Calculation:
The number of boys who qualified for the SBI PO exam in the year 2015 = {7/(2 + 7)} × 1800
⇒ (7/9) × 1800
⇒ 1400
Similarly,
| Year | Number of Boys | Number of Girls |
| 2015 | (7/9) × 1800 = 1400 | |
| 2016 | (6/11) × 2200 = 1200 | |
| 2017 | (5/13) × 2600 = 1000 | |
| 2019 | (5/8) × 3200 = 2000 |
Total number of boy candidates qualified in the year 2015 and 2019 together = 1400 + 2000
⇒ 3400
Total number of girl candidates qualified in the year 2016 and 2017 together = 1200 + 1000
⇒ 2200
The required difference = 3400 – 2200
⇒ 1200
∴ The difference between the number of boy candidates qualified in the year 2015 and 2019 together and the number of girl candidates who qualified in the year 2016 and 2017 together will be 1200.
Direction: Study the table carefully and answer the following questions.
The following table shows the total number of candidates who qualified for SBI PO in 6 different years and the ratio of boys to girls in them.
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2014 | 1500 | 3 : 2 |
| 2015 | 1800 | 7 : 2 |
| 2016 | 2200 | 5 : 6 |
| 2017 | 2600 | 8 : 5 |
| 2018 | 3000 | 8 : 7 |
| 2019 | 3200 | 5 : 3 |
75. The number of boys candidates who qualified for the exam in 2018 approximately what percent more or less than the number of girls candidates who qualified for the exam in the year 2019?
A. 33.33% more
B. 30% less
C. 25% more
D. 33.33% less
E. 20% more
Solution
Given:
| Year | Total Qualified Candidates | The ratio of boys to girls |
| 2018 | 3000 | 8 : 7 |
| 2019 | 3200 | 5 : 3 |
Formula Used:
Increase in percentage = {(Increase in value)/(Base value)} × 100
Calculation:
The number of boys candidates who qualified for the exam in 2018 = {8/(8 + 7)} × 3000
⇒ (8/15) × 3000
⇒ 1600
The number of girls candidates who qualified for the exam in 2019 = {3/(3 + 5)} × 3200
⇒ (3/8) × 3200
⇒ 1200
Increase in value = 1600 – 1200
⇒ 400
The required Increased percentage = (400/1200) × 100
⇒ 100/3
⇒ 33.33%
∴ The number of boys candidates who qualified for the exam in 2018 will be approximately 33.33% more than the number of girls candidates who qualified for the exam in the year 2019.
76. The ratio of the present ages of a girl and her grandmother is 1 : 3. Ten years ago, the age of grandmother was 4 more than 4 times the age of a girl. Find their ages?
A. 22 and 72
B. 26 and 78
C. 25 and 78
D. 26 and 77
E. 23 and 79
Solution
Given:
The ratio of the present ages of a girl and her grandmother is 1 : 3. Ten years ago, age of grandmother is 4 more than 4 times the age of a girl
Calculation:
Let the ages be x and 3x
Ten years ago
Girl’s age = x – 10 and Grandmother’s age = 3x – 10
According to question,
⇒ 3x – 10 = 4(x – 10) + 4
⇒ 3x – 10 = 4x – 40 + 4
⇒ x = 26
3x = 3 × 26 = 78
∴ Age of girl is 26 years and age of grandmother is 78 years.
77. A man reaches his office 30 min late, if he travel from his home at 30 km per hour and reaches 40 min early if he travel 40 km per hour. How far is his office from his home?
A. 120 km
B. 125 km
C. 130 km
D. 140 km
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
When man’s speed 30 kmph, he reaches his office 30 min late
And man’s speed 40 kmph, he reaches his office 40 min early
Formula used:
Time = dist./speed
Calculation:
Let the Distance between home and office = d
Suppose he reaches the office on time, the Time taken = x minutes
Case 1:
When he reaches office 30 minutes late
So, Time taken = x + 30
⇒ x+30 = d/30 …….(1)
Case 2:
When he reaches office 40 minutes early
So, Time taken = x – 40
⇒ x – 40 = d/40 …….(2)
Equation (1) – Equation (2)
⇒ 70 min = d/30 – d/40
⇒ 70/60 h = d/120
⇒ d = 140 km
∴ Distance between home and office is 140 km
Alternate Method
Given:
When man’s speed 30 kmph, he reaches his office 30 min late
And man’s speed 40 kmph, he reaches his office 40 min early
Formula used:
Distance = (S1xS2)/(S2-S1){diff. b/w time}
Calculation:
Difference between time = 30-(-40) = 70 min = 70/60 h
⇒ D = (30×40)/(40-30){70/60}
⇒ D = 140 km
∴ Distance between home and office is 140 km
78. A start a business with Rs. 12000, After 4 months B joined with Rs. 16000. Total profit after one year is Rs. 34000. Find the share of profit of A?
A. Rs. 19500
B. Rs. 20500
C. Rs. 18000
D. Rs. 16000
E. Rs. 21000
Solution
Calculation
A: Rs. 12000 for 12 months = 12000 × 12 = 144000
B: Rs. 16000 for 8 months = 16000 × 8 = 128000
Ratio of profit = 144000:128000 = 9:8
Total profit = 34000
A’s share = (9/17) × 34000 = Rs. 18000
79. A trader sells 40 meters of cloth for Rs. 8200 at a profit of Rs. 25 per metre of cloth. How much profit will the trader earn on 40 metres of cloth?
A. Rs. 950
B. Rs. 1500
C. Rs. 1000
D. Rs. 1200
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
40 meters of cloth, SP = Rs. 8200
Profit = Rs. 25 per metre of cloth
Calculation:
S.P. per metre = 8200/40 = Rs. 205
∴ C.P. per metre = RS. (205 – 25) = Rs. 180
∴ C.P. of 40 metre cloth
= Rs. (40 × 180) = Rs. 7200
∴ Gain = Rs. (8200 – 7200) = Rs. 1000
∴ Gain is Rs 1000
80. If the volume of a cylinder is 100π unit and the ratio of radius to height is 5 : 4 then find the curved surface area of the cylinder ?
A. 400π sq. unit
B. 40 sq. unit
C. 40π sq. unit
D. 140π sq. unit
E. None of these
Solution
GIVEN:
Volume of cylinder = 100π
⇒ Radius : Height = 5x : 4x
FORMULA USED:
Volume of cylinder = πr2h cu. Unit
CALCULATION:
⇒ πr2h = 100π unit
⇒ r2h = 100 unit
⇒ 25x2 X 4x = 100 unit
⇒ x3 = 1 unit
⇒ Radius = 5 unit & height = 4 unit.
⇒ Curved surface = 2πrh
⇒ Curved surface = 40π sq. unit
