1.What is the mascot chosen for the 7th North East Youth Festival 2024?
A. Lion
B. Tiger
C. Phayre’s leaf monkey
D. Peacock
Solutions
The mascot chosen for the 7th North East Youth Festival 2024 is Phayre’s leaf monkey. This selection was officially announced by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, symbolizing the essence of the eight northeastern states of India. The festival is scheduled to take place in Tripura from February 26 to February 29, marking a celebration that aims to showcase the vibrant culture and heritage of the region.
Phayre’s leaf monkey, also known as the Phayre’s langur, is a species of lutung found in parts of Southeast Asia, and its selection as the mascot reflects the festival’s commitment to celebrating and raising awareness about the rich biodiversity and ecological significance of the northeastern states.
2. Who inaugurated the Ayush Holistic Wellness Centre at the premises of the Supreme Court of India?
A. President of India
B. Chief Justice of India
C. Prime Minister of India
D. Health Minister of India
Solutions
The Correct answer is (b)
The Ayush Holistic Wellness Centre at the premises of the Supreme Court of India was inaugurated by the Chief Justice of India, DY Chandrachud, on February 22, 2024. This center is designed to promote holistic well-being, emphasizing the physical, mental, and emotional health of the Honorable Judges and staff of the Supreme Court.
This center is established under the Ministry of Ayush and is part of a broader effort to integrate traditional systems of medicine into the health and wellness practices of individuals.
The center offers a range of services and treatments based on Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy, which are the traditional systems of medicine in India collectively referred to as AYUSH. These services are tailored to enhance the overall well-being, stress management, and health of the Supreme Court’s personnel, acknowledging the demanding nature of their work and the importance of maintaining physical and mental health in such high-stress environments.
3. Where did the trilateral exercise ‘Dosti-16’ take place?
A. India
B. Sri Lanka
C. Maldives
D. Bangladesh
Solutions
The trilateral exercise ‘Dosti-16’ took place in the Maldives. This exercise is part of a series of trilateral maritime exercises involving the coast guards of India, the Maldives, and Sri Lanka, aimed at enhancing cooperation, strengthening friendship, improving mutual operational capability, and developing interoperability among the participating forces. The 16th edition of this exercise, held from February 22nd to 25th, underscores the commitment of these nations to collaborate in ensuring maritime safety and security in the region. Bangladesh also participated as an observer in this edition, highlighting the exercise’s growing importance and the interest of other regional players in maritime cooperation
4. Prime Minister Narendra Modi has inaugurated the which edition of Raisina Dialogue in New Delhi?
A. 5th
B. 9th
C. 7th
D. 8th
Solutions
The Correct answer is (b)
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the 9th edition of the Raisina Dialogue in New Delhi. The Raisina Dialogue, held from February 21 to February 23, 2024, is India’s flagship conference on geopolitics and geo-strategy, organized by the Ministry of External Affairs in collaboration with the Observer Research Foundation (ORF).
The theme for the 2024 Raisina Dialogue, “Chaturanga: Conflict, Contest, Cooperate, Create,” draws inspiration from the ancient Indian game of Chaturanga, which is considered a precursor to modern chess.
The Raisina Dialogue has established itself as a significant forum for leaders from government, business, academia, and civil society from around the world to engage in discussions that shape the international agenda.
5. Which national park is home to the Indian Rhinoceros?
A. Bandipur National Park
B. Kaziranga National Park
C. Ranthambore National Park
D. Kanha National Park
Solutions
Kaziranga National Park, located in the state of Assam, India, is renowned for its population of Indian Rhinoceros, also known as the Great One-Horned Rhinoceros.
This national park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is known to be one of the most important protected areas for the conservation of this endangered species.
The park’s marshy grasslands and tall elephant grass provide an ideal habitat for the Indian Rhinoceros, and it is estimated that around two-thirds of the world’s population of this species reside in Kaziranga National Park.
6. The founder of Homeopathy is –
A. Samuel Hahnemann
B. Hippocrates
C. Charaka
D. Sushrutha
Solutions
The correct answer is (a) Samuel Hahnemann. Samuel Hahnemann, a German physician, is considered the founder of homeopathy. In the late 18th century, Hahnemann developed the principles and practice of homeopathy based on the concept of “like cures like” and the use of highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s natural healing abilities. He outlined these principles in his book called “Organon of the Rational Art of Healing.” Hahnemann’s contributions laid the groundwork for the development and popularization of homeopathy as a complementary and alternative system of medicine.
7. Exercise Red Flag is an aerial combat exercise conducted between which countries?
A. United States and South Korea
B. United Kingdom and France
C. Australia and Japan
D. United States and NATO members
Solutions
Exercise Red Flag is an aerial combat exercise conducted between the United States and NATO members.
Exercise Red Flag is an aerial combat exercise conducted by the United States Air Force (USAF) and other allied countries. It aims to offer realistic air-combat training for military pilots and other flight crew members from the United States and allied countries.
The exercise is held several times a year at Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada. The first Red Flag exercise was held in 1975.
8. The massacre of British men, women, and children at Cawnpore (Kanpur) during the Revolt of 1857 was led by which rebel leader?
A. Nana Sahib
B. Bahadur Shah II
C. Kunwar Singh
D. Tantia Tope
Solutions
The massacre of British men, women, and children at Cawnpore (Kanpur) during the Revolt of 1857 was led by option (a) Nana Sahib.
Nana Sahib, also known as Rani Nana, was one of the prominent leaders of the Indian Rebellion of 1857 (also known as the Indian Mutiny or Sepoy Mutiny).
He was the adopted son of the last Peshwa of the Maratha Empire, Baji Rao II. After the annexation of the Maratha territories by the British, Nana Sahib’s pension was stopped, which fuelled his resentment against the British.
During the uprising, Nana Sahib and his forces captured British civilians and soldiers, including women and children, and held them hostage in the city of Cawnpore (now Kanpur). However, after a tense stand-off and negotiations, the hostages were eventually killed in a brutal massacre. The incident at
Cawnpore became one of the significant and tragic events of the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
9. When the offices of the President and Vice-President fall vacant simultaneously, who acts as President?
A. Prime Minister of India
B. The Chief Justice of India
C. The Speaker of Lok Sabha
D. The Comptroller and Auditor General of India
Solutions
When the offices of the President and Vice-President of India fall vacant simultaneously, the Chief Justice of India acts as the President. This provision is outlined in Article 65(1) of the Constitution of India. The Chief Justice of India assumes the responsibilities of the President until a newly elected President takes office.
10. The function of an assembler is____________?
A. To convert basic language into machine language
B. To convert high level language into machine language
C. To convert assemble language into machine language
D. To convert assemble language into high level language
Solutions
An assembler is a type of computer program that interprets software programs written in assembly language into machine language, code and instructions that can be executed by a computer.
11. In the following question, select the related number pair from the given alternatives.
79 : 96 : : ? : ?
