Direction: Study the following information to answer the given questions:
Nine boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are placed one above the other vertically, not necessarily in the same order. Only five boxes are placed between H and I. D is placed immediately above I. Only three boxes are placed between C and D. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G. F is placed below G but not at the bottom. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. One box is placed between F and E. Box G is placed above A
Question:
1.Find the odd one out.
A. CF
B. IG
C. HA
D. DC
E. EF
Solution
Boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I.
1. Only five boxes are placed between H and I.
2. D is placed immediately above I.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| H | I | D | ||
| H | I | |||
| D | ||||
| I | D | |||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
3. Only three boxes are placed between C and D.
4. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| C | H | I | D | |
| C | H | I | ||
| C | G | |||
| G | C | G | ||
| D | G | C | ||
| I | D | G | ||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
5. F is placed below G but not at the bottom.
6. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. So, Case 1, Case 2 and Case 3 is eliminated.
| Case 4 | Case 5 |
| D | |
| I | D |
| I | |
| G | |
| C | G |
| C | |
| F | |
| H | F |
| H |
7. One box is placed between F and E.
8. Box G is placed above A.
The final arrangement is,
| No. | Case 4 |
| 1 | D |
| 2 | I |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | G |
| 5 | C |
| 6 | A |
| 7 | F |
| 8 | H |
| 9 | E |
Every pair except DC has one box between them. But DC has three boxes between them.
Hence, DC is the odd one out.
Direction: Study the following information to answer the given questions:
Nine boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are placed one above the other vertically, not necessarily in the same order. Only five boxes are placed between H and I. D is placed immediately above I. Only three boxes are placed between C and D. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G. F is placed below G but not at the bottom. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. One box is placed between F and E. Box G is placed above A
Question:
2. How many boxes were placed between D and F?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
E. Five
Solution
Boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I.
1. Only five boxes are placed between H and I.
2. D is placed immediately above I.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| H | I | D | ||
| H | I | |||
| D | ||||
| I | D | |||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
3. Only three boxes are placed between C and D.
4. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| C | H | I | D | |
| C | H | I | ||
| C | G | |||
| G | C | G | ||
| D | G | C | ||
| I | D | G | ||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
5. F is placed below G but not at the bottom.
6. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. So, Case 1, Case 2 and Case 3 is eliminated.
| Case 4 | Case 5 |
| D | |
| I | D |
| I | |
| G | |
| C | G |
| C | |
| F | |
| H | F |
| H |
7. One box is placed between F and E.
8. Box G is placed above A.
The final arrangement is,
| No. | Case 4 |
| 1 | D |
| 2 | I |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | G |
| 5 | C |
| 6 | A |
| 7 | F |
| 8 | H |
| 9 | E |
Hence, five persons were placed between D and F.
3. Direction: Study the following information to answer the given questions:
Nine boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are placed one above the other vertically, not necessarily in the same order. Only five boxes are placed between H and I. D is placed immediately above I. Only three boxes are placed between C and D. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G. F is placed below G but not at the bottom. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. One box is placed between F and E. Box G is placed above A
Question:
Which box is placed second from the bottom?
A. F
B. E
C. C
D. A
E. H
Solution
Boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I.
1. Only five boxes are placed between H and I.
2. D is placed immediately above I.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| H | I | D | ||
| H | I | |||
| D | ||||
| I | D | |||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
3. Only three boxes are placed between C and D.
4. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| C | H | I | D | |
| C | H | I | ||
| C | G | |||
| G | C | G | ||
| D | G | C | ||
| I | D | G | ||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
5. F is placed below G but not at the bottom.
6. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. So, Case 1, Case 2 and Case 3 is eliminated.
| Case 4 | Case 5 |
| D | |
| I | D |
| I | |
| G | |
| C | G |
| C | |
| F | |
| H | F |
| H |
7. One box is placed between F and E.
8. Box G is placed above A.
The final arrangement is,
| No. | Case 4 |
| 1 | D |
| 2 | I |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | G |
| 5 | C |
| 6 | A |
| 7 | F |
| 8 | H |
| 9 | E |
Hence, H is placed second from the bottom.
4. Direction: Study the following information to answer the given questions:
Nine boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are placed one above the other vertically, not necessarily in the same order. Only five boxes are placed between H and I. D is placed immediately above I. Only three boxes are placed between C and D. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G. F is placed below G but not at the bottom. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. One box is placed between F and E. Box G is placed above A
Question:
Which box is placed three places below B?
A. A
B. C
C. D
D. E
E. F
Solution
Boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I.
1. Only five boxes are placed between H and I.
2. D is placed immediately above I.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| H | I | D | ||
| H | I | |||
| D | ||||
| I | D | |||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
3. Only three boxes are placed between C and D.
4. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| C | H | I | D | |
| C | H | I | ||
| C | G | |||
| G | C | G | ||
| D | G | C | ||
| I | D | G | ||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
5. F is placed below G but not at the bottom.
6. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. So, Case 1, Case 2 and Case 3 is eliminated.
| Case 4 | Case 5 |
| D | |
| I | D |
| I | |
| G | |
| C | G |
| C | |
| F | |
| H | F |
| H |
7. One box is placed between F and E.
8. Box G is placed above A.
The final arrangement is,
| No. | Case 4 |
| 1 | D |
| 2 | I |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | G |
| 5 | C |
| 6 | A |
| 7 | F |
| 8 | H |
| 9 | E |
Hence, Box A is placed three places below B.
5. Direction: Study the following information to answer the given questions:
Nine boxes A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are placed one above the other vertically, not necessarily in the same order. Only five boxes are placed between H and I. D is placed immediately above I. Only three boxes are placed between C and D. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G. F is placed below G but not at the bottom. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. One box is placed between F and E. Box G is placed above A
Question:
If B and G interchange their places, which box is placed two places above C?
A. D
B. I
C. B
D. G
E. A
Solution
Boxes: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I.
1. Only five boxes are placed between H and I.
2. D is placed immediately above I.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| H | I | D | ||
| H | I | |||
| D | ||||
| I | D | |||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
3. Only three boxes are placed between C and D.
4. As many boxes between C and H, as between D and G.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| H | D | |||
| C | H | I | D | |
| C | H | I | ||
| C | G | |||
| G | C | G | ||
| D | G | C | ||
| I | D | G | ||
| I | D | H | ||
| I | H |
5. F is placed below G but not at the bottom.
6. More than four boxes are placed between D and F. So, Case 1, Case 2 and Case 3 is eliminated.
| Case 4 | Case 5 |
| D | |
| I | D |
| I | |
| G | |
| C | G |
| C | |
| F | |
| H | F |
| H |
7. One box is placed between F and E.
8. Box G is placed above A.
The final arrangement is,
| No. | Case 4 |
| 1 | D |
| 2 | I |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | G |
| 5 | C |
| 6 | A |
| 7 | F |
| 8 | H |
| 9 | E |
After interchange
| No. | Case 4 |
| 1 | D |
| 2 | I |
| 3 | G |
| 4 | B |
| 5 | C |
| 6 | A |
| 7 | F |
| 8 | H |
| 9 | E |
Hence, If B and G interchange their position then G is placed two places above C.
6. DIRECTIONS: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among the given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: U ≥ R, H < L, P ≤ N, H = K, R = P
Conclusions:
I. U > P
II. U = P
A. Only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Either conclusion I or II follows
D. Neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. Both conclusion I and II follow
Solution
Given Statements : U ≥ R, H < L, P ≤ N, H = K, R = P
On combining : U ≥ R = P ≤ N , K = H < L
I. U > P → False ( As U ≥ R = P, it is a possibility but not definitely true, Hence U > P is False )
II. U = P → False (As U ≥ R = P, it is a possibility but not definitely true, Hence U = P is False )
Both the conclusion are false and greater than equal to make the complementary pair so it will be the case of either or.
Hence, Either I or II follows.
7. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements : B > Q > I, K < T = P < Q, B < N < R
Conclusions :
I. K < R
II. I > K
A. Both I and II Follow
B. Only II Follows
C. Either I or II Follows
D. Only I Follows
E. Neither I nor II Follows
Solution
Given statements: B > Q > I, K < T = P < Q, B < N < R
On combining: K < T = P < Q < B < N < R ; K < T = P < Q > I
Conclusions:
I.K < R → True (As K < T = P < Q < B < N < R → K < R)
II. I > K → False (K < T = P < Q > I → thus clear relation between I and K cannot be determined)
Hence, Only conclusion I Follows.
8. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: E ≥ A = W; B < X; E ≤ S ≤ T < B
Conclusions:
I. T > A
II. T ≤ A
A. Only I follow
B. Only II follow
C. Both I and II follows
D. Either I or II follows
E. Neither I nor II follows
Solution
Given Statements: E ≥ A = W; B < X; E ≤ S ≤ T < B
On Combining: X > B > T ≥ S ≥ E ≥ A = W
Conclusions:
I. T > A → False (As T ≥ S ≥ E ≥ A → T ≥ A. So, it is false)
II. T ≤ A → False (As T ≥ S ≥ E ≥ A → T ≥ A. So, it is false)
Hence, neither I nor II follows.
 Confusion Points
Confusion Points
Here the given condition between T and A is,
T ≥ S ≥ E ≥ A → T ≥ A.
It means that T is greater than equal to A this will be true for all conditions.
In the given conclusion three sign present between the T and A as <, >, =, but the three sign concept will be applicable when there is no relationship defined between the two elements in the given statement but here T ≥ A it is a definite statement between them so except that all will be considered as false.
Hence, Neither I nor II follows.
9. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Nine persons (J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, and R) are planning trips to Mumbai in different months (July, October, and November) and on different dates (16th, 19th, and 28th) within the same year. Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Only two persons go between L and K, and K travels three months after M on the same date. Q travels in October but not on an even date. J travels immediately before P. R travels immediately before L. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates.
Question:
How many people are going to Mumbai between M and R?
A. One
B. Three
C. Six
D. Seven
E. Four
Solution
1) Q travels in October but not on an even date. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates. Only two persons go between L and K.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | ||
| 19 | |||
| 28 | |||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | ||
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | L |
2) K travels three months after M on the same date. R travels immediately before L.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | M | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | M | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | R | ||
| 28 | L |
3) J travels immediately before P.
| Case 1 | Case 2(a) | Case 2(b) | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J | M | M |
| 19 | P | J | ||
| 28 | M | P | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | L | |
| 19 | R | J | ||
| 28 | L | P |
4) Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Case 2(a) and Case 2(b) are eliminated because it does not satisfy the given conditions.
The final arrangement is:
| Month | Dates | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J |
| 19 | P | |
| 28 | M | |
| October(31 days) | 16 | O |
| 19 | Q | |
| 28 | K | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | N |
| 19 | R | |
| 28 | L |
Hence, Four people are going to Mumbai between M and R.
10. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Nine persons (J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, and R) are planning trips to Mumbai in different months (July, October, and November) and on different dates (16th, 19th, and 28th) within the same year. Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Only two persons go between L and K, and K travels three months after M on the same date. Q travels in October but not on an even date. J travels immediately before P. R travels immediately before L. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates.
Question:
Which of the following month and date Q is going to Mumbai?
A. July 16
B. November 28
C. October 19
D. July 19
E. November 16
Solution
1) Q travels in October but not on an even date. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates. Only two persons go between L and K.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | ||
| 19 | |||
| 28 | |||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | ||
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | L |
2) K travels three months after M on the same date. R travels immediately before L.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | M | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | M | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | R | ||
| 28 | L |
3) J travels immediately before P.
| Case 1 | Case 2(a) | Case 2(b) | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J | M | M |
| 19 | P | J | ||
| 28 | M | P | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | L | |
| 19 | R | J | ||
| 28 | L | P |
4) Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Case 2(a) and Case 2(b) are eliminated because it does not satisfy the given conditions.
The final arrangement is:
| Month | Dates | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J |
| 19 | P | |
| 28 | M | |
| October(31 days) | 16 | O |
| 19 | Q | |
| 28 | K | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | N |
| 19 | R | |
| 28 | L |
Hence, Q is going to Mumbai on October 19.
11. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Nine persons (J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, and R) are planning trips to Mumbai in different months (July, October, and November) and on different dates (16th, 19th, and 28th) within the same year. Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Only two persons go between L and K, and K travels three months after M on the same date. Q travels in October but not on an even date. J travels immediately before P. R travels immediately before L. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates.
