1. Directions: Read the sentence given below to find out if it contains an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If the sentence is error-free, select No error or option 5. Ignore errors of punctuation if any
The rich were (A)/ the main beneficiaries (B)/ about the (C)/ tax cuts. (D)/ No error (E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is ‘C‘ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the third part of the given sentence, the use of the preposition ‘about‘ is incorrect.
- The preposition ‘about’ means on the subject of something.
- Example: She told me all about her family.
- The given sentence is talking about the rich who actually got the benefits of the tax cuts.
- Therefore, the preposition ‘of’ should be used in place of the preposition ‘about’.
- The preposition ‘of’ means belonging to, connected with, or part of something or somebody.
- Example: I am a firm believer in the benefits of exercise.
- Example: I am a firm believer in the benefits of exercise.
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
Correct Sentence: The rich were the main beneficiaries of the tax cuts.
2. Directions: Read the sentence given below to find out if it contains an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If the sentence is error-free, select No error or option 5. Ignore errors of punctuation if any.
I will (A)/ sent you (B)/ the information (C)/ when I get it. (D)/ No error (E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is ‘B‘ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the second part of the given sentence, the use of the past form of the verb ‘sent’ is incorrect.
- The given sentence is in the simple future tense used to talk about things that haven’t happened yet – an action or condition that will begin and end in the future.
- The simple future tense is formed by: will + root or base form of the verb.
- Example: I will learn a new language.
- Therefore, the base or root form of the verb ‘send’ should be used in place of the past form of the verb ‘sent’.
Hence, the correct answer is option 2.
Correct sentence: I will send you the information when I get it.
3. Directions: Read the sentence given below to find out if it contains an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If the sentence is error-free, select No error or option 5. Ignore errors of punctuation if any.
The boy (A)/ is not singing (B)/ a song, (C)/ isn’t he? (D)/ No error (E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is ‘D’ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the fourth part of the given sentence, the use of the negative question tag “isn’t he” is incorrect.
- The given statement in the sentence is a negative statement (not singing).
- When the statement is negative, we use a positive question tag.
- He is not a boy, is he?
- And, if the statement is positive, we use a negative question tag.
- He is a boy, isn’t he?
- Therefore, the positive question tag “is he” should be used in place of the negative question tag “isn’t he“.
Hence, the correct answer is option 4.
Correct Sentence: The boy is not singing a song, is he?
4. Directions: Read the sentence given below to find out if it contains an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If the sentence is error-free, select No error or option 5. Ignore errors of punctuation if any.
If you study (A)/ hard, you (B)/ will pass (C)/ your exams. (D)/ No error (E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is ‘E’ i.e. No error.
Key Points
- In the given sentence, no improvement is required in any of the parts or there is no error in the sentence.
- The given sentence is the first conditional sentence talking about things that might happen in the future, this describes possible things, which could easily come true.
- The first conditional sentence format: If + simple present, … simple future (will + base verb).
- When using the first conditional we use the simple present tense in the if-clause and simple future tense in the main clause.
- We use the ”present simple tense” to talk about the possible future condition and the ”will + base verb” to talk about the possible future result.
Hence, the correct answer is option 5.
Correct Sentence: If you study hard, you will pass your exams.
Additional Information
- The important thing about the first conditional is that there is a real possibility that the condition will happen.
- Sometimes, we use ”shall, can, or may”instead of ‘will.‘
- Example: If it’s sunny this afternoon, we can play cricket.
5. Read the sentence given below to find out if it contains an error. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. if the sentence is error free, select No error or option 5. Ignore errors of punctuation if any.
Much of us (A)/ are (B)/ obsessed (C)/ with thinning. (D)/ No error(E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is ‘A’ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- ‘Much‘ is used when we are speaking about a singular noun. ‘Many‘ is used when we are speaking about a plural noun.
- I don’t have much time.
- We have many friends, in many countries.
- Here, Us is a plural pronoun, so the use of Much is incorrect.
- Hence, option 1 is correct.
The correct sentence: Many of us are obsessed with thinning.
Additional Information
- MUCH precedes uncountable nouns:
- I don’t have much time, and you don’t have much money.
- I don’t have a lot of time, and you don’t have a lot of money.
- MANY precedes countable nouns:
- We have many friends, in many countries.
- We have a lot of friends, in a lot of countries.
6. In the following question, two columns are given containing three phrases each. In the first column phrases are A, B, C and in the second column, the phrases are D, E, F. A phrase from the first column may or may not connect with a phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. There are five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which the phrases can be joined to form a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. If none of the options given forms a correct sentence after combination, select ‘None of these’ as your answer.
| Column(1) | Column(2) |
| (A) All summer vacation long | (D) they just bummed around. |
| (B) Recent research seems to | (E) all these violation activities. |
| (C) No good will come of | (F) a quick glance. |
A. B-E
B. C-F
C. A-D and C-E
D. A-E
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is A-D and C-E.
Key Points
- There are two correct combinations in the given options to form a meaningful sentence.
- Part A and part D should join conceptually. Part A states ‘All summer vacation long’ and part D completes the sentence stating ”they just bummed around’.
- In A-D, the word bummed around means lazed around, without doing any significant work. So, A-D is the correct combination.
- Part C and part E should join conceptually. Part C states ‘No good will come of’ and part E completes the sentence stating ‘ all these violation activities‘.
- In C-E, the word violation means to treat (something sacred) with irreverence or disrespect. It is said that treating someone with disrespect won’t do any good to them. So, C-E is the correct combination.
The correct sentences are:
- A-D: All summer vacation long they just bummed around.
- C-E: No good will come of all these violation activities.
7. In the following question, two columns are given containing three phrases each. In the first column phrases are A, B, C and in the second column, the phrases are D, E, F. A phrase from the first column may or may not connect with a phrase from the second column to make a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. There are five options, four of which display the sequence(s) in which the phrases can be joined to form a grammatically and contextually correct sentence. If none of the options given forms a correct sentence after combination, select ‘None of these’ as your answer.
| Column(1) | Column(2) |
| (A) He’s put aside a tidy sum | (D) for his retirement. |
| (B) Danger didn’t | (E) established political parties. |
| (C) She had a sudden painful | (F) cramp in her left leg. |
A. B-E
B. A-F
C. C-D
D. C-F and A-D
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is C-F and A-D.
Key Points
- There are two correct combinations in the given options to form a meaningful sentence.
- Part C and part F should join conceptually. Part C states ‘She had a sudden painful’ and part F completes the sentence stating ‘cramp in her left leg’.
- C-F talks about a painful cramp she had on her leg. So, C-F is the correct combination.
- Part A and part D should join conceptually. Part A states ‘He’s put aside a tidy sum’ and part D completes the sentence stating ‘for his retirement.
- In A-D, the word tidy means (of an amount, especially of money) considerable. Here, he kept aside a considerable amount of money for his retirement. So, A-D is the correct combination.
The correct sentences are:
- C-F: She had a sudden painful cramp in her left leg.
- A-D: He’s put aside a tidy sum for his retirement.
8. In the following sentence, some parts have been printed in bold. One of the bold parts is incorrectly spelt. Pick up that part and choose its number. If there is no error in the bold parts, choose option 5- no error as the answer.
Sufferring from malnutrition and neglect and who knows what mental agonies she had.
A. Sufferring
B. Malnutrition
C. Neglect
D. Agonies
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is Sufferring.
Key Points
- In the sentence, out of all the bold parts ‘sufferring‘ is the word that has no meaning.
- So, ‘sufferring‘ is an incorrectly spelt word.
- The correct spelling is ‘suffering‘ which is the present participle of the word ‘suffer’.
- Suffer: experience or be subjected to (something bad or unpleasant).
- Therefore the correct answer is sufferring as it is wrongly spelt.
9. In the following sentence, some parts have been printed in bold. One of the bold parts is incorrectly spelt. Pick up that part and choose its number. If there is no error in the bold parts, choose option 5- no error as the answer.
Lathargy has taken over his entire existence and he spends his day languishing in idleness.
A. lathargy
B. existence
C. languishing
D. idleness
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is lathargy.
Key Points
- In the sentence, out of all the bold parts ‘lathargy‘ is the word that has no meaning.
- So, ‘lathargy‘ is an incorrectly spelt word.
- The correct spelling is ‘lethargy‘ which means a lack of energy and enthusiasm.
- Therefore the correct answer is lathargy as it is wrongly spelt.
Additional Information
- Languishing: Failing to make progress or be successful.
- Example: The country’s languishing stock market is a disgrace to investors.
10. In the following sentence, some parts have been printed in bold. One of the bold parts is incorrectly spelt. Pick up that part and choose its number. If there is no error in the bold parts, choose option 5- no error as the answer.
Students have been demanding cencelation of class 12th exams in view of the pandemic.
A. students
B. cencelation
C. view
D. pandemic
E. No error
Solution
The correct answer is cencelation.
Key Points
- In the sentence, out of all the bold parts ‘cencelation‘ is the word that has no meaning.
- So, ‘cencelation‘ is incorrectly spelt word.
- The correct spelling is ‘cancelation‘ which means the action of cancelling something.
Therefore the correct answer is cencelation as it is wrongly spelt.
11. The following questions consist of a sentence. Four of the words of the sentences are marked in bold, which may or may not be correctly spelled. Option corresponding to misspelled word is your answer. If there is no misspelled word in the sentence then choose (E), i.e., ‘All are correct’ as your answer.
Churchill then wanted to coerece the owners into a national agreement and statutory arbitration.
A. coerece
B. agreement
C. statutory
D. arbitration
E. no error
Solution
The misspelled word is ‘coerece‘.
Key Points
- The correct spelling is ‘coerce’.
- Coerce means to force somebody to do something, for example by threatening him/her.
- Example–
- He even managed to coerce the children into doing the dishes.
- Example–
- Hence, the correct answer is option 1.
Additional Information
Let us look at the meanings of the other emboldened words:
| WORD | MEANING |
| Agreement | the state of agreeing with somebody/something; a contract or decision that two or more people have made together |
| Statutory | decided by law |
| Arbitration | the process of solving an argument between people by helping them to agree to an acceptable solution |
12. The following questions consist of a sentence. Four of the words of the sentences are marked in bold, which may or may not be correctly spelled. Option corresponding to misspelled word is your answer. If there is no misspelled word in the sentence then choose (E), i.e., ‘All are correct’ as your answer.
For some inexplicaple reason, her spirits seemed to plummet earthwards.
A. inexplicaple
B. spirits
C. plummet
D. earthwards
E. no error
Solution
The misspelled word is ‘inexplicaple‘.
Key Points
- The correct spelling is ‘inexplicable‘.
- The meaning of inexplicable is- that cannot be explained.
- Example– Her sudden disappearance is quite inexplicable.
- Hence, the correct answer is option 1.
Additional Information
Let’s look at the meanings of the other options-
| WORD | MEANING |
| Spirits | the part of a person that is not physical; your thoughts and feelings, not your body |
| Plummet | to fall suddenly and quickly from a high level or position. |
| Earthwards | towards the ground or the earth. |
13. Directions: Select the most appropriate word to fill in the blank.
The Western world has _______ unprecedented sanctions against Russia and banned energy imports.
A. Composed
B. Disposed
C. Imposed
D. Enclosed
E. None of the above
Solution
The correct answer is ‘Imposed.‘
Key Points
- The given sentence is talking about the Western world forcing sanctions on Russia.
- Therefore, the most appropriate word to be filled in the blank is ‘Imposed’.
- Also, the use of the phrase ”unprecedented sanctions” in the sentence indicates the use of the word ‘imposed’ in the blank.
- The word ‘Imposed‘ means To force an unwelcome decision or ruling on someone.
- Example: Strict discipline is imposed on army recruits.
- Example: Strict discipline is imposed on army recruits.
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
Complete Sentence: The Western world has imposed unprecedented sanctions against Russia and banned energy imports.
Additional Information
- Let us explore the other options:
- Composed means Having one’s feelings and expression under control; calm.
- Disposed means Willing or being prepared to do something.
- Enclosed means Surrounded or closed off on all sides.
14. Directions: Choose the word for the given options that could fit in the blank correctly.
To my surprise, her smile was no longer one of lofty ______.
A. woes
B. disdain
C. sorrows
D. grief
E. troublesome
Solution
The correct answer is ‘disdain‘
Key Points
- Here in the blank, we need a noun.
- Let’s understand the meaning of options:
- ‘Disdain(noun)’ – Lack of respect accompanied by a feeling of intense dislike
- ‘Woes(noun)’ -Misery resulting from affliction
- ‘Sorrow(noun)’ – An emotion of great sadness associated with loss or bereavement
- ‘Grief(noun)‘ -Intense sorrow caused by loss of a loved one (especially by death)
- ‘Troublesome(adj)‘ – Causing difficulty or annoyance
- Hence, the correct answer is option 2.
The correct sentence is: To my surprise, her smile was no longer one of lofty disdain.
15. Directions: Choose the word for the given options that could fit in the blank correctly.
The majority did not, indeed, design to _________ property wholesale.
A. breach
B. confiscate
C. hidden
D. disputing
E. trickery
Solution
The correct answer is ‘confiscate’.
Key Points
- Here in the blank, we need a verb.
- Let’s understand the meaning of options:
- ‘breach(noun)’ – A failure to perform some promised act or obligation
- ‘confiscate(verb)’ – Take temporary possession of as a security, by legal authority
- ‘hidden(adj)’ – Not accessible to view
- ‘dispute(verb)‘ – Question the truth or validity of; take exception to
- ‘trickery(noun)‘ -Dishonest and underhand behaviour
- Hence, the correct answer is option 2.
The correct sentence is: The majority did not, indeed, design to confiscate property wholesale.
16. Directions: Choose the word for the given options that could fit in the blank correctly.
If you are ______ to see a dentist or oral surgeon, a sedation dentist is more suitable.
A. tired
B. petrified
C. cheered
D. elated
E. peeped
Solution
The correct answer is ‘petrified’
Key Points
- Here in the blank, we need a verb.
- A sedation dentist uses medication or drugs to relax the patient before or during a long dental procedure.
- The use of the adjective ‘sedation‘ makes it understood that the word in the blank must convey a negative meaning.
- Let’s understand the meaning of options:
- Petrified(verb) – Cause to become stone-like, stiff or dazed and stunned from fright
- Cheered(verb) – Give encouragement to
- Tired(adj) – Depleted of strength or energy
- Elated(adj) – Exultantly proud and joyful; in high spirits
- Peeped(verb) -Look furtively
- Hence, the correct answer is option 2.
The correct sentence is: If you are petrified to see a dentist or oral surgeon, a sedation dentist is more suitable.
17. Directions: Choose the word for the given options that could fit in the blank correctly.
The Court has ______ segregation in public beaches and buses.
A. nullified
B. passed
C. resolution
D. peeped
E. elated
Solution
The correct answer is ‘nullified‘
Key Points
- Here in the blank, we need an adjective.
- Let’s understand the meaning of options:
- Nullified(adj) – Deprived of legal force
- Passed(verb) – Go across or through
- Resolution(noun) – A formal expression by a meeting; agreed to by a vote
- Peeped(verb) – Look furtively
- Elated(adj) – Exultantly proud and joyful; in high spirits
- Hence, the correct answer is option 1.
The correct sentence is: The Court has nullified segregation in public beaches and buses.
18. Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage.
At the inauguration of the 18th edition of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the Indian diaspora as India’s “ambassadors to the world”, having “seamlessly assimilated” into the local society, served the community, and contributed to India’s growth and prosperity. The strength of the India-origin community worldwide of over 35 million — about 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs, who are foreign nationals — is their ability to adapt and thrive in different fields, including in politics, where Indian-origin people have become leaders of more than 30 other countries. Where they retain their Indian passports, the diaspora is known for its distinguished services in many professional spheres. The PBD’s purpose is to celebrate this success and discuss issues of importance. President Droupadi Murmu handed out about 27 Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards. The event, which was first held in 2003, is organised around January 9, when Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915. The latest event, held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, brought more than 3,000 delegates from across 70 countries, with much of the focus on how the diaspora can help in developing India (Viksit Bharat programme).
The achievements of the Indian diaspora are, no doubt, a matter of pride for all Indians, but it is important that the event is not limited to a simple self-congratulatory or laudatory exercise. The issues for the diaspora, particularly for those who are still Indian nationals, are more acute now. The increase in far-right populist governments, particularly in the West, is making visa and entry conditions for Indians more difficult, and it is important for the government to address such issues. Intractable global conflicts, especially in West Asia where more than nine million Indians live and work, are also putting lakhs of Indians in peril, and the PBD engagement would benefit from discussions between the community on how best to increase awareness and enhance safeguards for them. Given the broad spread of the diaspora, it is necessary to ensure that India’s ties with its diaspora be inclusive, and non-partisan on political issues. Recent actions by the government to deny or revoke OCI cards for those perceived to be critical of the government bely this necessity. Above all, it is important to acknowledge that one of the biggest drivers of Indians migrating is the lack of economic opportunities within India. While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible ________ and impact on the global
Question:
According to the passage, how many Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards were handed out by President Droupadi Murmu?
A. About 15
B. About 20
C. About 27
D. About 30
E. About 35
Solution
The correct answer is Option 3.
Key Points
- President Droupadi Murmu handed out about 27 Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards during the event.