A. 69 : 97
B. 114 : 131
C. 93 : 112
D. 122 : 143
Solutions
The pattern is
96 – 79 = 17
131 – 114 = 17
12. In the following question, select the odd word from the given alternatives.
A. West Bengal
B. Chandigarh
C. Kolkata
D. Lucknow
Solutions
The logic here is
All are capitals except (a).
13. Three of the following four numbers are alike in a certain way and one is different. Pick the number that is different from the rest.
A. 510
B. 1726
C. 2194
D. 2742
Solutions
except ‘c’ all are the cube of numbers and then subtract 2.
83 – 2= 510
123 – 2 = 1726
133 – 2 = 2197 -2 = 2195≠ 2194
143 – 2 = 2742
14. In the following question, select the odd letter/letters from the given alternatives.
A. GEHD
B. NLOK
C. OMPL
D. YWAV
Solutions
Except YWAV, rest all three are -2, +3, -4 series
15. In the following question, select the missing number from the given series.
4, 5, 7, 16, 28, 51, 95, ?
A. 145
B. 182
C. 174
D. 172
Solutions
The pattern followed here is
16 = 4 + 5 + 7,
28 = 5 + 7 + 16
51 =7 + 16 + 28,
95 = 16 + 28 + 51
174 = 28 + 51 + 95
16. Select the set in which the numbers are related in the same way as are the number of following set.
(5, 12, 20)
A. (3, 9, 16)
B. (7, 16, 28)
C. (1, 2, 4)
D. (4, 10, 18)
Solutions
(5, 12, 20) = 5 × 2 + 2 = 12 ,12 × 2-4 = 20
Similarly, (7, 16, 28) = 7 × 2 + 2 = 16, 16 × 2 – 4 = 28
17. Which of the following Venn diagram best represents the relationship between Football, Player and Field?
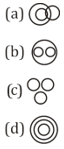
A. a
B. b
C. c
D. d
Solutions
Football, players and field all are different.
18. In the question two statements are given, followed by two conclusions, I and II. You have to consider the statements to be true even if it seems to be at variance from commonly known facts. You have to decide which of the given conclusions, if any, follows from the given statements.
I. All man is father.
II. All fathers are son.
Conclusion.
I. Some fathers are son.
II. No son is man.
A. Only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Both conclusions I and II follow
D. Neither conclusion I nor conclusion II follows
Solutions
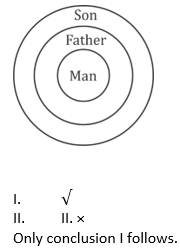
19. Which answer figure will complete the pattern in the question figure?
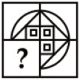
A. 
B. 
C. 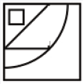 .
.
D. 
Answer A
20. In a certain code language, ‘-‘ represents ‘+’, ‘+’ represents ‘x’, ‘x’ represents ‘÷’ and ‘÷’ represents ‘-‘. Find out the answer to the following question.
12 + 38 x 19 ÷ 14 – 6 = ?
A. 48
B. 24
C. 30
D. 16
Solutions
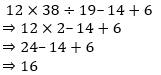
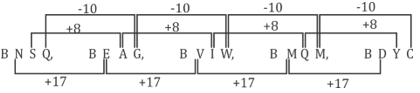
21. A series is given with one term missing. Select the correct alternative from the given ones that will complete the series.
BNSQ, BEAG, BVIW, BMQM, _______
A. BDAC
B. BDYC
C. BDYJ
D. ADAV
Solutions
22. Select the option that is related to the third word in the same way as the second word is related to the first word. (The words must be considered as meaningful English words and must not be related to each other based on the number of letters/number of consonants/vowels in the word).
DOG: BARK :: DOLPHIN: ?
A. CLICK
B. DRUM
C. GRUNT
D. BELLOW
Solutions
Animal and sound relation is used.
23. Select the option that is related to the fifth number in the same way as the second number is related to the first number and the fourth number is related to the third number.
15 : 197 :: 24 : 530 :: 9 : ?
A. 66
B. 65
C. 67
D. 78
Solutions
Second number = (First number – 1)² + 1
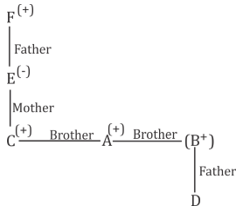
24. If A × B means that A is the brother of B, A – B means that A is the sister of B, A + B means that A is the father of B, A*B means that A is the mother of B, then which of the following expression shows that E is the paternal grandmother of D?
A. F-E+C+A-B×D
B. F+E*C×A×B+D
C. E+C-A×F*B+D
D. F*E+C-A+B×D
Solutions
In option (b), F + E* C × A × B + D
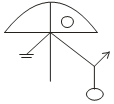
25. Select the correct mirror image of the given figure when the mirror is placed to the right of the figure.
A. 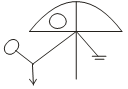
B. 
C. 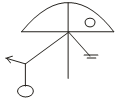
D. 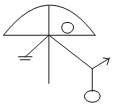
Answer B
26. Which layer of OSI model is also termed as an end-to-end layer?
A. Network Layer
B. Data-Link Layer
C. Physical layer
D. Transport Layer
Solutions
Transport layer is the fourth layer of OSI Model which ensures that messages are transmitted in the order in which they are sent without duplication of data.
Segments are the units of data in the transport layer.
The transport layer’s primary responsibility is to finish the data transfer.
It gets data from the higher layer and turns it into segments, which are smaller units.
This layer is known as an end-to-end layer because it establishes a reliable point-to-point link between the source and the destination.
27. In a Word processor, which of the following key is used to indent a paragraph?
A. Tab
B. Right arrow
C. Shift
D. Control
Solutions
In a word processor, the Tab key is used to align text by moving the cursor to a specified place.
It is part of the paragraph formatting feature, and it is normally done with the help of the tab key.
Tabs aid in the uniform distribution of text between the margins as well as indentation.
In word processing, the tab key is useful for making a document more readable.
Right-aligned, left-aligned, centred, and decimal-aligned are the most frequent custom tab configurations.
28. Which layer of TCP/IP model is analogous to the transport layer of the OSI model?
A. Network Access Layer
B. Internet Layer
C. Host-to-Host Layer
D. Application Layer
Solutions
The lowest layer of the TCP/IP model, the Host-to-Host layer, is concerned with the physical transport of data.
A network interface layer, or link layer, is another name for it.
This layer is similar to the transport layer of OSI Model.
It is in charge of end-to-end communication and error-free data transfer.
It protects upper-layer applications from data complexity.
29. A computer file sent along with an email message is termed as-
A. Add-on
B. Download
C. Plugin
D. Attachment
Solutions
An attachment also known as an email attachment is a file that is delivered along with an email message.
It could be a picture, a movie, a text document, or anything else.
Attachments can be sent and received in most email clients and webmail systems.