Question:
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way as per the given arrangement, forming a group. Find the one who doesn’t belong to that group.
A. O
B. M
C. J
D. K
E. N
Solution
1) Q travels in October but not on an even date. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates. Only two persons go between L and K.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | ||
| 19 | |||
| 28 | |||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | ||
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | L |
2) K travels three months after M on the same date. R travels immediately before L.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | M | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | M | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | R | ||
| 28 | L |
3) J travels immediately before P.
| Case 1 | Case 2(a) | Case 2(b) | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J | M | M |
| 19 | P | J | ||
| 28 | M | P | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | L | |
| 19 | R | J | ||
| 28 | L | P |
4) Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Case 2(a) and Case 2(b) are eliminated because it does not satisfy the given conditions.
The final arrangement is:
| Month | Dates | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J |
| 19 | P | |
| 28 | M | |
| October(31 days) | 16 | O |
| 19 | Q | |
| 28 | K | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | N |
| 19 | R | |
| 28 | L |
All except N belong to the month which has 31 days. Hence, N does not belong to that group.
12. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Nine persons (J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, and R) are planning trips to Mumbai in different months (July, October, and November) and on different dates (16th, 19th, and 28th) within the same year. Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Only two persons go between L and K, and K travels three months after M on the same date. Q travels in October but not on an even date. J travels immediately before P. R travels immediately before L. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates.
Question:
Who among the following people goes to Mumbai on November 19?
A. J
B. R
C. K
D. P
E. M
Solution
1) Q travels in October but not on an even date. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates. Only two persons go between L and K.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | ||
| 19 | |||
| 28 | |||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | ||
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | L |
2) K travels three months after M on the same date. R travels immediately before L.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | M | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | M | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | R | ||
| 28 | L |
3) J travels immediately before P.
| Case 1 | Case 2(a) | Case 2(b) | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J | M | M |
| 19 | P | J | ||
| 28 | M | P | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | L | |
| 19 | R | J | ||
| 28 | L | P |
4) Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Case 2(a) and Case 2(b) are eliminated because it does not satisfy the given conditions.
The final arrangement is:
| Month | Dates | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J |
| 19 | P | |
| 28 | M | |
| October(31 days) | 16 | O |
| 19 | Q | |
| 28 | K | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | N |
| 19 | R | |
| 28 | L |
Hence, R goes to Mumbai on November 19.
13. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Nine persons (J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, and R) are planning trips to Mumbai in different months (July, October, and November) and on different dates (16th, 19th, and 28th) within the same year. Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Only two persons go between L and K, and K travels three months after M on the same date. Q travels in October but not on an even date. J travels immediately before P. R travels immediately before L. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates.
Question:
Who does not go to Mumbai on an even date among the following people?
A. J
B. O
C. M
D. Q
E. L
Solution
1) Q travels in October but not on an even date. L travels in a month having an even number of days but does not go on odd dates. Only two persons go between L and K.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | ||
| 19 | |||
| 28 | |||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | ||
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | L |
2) K travels three months after M on the same date. R travels immediately before L.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | M | |
| 19 | |||
| 28 | M | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | |
| 19 | R | ||
| 28 | L |
3) J travels immediately before P.
| Case 1 | Case 2(a) | Case 2(b) | ||
| Month | Dates | Person | Person | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J | M | M |
| 19 | P | J | ||
| 28 | M | P | ||
| October(31 days) | 16 | K | K | |
| 19 | Q | Q | Q | |
| 28 | K | R | R | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | L | L | |
| 19 | R | J | ||
| 28 | L | P |
4) Consecutive alphabetical persons (like J & K, K & L, etc.) do not travel in the same month or on adjacent dates. Case 2(a) and Case 2(b) are eliminated because it does not satisfy the given conditions.
The final arrangement is:
| Month | Dates | Person |
| July(31 days) | 16 | J |
| 19 | P | |
| 28 | M | |
| October(31 days) | 16 | O |
| 19 | Q | |
| 28 | K | |
| November(30 days) | 16 | N |
| 19 | R | |
| 28 | L |
Hence, Q does not go to Mumbai on an even date.
14. Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Arun starts from point P and goes 8m North to reach point Q and then takes a left turn and goes 8m to reach point R. From R he takes a right turn and travels 10m to point S and after reaching there he takes a left turn and walks 12m to reach point T. From point T he takes a left turn and walks 18m to finally reach point V.
Question:
What is the shortest distance between V and Q?
A. 164
B. √164m
C. 464
D. √535m
E. √464m
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question,
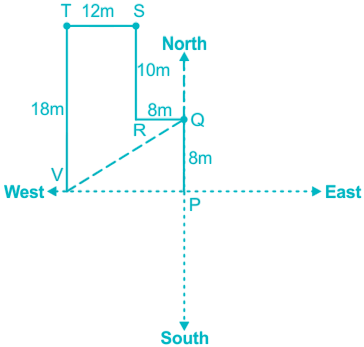
By using the Pythagorean Theorem,
VQ2 = PQ2 + UP2
VQ2 = 82 + 202
VQ = √464
VQ = √464m
Hence, √464m is the shortest distance between V and Q.
15. Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Arun starts from point P and goes 8m North to reach point Q and then takes a left turn and goes 8m to reach point R. From R he takes a right turn and travels 10m to point S and after reaching there he takes a left turn and walks 12m to reach point T. From point T he takes a left turn and walks 18m to finally reach point V.
Question:
What is the direction of T with respect to Q?
A. Northwest
B. Southwest
C. Eastwest
D. South
E. North
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question,
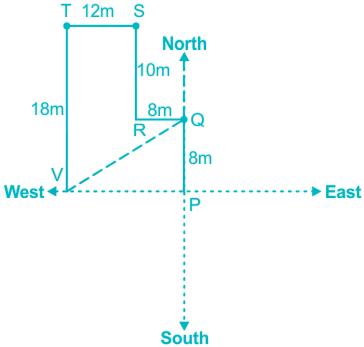
Hence, T is northwest direction of Q.
16. Directions: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Arun starts from point P and goes 8m North to reach point Q and then takes a left turn and goes 8m to reach point R. From R he takes a right turn and travels 10m to point S and after reaching there he takes a left turn and walks 12m to reach point T. From point T he takes a left turn and walks 18m to finally reach point V.
Question:
What is the direction of R with respect to V?
A. North
B. West
C. Northeast
D. East
E. Northsouth
Solution
We have drawn the figure according to the information given in the question,
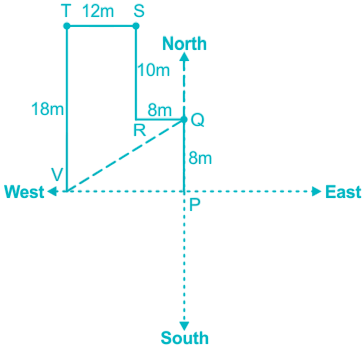
Hence, R is Northeast direction with respect to V.
17. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Eight people P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W, are sitting around a circular table, all of them are facing towards the center. W is sitting immediate left of P. Two people sit between W and Q. S is not neighbor of W.T sits immediate right of Q. U sits second to the left of T.U is not the neighbor of P. Q sits opposite to P and R sits opposite to S.
Question:
Who sits second to the right of P?
A. W
B. V
C. S
D. Q
E. T
Solution
People: P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, & W.
1). W is an immediate left of P.
2). Two people sit between W and Q.
Case I.
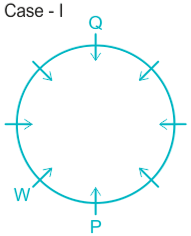
Case II.
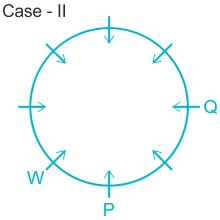
3). T sits immediate right of Q.
4). U sit second to the left of T.
Case I.
Case II.
5). Q sits opposite to P and U is not a neighbor of P. ( from here Case II got eliminated).
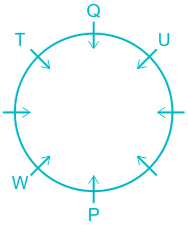
6). R sits opposite to S and S is not a neighbor of W.
7). This implies V sits in a vacant place.
The final arrangement will be:
Hence, S sits second to the right of P.
18. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Eight people P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W, are sitting around a circular table, all of them are facing towards the center. W is sitting immediate left of P. Two people sit between W and Q. S is not neighbor of W.T sits immediate right of Q. U sits second to the left of T.U is not the neighbor of P. Q sits opposite to P and R sits opposite to S.
Question:
Who sits opposite to W?
A. U
B. V
C. T
D. R
E. P
Solution
People: P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, & W.
1). W is an immediate left of P.
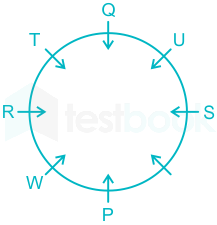
2). Two people sit between W and Q.
Case I.
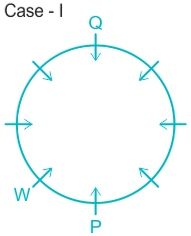
Case II.
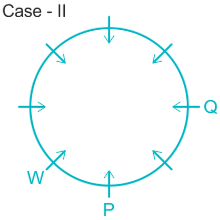
3). T sits immediate right of Q.
4). U sit second to the left of T.
Case I.
Case II.
5). Q sits opposite to P and U is not a neighbor of P. ( from here Case II got eliminated).
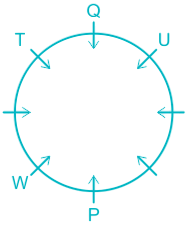
6). R sits opposite to S and S is not a neighbor of W.
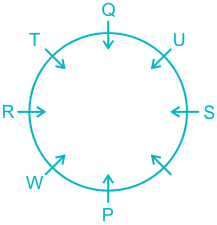
7). This implies V sits in a vacant place.
The final arrangement will be:
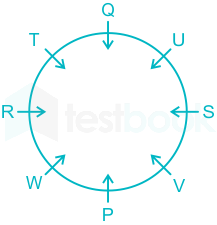
Hence, U sits opposite to W.
19. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Eight people P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W, are sitting around a circular table, all of them are facing towards the center. W is sitting immediate left of P. Two people sit between W and Q. S is not neighbor of W.T sits immediate right of Q. U sits second to the left of T.U is not the neighbor of P. Q sits opposite to P and R sits opposite to S.
Question:
Who sits immediate right of S?
A. One who is sitting exactly opposite to P
B. Q
C. One who is second to the right of V
D. V
E. Onw who is sitting immediate left of P
Solution
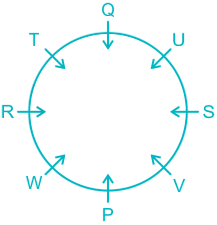
People: P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, & W.
1). W is an immediate left of P.
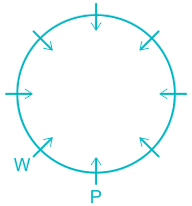
2). Two people sit between W and Q.
Case I.
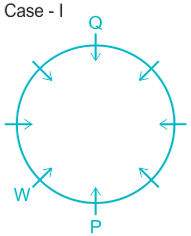
Case II.
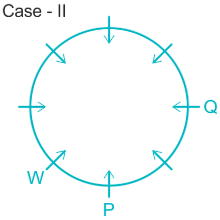
3). T sits immediate right of Q.
4). U sit second to the left of T.
Case I.
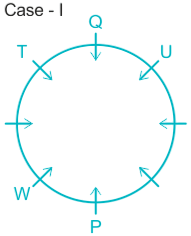
Case II.
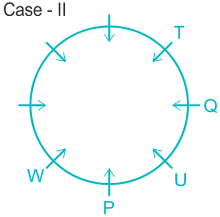
5). Q sits opposite to P and U is not a neighbor of P. ( from here Case II got eliminated).
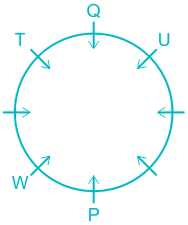
6). R sits opposite to S and S is not a neighbor of W.
7). This implies V sits in a vacant place.
The final arrangement will be:
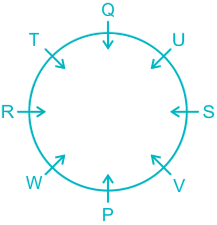
Hence, U sits immediate right of S.
20. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Eight people P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W, are sitting around a circular table, all of them are facing towards the center. W is sitting immediate left of P. Two people sit between W and Q. S is not neighbor of W.T sits immediate right of Q. U sits second to the left of T.U is not the neighbor of P. Q sits opposite to P and R sits opposite to S.
Question:
Who sits between W and V starting from left of V?
A. Q
B. T
C. V
D. P
E. R
Solution
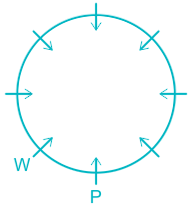
People: P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, & W.
1). W is an immediate left of P.
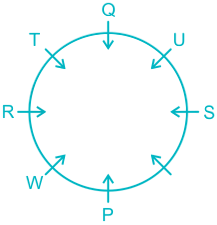
2). Two people sit between W and Q.
Case I.
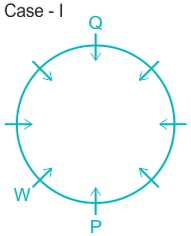
Case II.
3). T sits immediate right of Q.
4). U sit second to the left of T.
Case I.
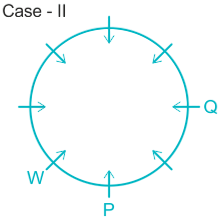
Case II.
5). Q sits opposite to P and U is not a neighbor of P. ( from here Case II got eliminated).
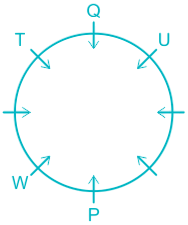
6). R sits opposite to S and S is not a neighbor of W.
7). This implies V sits in a vacant place.
The final arrangement will be:
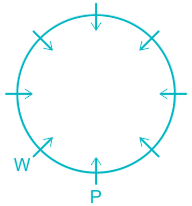
Hence, P sits between W and V.
21. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Eight people P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, and W, are sitting around a circular table, all of them are facing towards the center. W is sitting immediate left of P. Two people sit between W and Q. S is not neighbor of W.T sits immediate right of Q. U sits second to the left of T.U is not the neighbor of P. Q sits opposite to P and R sits opposite to S.
Question:
What is position of R with respect to U in clock wise direction?
A. Fourth to the left
B. Fourth to right
C. Third to thr left
D. Fifth to the left
E. Immediate right
Solution
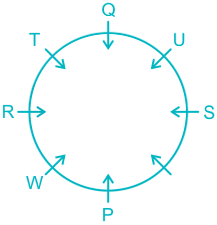
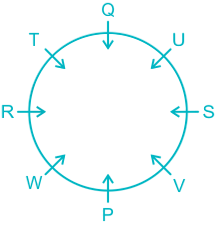
People: P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, & W.
1). W is an immediate left of P.
2). Two people sit between W and Q.
Case I.
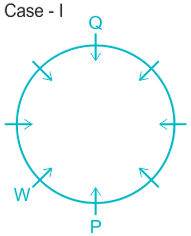
Case II.
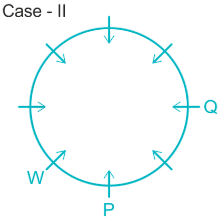
3). T sits immediate right of Q.
4). U sit second to the left of T.
Case I.
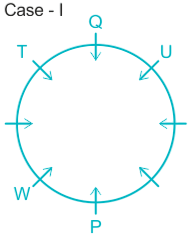
Case II.
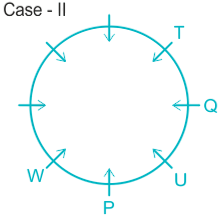
5). Q sits opposite to P and U is not a neighbor of P. ( from here Case II got eliminated).
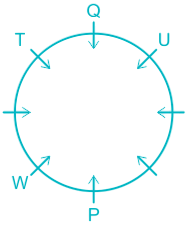
6). R sits opposite to S and S is not a neighbor of W.
7). This implies V sits in a vacant place.
The final arrangement will be:
Hence, R is fifth to the left position with respect to U.
22. In the series given below count each 5 which is not immediately preceded by 3 but is immediately followed by 7. How many such 5’s are there ?
1 5 7 3 5 7 4 7 3 7 2 5 6 5 8 5 7 4 5 6 5 5 7 1 5 7 7 5 5
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
Solution
Given series:
1 5 7 3 5 7 4 7 3 7 2 5 6 5 8 5 7 4 5 6 5 5 7 1 5 7 7 5 5
The number 5, which is not immediately preceded by 3 but is immediately followed by 7 is:
1 5 7 3 5 7 4 7 3 7 2 5 6 5 8 5 7 4 5 6 5 5 7 1 5 7 7 5 5
Here, the number 5 comes four times, which is not immediately preceded by 3 but is immediately followed by 7.
Hence, the correct answer is “4”.
23. Direction: In the question below, there are three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows them from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Some pants are not jeans.
No jeans is shirt.
No tie is shirt.
Conclusions:
I. No pant is tie.II. Some tie is pantOnly I follow
a. Only II follow
b. Either I or II follow
c. Neither I nor II follow
d. Both I and II follow
Solution
The least possible Venn Diagram for the given statements will be as follows,
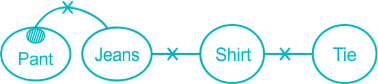
I. No pant is tie → False (as there is no direct relation given between tie and pant so we cannot say anything specifically. That’s why the answer is not known and it will be considered as false)
II. Some tie is pant → False (as there is no direct relation given between tie and pant so we cannot say anything specifically. That’s why the answer is not known and it will be considered as false)
Here is only two possibilities between pant and tie. Either some tie is pant or no tie is pant.Hence, Either I or II follow.
24. Direction: In the question below, there are three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows them from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
All bus are bike.
Some bike are plate.
No bus is plane.
Conclusions:
I. Some plane is bike.
II. No plane is plate.
a. Either I or II follow
b. Only II follow
c. Neither I nor II follow
d. Only I follow
e. Both I and II follow
Solution
The least possible Venn Diagram for the given statements will be as follows,
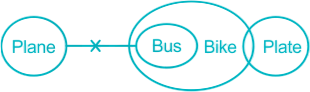
I. Some plane is bike → False (as there is no direct relation given between plane and bike so we cannot say anything specifically. That’s why the answer is not known and it will be considered as false)
II. No plane is plate → False (as there is no direct relation given between plane and plate so we cannot say anything specifically. That’s why the answer is not known and it will be considered as false)
Hence, Neither I nor II follow.
25. Direction: In the question below, there are three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows them from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Only animal are bird.
No Animal is human.
Some human is goat.
Conclusions:
I. Some goat can be bird.
II. No animal is goat.
a. Only I follow
b. Only II follow
c. Both follow
d. Either I or II follow
e. None follow
Solution
The least possible Venn Diagram for the given statements will be as follows,
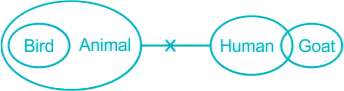
I. Some goat can be bird → False (as bird cannot be common with anything except animal)
II. No animal is goat → False (as there is no direct relation given between animal and goat so we cannot say anything specifically. That’s why the answer is not known and it will be considered as false)
Hence, Neither I nor II follow.
26. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight women – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather were assembled in a conference room to be awarded. Each person has a different level of qualification among B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD. Felicity did not study M.A. Amber completed an MBA. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA. Candice completed B.Com. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A. Gaia completed her PHD. Heather completed neither M.A. not M.C.A.
Question:
Who completed the MA?
a. Ellen
b. Dorothy
c. Candice
d. Brittany
e. Amber
Solution
Given:
Eight people – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather
Eight qualifications – B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD
1. Amber completed an MBA.
2. Candice completed B.Com.
3. Gaia completed her PHD.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | |
| Felicity | |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
4. Felicity did not study M.A.
5. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A.
6. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
7. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com.
8. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech.
9. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA.
10. Heather completed neither M.A. nor M.C.A.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | M.A. |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | B.Tech. |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather | B.A. |
Hence, Britanny completed the M.A.
27. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight women – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather were assembled in a conference room to be awarded. Each person has a different level of qualification among B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD. Felicity did not study M.A. Amber completed an MBA. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA. Candice completed B.Com. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A. Gaia completed her PHD. Heather completed neither M.A. not M.C.A.
Question:
What is the qualification of Ellen?
A. M.A.
B. B.Tech.
C. B.Com.
D. BBA
E. BA
Solution
Given:
Eight people – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather
Eight qualifications – B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD
1. Amber completed an MBA.
2. Candice completed B.Com.
3. Gaia completed her PHD.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | |
| Felicity | |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
4. Felicity did not study M.A.
5. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A.
6. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
7. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com.
8. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech.
9. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA.
10. Heather completed neither M.A. nor M.C.A.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | M.A. |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | B.Tech. |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather | B.A. |
Hence, Ellen completed the BBA.
28. Comprehension:(Que No. 26 – 30)
Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight women – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather were assembled in a conference room to be awarded. Each person has a different level of qualification among B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD. Felicity did not study M.A. Amber completed an MBA. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA. Candice completed B.Com. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A. Gaia completed her PHD. Heather completed neither M.A. not M.C.A.
Question:
Who is the highest educated in the group?
A. Amber
B. Brittany
C. Felicity
D. Heather
E. Gaia
Solution
Given:
Eight people – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather
Eight qualifications – B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD
1. Amber completed an MBA.
2. Candice completed B.Com.
3. Gaia completed her PHD.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | |
| Felicity | |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
4. Felicity did not study M.A.
5. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A.
6. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
7. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com.
8. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech.
9. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA.
10. Heather completed neither M.A. nor M.C.A.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | M.A. |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | B.Tech. |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather | B.A. |
Since, Gaia has completed the Phd.
Hence, Gaia is the most educated in the group.
29. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight women – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather were assembled in a conference room to be awarded. Each person has a different level of qualification among B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD. Felicity did not study M.A. Amber completed an MBA. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA. Candice completed B.Com. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A. Gaia completed her PHD. Heather completed neither M.A. not M.C.A.
Question:
Four of the five options given below follow a certain logic and form a group, identify the odd one out.
A. Felicity – M.C.A
B. Brittany – M.A.
C. Dorothy – B.Tech.
D. Ellen – B. A
E. Heather – B.A.
Solution
Given:
Eight people – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather
Eight qualifications – B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD
1. Amber completed an MBA.
2. Candice completed B.Com.
3. Gaia completed her PHD.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | |
| Felicity | |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
4. Felicity did not study M.A.
5. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A.
6. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
7. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com.
8. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech.
9. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA.
10. Heather completed neither M.A. nor M.C.A.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | M.A. |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | B.Tech. |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather | B.A. |
All except Ellen – B. A is a wrong combination as per the final arrangement
Hence, Ellen – B. A is the odd one out.
30. Comprehension:(Que No. 26 – 30)
Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight women – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather were assembled in a conference room to be awarded. Each person has a different level of qualification among B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD. Felicity did not study M.A. Amber completed an MBA. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA. Candice completed B.Com. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A. Gaia completed her PHD. Heather completed neither M.A. not M.C.A.
Question:
Who completed the MCA?
A. Brittany
B. Candice
C. Dorothy
D. Ellen
E. Felicity
Solution
Given:
Eight people – Amber, Brittany, Candice, Dorothy, Ellen, Felicity, Gaia, and Heather
Eight qualifications – B.A, BBA, B.Com, B.Tech, M.A, MBA, M.C.A, and PHD
1. Amber completed an MBA.
2. Candice completed B.Com.
3. Gaia completed her PHD.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | |
| Felicity | |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
4. Felicity did not study M.A.
5. Felicity completed either M.A. or M.C.A.
6. Either Ellen or Felicity completed BBA.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather |
7. Brittany did not study B.Tech or B.Com.
8. Neither Felicity nor Heather studied B.Tech.
9. Either Dorothy or Heather completed a BA.
10. Heather completed neither M.A. nor M.C.A.
| Women | Qualification |
| Amber | MBA |
| Brittany | M.A. |
| Candice | B.Com. |
| Dorothy | B.Tech. |
| Ellen | BBA |
| Felicity | M.C.A. |
| Gaia | PHD |
| Heather | B.A. |
Hence, Felicity completed the MCA.