- The event celebrates the success of the Indian diaspora and discusses important issues.
- The Pravasi Bharatiya Divas is organized around January 9, marking the date when Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915.
- The latest event was held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, bringing together more than 3,000 delegates from across 70 countries.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option 3.
Additional Information
- The Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) is an important event to honour the contributions of the Indian diaspora and discuss relevant issues.
- The Indian diaspora consists of over 35 million people worldwide, including about 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs, who are foreign nationals.
- The event held in Bhubaneswar focused on how the diaspora can assist in India’s development through the Viksit Bharat programme.
- Key challenges faced by the Indian diaspora include visa and entry conditions, intractable global conflicts, and safeguarding their interests.
19. Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage.
At the inauguration of the 18th edition of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the Indian diaspora as India’s “ambassadors to the world”, having “seamlessly assimilated” into the local society, served the community, and contributed to India’s growth and prosperity. The strength of the India-origin community worldwide of over 35 million — about 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs, who are foreign nationals — is their ability to adapt and thrive in different fields, including in politics, where Indian-origin people have become leaders of more than 30 other countries. Where they retain their Indian passports, the diaspora is known for its distinguished services in many professional spheres. The PBD’s purpose is to celebrate this success and discuss issues of importance. President Droupadi Murmu handed out about 27 Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards. The event, which was first held in 2003, is organised around January 9, when Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915. The latest event, held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, brought more than 3,000 delegates from across 70 countries, with much of the focus on how the diaspora can help in developing India (Viksit Bharat programme).
The achievements of the Indian diaspora are, no doubt, a matter of pride for all Indians, but it is important that the event is not limited to a simple self-congratulatory or laudatory exercise. The issues for the diaspora, particularly for those who are still Indian nationals, are more acute now. The increase in far-right populist governments, particularly in the West, is making visa and entry conditions for Indians more difficult, and it is important for the government to address such issues. Intractable global conflicts, especially in West Asia where more than nine million Indians live and work, are also putting lakhs of Indians in peril, and the PBD engagement would benefit from discussions between the community on how best to increase awareness and enhance safeguards for them. Given the broad spread of the diaspora, it is necessary to ensure that India’s ties with its diaspora be inclusive, and non-partisan on political issues. Recent actions by the government to deny or revoke OCI cards for those perceived to be critical of the government bely this necessity. Above all, it is important to acknowledge that one of the biggest drivers of Indians migrating is the lack of economic opportunities within India. While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible ________ and impact on the global
Question:
Which factor has NOT been cited as a reason for Indian migrations in the passage?
A. Lack of economic opportunities in India
B. Intractable global conflicts in West Asia
C. Increase in far-right populist governments making visa conditions more difficult
D. Discrimination based on religion within India
E. NRIs and PIOs’ contributions to India’s development
Solution
The correct answer is Option 4.
Key Points
- The following factors for Indian migrations are cited in the passage:
- Lack of economic opportunities in India.
- Intractable global conflicts in West Asia.
- Increase in far-right populist governments making visa conditions more difficult.
- NRIs and PIOs’ contributions to India’s development are discussed in the passage, but these contributions are the result of their migration, not the reason for it.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option 4.
Additional Information
- Option 1: Lack of economic opportunities in India – This is explicitly mentioned in the passage.
- Option 2: Intractable global conflicts in West Asia – This is also cited as a reason affecting the diaspora.
- Option 3: Increase in far-right populist governments making visa conditions more difficult – This is mentioned concerning the challenges facing the diaspora.
- Option 5: NRIs and PIOs’ contributions to India’s development – This factor is more about the positive impact of the diaspora rather than a reason for migration.
20. Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage.
At the inauguration of the 18th edition of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the Indian diaspora as India’s “ambassadors to the world”, having “seamlessly assimilated” into the local society, served the community, and contributed to India’s growth and prosperity. The strength of the India-origin community worldwide of over 35 million — about 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs, who are foreign nationals — is their ability to adapt and thrive in different fields, including in politics, where Indian-origin people have become leaders of more than 30 other countries. Where they retain their Indian passports, the diaspora is known for its distinguished services in many professional spheres. The PBD’s purpose is to celebrate this success and discuss issues of importance. President Droupadi Murmu handed out about 27 Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards. The event, which was first held in 2003, is organised around January 9, when Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915. The latest event, held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, brought more than 3,000 delegates from across 70 countries, with much of the focus on how the diaspora can help in developing India (Viksit Bharat programme).
The achievements of the Indian diaspora are, no doubt, a matter of pride for all Indians, but it is important that the event is not limited to a simple self-congratulatory or laudatory exercise. The issues for the diaspora, particularly for those who are still Indian nationals, are more acute now. The increase in far-right populist governments, particularly in the West, is making visa and entry conditions for Indians more difficult, and it is important for the government to address such issues. Intractable global conflicts, especially in West Asia where more than nine million Indians live and work, are also putting lakhs of Indians in peril, and the PBD engagement would benefit from discussions between the community on how best to increase awareness and enhance safeguards for them. Given the broad spread of the diaspora, it is necessary to ensure that India’s ties with its diaspora be inclusive, and non-partisan on political issues. Recent actions by the government to deny or revoke OCI cards for those perceived to be critical of the government bely this necessity. Above all, it is important to acknowledge that one of the biggest drivers of Indians migrating is the lack of economic opportunities within India. While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible ________ and impact on the global stage.
Question:
It can be inferred from the passage that the Indian government:
A. Only focuses on celebrating the success of its diaspora without addressing their issues.
B. Is aware of and is attempting to address the challenges faced by its diaspora.
C. Actively discourages its diaspora from retaining ties with India.
D. Primarily sees the Indian diaspora as potential economic contributors to the nation.
E. Ignores the role of the diaspora in international politics.
Solution
The correct answer is Option 2.
Key Points
- The passage mentions that the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) is not merely a self-congratulatory event, but also an opportunity to discuss important issues faced by the Indian diaspora.
- It indicates that the Indian government is addressing issues such as visa and entry conditions, global conflicts, and the need for inclusive and non-partisan ties with the diaspora.
- The government is also aware of the economic challenges that contribute to migration and recognizes the need to engage with the diaspora to help develop India.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option 2.
Additional Information
- Option 1: Only focuses on celebrating the success of its diaspora without addressing their issues – This is incorrect as the passage notes the government’s engagement with diaspora issues.
- Option 3: Actively discourages its diaspora from retaining ties with India – This is incorrect since the passage mentions the government’s celebration and recognition of the diaspora’s impact.
- Option 4: Primarily sees the Indian diaspora as potential economic contributors to the nation – This is not entirely accurate as the passage emphasizes both their contributions and the government’s efforts to address their issues.
- Option 5: Ignores the role of the diaspora in international politics – This is incorrect as the passage mentions the achievements of Indian-origin people in politics globally.
21. Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage.
At the inauguration of the 18th edition of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the Indian diaspora as India’s “ambassadors to the world”, having “seamlessly assimilated” into the local society, served the community, and contributed to India’s growth and prosperity. The strength of the India-origin community worldwide of over 35 million — about 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs, who are foreign nationals — is their ability to adapt and thrive in different fields, including in politics, where Indian-origin people have become leaders of more than 30 other countries. Where they retain their Indian passports, the diaspora is known for its distinguished services in many professional spheres. The PBD’s purpose is to celebrate this success and discuss issues of importance. President Droupadi Murmu handed out about 27 Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards. The event, which was first held in 2003, is organised around January 9, when Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915. The latest event, held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, brought more than 3,000 delegates from across 70 countries, with much of the focus on how the diaspora can help in developing India (Viksit Bharat programme).
The achievements of the Indian diaspora are, no doubt, a matter of pride for all Indians, but it is important that the event is not limited to a simple self-congratulatory or laudatory exercise. The issues for the diaspora, particularly for those who are still Indian nationals, are more acute now. The increase in far-right populist governments, particularly in the West, is making visa and entry conditions for Indians more difficult, and it is important for the government to address such issues. Intractable global conflicts, especially in West Asia where more than nine million Indians live and work, are also putting lakhs of Indians in peril, and the PBD engagement would benefit from discussions between the community on how best to increase awareness and enhance safeguards for them. Given the broad spread of the diaspora, it is necessary to ensure that India’s ties with its diaspora be inclusive, and non-partisan on political issues. Recent actions by the government to deny or revoke OCI cards for those perceived to be critical of the government bely this necessity. Above all, it is important to acknowledge that one of the biggest drivers of Indians migrating is the lack of economic opportunities within India. While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible ________ and impact on the global
Question:
Which of the following best states the central idea of the passage?
A. The Pravasi Bharatiya Divas is merely a self-congratulatory event.
B. The Indian diaspora significantly contributes to the global stage and faces substantial challenges.
C. The Indian government needs to revoke OCI cards from critical individuals.
D. The event’s primary purpose is to issue awards to distinguished NRIs and PIOs.
E. Visa and entry conditions are becoming increasingly difficult for the Indian diaspora.
Solution
The correct answer is Option 2.
Key Points
- The passage highlights both the significant contributions of the Indian diaspora on the global stage and the substantial challenges they face, including difficult visa and entry conditions, as well as the impact of global conflicts.
- The passage also underscores the importance of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) in addressing these issues and celebrating the achievements of the diaspora.
- It makes the case that the event should be more than just self-congratulatory, aiming to discuss and mitigate the critical issues faced by the diaspora.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option 2.
Additional Information
- Option 1: The Pravasi Bharatiya Divas is merely a self-congratulatory event – This is incorrect as the passage indicates that the event is also focused on discussing important issues faced by the diaspora.
- Option 3: The Indian government needs to revoke OCI cards from critical individuals – This is an issue mentioned in the passage, but it is not the central idea.
- Option 4: The event’s primary purpose is to issue awards to distinguished NRIs and PIOs – This is part of the event’s purpose, but not the central idea of the passage.
- Option 5: Visa and entry conditions are becoming increasingly difficult for the Indian diaspora – This is one of the challenges mentioned, but not the central idea of the passage.
22. Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage.
At the inauguration of the 18th edition of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the Indian diaspora as India’s “ambassadors to the world”, having “seamlessly assimilated” into the local society, served the community, and contributed to India’s growth and prosperity. The strength of the India-origin community worldwide of over 35 million — about 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs, who are foreign nationals — is their ability to adapt and thrive in different fields, including in politics, where Indian-origin people have become leaders of more than 30 other countries. Where they retain their Indian passports, the diaspora is known for its distinguished services in many professional spheres. The PBD’s purpose is to celebrate this success and discuss issues of importance. President Droupadi Murmu handed out about 27 Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards. The event, which was first held in 2003, is organised around January 9, when Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915. The latest event, held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, brought more than 3,000 delegates from across 70 countries, with much of the focus on how the diaspora can help in developing India (Viksit Bharat programme).
The achievements of the Indian diaspora are, no doubt, a matter of pride for all Indians, but it is important that the event is not limited to a simple self-congratulatory or laudatory exercise. The issues for the diaspora, particularly for those who are still Indian nationals, are more acute now. The increase in far-right populist governments, particularly in the West, is making visa and entry conditions for Indians more difficult, and it is important for the government to address such issues. Intractable global conflicts, especially in West Asia where more than nine million Indians live and work, are also putting lakhs of Indians in peril, and the PBD engagement would benefit from discussions between the community on how best to increase awareness and enhance safeguards for them. Given the broad spread of the diaspora, it is necessary to ensure that India’s ties with its diaspora be inclusive, and non-partisan on political issues. Recent actions by the government to deny or revoke OCI cards for those perceived to be critical of the government bely this necessity. Above all, it is important to acknowledge that one of the biggest drivers of Indians migrating is the lack of economic opportunities within India. While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible ________ and impact on the global stage.
Question:
According to the passage, which of the given statements is incorrect?
A) The Pravasi Bharatiya Divas event was first held in 2003.
B) The latest Pravasi Bharatiya Divas event was held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
C) More than 5 million Indians live and work in West Asia.
A. Only A
B. Only B
C. Only C
D. A and B
E. A and C
Solution
The correct answer is Option 3.
Key Points
- Statement A: The Pravasi Bharatiya Divas event was first held in 2003.
- This statement is correct as it accurately reflects the context provided in the passage.
- Statement B: The latest Pravasi Bharatiya Divas event was held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
- This statement is correct as per the information given in the passage.
- Statement C: More than 5 million Indians live and work in West Asia.
- This statement is incorrect because the passage mentions that more than nine million Indians live and work in West Asia.
- Hence, the statement C is identified as incorrect in the context of the passage.
Therefore, the correct answer is: ‘Only C’.
23. Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage.
At the inauguration of the 18th edition of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the Indian diaspora as India’s “ambassadors to the world”, having “seamlessly assimilated” into the local society, served the community, and contributed to India’s growth and prosperity. The strength of the India-origin community worldwide of over 35 million — about 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs, who are foreign nationals — is their ability to adapt and thrive in different fields, including in politics, where Indian-origin people have become leaders of more than 30 other countries. Where they retain their Indian passports, the diaspora is known for its distinguished services in many professional spheres. The PBD’s purpose is to celebrate this success and discuss issues of importance. President Droupadi Murmu handed out about 27 Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards. The event, which was first held in 2003, is organised around January 9, when Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915. The latest event, held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, brought more than 3,000 delegates from across 70 countries, with much of the focus on how the diaspora can help in developing India (Viksit Bharat programme).
The achievements of the Indian diaspora are, no doubt, a matter of pride for all Indians, but it is important that the event is not limited to a simple self-congratulatory or laudatory exercise. The issues for the diaspora, particularly for those who are still Indian nationals, are more acute now. The increase in far-right populist governments, particularly in the West, is making visa and entry conditions for Indians more difficult, and it is important for the government to address such issues. Intractable global conflicts, especially in West Asia where more than nine million Indians live and work, are also putting lakhs of Indians in peril, and the PBD engagement would benefit from discussions between the community on how best to increase awareness and enhance safeguards for them. Given the broad spread of the diaspora, it is necessary to ensure that India’s ties with its diaspora be inclusive, and non-partisan on political issues. Recent actions by the government to deny or revoke OCI cards for those perceived to be critical of the government bely this necessity. Above all, it is important to acknowledge that one of the biggest drivers of Indians migrating is the lack of economic opportunities within India. While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible ________ and impact on the global
Question:
What will fit in the blank taken from the passage: “While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible ________ and impact on the global stage.”
A. knowledge
B. success
C. contribution
D. entrepreneurship
E. perseverance
Solution
The correct answer is ‘success‘.
Key Points
- The word “success” fits contextually in the blank to highlight the achievements and impact of the diaspora.