Use the “Attach” command to send an attachment with your email, then browse to the file you want to attach.
You can attach a file to an email message by simply dragging it into the message pane in various email interfaces.
30. In computing, _________is an extension that adds a specific feature to an existing computer program.
A. Port
B. Interface
C. Connector
D. Plug-in
Solutions
A plug-in is a software component that may be added to a program to offer support for specific features or functions.
Plug-ins are typically used in browsers, but they can also be used in a variety of other applications.
The range of customisable choices included in browsers like Mozilla Firefox is an example of a plug-in.
Individual plug-ins for this free Web browser application can be downloaded to promote different results on devices.
31. Which among the following is a set of devices intended to help people who have disabilities?
A. Assistive technology
B. Specialized support
C. Computer aided development
D. Virtual Reality
Solutions
Hardware and software designed to assist persons with disabilities are referred to as assistive technology.
Some types of assistive technology are designed to help people with physical disabilities, while others are designed to help people with learning difficulties.
Hearing aids, wheelchairs, and prosthetics are examples of common assistance devices.
A variety of assistive technology is available which provides the opportunity for nearly all people to access information technology (IT).
32. A ________is the pressing of a single key in a physical or virtual keyboard.
A. Keystone
B. Keyframe
C. Keystroke
D. Keyport
Solutions
A keystroke is a term used for a single press of a key on a keyboard.
Keystrokes are used in programming to reply when a user presses a specific key.
When it comes to typing speed, keystroke tracking, hardware, software, and other human-computer interaction studies, the keystroke is crucial.
Operating systems and software applications rely on keystrokes to carry out their next actions.
33. Name the computer program designed to simplify the execution of lengthy or complicated tasks.
A. Backup Utility
B. Disk Defragmenter
C. Software Wizard
D. Antivirus
Solutions
A wizard is a piece of software that simplifies or advises a user on how to do a task.
It is a form of user interface in which the user is presented with a sequence of dialogue boxes that guide them through a series of well-defined actions.
Complex, infrequently performed, or unfamiliar tasks may be easier to complete with the help of a wizard.
34. Which one of the following search-engine does not track users or store search history?
A. Google
B. Bing
C. DuckDuckGo
D. Yahoo
Solutions
DuckDuckGo is a search engine that prioritises user privacy and does not alter search results based on the information provided by the user.
Instead of collecting personal data or logging user information, it presents advertising based on the term entered.
DuckDuckGo is an iOS and Android app as well as an extension Chrome browser for desktop use.
Gabriel Weinberg, a digital entrepreneur, established DuckDuckGo in 2008.
35. Graphics Interchange Format (GIF), an image file format can include a maximum of_______colors.
A. 256
B. 188
C. 126
D. 512
Solutions
GIF which stands for “Graphics Interchange Format” is a bitmap image format which was created by CompuServe in the year 1987.
It is one of the most commonly used images on the Internet and uses lossless compression that does not reduce the quality of the image.
GIF files can be used on a variety of platforms and programs.
The GIF format supports 8 bits per pixel in images comprised of 256 different colors.
36. In networking, which type of cable is also known as Ethernet cable?
A. Twisted Pair Cable
B. Fiber Optic Cable
C. Coaxial Cable
D. Patch
Solutions
Twisted pair cable also known as Ethernet cable is another types of cable in networking primarily developed a computer network.
This cable network is used to process all Local Area Networks.
The cable is constructed of two wires that are wrapped and twisted together.
This cable method decreases the interferences of the electromagnetic spectrum which helps to run devices smoothly with low noises from external devices.
37. In Computer Terminology, SIP stands for-
A. Session Initiation Protocol
B. Session Initiation Procedure
C. Session Instruction Protocol
D. Session Initiation Programming
Solutions
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is one of the most widely used protocols in VoIP.
It is an application layer protocol defined by IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) standard.
It controls multimedia communication sessions over the Internet in conjunction with other application layer protocols.
SIP can be used to start video conferences, file transfers, instant messaging sessions, and multiplayer games etc.
38. ‘PPM’ is used to measure the performance of which of the following hardware device?
A. Monitor
B. Keyboard
C. Mouse
D. Printer
Solutions
Pages per minute (PPM) is a printer speed measurement standard used to measure the printing speed of inkjet and laser printers.
The maximum PPM speed of the printer is measured using basic text pages, with no graphics, lines, or other objects.
PPM can also be used to measure the scanning speed of Scanner.
This measurement is particularly significant for scanners that use an automatic document feeder (ADF).
39. Common Internet File System (CIFS), is a part of which of the following protocol?
A. HTTPS
B. PPP
C. SMTP
D. SMB
Solutions
The Common Internet File System (CIFS) is a file system that allows users to share data over the Internet.
It is a component of the SMB protocol, which lets many computer types to share data and peripherals over a network.
Users can access files remotely using CIFS from a variety of platforms, including Windows, Mac, Linux, and others.
It defines a set of commands that computers can use to connect to a remote system and read and write files.
40. Google Drive, free cloud-based storage service was launched by Google in which year?
A. 2011
B. 2009
C. 2012
D. 2014
Solutions
Google Drive is a Google cloud storage service that lets users save up to 15 GB of files and information for free, with additional storage available for a cost.
This technology was first introduced in 2012, and it covers previous services such as Google Docs, which was first introduced in 2007.
Google Drive’s purpose is to give you a central location to store your files online that you can access from anywhere.
It was designed to work with Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7, as well as various Mac OS X versions when it first released.
41. Who was the first research scientist to convey the idea of the Personal Area Network?
A. Thomas Zimmerman
B. Konrad Zuse
C. Bob Kahn
D. John Backus
Solutions
Personal Area Network (PAN) is the computer network that connects devices or computers within the range of an individual.
The Personal Area Network was first proposed by Thomas Zimmerman, a research scientist.
The link between a Bluetooth earpiece and a smartphone is one of the most common real-world example of a PAN.
Laptops, tablets, printers, keyboards, and other technological devices can all be connected using PANs.
42. “Token passing”, is the most common access method of-
A. Bus Topology
B. Ring Topology
C. Star Topology
D. Tree topology
Solutions
Ring topology is a network configuration in which devices are connected in a ring and pass information to one another based on their proximity in the ring structure.
This type of architecture is more economical than bus topology and can handle larger loads.
Because messages are transmitted to each device in the ring, a ring topology is also known as an active topology.
Token passing is the most frequent ring topology access technique.
Token passing is a network access method that involves passing a token from one node to another.
43. Kindle, a small hand-held electronic device for reading books has been developed by_________.
A. Google
B. Amazon
C. Microsoft
D. Apple
Solutions
Amazon‘s Kindle is a small hand-held electronic gadget for reading books that was created by the internet retailer.
It lets you to read digital books, newspapers, magazines, and other electronic publications by downloading and reading them.
For listening to audiobooks or background music, the Kindle has a built-in speaker and headphone port.