31. Comprehension:(Que No. 31 – 33)
Directions: These questions are based on the following information.
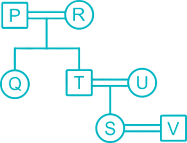
There are 7 member P, Q, R, S, T, U and V in a family. U is daughter-in-law of R. T is brother of Q. P and R is a Married couple. R has only two children. Q is daughter of P, who is not mother of Q. V is son-in-law of U. S is granddaughter of P.
Question:
How V related to S?
A. Brother
B. Sister
C. Husband
D. Wife
E. Father
Solution
From the given information,
1. P and R is a Married couple.
2. R has only two children.
3. Q is daughter of P, who is not mother of Q.
(So P is father of Q and husband of R)
4. T is brother of Q.
5. U is daughter-in-law of R.
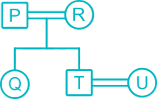
6. S is granddaughter of P.
7. V is son-in-law of U.
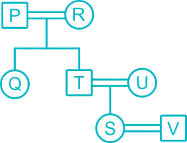
Hence, V is husband of S.
32. Comprehension:(Que No. 31 – 33)
Directions: These questions are based on the following information.
There are 7 member P, Q, R, S, T, U and V in a family. U is daughter-in-law of R. T is brother of Q. P and R is a Married couple. R has only two children. Q is daughter of P, who is not mother of Q. V is son-in-law of U. S is granddaughter of P.
Question:
How S related to Q?
A. Sister
B. Sister-in-law
C. Niece
D. Nepew
E. Brother
Solution
From the given information,
1. P and R is a Married couple.
2. R has only two children.
3. Q is daughter of P, who is not mother of Q.
(So P is father of Q and husband of R)
4. T is brother of Q.
5. U is daughter-in-law of R.
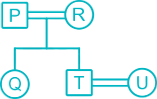
6. S is granddaughter of P.
7. V is son-in-law of U.
Hence, S is the Niece of Q.
33. Comprehension:(Que No. 31 – 33)
Directions: These questions are based on the following information.
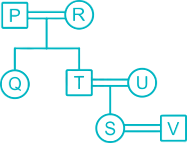
There are 7 member P, Q, R, S, T, U and V in a family. U is daughter-in-law of R. T is brother of Q. P and R is a Married couple. R has only two children. Q is daughter of P, who is not mother of Q. V is son-in-law of U. S is granddaughter of P.
Question:
How R is related to T?
A. Mother
B. Sister
C Wife
D. Sister-in-law
E. Father
Solution
From the given information,
1. P and R is a Married couple.
2. R has only two children.
3. Q is daughter of P, who is not mother of Q.
(So P is father of Q and husband of R)
4. T is brother of Q.
5. U is daughter-in-law of R.
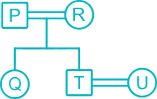
6. S is granddaughter of P.
7. V is son-in-law of U.
Hence, R is Mother of T.
34. In a certain code language “LION” is written as “NMUV” and “TABLE” is written as “VEHTO”. How is SPEAK written in that code language?
A. URRGM
B. UTKIU
C. UTKUU
D. UTKIIU
E. URGMR
Solution
The logic followed here is:
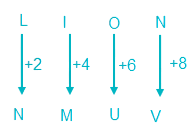
So, LION is coded as NMUV.
And,
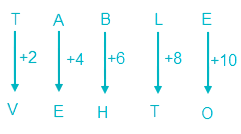
So, TABLE is coded as VEHTO.
Similarly,
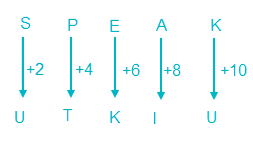
So, SPEAK is coded as UTKIU.
35. If it is possible to make a meaningful word with the second, fifth, sixth, and tenth letters of the word “HABITUATED” which of the following will be the second letter from the right end of that newly formed word? If more than one such word can be made, give M as the answer and if no such word can be made, give Y as the answer?
A. T
B. U
C. M
D. E
E. Y
Solution
Given word: HABITUATED
The second, fifth, sixth, and tenth letters of the word ”HABITUATED” are A, T, U, and D respectively.
No word can be formed with A, T, U, and D.
Hence, No word can be formed so Y is the answer.
36. Comprehension:(Que No. 36 – 40)
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons are sitting to enjoy a feast on an occasion in a row facing North. One person is sitting between H and O. Two persons are sitting between F and Q. Three persons are sitting between H and W. Three persons are sitting between O and E. Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W. A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. Four persons are sitting to the right of Q. Five persons are sitting between E and F.
Question:
Who is sitting at the extreme right end?
A. Z
B. W
C. R
D. H
E. F
Solution
Given:-
Ten persons are sitting in a row facing North,
1) Four persons are sitting to the right of Q.
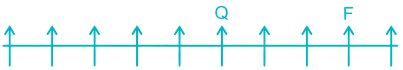
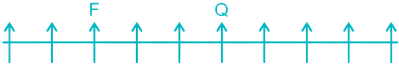
2) Two persons are sitting between F and Q. F can be to the left or to the right of Q.
Case I –
Case II –
3) Five persons are sitting between E and F. E can be to the left of F in Case I and to the right of F in Case II.
4) Three persons are sitting between O and E. O can be to the right of E in Case I and to the left of E in Case II.
5) One person is sitting between H and O. H can be to the left of O in Case I and to the right of O in Case II.
Case I –
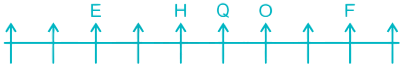
Case II –
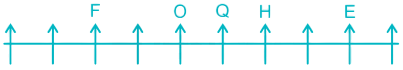
6) Three persons are sitting between H and W. This is not possible in Case II so it gets eliminated. In Case I, W is sitting to the left of H.
7) Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W.
Case I –
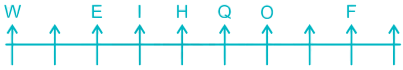
8) A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. There is only three place left so A will just between O and F, Z will just between W and E, R will at the extreme right end.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
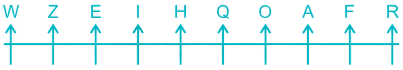
R is sitting at the extreme right end.
Hence, the correct answer is R.
37. Comprehension:(Que No. 36 – 40)
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons are sitting to enjoy a feast on an occasion in a row facing North. One person is sitting between H and O. Two persons are sitting between F and Q. Three persons are sitting between H and W. Three persons are sitting between O and E. Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W. A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. Four persons are sitting to the right of Q. Five persons are sitting between E and F.
Question:
What is the position of A with respect to the O and the E respectively?
A. Fifth to the left and Immediate right
B. Immediate left and Fifth to the right
C. Immediate right and Fifth to the left
D. Immediate right and Fifth to the right
E. Fifth to the right and Immediate right
Solution
Given:-
Ten persons are sitting in a row facing North,
1) Four persons are sitting to the right of Q.
2) Two persons are sitting between F and Q. F can be to the left or to the right of Q.
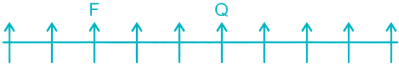
Case I –
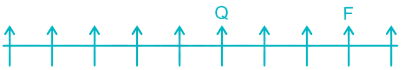
Case II –
3) Five persons are sitting between E and F. E can be to the left of F in Case I and to the right of F in Case II.
4) Three persons are sitting between O and E. O can be to the right of E in Case I and to the left of E in Case II.
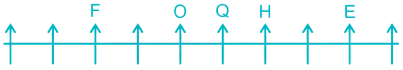
5) One person is sitting between H and O. H can be to the left of O in Case I and to the right of O in Case II.
Case I –
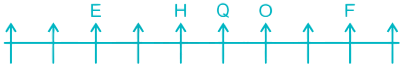
Case II –
6) Three persons are sitting between H and W. This is not possible in Case II so it gets eliminated. In Case I, W is sitting to the left of H.
7) Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W.
Case I –
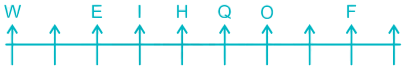
8) A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. There is only three place left so A will just between O and F, Z will just between W and E, R will at the extreme right end.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
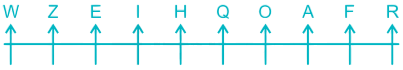
A is sitting to the immediate right of O and fifth to the right of E.
Hence, the correct answer is Immediate right and Fifth to the right.
38. Comprehension:(Que No. 36 – 40)
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons are sitting to enjoy a feast on an occasion in a row facing North. One person is sitting between H and O. Two persons are sitting between F and Q. Three persons are sitting between H and W. Three persons are sitting between O and E. Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W. A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. Four persons are sitting to the right of Q. Five persons are sitting between E and F.
Question:
How many persons are sitting between I and F?
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. More than Three
Solution
Given:-
Ten persons are sitting in a row facing North,
1) Four persons are sitting to the right of Q.
2) Two persons are sitting between F and Q. F can be to the left or to the right of Q.
Case I –
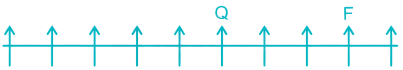
Case II –
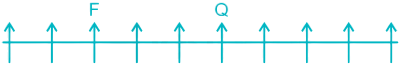
3) Five persons are sitting between E and F. E can be to the left of F in Case I and to the right of F in Case II.
4) Three persons are sitting between O and E. O can be to the right of E in Case I and to the left of E in Case II.
5) One person is sitting between H and O. H can be to the left of O in Case I and to the right of O in Case II.
Case I –
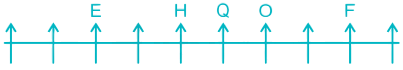
Case II –
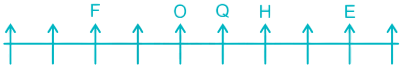
6) Three persons are sitting between H and W. This is not possible in Case II so it gets eliminated. In Case I, W is sitting to the left of H.
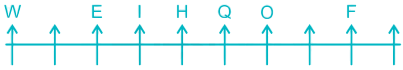
7) Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W.
Case I –
8) A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. There is only three place left so A will just between O and F, Z will just between W and E, R will at the extreme right end.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
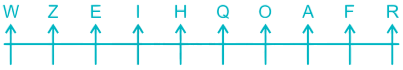
More than three persons are sitting between I and F.
Hence, the correct answer is More than three.
39. Comprehension:(Que No. 36 – 40)
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons are sitting to enjoy a feast on an occasion in a row facing North. One person is sitting between H and O. Two persons are sitting between F and Q. Three persons are sitting between H and W. Three persons are sitting between O and E. Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W. A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. Four persons are sitting to the right of Q. Five persons are sitting between E and F.
Question:
What is the position of Z from the left end?
A. First
B. Second
C. Fourth
D. Sixth
E. None of these
Solution
Given:-
Ten persons are sitting in a row facing North,
1) Four persons are sitting to the right of Q.
2) Two persons are sitting between F and Q. F can be to the left or to the right of Q.
Case I –
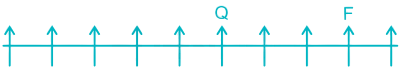
Case II –
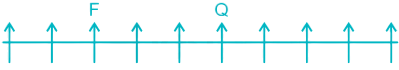
3) Five persons are sitting between E and F. E can be to the left of F in Case I and to the right of F in Case II.
4) Three persons are sitting between O and E. O can be to the right of E in Case I and to the left of E in Case II.
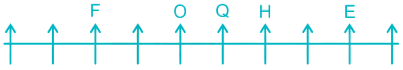
5) One person is sitting between H and O. H can be to the left of O in Case I and to the right of O in Case II.
Case I –
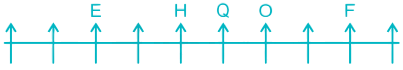
Case II –
6) Three persons are sitting between H and W. This is not possible in Case II so it gets eliminated. In Case I, W is sitting to the left of H.
7) Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W.
Case I –
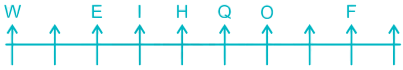
8) A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. There is only three place left so A will just between O and F, Z will just between W and E, R will at the extreme right end.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
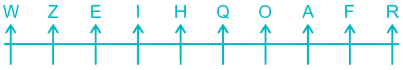
Z is second from the left end.
Hence, the correct answer is Second.