- It complements the idea of celebrating the accomplishments and the global influence of India’s talented people.
- Options 1, 3, 4, and 5 do not provide the same contextual and grammatical coherence as “success.”
Therefore, the correct answer is Option 2.
Complete Sentence: “While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible success and impact on the global stage.”
Additional Information
- Option 1: “knowledge” is less suitable as it focuses more on information and awareness rather than accomplishment.
- Option 3: “contribution” could fit, but “success” conveys the broader context of achievements better.
- Option 4: “entrepreneurship” is too specific and does not cover all forms of accomplishments.
- Option 5: “perseverance” emphasizes perseverance over the end achievements and impact.
24. Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage.
At the inauguration of the 18th edition of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the Indian diaspora as India’s “ambassadors to the world”, having “seamlessly assimilated” into the local society, served the community, and contributed to India’s growth and prosperity. The strength of the India-origin community worldwide of over 35 million — about 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs, who are foreign nationals — is their ability to adapt and thrive in different fields, including in politics, where Indian-origin people have become leaders of more than 30 other countries. Where they retain their Indian passports, the diaspora is known for its distinguished services in many professional spheres. The PBD’s purpose is to celebrate this success and discuss issues of importance. President Droupadi Murmu handed out about 27 Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards. The event, which was first held in 2003, is organised around January 9, when Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915. The latest event, held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, brought more than 3,000 delegates from across 70 countries, with much of the focus on how the diaspora can help in developing India (Viksit Bharat programme).
The achievements of the Indian diaspora are, no doubt, a matter of pride for all Indians, but it is important that the event is not limited to a simple self-congratulatory or laudatory exercise. The issues for the diaspora, particularly for those who are still Indian nationals, are more acute now. The increase in far-right populist governments, particularly in the West, is making visa and entry conditions for Indians more difficult, and it is important for the government to address such issues. Intractable global conflicts, especially in West Asia where more than nine million Indians live and work, are also putting lakhs of Indians in peril, and the PBD engagement would benefit from discussions between the community on how best to increase awareness and enhance safeguards for them. Given the broad spread of the diaspora, it is necessary to ensure that India’s ties with its diaspora be inclusive, and non-partisan on political issues. Recent actions by the government to deny or revoke OCI cards for those perceived to be critical of the government bely this necessity. Above all, it is important to acknowledge that one of the biggest drivers of Indians migrating is the lack of economic opportunities within India. While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible ________ and impact on the global stage.
Question:
Which of the following words is similar in meaning to “assimilated” in the context of the passage?
A. segregated
B. detached
C. incorporated
D. isolated
E. separated
Solution
The correct answer is: Option 3 i.e. incorporated.
Key Points
- The word “assimilated” means to take in and make a part of one’s own; absorb and integrate people, ideas, or culture into a wider society or culture. (अपनाना)
- Example: Over time, the rural population assimilated into the urban culture.
- “incorporated” means to take in or contain as part of a whole; include. (सम्मिलित)
- Example: The company incorporated new technology into its operations.
- Hence, “incorporated” is similar in meaning to “assimilated“.
Therefore, the correct answer is: incorporated.
Additional Information
Here are the other options explained along with their Hindi meanings and example sentences:
- Segregated (अलग किया हुआ): Set apart from the rest or from each other; isolate or divide.
- Example: The schools were segregated by race in the past.
- Detached (अलग किया हुआ): Separate or disconnected.
- Example: She felt detached from the community after moving to a new city.
- Isolated (अलग-थलग): Far away from other places, buildings, or people; remote.
- Example: The isolated village was difficult to reach due to the snow.
- Separated (अलग किया हुआ): To cause to move or be apart.
- Example: They separated the recycling into different bins.
25. Read the passage given below and then answer the questions given below the passage.
At the inauguration of the 18th edition of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the Indian diaspora as India’s “ambassadors to the world”, having “seamlessly assimilated” into the local society, served the community, and contributed to India’s growth and prosperity. The strength of the India-origin community worldwide of over 35 million — about 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs, who are foreign nationals — is their ability to adapt and thrive in different fields, including in politics, where Indian-origin people have become leaders of more than 30 other countries. Where they retain their Indian passports, the diaspora is known for its distinguished services in many professional spheres. The PBD’s purpose is to celebrate this success and discuss issues of importance. President Droupadi Murmu handed out about 27 Pravasi Bharatiya Samman awards. The event, which was first held in 2003, is organised around January 9, when Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915. The latest event, held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, brought more than 3,000 delegates from across 70 countries, with much of the focus on how the diaspora can help in developing India (Viksit Bharat programme).
The achievements of the Indian diaspora are, no doubt, a matter of pride for all Indians, but it is important that the event is not limited to a simple self-congratulatory or laudatory exercise. The issues for the diaspora, particularly for those who are still Indian nationals, are more acute now. The increase in far-right populist governments, particularly in the West, is making visa and entry conditions for Indians more difficult, and it is important for the government to address such issues. Intractable global conflicts, especially in West Asia where more than nine million Indians live and work, are also putting lakhs of Indians in peril, and the PBD engagement would benefit from discussions between the community on how best to increase awareness and enhance safeguards for them. Given the broad spread of the diaspora, it is necessary to ensure that India’s ties with its diaspora be inclusive, and non-partisan on political issues. Recent actions by the government to deny or revoke OCI cards for those perceived to be critical of the government bely this necessity. Above all, it is important to acknowledge that one of the biggest drivers of Indians migrating is the lack of economic opportunities within India. While there are no easy fixes for this, the loss to India of some of its most talented people must be counted, even as the country celebrates their incredible ________ and impact on the global
Question:
Which of the following words is the opposite in meaning to “inclusive” as used in the passage?
A. comprehensive
B. restricted
C. welcoming
D. extensive
E. universal
Solution
The correct answer is: Option 2 i.e. restricted.
Key Points
- The word “inclusive” means including all the services, facilities, or items normally expected or required; comprehensive; not excluding any section of society or any party involved in something. (समावेशी)
- Example: The club is renowned for its inclusive policies that welcome people from all backgrounds.
- “restricted” means limited in extent, number, scope, or action; kept within certain limits. (सीमित)
- Example: Access to the secret documents is restricted to authorized personnel only.
- Therefore, “restricted” is the opposite in meaning to “inclusive“.
Therefore, the correct answer is: restricted.
Additional Information
Here are the other options explained along with their Hindi meanings and example sentences:
- Comprehensive (व्यापक): Complete and including everything that is necessary.
- Example: The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the financial standing of the company.
- Welcoming (स्वागत करने वाला): Friendly or making you feel welcome.
- Example: The community was very welcoming to new members.
- Extensive (विस्तृत): Covering or affecting a large area.
- Example: The museum houses an extensive collection of ancient artefacts.
- Universal (सार्वभौमिक): Applicable to or common to all members of a group or set.
- Example: The desire for happiness is a universal trait among humans.
26. Rearrange the following five sentences/group of sentences (A), (B), (C), (D), and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
(A) Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation.
(B) The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
(C) Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety.
(D) The distinction between science, technology and engineering is not always clear.
(E) Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science.
Question:
Which of the following should be the THIRD sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is C.
Key Points
- The given passage is about the difference between science, engineering, and technology.
- The first sentence should be D because it introduces the topic by stating that the difference between science, engineering and technology is not clear.
- The next sentence should be A which defines science.
- The third sentence is C which defines technology. From the given sentences we can understand that the definition of technology can be written only after defining science.
- The fourth sentence is E which explains the definition of engineering. From the definition of engineering it is clear that it should be discussed only after defining science and technology.
- The last sentence is B which concludes the passage by stating how technologies can be developed.
- Hence, the correct sequence is DACEB.
Hint
- After going through the sentences carefully we can understand that the definitions of science, engineering and technology are discussed here. Therefore, D is suitable to begin the passage as the purpose of discussing the definitions of science, engineering and technology is clear from this sentence.
- Thus, we can identify the first sentence.
The following paragraph is formed after arranging the five sentences in proper sequence:
The distinction between science, engineering, and technology is not always clear. Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation. Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety. Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science. The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
Additional Information
- Observation: the process of closely examining something
27. Rearrange the following five sentences/group of sentences (A), (B), (C), (D), and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
(A) Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation.
(B) The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
(C) Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety.
(D) The distinction between science, technology and engineering is not always clear.
(E) Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science.
Question:
Which of the following should be the SECOND sentence after rearrangement?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is A.
Key Points
- The given passage is about the difference between science, engineering, and technology.
- The first sentence should be D because it introduces the topic by stating that the difference between science, engineering and technology is not clear.
- The next sentence should be A which defines science.
- The third sentence is C which defines technology. From the given sentences we can understand that the definition of technology can be written only after defining science.
- The fourth sentence is E which explains the definition of engineering. From the definition of engineering it is clear that it should be discussed only after defining science and technology.
- The last sentence is B which concludes the passage by stating how technologies can be developed.
- Hence, the correct sequence is DACEB.
HINT;
- After going through the sentences carefully we can understand that the definitions of science, engineering and technology are discussed here. Therefore, D is suitable to begin the passage as the purpose of discussing the definitions of science, engineering and technology is clear from this sentence.
- Thus, we can identify the first sentence.
The following paragraph is formed after arranging the five sentences in proper sequence:
The distinction between science, engineering, and technology is not always clear. Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation. Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety. Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science. The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ;
- Usability: the degree to which something is ready to be used
28. Rearrange the following five sentences/group of sentences (A), (B), (C), (D), and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
(A) Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation.
(B) The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
(C) Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety.
(D) The distinction between science, technology and engineering is not always clear.
(E) Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science.
Question:
Which of the following should be the FOURTH sentence after rearrangement?
A. B
B. C
C. D
D. E
E. A
Solution
The correct answer is E.
Key Points
- The given passage is about the difference between science, engineering, and technology.
- The first sentence should be D because it introduces the topic by stating that the difference between science, engineering and technology is not clear.
- The next sentence should be A which defines science.
- The third sentence is C which defines technology. From the given sentences we can understand that the definition of technology can be written only after defining science.
- The fourth sentence is E which explains the definition of engineering. From the definition of engineering it is clear that it should be discussed only after defining science and technology.
- The last sentence is B which concludes the passage by stating how technologies can be developed.
- Hence, the correct sequence is DACEB.
HINT
- After going through the sentences carefully we can understand that the definitions of science, engineering and technology are discussed here. Therefore, D is suitable to begin the passage as the purpose of discussing the definitions of science, engineering and technology is clear from this sentence.
- Thus, we can identify the first sentence.
The following paragraph is formed after arranging the five sentences in proper sequence:
The distinction between science, engineering, and technology is not always clear. Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation. Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety. Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science. The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
ADDTIONAL INFORMATION
- Distinction: difference
29. Rearrange the following five sentences/group of sentences (A), (B), (C), (D), and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
(A) Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation.
(B) The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
(C) Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety.
(D) The distinction between science, technology and engineering is not always clear.
(E) Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science.
Question:
Which of the following should be the LAST sentence after rearrangement?
A. C
B. D
C. B
D. A
E. E
Solution
The correct answer is B.
Key Points
- The given passage is about the difference between science, engineering, and technology.
- The first sentence should be D because it introduces the topic by stating that the difference between science, engineering and technology is not clear.
- The next sentence should be A which defines science.
- The third sentence is C which defines technology. From the given sentences we can understand that the definition of technology can be written only after defining science.
- The fourth sentence is E which explains the definition of engineering. From the definition of engineering it is clear that it should be discussed only after defining science and technology.
- The last sentence is B which concludes the passage by stating how technologies can be developed.
- Hence, the correct sequence is DACEB.
HINT ;
- After going through the sentences carefully we can understand that the definitions of science, engineering and technology are discussed here. Therefore, D is suitable to begin the passage as the purpose of discussing the definitions of science, engineering and technology is clear from this sentence.
- Thus, we can identify the first sentence.
The following paragraph is formed after arranging the five sentences in proper sequence:
The distinction between science, engineering, and technology is not always clear. Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation. Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety. Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science. The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
ADDTITIONAL INFORMATION
- Utility: usefulness or use
30. Rearrange the following five sentences/group of sentences (A), (B), (C), (D), and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
(A) Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation.
(B) The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
(C) Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety.
(D) The distinction between science, technology and engineering is not always clear.
(E) Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science.
Question:
Which of the following should be the FIRST sentence after rearrangement?
A. B
B. C
C. D
D. E
E. A
Solution
The correct answer is D.
Key Points
- The given passage is about the difference between science, engineering, and technology.
- The first sentence should be D because it introduces the topic by stating that the difference between science, engineering and technology is not clear.
- The next sentence should be A which defines science.
- The third sentence is C which defines technology. From the given sentences we can understand that the definition of technology can be written only after defining science.
- The fourth sentence is E which explains the definition of engineering. From the definition of engineering it is clear that it should be discussed only after defining science and technology.
- The last sentence is B which concludes the passage by stating how technologies can be developed.
- Hence, the correct sequence is DACEB.
HINT;
- After going through the sentences carefully we can understand that the definitions of science, engineering and technology are discussed here. Therefore, D is suitable to begin the passage as the purpose of discussing the definitions of science, engineering and technology is clear from this sentence.
- Thus, we can identify the first sentence.
The following paragraph is formed after arranging the five sentences in proper sequence:
The distinction between science, engineering, and technology is not always clear. Science is systematic knowledge of the physical or material world gained through observation and experimentation. Technologies are not usually exclusively products of science, because they have to satisfy requirements such as utility, usability, and safety. Engineering is the goal-oriented process of designing and making tools and systems to exploit natural phenomena for practical human means, often using results and techniques from science. The development of technology may draw upon many fields of knowledge, including scientific, engineering, mathematical, linguistic, and historical knowledge, to achieve some practical result.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
- Exploit: take advantage of
31. Directions: Study the pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
Aman spent his free time watching web series on five different OTT platforms (A, B, C, D, and E). The pie chart below shows the percentage distribution of time spent on OTT platforms out of the total time spent. The total time spent by Aman is 140 hours (in one month).