The original Kindle was introduced in November 2007, and since then, various updates have been issued.
44. Which of the following term is used to describe “unwanted” email from a company or website?
A. Graymail
B. Redmail
C. Brownmail
D. Whitemail
Solutions
Graymail refers to unsolicited email messages that do not meet the definition of spam.
Graymail, unlike spam, contains messages from mailing lists and newsletters subscribed by the user.
These messages can clog up your inbox over time and be easily mistaken for spam.
Newsletters that you sign up for, as well as communications you receive when you sign up for an online service, are examples of graymail.
45. Which among the following was the first version of Windows that needed a hard drive?
A. Windows 2.0
B. Windows 95
C. Windows 3.0
D. Windows CE
Solutions
Windows 3.0 was the first version of this generation of Windows which was released on May 22, 1990.
It was the first version of Windows that needed a hard drive.
It has a redesigned graphical user interface (GUI) that displays apps as clickable icons.
It featured 256 colours, making the interface more vibrant and sophisticated.
Microsoft declared Windows 3.0 outdated and stopped providing support and updates for the system in 2001.
46.

A. 24
B. 16
C. 18
D. 20
Solutions

47.

A. 0.5
B. 0.3
C. 0.2
D. 1
Solutions
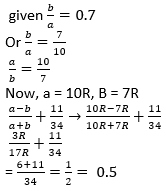
48.

A. 303/25
B. 313/25
C. 323/25
D. 333/25
Solutions
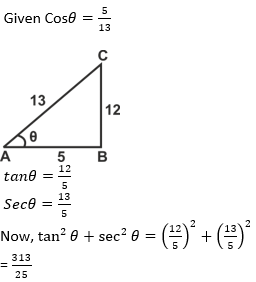
49.
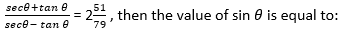
A. 91/144
B. 65/144
C. 35/72
D. 39/72
Solutions

50. Find the number of prime factors in the product (30)5 x (24)5.
A. 45
B. 10
C. 30
D. 35
Solutions
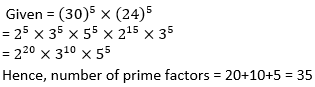
51. Given a histogram, we can easily draw:
A. frequency polygon only
B. frequency curve only
C. both the frequency polygon and the frequency curve
D. neither the frequency polygon nor the frequency curve
Answer C
52.
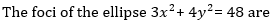
A. (0, ±2)
B. (±2, 0)
C. (0, ±4)
D. (±4, 0)
Solutions
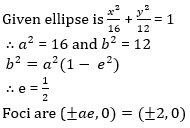
53. The foot of perpendicular from the point A(1, 3, 4) on the plane 2x – y + z + 3 = 0 is
A. (1, 4, 3)
B. (-1, 4, 3)
C. (2, 3, 1)
D. none of these
Solutions

54. Projection of P(x, y, z) on plane YOZ is:
A. (0, y, z)
B. (x, 0, 0)
C. (0, y, 0)
D. none of these
Solutions
on YOZ plane, we have x = 0
So, the projection of P(x, y, z) on YOZ plane is (0, y, z).
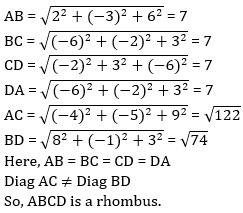
55. The points A(5, -1, 1), B(7, -4, 7), C(1, -6, 10) and D(-1, -3, 4) are vertices of:
A. a rectangle
B. a square
C. a rhombus
D. none of these
Solutions
56. The distance between the centre of two circles having radii 5 cm and 6 cm is √10 cm. Find the length (in cm) of direct common tangent.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Solutions
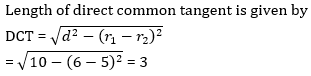
57.

A. – 3
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Solutions
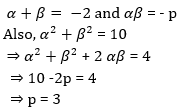
58. If mean of the following set is 5. Find the value of k
{2, 5, 6, 3, 8, k, 7}
A. 2
B. 4
C. 1
D. 3
Solutions
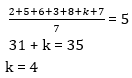
59. Find tan10°. tan20°. tan70°. tan80°
A. 0
B. 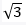
C. 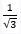
D. 1
Solutions
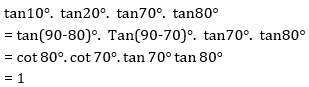
60. The volume of cube is 50,653 cm³. find its total surface area
A. 8214 cm²
B. 7132 cm²
C. 9216 cm²
D. 8562 cm²
Solutions
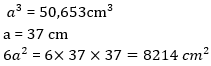
61. If the standard deviation of 15 items is 6 and each item is decreased by 1, then standard deviation will be
A. 5
B. 7
C. 9
D. 6
Solutions
If each item of a data is increased or decreased by the same constant, then standard deviation of the data remains unchanged, i.e. SD is 6.
62. What is the average of first 11 multiples of 11?
A. 22
B. 44
C. 55
D. 66
Solutions
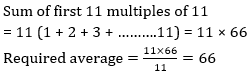
63. The number of nilpotent elements in Z4 are:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 0
Solutions

64.
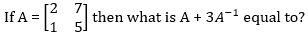
A. 3I
B. 5I
C. 7I
D. None of above
Solutions
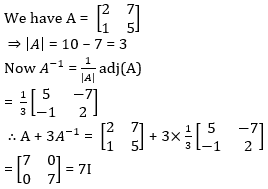
65. If any two adjacent rows or columns of a determinant are interchanged in position, the value of the determinant:
A. Becomes zero
B. Remains the same
C. Changes its sign
D. Is doubled
Solutions
If any two adjacent rows or columns of a determinant are interchanged in position, the value of the determinant changes its sign.
66. What is the SI unit of time?
A. Hour
B. Minute
C. Second
D. Millisecond
Solutions
(a) Hour
An hour is a unit of time that is equal to 60 minutes or 3,600 seconds. It is not the SI unit of time.
(b) Minute
A minute is a unit of time that is equal to 60 seconds. It is not the SI unit of time.
(c) Second
The second is the base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as the duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation
corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium-133 atom.
(d) Millisecond
A millisecond is a unit of time that is equal to one-thousandth of a second. It is not the base SI unit of time, but rather a derived unit (1ms = 0.001 s).
Given the options, the correct answer is:
(c) Second
The second (s) is the SI unit of time.
67. Which of the following is a fundamental quantity?
A. Volume
B. Force
C. Mass
D. Speed
Solutions
Fundamental Quantities:
Fundamental quantities are the basic physical quantities that are not derived from other quantities.
They include:
Length (meter, m)
Mass (kilogram, kg)
Time (second, s)
Electric current (ampere, A)
Temperature (kelvin, K)
Amount of substance (mole, mol)
Luminous intensity (candela, cd)
Derived Quantities:
Derived quantities are derived from the fundamental quantities through multiplication or division.