40. Comprehension:(Que No. 36 – 40)
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Ten persons are sitting to enjoy a feast on an occasion in a row facing North. One person is sitting between H and O. Two persons are sitting between F and Q. Three persons are sitting between H and W. Three persons are sitting between O and E. Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W. A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. Four persons are sitting to the right of Q. Five persons are sitting between E and F.
Question:
Who is sitting immediately next to Q?
A. The one who is sitting fourth to the right of W.
B. The one who is sitting exactly between Q and R.
C. The one who is sitting exactly between O and F.
D. The one who is sitting fifth to the right of W.
E. All of the above
Solution
Given:-
Ten persons are sitting in a row facing North,
1) Four persons are sitting to the right of Q.
2) Two persons are sitting between F and Q. F can be to the left or to the right of Q.
Case I –
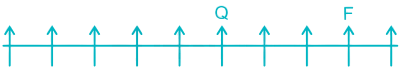
Case II –
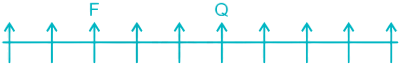
3) Five persons are sitting between E and F. E can be to the left of F in Case I and to the right of F in Case II.
4) Three persons are sitting between O and E. O can be to the right of E in Case I and to the left of E in Case II.
5) One person is sitting between H and O. H can be to the left of O in Case I and to the right of O in Case II.
Case I –
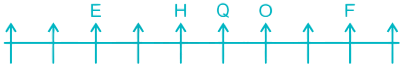
Case II –
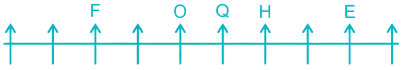
6) Three persons are sitting between H and W. This is not possible in Case II so it gets eliminated. In Case I, W is sitting to the left of H.
7) Two persons are sitting between I and W. I is sitting to the right of W.
Case I –
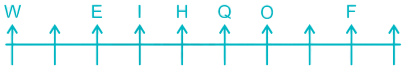
8) A is sitting to the right of Z and to the left of R. There is only three place left so A will just between O and F, Z will just between W and E, R will at the extreme right end.
Thus, the final arrangement is –
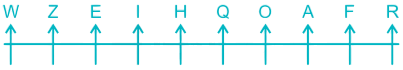
Hence, The one who is sitting fourth to the right of W.
41. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
11, 12, 26, 81, 328, ?
A. 1540
B. 1545
C. 1640
D. 1645
E. 1700
Solution
GIVEN:
11, 12, 26, 81, 328, ?
Concept Used:
Series is continuously multiplying and addition in increasing order.
Calculation:
The series follows the following pattern:
⇒ 11 × 1 + 1 = 12
⇒ 12 × 2 + 2 = 26
⇒ 26 × 3 + 3 = 81
⇒ 81 × 4 + 4 = 328
⇒ 328 × 5 + 5 = 1645
∴ The required value of “?” is 1645.
42. What will come in the place of question mark (?) in the following number series?60, 90, 144, 252, 504, 1260, ?
A. 6040
B. 5040
C. 3040
D. 4040
E. 7040
Solution
Given:
60, 90, 144, 252, 504, 1260, ?
Calculation:
The pattern of the series can be explained as,
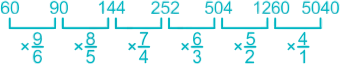
∴ The value of ? is 5040.
43. What should come in place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following number series?
399, 360, 323, 288, 255, ?
A. 225
B. 224
C. 223
D. 324
E. 220
Solution
Calculation:
399 – 39 = 360
360 – 37 = 323
323 – 35 = 288
288 – 33 = 255
255 – 31 = 224
∴ ? = 224
44. What will come in the place of question mark (?) in the following number series?
300, 297, 285, 263, 230, ?
A. 185
B. 187
C. 186
D. 200
E. 270
Solution
Given:
300, 297, 285, 263, 230, ?
Calculation:
From the above series, the logic can be explained as
300 – 297 = 3
297 – 285 = 12
285 – 263 = 22
263 – 230 = 33
230 – ? = let’s say x
Taking the double difference
12 – 3 = 9
22 – 12 = 10
33 – 22 = 11
By observing the pattern of double difference we can say
x – 33 = 12
⇒ x = 45
So, 230 – ? = 45
⇒ ? = 185
∴ The value of ? will be 185.
45. What should come in place of the question mark (?) in the following number series?
576, ?, 676, 729, 784, 841
A. 675
B. 625
C. 685
D. 645
E. None of these
Solution
576 = 242
625 = 252
676 = 262
729 = 272
784 = 282841 = 292
46. A, B, and C started a business with an investment ratio of 10 : 12 : 15 for one year. C stayed for 1 year in the business, but the other two left after some months (both left at different months). If the profit is divided in the ratio of 5 : 8 : 15. Then for how many months B stayed in the business?
A. 6 months
B. 8 months
C. 10 months
D. 12 months
E. 4 months
Solution
Given:
A, B, and C started a business with an investment ratio of 10 : 12 : 15
C stayed for 1 year in the business, but the other two left after some months
The profit is divided in the ratio of 5 : 8 : 15
Calculation:
Let, A stayed in the business after p months
B stayed in the business after q months
According to the question,
⇒ (10 × p) : (12 × q) : (15 × 12) = 5 : 8 : 15
So, we can write that
⇒ (12 × q) : (15 × 12) = 8 : 15
⇒ q = 8
∴ B stayed in the business after 8 months
47. Directions: The given table shows the total number of players playing (Volleyball + Football + Cricket) from five different schools.
| Schools | Total number of players playing all the three games | Percentage of number of players playing Volleyball | Ratio between number of players playing football to cricket |
| A | 400 | 40% | 3: 5 |
| B | 500 | 25% | 2: 3 |
| C | 350 | 20% | 3: 4 |
| D | 450 | 30% | 4: 5 |
| E | 600 | 33.33% | 1: 4 |
Note:
Total number of players = Number of players played Volleyball + Number of players played football + Number of players played cricket
Question:
Find the difference between the number of players playing cricket in school C and D together and the number of players playing football in school D and E together.
A. 150
B. 115
C. 175
D. 200
E. 100
Solution
General solution:
School A:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 400
Number of players playing volleyball = 400 × (40/100) = 160
Number of players playing football and cricket = (400 – 160) = 240
Number of players playing football = 240/8 × 3 = 90
Number of players playing cricket = 240 – 90 = 150
School B:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 500
Number of players playing volleyball = 500 × (25/100) = 125
Number of players playing football and cricket = (500 – 125) = 375
Number of players playing football = 375/5 × 2 =150
Number of players playing cricket = 375 – 150 = 225
School C:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 350
Number of players playing volleyball = 350 × (20/100) = 70
Number of players playing football and cricket = (350 – 70) = 280
Number of players playing cricket = 280/7 × 4 = 160
Number of players playing football = 280 – 160 = 120
School D:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 450
Number of players playing volleyball = 450 × (30/100) = 135
Number of players playing football and cricket = (450 – 135) = 315
Number of players playing cricket = 315/9 × 5 = 175
Number of players playing football = 315 – 175 = 140
School E:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 600
Number of players playing volleyball = 600 × 1/3 = 200
Number of players playing football and cricket = (600 – 200) = 400
Number of players playing football = 400/5 × 1 = 80
Number of players playing cricket = 400 – 80 = 320
| Schools | Number of players playing volleyball | Number of players playing football | Number of players playing cricket |
| A | 160 | 90 | 150 |
| B | 125 | 150 | 225 |
| C | 70 | 120 | 160 |
| D | 135 | 140 | 175 |
| E | 200 | 80 | 320 |
Solution:
Number of players playing cricket in school C = 160
Number of players playing cricket in school D = 175
Number of players playing football in school D = 140
Number of players playing football in school E = 80
Required difference = (160 + 175) – (140 + 80) = 335 – 220 = 115
48. Directions: The given table shows the total number of players playing (Volleyball + Football + Cricket) from five different schools.
| Schools | Total number of players playing all the three games | Percentage of number of players playing Volleyball | Ratio between number of players playing football to cricket |
| A | 400 | 40% | 3: 5 |
| B | 500 | 25% | 2: 3 |
| C | 350 | 20% | 3: 4 |
| D | 450 | 30% | 4: 5 |
| E | 600 | 33.33% | 1: 4 |
Note:
Total number of players = Number of players played Volleyball + Number of players played football + Number of players played cricket
Question:
Number of players playing cricket in school B is what percentage of the number of players playing volleyball in school E.
A. 125%
B. 130%
C. 140%
D. 112.5%
E. 120%
Solution
General solution:
School A:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 400
Number of players playing volleyball = 400 × (40/100) = 160
Number of players playing football and cricket = (400 – 160) = 240
Number of players playing football = 240/8 × 3 = 90
Number of players playing cricket = 240 – 90 = 150
School B:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 500
Number of players playing volleyball = 500 × (25/100) = 125
Number of players playing football and cricket = (500 – 125) = 375
Number of players playing football = 375/5 × 2 =150
Number of players playing cricket = 375 – 150 = 225
School C:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 350
Number of players playing volleyball = 350 × (20/100) = 70
Number of players playing football and cricket = (350 – 70) = 280
Number of players playing cricket = 280/7 × 4 = 160
Number of players playing football = 280 – 160 = 120
School D:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 450
Number of players playing volleyball = 450 × (30/100) = 135
Number of players playing football and cricket = (450 – 135) = 315
Number of players playing cricket = 315/9 × 5 = 175
Number of players playing football = 315 – 175 = 140
School E:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 600
Number of players playing volleyball = 600 × 1/3 = 200
Number of players playing football and cricket = (600 – 200) = 400
Number of players playing football = 400/5 × 1 = 80
Number of players playing cricket = 400 – 80 = 320
| Schools | Number of players playing volleyball | Number of players playing football | Number of players playing cricket |
| A | 160 | 90 | 150 |
| B | 125 | 150 | 225 |
| C | 70 | 120 | 160 |
| D | 135 | 140 | 175 |
| E | 200 | 80 | 320 |
Solution:
Number of players playing cricket in school B = 225
Number of players playing volleyball in school E = 200
Required percentage = 225/200 × 100 = 112.5%
49. Directions: The given table shows the total number of players playing (Volleyball + Football + Cricket) from five different schools.
| Schools | Total number of players playing all the three games | Percentage of number of players playing Volleyball | Ratio between number of players playing football to cricket |
| A | 400 | 40% | 3: 5 |
| B | 500 | 25% | 2: 3 |
| C | 350 | 20% | 3: 4 |
| D | 450 | 30% | 4: 5 |
| E | 600 | 33.33% | 1: 4 |
Note:
Total number of players = Number of players played Volleyball + Number of players played football + Number of players played cricket
Question:
Find the total number of players playing football in all the schools.
A. 625
B. 675
C. 580
D. 735
E. 755
Solution
General solution:
School A:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 400
Number of players playing volleyball = 400 × (40/100) = 160
Number of players playing football and cricket = (400 – 160) = 240
Number of players playing football = 240/8 × 3 = 90
Number of players playing cricket = 240 – 90 = 150
School B:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 500
Number of players playing volleyball = 500 × (25/100) = 125
Number of players playing football and cricket = (500 – 125) = 375
Number of players playing football = 375/5 × 2 =150
Number of players playing cricket = 375 – 150 = 225
School C:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 350
Number of players playing volleyball = 350 × (20/100) = 70
Number of players playing football and cricket = (350 – 70) = 280
Number of players playing cricket = 280/7 × 4 = 160
Number of players playing football = 280 – 160 = 120
School D:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 450
Number of players playing volleyball = 450 × (30/100) = 135
Number of players playing football and cricket = (450 – 135) = 315
Number of players playing cricket = 315/9 × 5 = 175
Number of players playing football = 315 – 175 = 140
School E:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 600
Number of players playing volleyball = 600 × 1/3 = 200
Number of players playing football and cricket = (600 – 200) = 400
Number of players playing football = 400/5 × 1 = 80
Number of players playing cricket = 400 – 80 = 320
| Schools | Number of players playing volleyball | Number of players playing football | Number of players playing cricket |
| A | 160 | 90 | 150 |
| B | 125 | 150 | 225 |
| C | 70 | 120 | 160 |
| D | 135 | 140 | 175 |
| E | 200 | 80 | 320 |
Solution:
Number of players playing football in school A = 90
Number of players playing football in school B = 150
Number of players playing football in school C = 120
Number of players playing football in school D = 140
Number of players playing football in school E = 80
Required sum = (90 + 150 + 120 + 140 + 80) = 580
50. Directions: The given table shows the total number of players playing (Volleyball + Football + Cricket) from five different schools.
| Schools | Total number of players playing all the three games | Percentage of number of players playing Volleyball | Ratio between number of players playing football to cricket |
| A | 400 | 40% | 3: 5 |
| B | 500 | 25% | 2: 3 |
| C | 350 | 20% | 3: 4 |
| D | 450 | 30% | 4: 5 |
| E | 600 | 33.33% | 1: 4 |
Note:
Total number of players = Number of players played Volleyball + Number of players played football + Number of players played cricket
Question:
Find the ratio between the number of players playing volleyball in school B and D to the number of players playing cricket in school A and C.