Question:
The total time spent (in hours) by Aman on platforms A and C together is
A. 52 hours
B. 56 hours
C. 66 hours
D. 36 hours
E. 76 hours
Solution
Given:
The total time spent by Aman = 140 hours
Now,
Time spent on platform A = 140 × 25/100 = 35 hours
Time spent on platform B = 140 × 35/100 = 49 hours
Time spent on platform C = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Time spent on platform D = 140 × 10/100 = 14 hours
Time spent on platform E = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Calculation:
The total time spent by Aman on platforms A and C together = 35 + 21
⇒ 56 hours
Hence, the correct answer is option 2.
32. Directions: Study the pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
Aman spent his free time watching web series on five different OTT platforms (A, B, C, D, and E). The pie chart below shows the percentage distribution of time spent on OTT platforms out of the total time spent. The total time spent by Aman is 140 hours (in one month).

Question:
Find the ratio of time spent (in hours) on platform B to the time spent (in hours) on platform E by Aman.
A. 3:7
B. 7:9
C. 7:3
D. 9:5
E. 6:13
Solution
Given:
The total time spent by Aman = 140 hours
Now,
Time spent on platform A = 140 × 25/100 = 35 hours
Time spent on platform B = 140 × 35/100 = 49 hours
Time spent on platform C = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Time spent on platform D = 140 × 10/100 = 14 hours
Time spent on platform E = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Calculation:
Time spent on platform B = 49 hours
Time spent on platform E = 21 hours
Required ratio = 49/21
⇒ 7:3
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
33. Directions: Study the pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
Aman spent his free time watching web series on five different OTT platforms (A, B, C, D, and E). The pie chart below shows the percentage distribution of time spent on OTT platforms out of the total time spent. The total time spent by Aman is 140 hours (in one month).