Examples include:
Volume: Derived from length (cubic meters, m3)
Force: Derived from mass and acceleration (newtons, N=kg⋅m/s2)
Speed: Derived from length and time (meters per second, m/s)
Given the options:
(a) Volume: A derived quantity (length cubed).
(b) Force: A derived quantity (mass times acceleration).
(c) Mass: A fundamental quantity.
(d) Speed: A derived quantity (length divided by time).
Therefore, the correct answer is:
(c) Mass
Mass is a fundamental quantity.
68. Which of the following is not a derived unit?
A. Newton
B. Joule
C. Meter
D. Pascal
Solutions
The meter is a fundamental unit, not a derived unit.
Fundamental Units:
These are basic units that are not derived from other units. Examples include meter (length), kilogram (mass), second (time), ampere (electric current), kelvin (temperature), mole (amount of substance), and candela (luminous intensity).
Derived Units:
These units are derived from the fundamental units through multiplication or division. Examples include:
Newton (N): The unit of force, which is derived from kg⋅m⋅S-2 (mass × acceleration).
Joule (J): The unit of energy, which is derived from kg⋅m2⋅S-2 (force × distance).
Pascal (Pa): The unit of pressure, which is derived from N⋅m-2 (force per unit area).
Given the options:
(a) Newton is a derived unit of force.
(b) Joule is a derived unit of energy.
(c) Meter is a fundamental unit of length.
(d) Pascal is a derived unit of pressure.
69. Which of the following statements is true about mass?
A. Mass is a force.
B. Mass is measured in newtons.
C. Mass is the amount of matter in an object.
D. Mass depends on gravity.
Solutions
(a) Mass is a force.
This statement is incorrect. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, not a force. Force is a vector quantity that results from the interaction between objects and is measured in newtons (N). Mass is a scalar quantity.
(b) Mass is measured in newtons.
This statement is also incorrect. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) in the International System of Units (SI). Newtons (N) are the units for force, not mass.
(c) Mass is the amount of matter in an object.
This statement is correct. Mass is a fundamental property of an object that quantifies the amount of matter it contains. It is a scalar quantity and is invariant, meaning it does not change regardless of the object’s location or the gravitational field it is in.
(d) Mass depends on gravity.
This statement is incorrect. Mass is an intrinsic property of an object and does not depend on gravity. What depends on gravity is weight, which is the force exerted by gravity on an object. Weight is calculated as the product of mass and the acceleration due to gravity (Weight = Mass × Gravitational Acceleration).
Therefore, the correct answer is:
c) Mass is the amount of matter in an object.
Detailed Explanation:
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter contained in a physical body.
It is one of the fundamental properties of matter and is independent of the object’s location or the gravitational field acting on it.
The unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) is the kilogram (kg).
Mass is a measure of matter and is measured in kilograms (kg).
Weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object and is measured in newtons (N). It is given by the equation:
Weight = Mass × Gravitational Acceleration
Force is an interaction that changes the motion of an object and is measured in newtons (N).
70. Weight is a measure of:
A. Mass
B. Volume
C. Density
D. Gravitational force
Solutions
Weight is a measure of the gravitational force acting on an object. Hence, the correct answer is (d) Gravitational force.
Weight:
Weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object. It depends on both the mass of the object and the acceleration due to gravity.
The formula for weight is:
Weight=Mass × Gravitational Acceleration
In the SI system, weight is measured in newtons (N), where mass is measured in kilograms (kg), and gravitational acceleration is approximately 9.81m/s2 on Earth.
Given the options:
(a) Mass: Mass is the amount of matter in an object and is measured in kilograms (kg). While mass is a factor in determining weight, weight itself is not a measure of mass.
(b)Volume: Volume is the amount of space an object occupies and is measured in cubic meters (m³). Weight is not a measure of volume.
(c) Density: Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance and is measured in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). Weight is not a measure of density.
(d) Gravitational force: Weight is indeed a measure of the gravitational force acting on an object. It is the force with which gravity pulls on the object’s mass.
71. The weight of an object is:
A. The same on the moon as on the earth
B. More on the moon than on the earth
C. Less on the moon than on the earth
D. Zero on the moon
Solutions
The weight of an object is less on the moon than on the earth due to the moon’s lower gravitational force.
Weight:
Weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object’s mass.
The formula for weight is:
Weight = Mass × Gravitational Acceleration
The gravitational acceleration on the moon is approximately 1/6th of that on Earth. The gravitational acceleration on Earth is approximately 9.81 m/s2, while on the moon it is about 1.63 m/s2.
Given this difference in gravitational acceleration, let’s analyze the options:
(a) The same on the moon as on the earth: This statement is incorrect. Since gravitational acceleration on the moon is much less than on Earth, the weight of an object on the moon would be less than its weight on Earth.
(b) More on the moon than on the earth: This statement is incorrect. The gravitational acceleration on the moon is less than on Earth, so the weight of an object on the moon would be less, not more.
(c) Less on the moon than on the earth: This statement is correct. Because the moon’s gravitational acceleration is about 1/61/6th of Earth’s, the weight of an object on the moon would be approximately 1/61/6th of its weight on Earth.
(d) Zero on the moon: This statement is incorrect. While the weight on the moon is less than on Earth, it is not zero. The moon does have gravity, although weaker, and thus objects still have weight.
Hence, the correct answer is (c) Less on the moon than on the earth.
72. The typical operating voltage for LED’s ranges from
A. 0.2 V to 0.6 V
B. 6 V to 10 V
C. 1.5 V to 2.5 V
D. 9 V to 10 V
Solutions
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them.
The operating voltage of LEDs varies depending on the type and color of the LED, but it generally falls within a certain range.
(a) 0.2 V to 0.6 V
This voltage range is too low for typical LEDs. LEDs generally require a higher forward voltage to operate.
(b) 6 V to 10 V
This voltage range is too high for standard LEDs. Typical LEDs do not require such high voltages to operate.
(c) 1.5 V to 2.5 V
This voltage range is correct for many standard LEDs, especially those that emit visible light. For example, red, green, and yellow LEDs often have a forward voltage in this range. Blue and white LEDs might have a slightly higher forward voltage, typically around 3 V to 3.5 V.
(d) 9 V to 10 V
This voltage range is also too high for standard LEDs. Some specialized LEDs or LED arrays might operate at higher voltages, but typical single LEDs do not.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
(c) 1.5 V to 2.5 V
The typical operating voltage for LEDs ranges from 1.5 V to 2.5 V.
73. Which of the following is an object that is launched into space to gather information and send it back to Earth?
A. asteroid
B. space station
C. satellite
D. constellation
Solutions
(a) Asteroid:
An asteroid is a small rocky body that orbits the Sun. Asteroids are not launched from Earth; they are natural celestial objects found mainly in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
(b) Space station:
A space station is a large spacecraft in orbit around Earth where astronauts can live and work for extended periods. While space stations, such as the International Space Station (ISS), can conduct scientific research, they are not typically launched to gather information and send it back to Earth in the same manner as satellites.