A. 28: 31
B. 12: 19
C. 26: 31
D. 13: 21
E. 13: 15
Solution
General solution:
School A:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 400
Number of players playing volleyball = 400 × (40/100) = 160
Number of players playing football and cricket = (400 – 160) = 240
Number of players playing football = 240/8 × 3 = 90
Number of players playing cricket = 240 – 90 = 150
School B:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 500
Number of players playing volleyball = 500 × (25/100) = 125
Number of players playing football and cricket = (500 – 125) = 375
Number of players playing football = 375/5 × 2 =150
Number of players playing cricket = 375 – 150 = 225
School C:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 350
Number of players playing volleyball = 350 × (20/100) = 70
Number of players playing football and cricket = (350 – 70) = 280
Number of players playing cricket = 280/7 × 4 = 160
Number of players playing football = 280 – 160 = 120
School D:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 450
Number of players playing volleyball = 450 × (30/100) = 135
Number of players playing football and cricket = (450 – 135) = 315
Number of players playing cricket = 315/9 × 5 = 175
Number of players playing football = 315 – 175 = 140
School E:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 600
Number of players playing volleyball = 600 × 1/3 = 200
Number of players playing football and cricket = (600 – 200) = 400
Number of players playing football = 400/5 × 1 = 80
Number of players playing cricket = 400 – 80 = 320
| Schools | Number of players playing volleyball | Number of players playing football | Number of players playing cricket |
| A | 160 | 90 | 150 |
| B | 125 | 150 | 225 |
| C | 70 | 120 | 160 |
| D | 135 | 140 | 175 |
| E | 200 | 80 | 320 |
Solution:
Number of players playing volleyball from school B = 125
Number of players playing volleyball from school D = 135
Number of players playing cricket from school A = 150
Number of players playing cricket from school C = 160
Required ratio = (260: 310) = 26: 31
51. Directions: The given table shows the total number of players playing (Volleyball + Football + Cricket) from five different schools.
| Schools | Total number of players playing all the three games | Percentage of number of players playing Volleyball | Ratio between number of players playing football to cricket |
| A | 400 | 40% | 3: 5 |
| B | 500 | 25% | 2: 3 |
| C | 350 | 20% | 3: 4 |
| D | 450 | 30% | 4: 5 |
| E | 600 | 33.33% | 1: 4 |
Note:
Total number of players = Number of players played Volleyball + Number of players played football + Number of players played cricket
Question:
1/4th and 1/3rd of volleyball players and football players respectively from school A are females. If the total number of females playing in school A are 140. Find the number of female players playing cricket in school A.
A. 40
B. 70
C. 90
D. 50
E. 60
Solution
General solution:
School A:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 400
Number of players playing volleyball = 400 × (40/100) = 160
Number of players playing football and cricket = (400 – 160) = 240
Number of players playing football = 240/8 × 3 = 90
Number of players playing cricket = 240 – 90 = 150
School B:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 500
Number of players playing volleyball = 500 × (25/100) = 125
Number of players playing football and cricket = (500 – 125) = 375
Number of players playing football = 375/5 × 2 =150
Number of players playing cricket = 375 – 150 = 225
School C:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 350
Number of players playing volleyball = 350 × (20/100) = 70
Number of players playing football and cricket = (350 – 70) = 280
Number of players playing cricket = 280/7 × 4 = 160
Number of players playing football = 280 – 160 = 120
School D:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 450
Number of players playing volleyball = 450 × (30/100) = 135
Number of players playing football and cricket = (450 – 135) = 315
Number of players playing cricket = 315/9 × 5 = 175
Number of players playing football = 315 – 175 = 140
School E:
Total number of players playing all the three games = 600
Number of players playing volleyball = 600 × 1/3 = 200
Number of players playing football and cricket = (600 – 200) = 400
Number of players playing football = 400/5 × 1 = 80
Number of players playing cricket = 400 – 80 = 320
| Schools | Number of players playing volleyball | Number of players playing football | Number of players playing cricket |
| A | 160 | 90 | 150 |
| B | 125 | 150 | 225 |
| C | 70 | 120 | 160 |
| D | 135 | 140 | 175 |
| E | 200 | 80 | 320 |
Solution:
Number of female players playing volleyball from school A = 160 × 1/4 = 40
Number of female players playing football from school A = 90 × 1/3 = 30
Total number of female players playing all the games from school A = 140
Number of female players playing cricket from school A = 140 – (40 + 30) = 70
52. In the given question, two equations numbered I and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 2x2 – 5x – 12 = 0
II. y2 – 10y + 24 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between them cannot be established
Solution
Given:
2×2 – 5x – 12 = 0
y2 – 10y + 24 = 0
Calculation:
From I,
2×2 – 5x – 12 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 8x + 3x – 12 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 4) + 3(x – 4) = 0
⇒ (2x + 3)(x – 4) = 0
⇒ x = -3/2, 4
From II,
y2 – 10y + 24 = 0
⇒ y2 – 6y – 4y + 24 = 0
⇒ y(y – 6) – 4(y – 6) = 0
⇒ (y – 4)(y – 6) = 0
⇒ y = 4, 6
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| -3/2 | 4 | x < y |
| -3/2 | 6 | x < y |
| 4 | 4 | x = y |
| 4 | 6 | x < y |
∴ x ≤ y.
53. Two equations I and II are given below in question. You have to solve these equations and give the answer.
I. x2 – 25x + 156 = 0
II. y2 – 26y + 169 = 0
A. x < y
B. x > y
C. x ≤ y
D. x ≥ y
E. x = y or the relation between x and y can’t be established.
Solution
Given:
I. x2 – 25x + 156 = 0
II. y2 – 26y + 169 = 0
Calculation:
I. x2 – 25x + 156 = 0
⇒ x2 – 13x – 12x + 156 = 0
⇒ x(x – 13) – 12(x – 13)= 0
⇒ (x – 13)(x – 12) = 0
⇒ x = 13, 12
II. y2 – 26y + 169 = 0
⇒ y2 – 13y – 13y + 169 = 0
⇒ y(y – 13) – 13(y – 13) =0
⇒ (y – 13)(y – 13) = 0
⇒ y = 13, 13
| Value of ‘x’ | Relation | Value of ‘y’ |
| 13 | = | 13 |
| 12 | < | 13 |
When we compared the values of ‘x’ and ‘y’ in the table above, we found that there are TWO relations between X and Y i.e. < and =. So, a relation between x and y is “x ≤ y”.
∴ After comparison, all the values of x and y the relation is “x ≤ y”.
54. In the given questions, two equations numbered l and II are given. You have to solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 5x – 6 = 0
II. 3y2 – 20y + 17 = 0
A. x < y
B. No relation in x and y or x = y
C. x > y
D. x ≤ y
E. x ≥ y
Solution
Calculations:
From I,
x2 + 5x – 6 = 0
⇒ x2 + 6x – x – 6 = 0
⇒ x(x + 6) – 1(x + 6) = 0
⇒ (x + 6)(x – 1) = 0
⇒ x = -6, 1
From II,
3y2 – 20y + 17 = 0
⇒ 3y2 – 3y – 17y + 17 = 0
⇒ 3y(y – 1) – 17(y – 1) = 0
⇒ (y – 1)(3y – 17) = 0
Taking,
⇒ y – 1 = 0 or 3y – 17 = 0
⇒ y = 1 or y = 17/3
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| x | Y | Relation |
| – 6 | 1 | x < y |
| – 6 | 17/3 | x < y |
| 1 | 1 | x = y |
| 1 | 17/3 | x < y |
∴ After comparing x and y both, x ≤ y.
55. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 5x – 50 = 0
II. y2 + 15y + 50 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. No relation in x and y or x = y
Solution
Given:
I. x2 – 5x – 50 = 0
II. y2 + 15y + 50 = 0
Calculation:
From I
x2 – 5x – 50 = 0
⇒ x2 – 10x + 5x – 50 = 0
⇒ x(x – 10) + 5(x – 10) = 0
⇒ (x – 10)(x + 5) = 0
⇒ x = 10, -5
From II
y2 + 15y + 50 = 0
⇒ y2 + 10y + 5y + 50 = 0
⇒ y(y + 10) + 5(y + 10) = 0
⇒ (y + 10)(y + 5) = 0
⇒ y = -10, -5
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation)
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation between x & y |
| 10 | -10 | x > y |
| 10 | -5 | x > y |
| -5 | -10 | x > y |
| -5 | -5 | x = y |
∴ x ≥ y
Important Points
| Sign Method | ||
| Equation | Sign | Remark |
| ax2 + bx + c = 0 | -Ve, -Ve | Same signs |
| ax2 – bx + c = 0 | +Ve, +Ve | Same signs |
| ax2 + bx – c = 0 | -Ve, +Ve | Larger root is negative smaller root is positive |
| ax2 – bx – c = 0 | -Ve, +Ve | Larger root is positive smaller root is negative |
56. A vessel containing mixture of milk, water and honey are in the ratio 7: 5: 4. If 12 litres of milk and 9 litres of honey is added then the ratio of milk and honey together to the total mixture is 8: 11. Find the initial quantity of water present in the mixture.
A. 35 litres
B. 25 litres
C. 40 litres
D. 45 litres
E. 55 litres
Solution
Solution:
Milk in the mixture initially = 7a
Water in the mixture initially = 5a
Honey in the mixture initially = 4a
If 12 litres of milk and 9 litres of honey is added, then the ratio of milk and honey to the total mixture is 8: 11
(7a + 12 + 4a + 9)/(7a + 12 + 4a + 9 + 5a) = 8/11
(11a + 21)/ (16a + 21) = 8/11
(121a + 231) = (128a + 168)
7a = 63
a = 9
Initial quantity of water in the mixture = 9 × 5 = 45
57. Kamal has scored an average of 80 marks in 5 subjects. After rechecking it is found that his marks in History and Geography were wrongly entered as 85 and 90 respectively, instead of 75 and 80 respectively. Find the percentage change of Kamal’s average score.
A. 5% decrease
B. 5% increase
C. 5.26% increase
D. 5.26% decrease
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Kamal scored an average of 80 in 5 subjects
Marks of History & Geography is wrongly entered as 85 and 90 respectively
Actual marks in History & Geography are 75 and 80 respectively
Concept Used:
Average (A) = S/N
Where S = sum of observations, and N = number of observations
Calculation:
The total marks in 5 subjects = 80 × 5 = 400
Total marks of wrong input = 85 + 90 = 175
Actual total marks = 75 + 80 = 155
Net error marks = 175 – 155 = 20
Now, total marks of Kamal = 400 – 20 = 380
So, the average marks of Kamal = 380/5 = 76
His average marks decreased by = 100 × (80 – 76)/80 = 5%
∴ The correct answer is option 1
58.
Directions: The following line graph shows the number of students studying in school A, B and C in four different years 2000, 2001, 2002 and 2003.
Question:
If the number of students studying in School A in 2004 is 50 more than the number of students studying in School A in 2003, then find the average number of students studying in School A from 2000 to 2004.
A. 220
B. 280
C. 260
D 230
E. 320
Solution
Solution:
Number of students studying in school A in 2004 = 150 + 50 = 200
The average number of students studying in school A from 2000 to 2004
Required average = (400 + 300 + 250 + 150 + 200)/ 5 = 260
59.
Directions: The following line graph shows the number of students studying in school A, B and C in four different years 2000, 2001, 2002 and 2003.
Question:
If the total number of students studying in School A in 2000 and 2001 is increased by 25% and the number of students studying in School C in 2001 and 2002 is decreased by 10%, then find the ratio between the number of students studying in School A in 2000 and 2001 to the number of students studying in school C in 2001 and 2002.