Question:
Time spent (in hours) on OTT platform A is what percent more/less than time spent (in hours) on OTT platform D.
A. 250%
B. 50%
C. 150%
D. 300%
E. 125%
Solution
Given:
The total time spent by Aman = 140 hours
Now,
Time spent on platform A = 140 × 25/100 = 35 hours
Time spent on platform B = 140 × 35/100 = 49 hours
Time spent on platform C = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Time spent on platform D = 140 × 10/100 = 14 hours
Time spent on platform E = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Calculation:
Time spent on platform A = 35 hours
Time spent on platform D = 14 hours
So (35 – 14)/14 × 100
⇒ 150%
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
34. Directions: Study the pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
Aman spent his free time watching web series on five different OTT platforms (A, B, C, D, and E). The pie chart below shows the percentage distribution of time spent on OTT platforms out of the total time spent. The total time spent by Aman is 140 hours (in one month).

Question:
Time spent (in hours) on OTT platform C is what percent of time spent (in hours) on OTT platform B and OTT platform E together.
A. 43.75%
B. 41.65%
C. 30%
D. 46%
E. 45%
Solution
Given:
The total time spent by Aman = 140 hours
Now,
Time spent on platform A = 140 × 25/100 = 35 hours
Time spent on platform B = 140 × 35/100 = 49 hours
Time spent on platform C = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Time spent on platform D = 140 × 10/100 = 14 hours
Time spent on platform E = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Calculation:
Time spent on platform B = 49 hours
Time spent on platform E = 21 hours
Time spent on platform C = 21 hours
So 21 /70 × 100
⇒ 30%
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
35. Directions: Study the pie chart carefully and answer the following questions:
Aman spent his free time watching web series on five different OTT platforms (A, B, C, D, and E). The pie chart below shows the percentage distribution of time spent on OTT platforms out of the total time spent. The total time spent by Aman is 140 hours (in one month).

Question:
The average time spent (in hours) on OTT platform B, C, and D together is
A. 38 hours
B. 55 hours
C. 28 hours
D. 35 hours
E. 48 hours
Solution
Given:
The total time spent by Aman = 140 hours
Now,
Time spent on platform A = 140 × 25/100 = 35 hours
Time spent on platform B = 140 × 35/100 = 49 hours
Time spent on platform C = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Time spent on platform D = 140 × 10/100 = 14 hours
Time spent on platform E = 140 × 15/100 = 21 hours
Calculation:
Time spent on platform B = 49 hours
Time spent on platform C = 21 hours
Time spent on platform D = 14 hours
So (49 + 21 + 14) / 3
⇒ 84/3
⇒ 28 hours
Hence, the correct answer is option 3.
36. A sells goods to B at a loss of 10%, B sells it to C at a loss of 10%, C sells it to D at a loss of 10%, if D pay Rs.3,645 for it, Find loss of B.
A. Rs. 550
B. Rs. 500
C. Rs. 400
D. Rs. 450
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
A’s loss percent = 10%
B’s loss percent = 10%
C’s loss percent = 10%
D’s cost price = Rs.3,645
Concept:
Loss = Cost price – Selling price
Calculation:
Let, cost price for A be Rs.1000x
Cost price of B = {(100 – 10)/100} × 1000x = Rs.900x
Cost price of C = {(100 – 10)/100} × 900x = Rs.810x
Cost price of D = {(100 – 10)/100} × 810x = Rs.729x = 3645
⇒ x = 5
Loss of B = (900x – 810x) × 5 = Rs.450
∴ Loss of B is Rs.450.
37. Find the value of x.
2⁴/4⁴ × 16 × 2x ÷ 2² × 64 = 4⁴
A. 4
B. 9
C. 6
D. 8
E. 7
Solution:
2⁴/4⁴ × 16 × 2x ÷ 2² × 64 = 4⁴
2⁴/2⁸ × 16 × 2x/2² × 64 = 16 × 16
1/2⁴ × 16 × 2x/4 × 64 = 16 × 16
x/2 × 64 = 16 × 16
32x = 16 × 16
x = 8
38. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
520 × 15 ÷ 45 = ? × 13
A. 2.67
B. 15.50
C. 13.33
D. 22.67
E. 7.33
Solution
Concept Used:
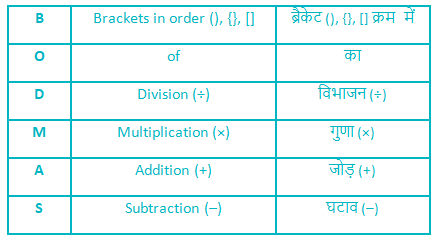
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:
Calculation:
520 × 15 ÷ 45 = ? × 13
⇒ 520 × 15/45 = ? × 13
⇒ 520 × 1/3 = ? × 13
⇒ 520/3 = ? × 13
⇒ (520/3) × (1/13) = ?
⇒ 40/3 = 13.33 = ?
∴ The value of ? is 13.33.
39. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
33 – 3 of (1 + 22) – 5 = ?
A. 3
B. 5
C. 7
D. 2
E. None
Solution
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
33 – 3 of (1 + 22) – 5 = ?
⇒ 27 – 3 of (1 + 4) – 5
⇒ 27 – 3 × 5 – 5
⇒ 27 – 15 – 5
⇒ 12 – 5
⇒ 7
∴ The required result will be 7.
40. Find the value of ‘?’ in the following question.
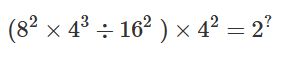
A. 4
B. 8
C. 6
D. 10
E. 3
Solution
Concept used:
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below:
Step-1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Now,
Calculations:
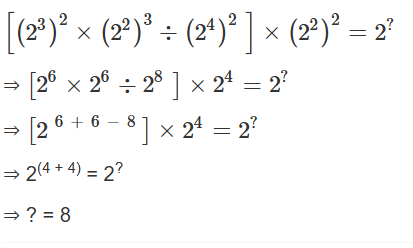
41. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following equation?
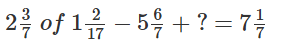
A.
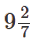
B.
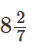
C.
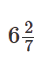
D.
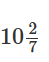
E.
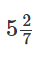
Solution
(17/7) × (19/17) – 41/7 + ? = 50/7
⇒ 19/7 – 41/7 + ? = 50/7
⇒ -22/7 + ? = 50/7
⇒ ? = 50/7 + 22/7
⇒ ? = 72/7
⇒ ? = 10 2/7
42. What value should come in place of ‘x’ in the following question?
√6889 – √2116 + √2704 ÷ √676 × 3 = x
A. 45
B. 43
C. 54
D. 55
E. None of these
Solution
Concept:
This type of question can be solved by the help of BODMAS
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below:
Step-1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first and in the bracket,
Step-2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Calculation:
⇒ 83 – 46 + 52/26 × 3 = x
⇒ 37 + 6 = x
⇒ 43 = x
∴ Value of x is 43
43. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
70% of (2/3) of 630 =?
A. 350
B. 200
C. 294
D. 250
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
70% of (2/3) of 630 =?
Concept used:
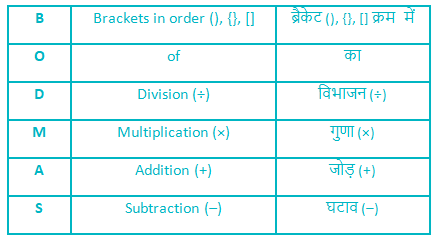
Calculation:
70% of (2/3) of 630 =?
⇒ (70/100) × (2/3) × 630 =?
⇒ ? = 294
∴ 294 will come in place of the question mark (‘?’).
44. What should come in place of question mark (?) in the following questions?
25% of 88 × ? ÷ 2 = 66
A. 10
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
E. None of these
Solution
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below:
Step-1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and in the bracket,
Step-2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next,
Step-3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated,
Step-4: Last but not least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Now,
Calculations:
Considering the following question
25% of 88 × ? ÷ 2 = 66
⇒ ¼ × 88 × ? ÷ 2 = 66
⇒ 22 × ? ÷ 2 = 66
⇒ 11 × ? = 66
∴ ? = 6
45. The average weight of P and Q is 50 Kg. The average weight of Q and R is 62 kg and the average weight of P and R is 52 kg. Then the weight of P is?
A. 45 kg
B. 35 kg
C. 30 kg
D. 40 kg
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Average weight of P and Q = 50 Kg
Average weight of Q and R = 62 kg
Average weight of P and R = 52 kg
Formula:
Average weight = total weight / number of person
Calculation:
Let, P, Q and R represent their respective weights. Then we have:
⇒ P + Q = (50 × 2) = 100 —(i)
⇒ Q + R = (62 × 2) = 124 —(ii)
⇒ P + R = (52 × 2) = 104 —(iii)
Adding (i), (ii) and (iii), we get: (P + Q + R) = 328 or P + Q + R = 164 —(iv)
Subtracting (ii) from (iv), we get P = 40.
⇒ P’s weight = 40 kg.
∴ The weight of P is 40 kg.
46. Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the questions given below.
In a village there are 1600 students. The ratio of male and female is 3 : 5. The students like Hindi language or English language or both. 12% of the male like only Hindi language. 22% of the female like only English language. 24% of the total students like only Hindi language and the number of male who like both language is six times the number of male who like only Hindi language.
Question:
Find the total number of student who like only English language.
A. 316
B. 1216
C. 900
D. 384
E. None of these
Solution:
Given: Total number of students in the village = 1600
Ratio of male and female students = 3 : 5
Male who like only Hindi language = 12%
Female who like only English language = 22%
Total students who like only Hindi language = 24%
Calculation: Total number of male students in the village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 3
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 3
⇒ 200 × 3
⇒ 600
Total number of female students in ther village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 5
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 5
⇒ 200 × 5
⇒ 1000
Males who like only Hindi language = 600 × (12 / 100)
⇒ 6 × 12
⇒ 72
Total number of students like only Hindi language = 1600 × (24 / 100)
⇒ 16 × 24
⇒ 384
Female who likes only Hindi language = 384 – 72
⇒ 312
Number of males who like both languages = 72 × 6
⇒ 432
Number of males who like only English language = 600 – (432 + 72)
⇒ 96
Number of females who like only English language = 1000 × (22 / 100)
⇒ 10 × 22
⇒ 220
Total number of students who like only English language = 96 + 220
⇒ 316
Number of females who like both the languages = 1000 – (312 + 220)
⇒ 1000 – 532
⇒ 468
Total number of students who like both the languages = 432 + 468
⇒ 900
47. Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the questions given below.
In a village there are 1600 students. The ratio of male and female is 3 : 5. The students like Hindi language or English language or both. 12% of the male like only Hindi language. 22% of the female like only English language. 24% of the total students like only Hindi language and the number of male who like both language is six times the number of male who like only Hindi language.
Question:
Find the number of females who like both the languages.
A. 432
B. 468
C. 316
D. 312
E. None of these
Solution:
Given: Total number of students in the village = 1600
Ratio of male and female students = 3 : 5
Male who like only Hindi language = 12%
Female who like only English language = 22%
Total students who like only Hindi language = 24%
Calculation: Total number of male students in the village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 3
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 3
⇒ 200 × 3
⇒ 600
Total number of female students in the village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 5
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 5
⇒ 200 × 5
⇒ 1000
Males who like only Hindi language = 600 × (12 / 100)
⇒ 6 × 12
⇒ 72
Total number of students like only Hindi language = 1600 × (24 / 100)
⇒ 16 × 24
⇒ 384
Female who likes only Hindi language = 384 – 72
⇒ 312
Number of males who like both languages = 72 × 6
⇒ 432
Number of males who like only English language = 600 – (432 + 72)
⇒ 96
Number of females who like only English language = 1000 × (22 / 100)
⇒ 10 × 22
⇒ 220
Total number of students who like only English language = 96 + 220
⇒ 316
Number of females who like both the languages = 1000 – (312 + 220)
⇒ 1000 – 532
⇒ 468
Total number of students who like both the languages = 432 + 468
⇒ 900
∴ Total number of females who like both the languages = 468
48. Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the questions given below.
In a village there are 1600 students. The ratio of male and female is 3 : 5. The students like Hindi language or English language or both. 12% of the male like only Hindi language. 22% of the female like only English language. 24% of the total students like only Hindi language and the number of male who like both language is six times the number of male who like only Hindi language.
Question:
Find the difference between the number of females and males who like only Hindi.
A. 124
B. 36
C. 240
D. 68
E. None of these
Solution:
Given: Total number of students in the village = 1600
Ratio of male and female students = 3 : 5
Male who like only Hindi language = 12%
Female who like only English language = 22%
Total students who like only Hindi language = 24%
Calculation: Total number of male students in the village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 3
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 3
⇒ 200 × 3
⇒ 600
Total number of female students in the village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 5
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 5
⇒ 200 × 5
⇒ 1000
Males who like only Hindi language = 600 × (12 / 100)
⇒ 6 × 12
⇒ 72
Total number of students like only Hindi language = 1600 × (24 / 100)
⇒ 16 × 24
⇒ 384
Female who likes only Hindi language = 384 – 72
⇒ 312
Number of males who like both languages = 72 × 6
⇒ 432
Number of males who like only English language = 600 – (432 + 72)
⇒ 96
Number of females who like only English language = 1000 × (22 / 100)
⇒ 10 × 22
⇒ 220
Total number of students who like only English language = 96 + 220
⇒ 316
Number of females who like both the languages = 1000 – (312 + 220)
⇒ 1000 – 532
⇒ 468
Total number of students who like both the languages = 432 + 468
⇒ 900