(c) Satellite:
A satellite is an artificial object that is intentionally placed into orbit around Earth or another celestial body. Satellites are used for various purposes, including gathering information (e.g., weather data, communications, scientific observations) and sending it back to Earth.
(d) Constellation:
A constellation is a group of stars that form a recognizable pattern in the night sky. Constellations are not objects launched into space; they are natural groupings of stars as seen from Earth.
Given the options, the correct answer is:
(c) Satellite
A satellite is an object that is launched into space to gather information and send it back to Earth.
74. Capacitors for integrated circuits
A. cannot be made using diffusion techniques.
B. can be made with very high values of capacitance.
C. are always discrete components connected externally.
D. can be made using silicon dioxide as the dielectric.
Solutions
can be made using silicon dioxide as the dielectric.
75. Which of the following matter is made up of only one type of atoms?
A. compound
B. particle
C. element
D. mixture
Solutions
An atom consists of particles (i.e. electrons, protons) and if only one type of atoms combined together by co-valent bonding it forms an element.
76. Which of the following is the lightest of the three main particles found in an atom?
A. electron
B. proton
C. neutron
D. nucleus
Solutions
An atom consists of a central nucleus of positive charge (protons) around which small negatively charged particles, called electrons revolve in different paths or orbits and electron mass is lowest among all particles so it is lightest.
77. In the given circuit. if the power consumed by 5Ω resistor is 100 Ω. then p.f. of the circuit is
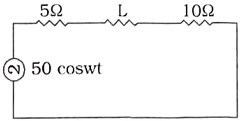
A. 0.8
B. 0.6
C. 0.5
D. Zero
Solutions
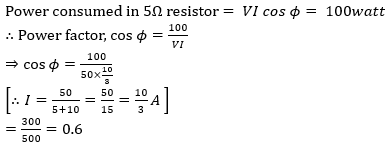
78. The magnitude of variation in the output voltage for a 10 V regulated dc power supply of 0.002% regulation will be
A. 0.2 mV
B. 0.002 mV.
C. 0.02 mV
D. 0.2 μV.
Solutions
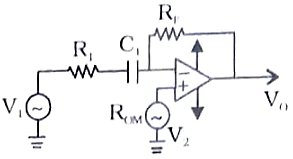
79. For the circuit shown in Fig. the output voltage is given by
A. 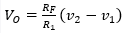
B. 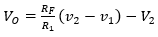
C. 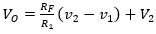
D. 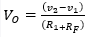
Solutions
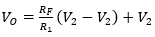
80. Acceleration depends on the mass of an object and the
A. direction of the wind
B. amount of inertia
C. force pushing or pulling the object
D. None of these
Solutions
Acceleration = Force × mass So acceleration in an object is depends upon the mass of the object and force applied into the mass of the object.
81. Which one of the following statements is not true?
A. Capacitance is a measure of a capacitor’s capability to store charge.
B. A capacitor offers high impedance to ac but very low impedance to dc.
C. A capacitor is also used as bypass capacitor.
D. Capacitors are used to couple alternating voltages from one circuit to another and at the same time to block dc voltage from reaching the next circuit.
Solutions
Since capacitor blocks the dc and pass the ac components of current so it offers high impedance to dc but very low impedance to ac.
82. A voltage source having an open-circuit voltage of 100 V and internal resistance of 50Ω is equivalent to a current source
A. 2A in parallel with 50 Ω
B. 2A with 50 Ω in series
C. 0.5A in parallel with 50 Ω
D. 2A in parallel with 100 Ω
Solutions
83. A+A. B= …..
A. B
B. A
C. 
D. 
Solutions

84. An electric iron designed for 110 V AC supply was rated at 500 W. It was put across a 220 V supply. Assuming that at 110 V Supplied 500 W output (i.e no losses) at the new voltage will supply
A. 2500 W
B. 250 W
C. 500 W
D. 2000 W
Solutions
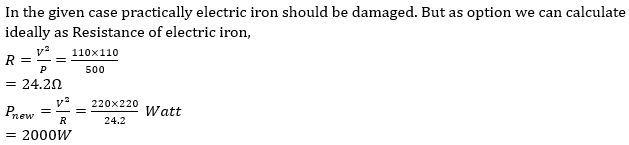
85. A very lossy, λ/4 long, 50-ohm transmission line is open circuited at the load end. The input impedance measured at the other end oi the line is approximately.
A. 0
B. ∞
C. 50 ohms
D. None of the above
Solutions
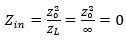
86. For a single mode optical cable with 0.25 dB/km loss. the optical power 100 km from a 0.1 mW source will be
A. -30 dBm
B. -35 dBm
C. -40 dBm
D. -45 dBm
Solutions

87. The intermediate frequency of a super-heterodyne receiver is 450 KHZ. If it is tuned to 1200 KHz. the image frequency will be
A. 750 KHz
B. 900 KHz
C. 1600 KHz
D. 2100 KHz
Solutions
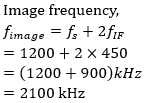
88.
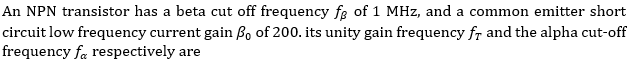
A. 200 MHz. 201 MHz
B. 200 MHz 199 MHz
C. 199 MHz. 200 MHz
D. 201 MHZ. 200 MHz
Solutions
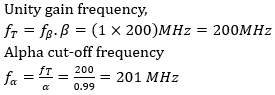
89.

A. 52.3%
B. 25.65%
C. 75%
D. 78.6%
Solutions

90. A broadside array operating at 100 cm wavelength consist of 4 half wave dipoles spaced 50 cm apart. Each element carries radio frequency current in the same phase and of magnitude 0.5 A. The radiated power will be _______if the radiation resistance is 146 ohms.
A. 146W
B. 73W
C. 36.5 W
D. 18.25 W
Solutions
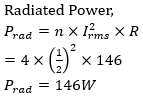
91.
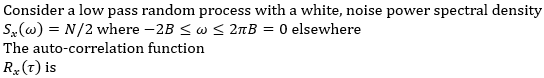
A. 2NB sinc(2πBτ)
B. πNB sinc(2πBτ)
C. NB sinc(2πBτ)
D. None of these
Solutions
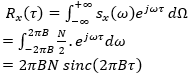
92. The coupling between the two inductors is increased from zero in the circuit shown.
Which of the. Following statements is true?
A. The resonant frequency will increase and the Q will decrease
B. The resonant frequency and Q will both increase
C. The resonant frequency and Q will both decrease
D. The resonant frequency will decrease and the Q will increase
Solutions
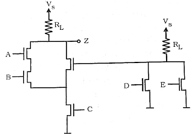
93. Write a Boolean Expression for Z in terms of A, B, C, D and E You need not simplify the expression
A. 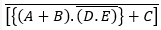
B. 