A. 171: 87
B. 135: 89
C. 123: 17
D. 175: 72
E. 89: 81
Solution
Solution:
Number of students studying in school A in 2000 and 2001 = (400 + 300) × 125/100 = 875
Number of students studying in School C in 2001 and 2002 = (250 + 150) × 90/100 = 360
Required ratio = 875: 360 = 175: 72
60.
Directions: The following line graph shows the number of students studying in school A, B and C in four different years 2000, 2001, 2002 and 2003.
Question:
If the number of students (boys to girls) studying in School B in 2002 is in the ratio of 4: 3 and the number of students (boys to girls) studying in School C in 2003 is in the ratio of 8: 7. Find the sum of the number of girls studying in school B in 2002 and number of girls studying in School C in 2003.
A. 265
B. 210
C. 230
D. 245
E. 290
Solution
Solution:
Number of girls studying in School B in 2002 = 350/7 × 3 = 150
Number of girls studying in School C in 2003 = 300/15 × 7 = 140
Required total = (150 + 140) = 290
61.
Directions: The following line graph shows the number of students studying in school A, B and C in four different years 2000, 2001, 2002 and 2003.

Question:
If the number of students studying in School B in all the years is considered as the pie chart, find the approximate value of the central angle formed by students studying in 2002 in School B.
A. 93°
B. 84°
C. 87°
D. 89°
E. 82°
Solution
Solution:
Total number of students studying in the school B in all the years = (300 + 350 + 350 + 450) = 1450
Required angle = 350/1450 × 360 = 86.89° = 87°
62. Directions: The following line graph shows the number of students studying in school A, B and C in four different years 2000, 2001, 2002 and 2003.

Question:
The number of students studying in School A in 2000 is what percentage of the number of students studying in School C in 2003.
A. 120%
B. 140%
C. 133.33%
D. 150%
E. 125%
Solution
Solution:
Number of students studying in school A in 2000 = 400
Number of students studying in School C in 2003 = 300
Required percentage = 400/300 × 100 = 133.33%
63. A train crosses a 500 m long platform in 2 minutes at the speed of 72 km/hr, then find in how much time it crosses another train of same length travelling at a speed of 108 km/hr in opposite direction.
A. 76 seconds
B. 84 seconds
C. 96 seconds
D. 120 seconds
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
The speed of train = 72 km/hr
The length of platform = 500 m
The speed of another train = 108 km/hr
Formula used:
Distance = speed × time
Concept used:
To convert speed from km/hr to m/s the multiply with 5/18
Relative speed concept,
Speed of both trains will add when the train moves in the opposite direction
Speed of both the train will subtract when the train moves in the same direction
Calculation:
Let the length of train be l
Now, Distance = speed × time
⇒ l + 500 = 72 × 5/18 × 120
⇒ l = 1900 m
The total length of both the train = 2 × 1900 = 3800 m
Both trains moving in the opposite direction so speed = (20 + 30) = 50 m/s
Time = 3800/50 = 76 second
∴ The time taken to cross another train is 76 seconds
64. What approximate value should come in the place of the question mark (?) in the following equation?
49.99% of 199.99 + 59.99% of 299.99 = ? – 29.99% of 249.99
A. 355
B. 370
C. 380
D. 320
E. 300
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
49.99% of 199.99 + 59.99% of 299.99 = ? – 29.99% of 249.99
⇒ 50% of 200 + 60% of 300 = ? – 30% of 250
⇒ 100 + 180 = ? – 75
⇒ 280 = ? – 75
⇒ ? = 355
Hence, 355 will come in the place of (?).
65. What approximate value should come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
189 + 231.10 – 200.20 – 66.89 + 119.12 = ? + 80.12−−−−√80.12 x 8.36
A. 175
B. 95
C. 200
D. 215
E. 120
Solution
Solution :
Concept used :
Follow the BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the question is given below:
Step 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘ Brackets ‘ must be solved first and in the bracket,
Step 2: Any mathematical ‘ of ‘ or ‘exponent’ must be solved next,
Step 3: Next, The part of the equation that contains ‘Division’ and ‘multiplication’ are calculated,
Step 4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contains ‘Addition ‘ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
189 + 231.10 – 200.20 – 66.89 + 119.12 = ? + 80.12−−−−√80.12 x 8.36
⇒ 189 + 231 – 200 – 67 + 119 = ? + 9 x 8
⇒ 420 – 267 + 119 = ? + 72
⇒ 539 – 267 = ? + 72
⇒ 272 = ? + 72
⇒ ? =200
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
66. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
124.83 × 59.82 ÷ 24.94 + 169.79 × 13.96 ÷ 1.98 + 124.96 = ?2
A. 49
B. 36
C. 35
D. 47
E. 40
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
124.83 × 59.82 ÷ 24.94 + 169.79 × 13.96 ÷ 1.98 + 124.96 = ?2
⇒ 125 × 60 ÷ 25 + 170 × 14 ÷ 2 + 125 = ?2
⇒ 125 × 2.4 + 170 × 7 + 125 = ?2
⇒ 300 + 1190 + 125 = ?2
⇒ 1615 = ?2
⇒ ? ≈ 40
Hence, 40 will come in the place of (?).
67. What approximate value should come in the place of the question mark (?) in the following equation?
24.95% of 199.99 + 44.99% of 299.99 = ? + 59.97% of 399.99
A. 54
B. – 54
C. 55
D. – 55
E. – 60
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
24.95% of 199.99 + 44.99% of 299.99 = ? + 59.97% of 399.99
⇒ 25% of 200 + 45% of 300 = ? + 60% of 400
⇒ 50 + 135 = ? + 240
⇒ 185 = ? + 240
⇒ ? = -55
Hence, -55 will come in the place of (?).
68. What approximate value should come in the place of the question mark (?) in the following equation?
38.98 ÷ 12.99 × 16.97 + 43.94 = ? + 99.99 ÷ 4.97 × 6.98
A. 45
B. 40
C. 35
D. – 40
E. – 45
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
38.98 ÷ 12.99 × 16.97 + 43.94 = ? + 99.99 ÷ 4.97 × 6.98
⇒ 39 ÷ 13 × 17 + 44 = ? + 100 ÷ 5 × 7
⇒ 3 × 17 + 44 = ? + 20 × 7
⇒ 51 + 44 = ? + 140
⇒ 95 = ? + 140
⇒ 95 – 140 = ?
⇒ ? = – 45
Hence, -45 will come in the place of (?).
69. What approximate value should come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
25.12% of ? + 60.20% of 140 = 7055.90−−−−−−√7055.90 x 5.20 – 6.34 x 6.20
A. 1160
B. 1260
C. 1200
D. 1100
E. 1220
Solution
Solution :
Concept used :
Follow the BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the question is given below:
Step 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘ Brackets ‘ must be solved first and in the bracket,
Step 2: Any mathematical ‘ of ‘ or ‘exponent’ must be solved next,
Step 3: Next, The part of the equation that contains ‘Division’ and ‘multiplication’ are calculated,
Step 4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contains ‘Addition ‘ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
⇒ 25/100 x ? + 60/100 x 140 = 7055.90−−−−−−√7055.90 x 5 – 6 x 6
⇒ 1/4 x ? + 84 = 84 x 5 – 36
⇒ 1/4 x ? + 84 = 420 – 36
⇒ 1/4 x ? = 420 – 120
⇒ 1/4 x ? = 300
⇒ ? = 1200
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
70. Ram spends 20% of his monthly income on Rent. Out of the remaining, he spends 10% on his children’s education, 30% on food, and 12% on the bills. Now he is left with Rs. 28800 after all these expenditures. Find his monthly income.
A. Rs. 60000
B. Rs. 75000
C. Rs. 65000
D. Rs. 70000
E. Rs. 80000
Solution
Given:
Ram spends 20% of his monthly income on Rent.
Out of the remaining, he spends 10% on his children’s education, 30% on food, and 12% on the bills
He is left with Rs. 28800 after all these expenditures
Calculation:
Let, Ram’s monthly income = 100a
After paying rent his remaining amount = 100a × (100 – 20)/100 = 80a
On this remaining amount, total expenditure = (10 + 30 + 12) = 52%
So, his saving = 80a × (100 – 52)% = 80a × 48/100
According to the question,
⇒ 80a × 48/100 = 28800
⇒ a = 750
Ram’s income = 100 × 750 = Rs. 75000
∴ The correct answer is option 2
71. Raj has invested Rs 12,000 at some rate of simple interest for 4 years and received Rs. 14,160. What will be the simple interest received by him after 4 years, if he increases the principal amount by Rs. 1,800 and the rate of interest by 4% points per annum?
A. Rs. 4,662
B. Rs. 4,992
C. Rs. 4,962
D. Rs. 4,692
E. Rs. 4,690
Solution
Given:
Initial principal = Rs. 12,000
Initial time = 4 years
and Amount received = Rs. 14,160
Formula used:
(1) S.I = (P × R × T)/100
where, S.I = Simple Interest,
P = Principal,
R = Rate of Interest
and T = Time
(2) Amount = Principal + Interest
Calculation:
Let the rate of interest be R%.
Then,
Amount = Principal + S.I
⇒ S.I = Rs. 14,160 – Rs. 12,000
⇒ (P × R × T)/100 = Rs. 2,160
⇒ (Rs. 12,000 × R × 4)/100 = Rs. 2,160
⇒ R = 4.5%
New rate of interest = (R + 4)%
⇒ (4.5 + 4)%
⇒ 8.5%
and New principal amount = Rs. 12,000 + Rs. 1,800
⇒ Rs. 13,800
Now, S.I = (P × R × T)/100
⇒ (Rs. 13,800 × 8.5 × 4)/100
⇒ Rs. 4,692
∴ The simple interest received by him is Rs. 4,692.
72. C can complete 4/7 of a work in 14 days. C and D together complete 2/7 of the same work in 4 2/3 days. Find the time taken by D to complete the entire work alone.
A. 28 days
B. 32 days
C. 49 days
D. 35 days
E. 23 days
Solution
C can complete 4/7 of the work in 14 days.
Work done by C in 1 day = (4/7) / 14 = 4/98 = 2/49
C and D together complete 2/7 of the work in 4 2/3 days (14/3) days:
Work done by C and D in 1 day = (2/7) / (14/3) = 2/7 × 3/14 = 6/98 = 3/49
D’s 1-day work = 3/49 − 2/49 = 1/49
If D does 1/49 of the work in 1 day, the time taken to complete the entire work is:
Time taken by D = 1 / (1/49) = 49 days.
Thus, D will take 49 days to complete the work alone.
73. If the speed of the stream is 3 kmph. The distance between the two points A and B is 45 km. Total time taken by the boat to cover both upstream and downstream for a distance A and B is 8 hours. Find the speed of the boat in still water.
A. 13 kmph
B. 10 kmph
C. 12 kmph
D. 9 kmph
E. 15 kmph
Solution
Solution:
Speed of the boat in still water = a
Speed of the stream = 3kmph
Total time taken by the boat to cover upstream and downstream is 8 hours
45/(a + 3) + 45/ (a – 3) = 8
45 × (a – 3) + 45 × (a + 3) = 8 × (a – 3) (a + 3)
(45a – 135) + 45a + 135 = 8 × (a2 + 3a – 3a – 9)
90a = 8 × (a2 – 9)
90a = 8a2 – 72
8a2 – 90a – 72 = 0
a = 12, a = -3/4
Speed cannot be negative
Speed of the boat in still water = 12 kmph
Hence, option(3) is correct.
74. Direction : Study the below data carefully and answer accordingly.
There are 4000 players in a sports academy. They are playing in three sports namely, Cricket, Football, and Hockey. The Ratio of male to female players is 11 ∶ 9. 40% of the players are playing cricket. Men playing football are 25% of total male players. The numbers of female players in football are half the number of players in cricket. The ratio of male and female players in hockey is 4 ∶ 3.
Question:
The number of male players in football is what percent more than the number of females players in hockey?