Difference between the number of females and males who like only Hindi language = 312 – 72
∴ 240
49. Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the questions given below.
In a village there are 1600 students. The ratio of male and female is 3 : 5. The students like Hindi language or English language or both. 12% of the male like only Hindi language. 22% of the female like only English language. 24% of the total students like only Hindi language and the number of male who like both language is six times the number of male who like only Hindi language.
Question:
Find the total number of males who like only one language.
A. 432
B. 296
C. 408
D. 168
E. None of these
Solution:
Given: Total number of students in the village = 1600
Ratio of male and female students = 3 : 5
Male who like only Hindi language = 12%
Female who like only English language = 22%
Total students who like only Hindi language = 24%
Calculation: Total number of male students in the village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 3
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 3
⇒ 200 × 3
⇒ 600
Total number of female students in the village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 5
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 5
⇒ 200 × 5
⇒ 1000
Males who like only Hindi language = 600 × (12 / 100)
⇒ 6 × 12
⇒ 72
Total number of students like only Hindi language = 1600 × (24 / 100)
⇒ 16 × 24
⇒ 384
Female who likes only Hindi language = 384 – 72
⇒ 312
Number of males who like both languages = 72 × 6
⇒ 432
Number of males who like only English language = 600 – (432 + 72)
⇒ 96
Number of females who like only English language = 1000 × (22 / 100)
⇒ 10 × 22
⇒ 220
Total number of students who like only English language = 96 + 220
⇒ 316
Number of females who like both the languages = 1000 – (312 + 220)
⇒ 1000 – 532
⇒ 468
Total number of students who like both the languages = 432 + 468
⇒ 900

Total number of males who likes only one language = 72 + 96
∴ 168
50. Direction: Read the following data carefully and answer the questions given below.
In a village there are 1600 students. The ratio of male and female is 3 : 5. The students like Hindi language or English language or both. 12% of the male like only Hindi language. 22% of the female like only English language. 24% of the total students like only Hindi language and the number of male who like both language is six times the number of male who like only Hindi language.
Question:
Find the total number of students who like both the languages.
A. 316
B. 900
C. 384
D. 532
E. None of these
Solution:
Given: Total number of students in the village = 1600
Ratio of male and female students = 3 : 5
Male who like only Hindi language = 12%
Female who like only English language = 22%
Total students who like only Hindi language = 24%
Calculation: Total number of male students in the village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 3
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 3
⇒ 200 × 3
⇒ 600
Total number of female students in ther village = {1600 / (5 + 3)} × 5
⇒ {1600 / 8} × 5
⇒ 200 × 5
⇒ 1000
Males who like only Hindi language = 600 × (12 / 100)
⇒ 6 × 12
⇒ 72
Total number of students like only Hindi language = 1600 × (24 / 100)
⇒ 16 × 24
⇒ 384
Female who likes only Hindi language = 384 – 72
⇒ 312
Number of males who like both languages = 72 × 6
⇒ 432
Number of males who like only English language = 600 – (432 + 72)
⇒ 96
Number of females who like only English language = 1000 × (22 / 100)
⇒ 10 × 22
⇒ 220
Total number of students who like only English language = 96 + 220
⇒ 316
Number of females who like both the languages = 1000 – (312 + 220)
⇒ 1000 – 532
⇒ 468
Total number of students who like both the languages = 432 + 468
∴ 900
51. The radius of 2 cylindrical cones are in ratio 4 : 7 and the ratio of their volume is 3 : 7 then find the ratio of their heights.
A. 3 : 7
B. 4 : 9
C. 21 : 16
D. 20 : 21
E. 5 : 7
Solution
Formula used:
Volume of cone = (1 / 3) π r2 h
Calculation:
Let the radius of cones be 4r and 7r
Height of 1st cone = h1
Height of 2nd cone = h2
⇒ Volume of 1st cone = (1/3) × π × (4r)2 × h1 —-1
⇒ Volume of 2nd cone = (1/3) × π × (7r)2 × h2 —-2
Divide equation 1 by 2
⇒ h1/h2 = 21 / 16∴ The ratio of heights, h1 : h2 is 21 : 16
52. The jeweler keeps the ratio 3 : 2 of gold and copper to make jewelry. 20 grams of the mixture is replaced by copper and the ratio of gold and copper became 5 : 4. Find the amount of gold in the initial mixture.
A. 170
B. 165
C. 160
D. 162
E. 172
Solution
Given
Ratio of gold and copper to make jewelry = 3 : 2
Mixture replace by copper = 20 gram
New ratio = 5 : 4
Formula used
Quantity of cheaper / Quantity of dearer = (Price of dearer – Average price) / (Average price – Price of cheaper)
Calculation
Let the amount of gold and copper in the initial mixture respectively = 3x gram and 2x gram.
Amount of gold in 20 grams of mixture = 3x/5x × 20 = 12 grams
Amount of copper in 20 grams of mixture = 2x/5x × 20 = 8 grams
According to the question
⇒ (3x – 12)/(2x – 8 + 20) = 5/4
⇒ x = 54
The amount of gold in the initial mixture = 3x = 3 × 54 = 162
∴ The amount of gold in the initial mixture is 162.
53. The ratio of the speed train A and B is 4 : 5. If train A takes 1.5 hours to travel 150 km. Then find out the time taken by the train B to travel the same distance.
A. 72 min
B. 80 min
C. 95 min
D. 65 min
E. 60 min
Solution
GIVEN:
Speed Ratio of train A and B is 4 : 5
Time taken by train A is 1.5 hours.
Distance to be traveled = 150 k.m. (Super flows data)
CONCEPT:
Speed ratio is inversely proportional to time and directly proportional to Distance.
∴ Time ratio = 5 : 4
CALCULATIONS:
Let the time taken by Train A be 5x
And time taken by train B = 4x
⇒ 5x = 1.5 hour = 90 minute

54. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 8x + 7 = 0
II. y2 – 1 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
Solution
Given:
I. x 2 – 8x + 7 = 0
II. y2 – 1 = 0
Calculation:
From I,
x2 – 8x + 7 = 0
⇒ x2 – 7x – x + 7 = 0
⇒ x(x – 7) – 1(x – 7) = 0
⇒ (x – 7)(x – 1) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (x – 7) = 0 or (x – 1) = 0
⇒ x = 7 or 1
From II,
y2 – 1 = 0
⇒ y2 = 1
⇒ y = ±√1
⇒ y = ±1
⇒ y = 1 or -1
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 7 | 1 | x > y |
| 7 | -1 | x > y |
| 1 | 1 | x = y |
| 1 | -1 | x > y |
∴ x ≥ y.
55. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 4x + 4 = 0
II. y2 – 6y + 9 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
Solution
Given:
I. x2 – 4x + 4 = 0
II. y2 – 6y + 9 = 0
Calculation:
From I,
x2 – 4x + 4 = 0
⇒ x2 – 2x – 2x + 4 = 0
⇒ x(x – 2) – 2(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 2)(x – 2) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (x – 2) = 0
⇒ x = 2
From II,
y2 – 6y + 9 = 0
⇒ y2 – 3y – 3y + 9 = 0
⇒ y(y – 3) – 3(y – 3) = 0
⇒ (y – 3)(y – 3) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (y – 3) = 0
⇒ y = 3
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 2 | 3 | x < y |
∴ x < y.
56. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 2x2 – 4x + 2 = 0
II. 2y2 + y – 1 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. No relation in x and y or x = y
Solution
Given:
I. 2x2 – 4x + 2 = 0
II. 2y2 + y – 1 = 0
Calculation:
From I
2x2 – 4x + 2 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 2x – 2x + 2 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 1) – 2(x – 1) = 0
⇒ (x – 1)(2x – 2) = 0
⇒ x = 1, 1
From II
2y2 + y – 1 = 0
⇒ 2y2 + 2y – y – 1 = 0
⇒ 2y(y + 1) – 1(y + 1) = 0
⇒ (y + 1)(2y – 1) = 0
⇒ y = -1, 1/2
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation)
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation between x & y |
| 1 | -1 | x > y |
| 1 | 1/2 | x > y |
| 1 | -1 | x > y |
| 1 | 1/2 | x > y |
∴ x > y
IMPORTANT POINT ;
| Sign Method | ||
| Equation | Sign | Remark |
| ax2 + bx + c = 0 | -Ve, -Ve | Same signs |
| ax2 – bx + c = 0 | +Ve, +Ve | Same signs |
| ax2 + bx – c = 0 | -Ve, +Ve | Larger root is negative smaller root is positive |
| ax2 – bx – c = 0 | -Ve, +Ve | Larger root is positive smaller root is negative |
57. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 51x + 50 = 0
II. y2 + 50y – 51 = 0
A. x < y
B. x > y
C. x ≤ y
D. x ≥ y
E. x = y or the relation between x and y can’t be established.
Solution
Given:
I. x2 – 51x + 50 = 0
II. y2 + 50y – 51 = 0
Calculation:
I. x2 – 51x + 50 = 0
⇒ x2 – 50x – x + 51 = 0
⇒ x(x – 50) – 1(x – 50)= 0
⇒ (x – 50)(x – 1) = 0
⇒ x = 50, 1
II. y2 + 50y – 51 = 0
⇒ y2 + 51y – y – 51 = 0
⇒ y(y + 51) – 1(y + 51) = 0
⇒ (y + 51)(y – 1) = 0
⇒ y = (-51), 1
| Value of ‘x’ | Relation | Value of ‘y’ |
| 50 | > | -51 |
| 50 | > | 1 |
| 1 | > | -51 |
| 1 | = | 1 |
∴ After comparison, all the values of x and y the relation is “x ≥ y”.
58. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 20x + 100 = 0
II. y2 – 100 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
Solution
Given:
I. x2 – 20x + 100 = 0
II. y2 – 100 = 0
Calculation:
x2 – 20x + 100 = 0
⇒ x2 – 10x – 10x + 100 = 0
⇒ x(x – 10) – 10(x – 10) = 0
⇒ (x – 10)(x – 10) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (x – 10) = 0
⇒ x = 10
From II,
y2 – 100 = 0
⇒ y2 = 100
⇒ y = ±√100
⇒ y = ±10
⇒ y = 10 or -10
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 10 | 10 | x = y |
| 10 | -10 | x > y |
∴ x ≥ y.
59. The ratio between the savings of A and B is 3 : 4. The difference between the savings of B and A is Rs.2000. Find the average savings of A and B.
A. Rs.7000
B. Rs.6500
C. Rs.8000
D. Rs.8600
E. Rs.9000
Solution
Given:
The ratio between the savings of A and B is 3 : 4. The difference between the
savings of B and A is Rs.2000
Calculation:
Let savings of A and B be Rs.3n and Rs.4n respectively.
⇒ 4n – 3n = 2000
⇒ n = 2000
The savings of A = 2000 × 3 = Rs.6000
The savings of B = 2000 × 4 = Rs.8000
Total savings of A and B = 6000 + 8000 = Rs.14000
Required average = 14000/2 = Rs.7000
Therefore the correct answer is Rs.7000
60. If there are 6 subjects attempted by a student of class 10, in how many ways can that student fail.
A. 64
B. 32
C. 63
D. 31
E. None of these
Solution
Concept:-
There are two ways in each subject to perform, either student passes or fails.
Calculation:-
Total number of ways of getting result = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 64
Cases of failing = 63 (as in 1 case he passes in all subjects)
61. Three pipes A, B, C can fill a tank in 5 hour, 2 hour and 10 hour respectively. if the pipes are open alternatively for one hour each starting with pipe A then in how much time the tank will fill completely?
A. 2 hours
B. 4 hours
C. 3 hours
D. 5 hours
E. 1.5 hours
Solution
GIVEN:
time taken by pipe A =5 hours
time taken by pipe B = 2 hours
time taken by pipe C = 10 hours
EXPLANATION:
part of the tank filled by A in one hour =1515
part of the tank filled by B in one hour =1212
part of the tank filled by C in one hour =110110
part of the tank filled in 3 hours =12+15+110=810=4512+15+110=810=45
remaining part = 1−45=151−45=15
this will be filled by pipe A in =15×5=1hour15×5=1hour
∴ total time = 3 + 1 = 4 hours
Alternate Method
let capacity of tank = 10 (L.C.M of 5, 2,10)
the efficiency of pipe A per hour = 2
the efficiency of pipe B per hour = 5
the efficiency of pipe C per hour = 1
tank filled in 3 hours = 2 + 5 + 1 = 8
remaining part = 10 – 8 = 2
pipe A will fill it in 1 hour
total time =3 + 1 = 4 hours
62. A boat can travel with a speed of 29 km/hr in still water. If the speed of the stream is 6 km/hr. Find the time taken by the boat to go 175 km downstream and 115 km upstream.
A. 9 hours
B. 11 hours
C. 10 hours
D. 15 hours
E. None of these
Solution
Given:
Speed of boat in still water = 29 km/hr
Speed of stream = 6 km/hr
Concept Used:
Time taken by boat in downstream (in hour)
⇒ Total distance/(Speed of boat in still water + Speed of water)
Time taken by boat in upstream (in hour)
⇒ Total distance/(Speed of boat in still water – Speed of water)
Calculation:
Time taken by boat in downstream:
Total distance = 175 km
⇒ 175/(29 + 6)
⇒ 175/35
⇒ 5 Hours
Time taken by boat in upstream:
Total distance = 115 km
⇒ 115/(29 – 6)
⇒ 115/23
⇒ 5 Hours
Total time = 5 + 5
⇒ 10 Hours
∴ The time taken by the boat to go 175 km downstream and 115 km upstream is 10 Hours.
63. A merchant marked the price of an article by increasing its production cost by 40%. Now he allows 20% discount and gets a profit of Rs. 48 after selling it. The production cost is
A. ₹320
B. ₹360
C. ₹400
D. ₹440
E. None of These
Solution:
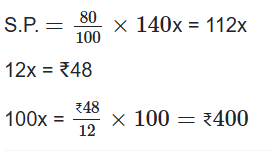
64. Amruth invests Rs. 15000, a bank offers an invest of 12% per annum which is compounded half yearly, what is total amount he will earn after 3 years? (approximately).
A. Rs.16,641
B. Rs.16,741
C. Rs.17,156
D. Rs.21277
E. Rs.18,990
Solution
Formula used: Amount = P[1 + (r/2)/100]2n
Given: P = 15000 Rs.
r = 12%
n = 3 years
Amount = P[1 + (r/2)/100]2n
A = 15000 [1 + (12/2)/100]2*3
A = 21277.78 = 21277 Rs.
65. The breadth and diagonal of the rectangle are 10 cm and 26 cm respectively. Find the perimeter of the rectangle.
A. 54 cm
B. 48 cm
C. 32 cm
D. 24 cm
E. 68 cm
Solution
Solution:
Breadth of the rectangle = 10 cm
The diagonal of the rectangle = 26 cm
Length of the rectangle = l cm
26² = 10² + l²
676 = 100 + l²s
l² = 576
l = 24 cm
Perimeter of the rectangle = 2 x (24 + 10)
= 2× 34
= 68 cm
66. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions:
Eight boxes are kept one above another to make up a stack. The topmost box is numbered as 8 while the bottommost box is numbered as 1. Each box is filled with different fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple. But not necessarily in the same order.Watermelon is kept in box number 7. Strawberry is kept in an odd number box. The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry. Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange. Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples. Banana is kept in an even numbered box. Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box.
Question:
Which fruit is filled in the topmost box?
A. Banana
B. Watermelon
C. Orange
D. Grapes
E. None of these
Solution
Boxes: 1 to 8 in descending order
Fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple.
1) Watermelon is kept in box number 7.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | |||
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | |||
| 5 | Strawberry | ||
| 4 | Mango | ||
| 3 | Strawberry | ||
| 2 | Mango | ||
| 1 | Strawberry |
2) Strawberry is kept in an odd number box.
3) The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry.
As the 3rd case does not fulfill the above condition, it is eliminated.
4) Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange.
5) Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples.
6) Banana is kept in an even-numbered box.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
7) Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box. So, Chickoo will be kept in box number 3.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | Chickoo |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
As the 1st and 2nd case does not fulfill the above condition, they are eliminated.
The final arrangement will be:
| Box | Fruits |
| 8 | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango |
| 3 | Chickoo |
| 2 | Grapes |
| 1 | Apple |
Hence, Orange is filled in the topmost box.
67. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions:
Eight boxes are kept one above another to make up a stack. The topmost box is numbered as 8 while the bottommost box is numbered as 1. Each box is filled with different fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple. But not necessarily in the same order.Watermelon is kept in box number 7. Strawberry is kept in an odd number box. The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry. Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange. Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples. Banana is kept in an even numbered box. Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box.
Question:
Apples are kept in which box?
A. 4th box
B. 1st box
C. 2nd box
D. 3rd box
E. None of these
Solution
Boxes: 1 to 8 in descending order
Fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple.
1) Watermelon is kept in box number 7.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | |||
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | |||
| 5 | Strawberry | ||
| 4 | Mango | ||
| 3 | Strawberry | ||
| 2 | Mango | ||
| 1 | Strawberry | ||
2) Strawberry is kept in an odd number box.
3) The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry.
As the 3rd case does not fulfill the above condition, it is eliminated.
4) Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange.
5) Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples.
6) Banana is kept in an even-numbered box.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
7) Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box. So, Chickoo will be kept in box number 3.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | Chickoo |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
As the 1st and 2nd case does not fulfill the above condition, they are eliminated.
The final arrangement will be:
| Box | Fruits |
| 8 | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango |
| 3 | Chickoo |
| 2 | Grapes |
| 1 | Apple |
Hence, Apple is filled in 1st number box.
68. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions:
Eight boxes are kept one above another to make up a stack. The topmost box is numbered as 8 while the bottommost box is numbered as 1. Each box is filled with different fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple. But not necessarily in the same order.Watermelon is kept in box number 7. Strawberry is kept in an odd numbered box. The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry. Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange. Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples. Banana is kept in an even numbered box. Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box.
Question:
Apples are kept in which box?
A. 4th box
B. 1st box
C. 2nd box
D. 3rd box
E. None of these
Solution
Boxes: 1 to 8 in descending order
Fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple.
1) Watermelon is kept in box number 7.
2) Strawberry is kept in an odd numbered box.
3) The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | |||
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | |||
| 5 | Strawberry | ||
| 4 | Mango | ||
| 3 | Strawberry | ||
| 2 | Mango | ||
| 1 | Strawberry |
As the 3rd case does not fulfill the above condition, it is eliminated.
4) Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange.
5) Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples.
6) Banana is kept in an even-numbered box.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
7) Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box. So, Chickoo will be kept in box number 3.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | Chickoo |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
As the 1st and 2nd case does not fulfill the above condition, they are eliminated.
The final arrangement will be:
| Box | Fruits |
| 8 | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango |
| 3 | Chickoo |
| 2 | Grapes |
| 1 | Apple |
Hence, Apple is filled in 1st number box.
69. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions:
Eight boxes are kept one above another to make up a stack. The topmost box is numbered as 8 while the bottommost box is numbered as 1. Each box is filled with different fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple. But not necessarily in the same order.Watermelon is kept in box number 7. Strawberry is kept in an odd number box. The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry. Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange. Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples. Banana is kept in an even numbered box. Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box.
Question:
Which of the following condition is true?
A. Strawberry- 3rd box
B. Chickoo- 1st box
C. Banana- 8th box
D. Grapes- 2nd box
E. None of these
Solution
Boxes: 1 to 8 in descending order
Fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple.
1) Watermelon is kept in box number 7.
2) Strawberry is kept in an odd number box.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | |||
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | |||
| 5 | Strawberry | ||
| 4 | |||
| 3 | Strawberry | ||
| 2 | |||
| 1 | Strawberry |
3) The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry.
As the 3rd case does not fulfill the above condition, it is eliminated.
4) Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange.
5) Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples.
6) Banana is kept in an even-numbered box.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
7) Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box. So, Chickoo will be kept in box number 3.
As the 1st and 2nd case does not fulfill the above condition, they are eliminated.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | Chickoo |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
The final arrangement will be:
| Box | Fruits |
| 8 | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango |
| 3 | Chickoo |
| 2 | Grapes |
| 1 | Apple |
As Grapes are kept in the 2nd no box.
Hence, the condition ‘Grapes- 2nd box’ is true and the other conditions are false.
70. Directions: Study the following information and answer the given questions:
Eight boxes are kept one above another to make up a stack. The topmost box is numbered as 8 while the bottommost box is numbered as 1. Each box is filled with different fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple. But not necessarily in the same order.Watermelon is kept in box number 7. Strawberry is kept in an odd number box. The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry. Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange. Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples. Banana is kept in an even numbered box. Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box.
Question:
How many boxes are there between the Box of Chickoo and Orange?
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 3
E. None of these
Solution
Boxes: 1 to 8 in descending order
Fruits: Banana, Orange, Chickoo, Watermelon, Strawberry, Grapes, Mango, Apple.
1) Watermelon is kept in box number 7.
2) Strawberry is kept in an odd number box.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | |||
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | |||
| 5 | Strawberry | ||
| 4 | |||
| 3 | Strawberry | ||
| 2 | |||
| 1 | Strawberry |
3) The box of Mango is kept just below the box of Strawberry.
As the 3rd case does not fulfill the above condition, it is eliminated.
4) Three boxes are kept between the box of Mango and Orange.
5) Box of Grapes is just above the box of Apples.
6) Banana is kept in an even-numbered box.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
7) Chickoo is not kept in the lowermost box. So, Chickoo will be kept in box number 3.
As the 1st and 2nd case does not fulfill the above condition, they are eliminated.
| Box | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
| 8 | Orange | Banana | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon | Watermelon | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana | Orange | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry | Grapes | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango | Apples | Mango |
| 3 | Grapes | Strawberry | Chickoo |
| 2 | Apples | Mango | Grapes |
| 1 | Apples |
The final arrangement will be:
| Box | Fruits |
| 8 | Orange |
| 7 | Watermelon |
| 6 | Banana |
| 5 | Strawberry |
| 4 | Mango |
| 3 | Chickoo |
| 2 | Grapes |
| 1 | Apple |
Hence, 4 boxes are there between the box of Chickoo and Orange.
71. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language
‘da ra sa va’ means ‘i were my me’
‘ta ba va sa’ means ‘we were me was’
‘ha ba da na’ means ‘i was she you’
‘ba sa ya va’ means ‘they were was me’.
Question:
What would be the code for ‘i we they’?
A. ta ha va
B. ta ra va
C. da sa ba
D. da ba na
E. da ta ya
Solution

Hence, ‘da ta ya‘ is the code for ‘i we they‘.
72. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language
‘da ra sa va’ means ‘i were my me’
‘ta ba va sa’ means ‘we were me was’
‘ha ba da na’ means ‘i was she you’
‘ba sa ya va’ means ‘they were was me’.
Question:
What would be the code for ‘she you’?
A. ha ba
B. na da
C. ha na
D. va sa
E. ta ba
Solution

Hence, ‘ha na‘ is the code for ‘she you‘.
73. Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language
‘da ra sa va’ means ‘i were my me’
‘ta ba va sa’ means ‘we were me was’
‘ha ba da na’ means ‘i was she you’
‘ba sa ya va’ means ‘they were was me’.
Question:
Which of the following means ‘me’ in that code language?
A. sa
B. va
C. Either ‘sa’ or ‘va’
D. ra
E. da
Solution

Hence, either ‘sa‘ or ‘va‘ is the code for ‘me‘.
74. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Eight persons C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T sit around a circular table and each person faces towards the centre attended a meeting but not necessarily in same order. Only one person sits between J and R. T sits three places away from C. N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F. As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P. F does not face T. The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. P does not sit immediate to the left of C. R and N sit immediate next to each other. R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.
Question:
Who among the following person sits second to the right of the person who sits immediate left to J?
A. R
B. C
C. P
D. N
E. T
Solution
Here, persons are C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T.
1) T sits three places away from C.
2) Only one person sits between J and R.
3) As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P.
4) R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.