C. 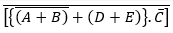
D. 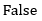
Solutions
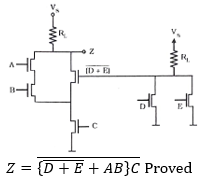
94. A parallel plate capacitor of 100 pF having an air dielectric is charged to 10 kilovolts. It is then electrically isolated. The plates are pulled away from each other until the distance is ten times more than before. Estimate the energy needed to pull the plates.
A. 0.05 Joules
B. 50 Joules
C. 500 Joules
D. -50 Joules
Solutions
95. In a P-N junction diode, the region around the junction is known as:
A. Depletion region
B. Active region
C. Inactive region
D. Conduction region
Solutions
The region around the junction in a P-N junction diode is known as the depletion region, where mobile charge carriers are depleted.
Hence, the correct answer is a) Depletion region.
96. Which component in the CRO generates the electron beam?
A. Vertical deflection plates
B. Cathode ray tube (CRT)
C. Horizontal deflection plates
D. Time base generator
Solutions
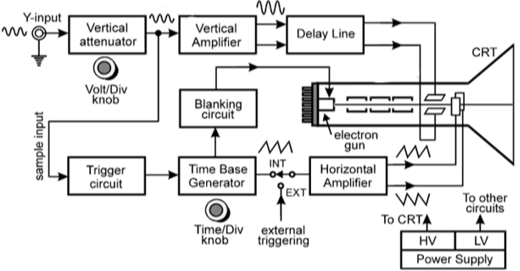
To determine which component in the Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) generates the electron beam,
let’s review the functions of the components listed: –
Vertical deflection plates: –
These plates are responsible for deflecting the electron beam vertically, which corresponds to the amplitude of the input signal.
They do not generate the electron beam.
Cathode ray tube (CRT): –
The CRT is the primary component in a CRO that generates the electron beam.
Inside the CRT, there is an electron gun that emits electrons. These electrons are then accelerated and focused into a beam, which is directed towards the screen of the CRO.
The electron gun typically consists of a cathode, control grid, and accelerating anodes, which work together to produce and control the electron beam.
Horizontal deflection plates: –
These plates are responsible for deflecting the electron beam horizontally, which corresponds to the time base of the input signal.
They do not generate the electron beam.
Time base generator: –
The time base generator controls the horizontal sweep of the electron beam across the screen, ensuring that the waveform is displayed over time.
It does not generate the electron beam.
Given the functions of the components, the correct answer is:
(b) Cathode ray tube (CRT)
Detailed Explanation:
Cathode ray tube (CRT):-
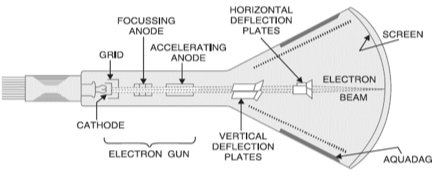
The cathode ray tube (CRT) is the essential part of a Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) responsible for generating the electron beam. Here is a more detailed look at how it works:
Electron Gun: The CRT contains an electron gun, which is a critical component that generates the electron beam. The electron gun consists of:
Cathode: The cathode is heated to emit electrons through a process called thermionic emission.
Control Grid: The control grid modulates the flow of electrons, controlling the intensity of the electron beam.
Accelerating Anodes: The accelerating anodes accelerate the electrons emitted from the cathode, forming a high-speed electron beam.
Electron Beam: The emitted electrons are accelerated and focused into a narrow beam by the accelerating anodes and focusing systems within the CRT.
Deflection Plates: Once the electron beam is generated, it passes through the deflection plates. There are two sets of deflection plates:
Vertical Deflection Plates: These plates control the vertical movement of the electron beam, corresponding to the amplitude of the input signal.
Horizontal Deflection Plates: These plates control the horizontal movement of the electron beam, corresponding to the time base or sweep of the signal.
Screen: The electron beam strikes the phosphorescent screen of the CRT, creating a visible trace that represents the electrical signal being measured.
Thus, the CRT, with its electron gun, is the component that generates the electron beam in a CRO.
97. Which of the following bridges is used for measuring dielectric loss and capacitance of cables and insulating materials?
A. Maxwell Bridge
B. Anderson Bridge
C. Hay Bridge
D. Schering Bridge
Solutions
The Schering Bridge is used for measuring dielectric loss and capacitance of cables and insulating materials. Hence, the correct answer is (d) Schering Bridge.
(a) Maxwell Bridge
The Maxwell Bridge is primarily used for measuring inductance by comparing it to a known capacitance and resistance.
(b) Anderson Bridge
The Anderson Bridge is an improvement over the Maxwell Bridge and is also used for precise measurement of inductance, particularly for low Q-factor inductors.
(c) Hay Bridge
The Hay Bridge is designed for measuring high-Q inductors.
(d) Schering Bridge
The Schering Bridge is specifically designed for measuring the dielectric loss and capacitance of cables and insulating materials.
It works by balancing the bridge with a known capacitance and measuring the unknown capacitance and its associated dielectric loss.
Detailed Explanation:
The Schering Bridge is an AC bridge circuit used to measure the capacitance and dissipation factor (dielectric loss) of electrical insulating materials, including cables.
The bridge operates on the principle of balancing the capacitive reactance with known components to determine the unknown capacitance and dielectric loss.
The Schering bridge is an electrical circuit used for measuring the insulating properties of electrical cables and equipment. It is an AC bridge circuit, developed by Harald Schering.
It has the advantage that the balance equation is independent of frequency. The connections of the Schering bridge under balance conditions are shown in the figure below. In this diagram.
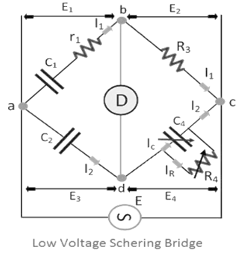
In this diagram:
C1 = capacitor whose capacitance is to be determined,
R1 = a series resistance representing the loss in the capacitor C1,
C2 = a standard capacitor,
R3 = a variable non-inductive resistance,
C4 = a variable capacitor,
R4 = a non-inductive resistance in parallel with the variable capacitor C4.
Capacitance Measurement: –
In the Schering Bridge, one arm contains the unknown capacitance (along with its associated loss resistance), and the other arms contain known resistances and capacitances. By adjusting these known components, the bridge is balanced, and the unknown capacitance is determined.
Dielectric Loss Measurement: –
The dielectric loss, represented as a dissipation factor or loss tangent, is also determined using the Schering Bridge. This factor is crucial in assessing the quality and efficiency of insulating materials, as higher dielectric losses indicate greater energy dissipation as heat within the material.
The Schering Bridge’s ability to accurately measure both the capacitance and the dielectric loss of insulating materials makes it a valuable tool in the evaluation and quality control of electrical insulation.