A. 20%
B. 23.22%
C. 18%
D. 22.22%
E. None of these
Solution
 Shortcut Trick
Shortcut Trick
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 40% of total players | ||
| Football | 20% of total players | 25% of 11x | |
| Hockey | 4y | 3y | |
| 11x | 9x | ||
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 1050 | 550 | 1600 |
| Football | 550 | 800 | 1350 |
| Hockey | 600 | 450 | 1050 |
| 2200 | 1800 | 4000 |
Alternate Method
Given:
Total players = 4000
Ratio of male and female players = 11 ∶ 9
Total number of players in cricket = 40% of the total players
Male players in football = 25% of total male players
Female players in football = (1/2) of the players in cricket
The ratio of male and female players in hockey = 4 ∶ 3
Calculation:
Let the male and female players be 11x and 9x respectively
Now,
11x + 9x = 4000
⇒ 20x = 4000
⇒ x = 200
Number of male players = 11 × 200
⇒ 2200
Total number of Players in cricket = 40% of 4000
⇒ (40/100) × 4000
⇒ 40 × 40
⇒ 1600
Now,
Female players in football = (1/2) × 1600
⇒ 800
Now,
Male players in football = 25% of 2200
⇒ (25/100) × 2200
⇒ 25 × 22
⇒ 550
Now,
Total number of players in football = (800 + 550)
⇒ 1350
Now,
Total number of Players in hockey = 4000 – (Total number of Players in cricket + Total number of players in football)
⇒ 4000 – (1600 + 1350)
⇒ 4000 – 2950
⇒ 1050
Now,
Let the male and female players in hockey be 4x and 3x respectively
Now,
4x + 3x = 1050
⇒ 7x = 1050
⇒ x = 1050/7
⇒ x = 150
Now,
Number of female players in hockey = 3x
⇒ 3 × 150
⇒ 450
Now,
Required percentage = [(550 – 450)/450] × 100
⇒ (100/450) × 100
⇒ (10/45) × 100
⇒ 1000/45
⇒ 22.22%
∴ The number of male players in football is 22.22% more than the number of female players in hockey
75. Direction : Study the below data carefully and answer accordingly.
There are 4000 players in a sports academy. They are playing in three sports namely, Cricket, Football, and Hockey. The Ratio of male to female players is 11 ∶ 9. 40% of the players are playing cricket. Men playing football are 25% of total male players. The numbers of female players in football are half the number of players in cricket. The ratio of male and female players in hockey is 4 ∶ 3.
Question:
What percent male players playing cricket from the total number of male players?
A. 37.35%
B. 27.25%
C. 40%
D. 47.72%
E. 20%
Solution
 Shortcut Trick
Shortcut Trick
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 40% of total players | ||
| Football | 20% of total players | 25% of 11x | |
| Hockey | 4y | 3y | |
| 11x | 9x | ||
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 1050 | 550 | 1600 |
| Football | 550 | 800 | 1350 |
| Hockey | 600 | 450 | 1050 |
| 2200 | 1800 | 4000 |
Alternate Method
Given:
Total players = 4000
Ratio of male and female players = 11 ∶ 9
Total number of players in cricket = 40% of the total players
Male players in football = 25% of total male players
Female players in football = (1/2) of the players in cricket
The ratio of male and female players in hockey = 4 ∶ 3
Calculation:
Let the male and female players be 11x and 9x respectively
Now,
11x + 9x = 4000
⇒ 20x = 4000
⇒ x = 200
Number of male players = 11 × 200
⇒ 2200
Total number of Players in cricket = 40% of 4000
⇒ (40/100) × 4000
⇒ 40 × 40
⇒ 1600
Now,
Female players in football = (1/2) × 1600
⇒ 800
Now,
Male players in football = 25% of 2200
⇒ (25/100) × 2200
⇒ 25 × 22
⇒ 550
Now,
Total number of players in football = (800 + 550)
⇒ 1350
Now,
Total number of Players in hockey = 4000 – (Total number of Players in cricket + Total number of players in football)
⇒ 4000 – (1600 + 1350)
⇒ 4000 – 2950
⇒ 1050
Now,
Let the male and female players in hockey be 4x and 3x respectively
Now,
4x + 3x = 1050
⇒ 7x = 1050
⇒ x = 1050/7
⇒ x = 150
Now,
Number of male players in hockey = 4x
⇒ 4 × 150
⇒ 600
Now,
Total male players in cricket = 2200 – (Male players in football – Male players in hockey)
⇒ 2200 – (550 + 600)
⇒ 2200 – 1150
⇒ 1050
Now,
Required percent = (1050 /2200) × 100
⇒ 1050/22
⇒ 47.72
∴ Male players in the cricket will be 47.72%
76. Comprehension:(Que No. 34 – 38)
Direction : Study the below data carefully and answer accordingly.
There are 4000 players in a sports academy. They are playing in three sports namely, Cricket, Football, and Hockey. The Ratio of male to female players is 11 ∶ 9. 40% of the players are playing cricket. Men playing football are 25% of total male players. The numbers of female players in football are half the number of players in cricket. The ratio of male and female players in hockey is 4 ∶ 3.
Question:
What is the ratio of female players in football to the female players in hockey?
A. 7 : 9
B. 9 : 7
C., 9 : 16
D. 16 : 9
E. None of these
Solution
 Shortcut Trick
Shortcut Trick
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 40% of total players | ||
| Football | 20% of total players | 25% of 11x | |
| Hockey | 4y | 3y | |
| 11x | 9x | ||
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 1050 | 550 | 1600 |
| Football | 550 | 800 | 1350 |
| Hockey | 600 | 450 | 1050 |
| 2200 | 1800 | 4000 |
Alternate Method
Given:
Total players = 4000
Ratio of male and female players = 11 ∶ 9
Total number of players in cricket = 40% of the total players
Male players in football = 25% of total male players
Female players in football = (1/2) of the players in cricket
The ratio of male and female players in hockey = 4 ∶ 3
Calculation:
Let the male and female players be 11x and 9x respectively
Now,
11x + 9x = 4000
⇒ 20x = 4000
⇒ x = 200
Number of male players = 11 × 200
⇒ 2200
Total number of Players in cricket = 40% of 4000
⇒ (40/100) × 4000
⇒ 40 × 40
⇒ 1600
Now,
Female players in football = (1/2) × 1600
⇒ 800
Now,
Male players in football = 25% of 2200
⇒ (25/100) × 2200
⇒ 25 × 22
⇒ 550
Now,
Total number of players in football = (800 + 550)
⇒ 1350
Now,
Total number of Players in hockey = 4000 – (Total number of Players in cricket + Total number of players in football)
⇒ 4000 – (1600 + 1350)
⇒ 4000 – 2950
⇒ 1050
Now,
Let the male and female players in hockey be 4x and 3x respectively
Now,
4x + 3x = 1050
⇒ 7x = 1050
⇒ x = 1050/7
⇒ x = 150
Now,
Number of male players in hockey = 4x
⇒ 4 × 150
⇒ 600
Number of female players in hockey = 3x
⇒ 3 × 150
⇒ 450
Now,
Required ratio = 800 ∶ 450
⇒ 80 ∶ 45
⇒ 16 ∶ 9
∴ The Ratio of female players in football to the female players in hockey will be 16 ∶ 9
77. Comprehension
Direction : Study the below data carefully and answer accordingly.
There are 4000 players in a sports academy. They are playing in three sports namely, Cricket, Football, and Hockey. The Ratio of male to female players is 11 ∶ 9. 40% of the players are playing cricket. Men playing football are 25% of total male players. The numbers of female players in football are half the number of players in cricket. The ratio of male and female players in hockey is 4 ∶ 3.
Question:
What is the difference between the number of male players in hockey and football?
A. 55
B. 45
C. 60
D. 50
E. None of these
Solution
 Shortcut Trick
Shortcut Trick
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 40% of total players | ||
| Football | 20% of total players | 25% of 11x | |
| Hockey | 4y | 3y | |
| 11x | 9x | ||
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 1050 | 550 | 1600 |
| Football | 550 | 800 | 1350 |
| Hockey | 600 | 450 | 1050 |
| 2200 | 1800 | 4000 |
Alternate Method
Given:
Total players = 4000
Ratio of male and female players = 11 ∶ 9
Total number of players in cricket = 40% of the total players
Male players in football = 25% of total male players
Female players in football = (1/2) of the players in cricket
The ratio of male and female players in hockey = 4 ∶ 3
Calculation:
Let the male and female players be 11x and 9x respectively
Now,
11x + 9x = 4000
⇒ 20x = 4000
⇒ x = 200
Number of male players = 11 × 200
⇒ 2200
Total number of Players in cricket = 40% of 4000
⇒ (40/100) × 4000
⇒ 40 × 40
⇒ 1600
Now,
Female players in football = (1/2) × 1600
⇒ 800
Now,
Male players in football = 25% of 2200
⇒ (25/100) × 2200
⇒ 25 × 22
⇒ 550
Now,
Total number of players in football = (800 + 550)
⇒ 1350
Now,
Total number of Players in hockey = 4000 – (Total number of Players in cricket + Total number of players in football)
⇒ 4000 – (1600 + 1350)
⇒ 4000 – 2950
⇒ 1050
Now,
Let the male and female players in hockey be 4x and 3x respectively
Now,
4x + 3x = 1050
⇒ 7x = 1050
⇒ x = 1050/7
⇒ x = 150
Now,
Number of male players in hockey = 4x
⇒ 4 × 150
⇒ 600
Number of female players in hockey = 3x
⇒ 3 × 150
⇒ 450
Now,
Required difference = (600 – 550)
⇒ 50
∴ The difference between the number of male players in hockey and football will be 50 players.
78. Comprehension
Direction : Study the below data carefully and answer accordingly.
There are 4000 players in a sports academy. They are playing in three sports namely, Cricket, Football, and Hockey. The Ratio of male to female players is 11 ∶ 9. 40% of the players are playing cricket. Men playing football are 25% of total male players. The numbers of female players in football are half the number of players in cricket. The ratio of male and female players in hockey is 4 ∶ 3.
Question:
What is the number of female players in football?
A. 700
B. 750
C. 850
D. 800
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Total players = 4000
Ratio of male and female players = 11 ∶ 9
Total number of players in cricket = 40% of the total players
Female players in football = (1/2) of the players in cricket
Calculation:
Players in cricket = 40% of 4000
⇒ (40/100) × 4000
⇒ 40 × 40
⇒ 1600
Now,
Female players in football = (1/2) × 1600
⇒ 800
∴ The Number of females players in the football will be 800
Alternate Method
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 40% of total players | ||
| Football | 20% of total players | 25% of 11x | |
| Hockey | 4y | 3y | |
| 11x | 9x | ||
| Sports | Male | Female | |
| Cricket | 1050 | 550 | 1600 |
| Football | 550 | 800 | 1350 |
| Hockey | 600 | 450 | 1050 |
| 2200 | 1800 | 4000 |
79. By selling one of his briefcase, a shopkeeper earns 30% profit, by offering a discount of 10%. If the difference between the marked price and the cost price is Rs. 600, then find the selling price of the briefcase.
A. Rs. 1350
B. Rs. 1950
C. Rs. 1755
D. Rs. 1955
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
A shopkeeper earns 30% profit, by offering a discount of 10%
The difference between the marked price and the cost price is Rs. 600
Concept Used:
CP/MP = (100 – D)/(100 + P)
Selling price (SP) = MP × (100 – D)/100
Where, CP = cost price, MP = marked price, D = discount % and P = profit %
Calculation:
CP/MP = (100 – 10)/(100 + 30) = 9/13
Let, CP = 9a, and MP = 13a
According to the question,
⇒ 13a – 9a = 600
⇒ a = 600/4 = 150
So, the MP of the article = 150 × 13 = Rs. 1950
The SP of the article = 1950 × (100 – 10)/100 = Rs. 1755
∴ The correct answer is option 3
80. The width of a rectangular garden is 1.5 times the radius of a circular pond, and the length of the garden is 20 meters. If the area of the pond is 2464 m2, find the perimeter of the garden.
A. 148
B. 136
C. 124
D. 168
E. 218
Solution
Formula Used:
The area of a circle is given by the formula:
Area = πr2
Calculation:
Area of the pond = 2464 m2 and taking π = 22/7
2464 = 22/7 r2
2464 × 7 = 22r2
17248 = 22r2
r2 = 17248 / 22 = 784
r = 28 m
The width of the garden is 1.5 × the radius of the pond:
Width = 1.5 × 28 = 42 m
The perimeter of a rectangle is given by the formula:
Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width)
Substitute the values of length and width:
Perimeter = 2 × (20 + 42) = 2 × 62 = 124 m
Thus, the correct answer is 124 m