98. What type of indicating instrument is a galvanometer?
A. Measures voltage
B. Measures current
C. Measures resistance
D. Measures power
Solutions
A galvanometer is an indicating instrument that is used to measure small electric currents.
It operates based on the deflection of a needle in response to an electric current passing through a coil placed in a magnetic field.
A galvanometer is an electromechanical instrument used for detecting and measuring small electric currents.
It operates on the principle of electromagnetic deflection, where a current passing through a coil generates a magnetic field that interacts with a permanent magnet, causing a needle to deflect.
Working Principle
Construction: –
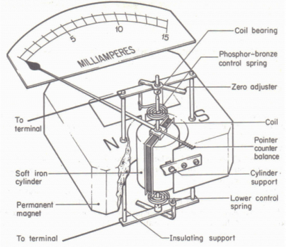
Coil: A lightweight, rectangular coil of wire is mounted on a pivot or suspension. The coil is free to rotate around its axis.
Magnet: The coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field generated by a permanent magnet.
Pointer: A pointer is attached to the coil, which moves over a calibrated scale.
Spring: A restoring spring provides a counteracting force to return the coil to its zero position when no current flows.
Operation: –
When an electric current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field.
This magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of the permanent magnet, creating a torque on the coil.
The coil, along with the attached pointer, rotates. The amount of rotation is proportional to the current passing through the coil.
The restoring spring exerts an opposing torque, balancing the electromagnetic torque. The equilibrium position of the pointer indicates the current.
Deflection:
The deflection angle of the pointer is directly proportional to the current passing through the coil. This relationship allows for the measurement of current.
Types of Galvanometers
(a) D’Arsonval Galvanometer
The most common type, which uses a moving coil in a magnetic field.
Highly sensitive and used in laboratory experiments.
(b) Ballistic Galvanometer
Designed to measure the quantity of charge discharged through it.
Used in applications requiring the measurement of brief current pulses.
(c) Astatic Galvanometer
Consists of two coils with opposite magnetic fields to reduce the influence of external magnetic fields.
Applications of Galvanometers
Detection of Small Currents:
Used in laboratories to detect and measure minute currents in circuits.
Analog Meters:
The basic mechanism of moving-coil ammeters and voltmeters is similar to that of a galvanometer.
Bridge Circuits:
Employed in bridge circuits (e.g., Wheatstone bridge) to detect balance by indicating zero current.
Electromagnetic Experiments:
Used in various physics experiments to study the behavior of electric currents and magnetic fields.
Advantages: –
High Sensitivity: Can detect very small currents.
Direct Measurement: Provides a direct visual indication of current.
Limitations:
Fragility: The delicate construction makes it susceptible to damage.
Limited Range: Suitable only for small currents.
Temperature Sensitivity: Performance can be affected by temperature variations.
99. Which of the following quantities can be directly measured by a PMMC instrument without any additional circuitry?
A. AC current
B. AC voltage
C. DC voltage
D. Frequency
Solutions
PMMC instruments can directly measure DC voltage and DC current without any additional circuitry. Hence, the correct answer is (c) DC voltage.
Permanent Magnet Moving Coil (PMMC) instruments are highly accurate and sensitive devices used for measuring direct current (DC) and voltage.
They are based on the principle of electromagnetic deflection, where the interaction between a magnetic field and an electric current produces a mechanical deflection that is proportional to the current.
Construction
A typical PMMC instrument consists of the following components:
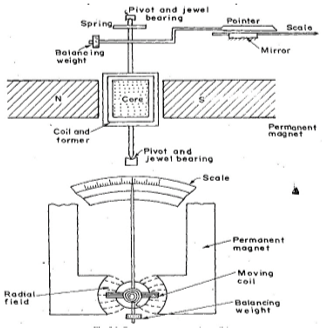
Permanent Magnet:
Provides a steady and strong magnetic field.
The magnets are usually made of materials like Alnico or rare-earth elements.
Moving Coil:
A lightweight, rectangular coil of fine wire wound on an aluminum or non-magnetic frame.
The coil is free to rotate between the poles of the permanent magnet.
Control Spring:
Two control springs, made of phosphor bronze, are attached to the coil.
These springs not only provide the necessary restoring torque but also carry current to the coil.
Pointer:
Attached to the coil, the pointer moves over a calibrated scale to indicate the measurement.
Scale:
A calibrated scale, often accompanied by a mirror to minimize parallax error, displays the measurement reading.
Damping Mechanism:
Eddy current damping is commonly used to stabilize the pointer quickly.
This is achieved by placing a metallic former within the magnetic field, which generates eddy currents that oppose the coil’s motion.
Working Principle
The PMMC instrument operates on the principle of the interaction between the magnetic field of the permanent magnet and the magnetic field produced by the current flowing through the moving coil.
Here’s how it works:
Current Flow:
When an electric current flows through the moving coil, it generates a magnetic field around the coil.
Magnetic Interaction:
The interaction between the magnetic field of the coil and the permanent magnet produces a torque that causes the coil to rotate.
Pointer Deflection:
The rotation of the coil moves the pointer attached to it over the calibrated scale. The angle of deflection is directly proportional to the current flowing through the coil.
Restoring Torque:
The control springs exert a restoring force that increases with the deflection angle, balancing the electromagnetic torque.
When the torques are balanced, the pointer stabilizes at a position that indicates the current or voltage.
Advantages
High Accuracy: PMMC instruments provide precise and reliable measurements due to their linear scale and low friction.
Good Sensitivity: They are highly sensitive to small changes in current or voltage.
Low Power Consumption: They require very little power to operate.
Robust and Durable: The construction of PMMC instruments makes them robust and suitable for long-term use.
Disadvantages
Limited to DC Measurements: – PMMC instruments cannot be used for AC measurements directly. AC measurements require rectification before they can
be measured with a PMMC instrument.
Cost: – They can be more expensive compared to other types of measuring instruments.
Fragility: – The moving parts and delicate springs can be susceptible to mechanical damage if not handled carefully.
Applications
PMMC instruments are widely used in:
Multimeters: For measuring DC voltage and current.
Laboratory Instruments: Where precise measurements are critical.
Electrical and Electronic Testing: For accurate and sensitive current and voltage measurements.
Control Panels: In industries for monitoring and control applications.
Summary
Permanent Magnet Moving Coil (PMMC) instruments are essential tools for accurate measurement of DC current and voltage.
Their high sensitivity, precision, and linearity make them ideal for various applications in electrical and electronic measurements.
Understanding the construction and working principle of PMMC instruments is crucial for effectively utilizing them in practical scenarios.
100. What is the size of the address bus in a microprocessor that can address up to 64KB of memory?
A. 8 bits
B. 16 bits
C. 32 bits
D. 64 bits
Solutions
To address 64KB (which is 216 bytes) of memory, a 16-bit address bus is required. Hence, the correct answer is (b) 16 bits.