5) N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F.
6) F does not face T.
7) R and N sit immediate next to each other. Therefore, case 1 and 3 are eliminated.
8) P does not sit immediate to the left of C. Therefore, case 4 is eliminated.
9) The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. Therefore, case 2(b) is eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
Since, O sits immediate left to J and C sits second to the right of O.
Hence, the correct answer is C.
75. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Eight persons C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T sit around a circular table and each person faces towards the centre attended a meeting but not necessarily in same order. Only one person sits between J and R. T sits three places away from C. N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F. As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P. F does not face T. The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. P does not sit immediate to the left of C. R and N sit immediate next to each other. R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.
Question:
Find the odd one out.
A. NC
B. RP
C. OF
D. JC
E. TJ
Solution
Here, persons are C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T.
1) T sits three places away from C.
2) Only one person sits between J and R.
3) As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P.
4) R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.


5) N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F.
6) F does not face T.
7) R and N sit immediate next to each other. Therefore, case 1 and 3 are eliminated.
8) P does not sit immediate to the left of C. Therefore, case 4 is eliminated.
9) The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. Therefore, case 2(b) is eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows

Since, each pair except JC represents person sitting opposite to each other whereas J and C sit adjacent to each other.
Hence, the odd one is JC.
76. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Eight persons C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T sit around a circular table and each person faces towards the centre attended a meeting but not necessarily in same order. Only one person sits between J and R. T sits three places away from C. N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F. As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P. F does not face T. The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. P does not sit immediate to the left of C. R and N sit immediate next to each other. R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.
Question:
In some way N is related to O and C is related to F, then in the same way T is related to whom?
A. P
B. C
C. R
D. O
E. N
Solution
Here, persons are C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T.
1) T sits three places away from C.
2) Only one person sits between J and R.
3) As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P.
4) R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.


5) N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F.
6) F does not face T.
7) R and N sit immediate next to each other. Therefore, case 1 and 3 are eliminated.
8) P does not sit immediate to the left of C. Therefore, case 4 is eliminated.
9) The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. Therefore, case 2(b) is eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows

Since, O sits second to the right of N and F sits second to the right of C and in the same way R sits second to the right of T.
Hence, the correct answer is R.
77. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Eight persons C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T sit around a circular table and each person faces towards the centre attended a meeting but not necessarily in same order. Only one person sits between J and R. T sits three places away from C. N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F. As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P. F does not face T. The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. P does not sit immediate to the left of C. R and N sit immediate next to each other. R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.
Question:
Which of the following statement(s) is/ are correct?
A. T sits immediate right to N.
B. F sits second to the left of P.
C. C. R sits second to the left of J.
D. C and O sits opposite to each other.
E. Only two persons sit between R and P.
Solution
Here, persons are C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T.
1) T sits three places away from C.
2) Only one person sits between J and R.
3) As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P.
4) R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.


5) N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F.
6) F does not face T.
7) R and N sit immediate next to each other. Therefore, case 1 and 3 are eliminated.

8) P does not sit immediate to the left of C. Therefore, case 4 is eliminated.
9) The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. Therefore, case 2(b) is eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows

Since, T sits immediate left to N. Therefore, statement first is incorrect.
F sits immediate right to P. Therefore, statement second is incorrect.
R sits second to the left of J. Therefore, statement third is correct.
C sits second to the right of O. Therefore, statement fourth is incorrect.
Three persons sit between R and P. Therefore, statement fifth is incorrect.
Hence, the correct statement is R sits second to the left of J.
78. Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on given information.
Eight persons C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T sit around a circular table and each person faces towards the centre attended a meeting but not necessarily in same order. Only one person sits between J and R. T sits three places away from C. N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F. As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P. F does not face T. The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. P does not sit immediate to the left of C. R and N sit immediate next to each other. R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.
Question:
Who sits second to the right of the person who sits opposite to N?
A. T
B. P
C. C
D. R
E. F
Solution
Here, persons are C, F, J, N, O, P, R and T.
1) T sits three places away from C.
2) Only one person sits between J and R.
3) As many person sit between R and T as many between T and P.
4) R and C do not sit adjacent to each other.


5) N sits second to the left of the person who sits opposite to F.
6) F does not face T.
7) R and N sit immediate next to each other. Therefore, case 1 and 3 are eliminated.

8) P does not sit immediate to the left of C. Therefore, case 4 is eliminated.
9) The person who sits opposite to N is an immediate neighbour of J. Therefore, case 2(b) is eliminated. Hence, the final arrangement is as follows
Since, C sits opposite to N and F sits second to the right of C.
Therefore, the correct answer is F.
79. DIRECTIONS: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among the given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements : U ≥ R, H < L, P ≤ N, H = K
Conclusions :
I. U > P
II. N > H
A. Only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Either conclusion I or II follows
D. Both conclusion I and II follows
E. Neither conclusion I nor II follows
Solution
Given Statements : U ≥ R, H < L, P ≤ N, H = K
On Combining : K = H < L, U ≥ R, P ≤ N
I. U > P → False ( As there is no direct relation between U and P)
II. N > H → False (As there is no direct relation between N and H)
Hence, Neither I nor II follows.
80. DIRECTIONS: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among the given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements : T ≤ A, L = M < D, D ≥ A
Conclusions :
I. M = T
II M > A
A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Neither I nor II follows
D. Either I or II follows
E. Both I and II follow
Solution
Given statements : T ≤ A, L = M < D, D ≥ A
On combining : T ≤ A ≤ D > M = L
I. M = T → False (as M < D ≥ A ≥ T, there is no direct relation is given between the two, we cannot say that it is definitely true, Hence M = T is false)
II. M > A → False (as M < D ≥ A ≥ T there is no direct relation is given between the two, we cannot say that is definitely true, Hence M > A is false)
Hence, Neither I nor II follows.
81. In each of the following questions, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the following options holds true:
Statement: B > J, V > J, V = M, L < M
Conclusions:
I: B > V
II: L > B
A. If conclusion I follows.
B. If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
C. If either conclusion I or II follows.
D. If both conclusion I and II follows.
E. If conclusion II follows.
Solution
From the given Information,
Statement: B > J, V > J, V = M, L < M
On combining we get: B > J < V = M > L
Conclusions:
I: B > V → False (no relation found between B and V, hence given conclusion is false.)
II: L > B → False (According to the given information, no relation was found between L and B, hence given conclusion is false.)
Hence, If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
82. Direction: Study the following series of sets of numbers. Carefully answer the question given below.
364 297 752 425 683
Question:
If 2 is added to the 3rd digit of each number and then position of first digit and third digit are interchanged, then which among the following number is second highest?
A. 297
B. 683
C. 425
D. 364
E. 752
Solution
Given series:- 364 297 752 425 683
Adding 2 to 3rd digit:- 366 299 754 427 685
Interchanging first and third digit:- 663 992 457 724 586
Hence, second highest number is 724 which resulted from 425.
Hence, “425” is correct answer.
83. Direction: Study the following series of sets of numbers. Carefully answer the question given below.
364 297 752 425 683
Question:
If in each number 1 is subtracted from first digit of each number and then position of 1st and 3rd are interchanged, then how many even numbers are there in the given series?
A. Three
B. Four
C. One
D. Two
E. Zero
Solution
Given series:- 364 297 752 425 683
Subtracting 1 from first digit:- 264 197 652 325 583
Interchanging 1st and 3rd digit:- 462 791 256 523 385
Hence, there are only two even numbers i.e. 462 and 256
Hence, “Two” is the correct answer.
84. Direction: Study the following series of sets of numbers. Carefully answer the question given below.
364 297 752 425 683
Question:
If in each number three digits are arranged in ascending order, which of the following is 2nd highest number among the given series?
A. 297
B. 683
C. 425
D. 364
E. 752
Solution
Given series:- 364 297 752 425 683
Arranging three digit number in ascending order:- 346 279 257 245 368
Hence, second highest number is 346 which resulted from “364”.
Hence, “364” is the correct answer.
Note: Ascending order means increasing order
85. Direction: Study the following series of sets of numbers. Carefully answer the question given below.
364 297 752 425 683
Question:
If 1 is added to the first digit of each number and 1 is subtracted from third digit of each number then which of the following number is divisible by 3?
A. 752
B. 297
C. 364
D. 425
E. 683
Solution
Given series:- 364 297 752 425 683
Adding 1 to first digit:- 464 397 852 525 783
Subtracting 1 from third digit:- 463 396 851 524 782
Number which is divisible by 3 is “396” which resulted from “297”.
Hence, “297” is the correct answer.
86. Direction: Study the following series of sets of numbers. Carefully answer the question given below.
364 297 752 425 683
Question:
If each number is multiplied by 3, then what is the multiplication of the 3rd digit of the highest number and 2nd digit of the lowest number?
A. 42
B. 45
C. 36
D. 35
E. 40
Solution
Given series:- 364 297 752 425 683
Number multiplied by 3:- 1092 891 2256 1275 2049
3rd digit of highest number:- 5 (2256 – the highest number in the given series)
2nd digit of lowest number:- 9 (891 – the lowest number in the given series)
Resultant would be:- 5×9 = 45
Hence, “45” is the correct answer.
87. Directions: Read the information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, A, D, G, J, L, M, and P, are scheduled to go abroad in seven different months: March, May, June, July, September, October, and December, but not necessarily in the same order. Each person goes in a different month.
P goes immediately after D. L goes in a month that has 30 days. J goes in a month that has 30 days. M goes after J. Two people go between M and A. Two people go between L and G. M does not go in October. A and P do not go in March and December respectively.
Question:
Which of the following statements is definitely true?
A. L goes in September
B. J goes before L
C. Two people go between D and A
D. M goes in July
E. A goes just before G
Solution
1. L goes in a month that has 30 days.
Here, we have two cases, i.e., Case 1 and Case 2.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | ||
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | ||
| December (31) | ||
2. Two people go between L and G.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
3. J goes in a month that has 30 days.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
4. M goes after J.
5. M does not go in October.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | M/ | |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | M/ |
6. Two people go between M and A.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | A | M/A |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | A/M |
7. P goes immediately after D.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2.
This is our final arrangement,
| Months | Persons |
| Case 1 | |
| March (31) | D |
| May (31) | P |
| June (30) | L |
| July (31) | A |
| September (30) | J |
| October (31) | G |
| December (31) | M |
Hence, the correct answer is Two people go between D and A.
88. Directions: Read the information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, A, D, G, J, L, M, and P, are scheduled to go abroad in seven different months: March, May, June, July, September, October, and December, but not necessarily in the same order. Each person goes in a different month.
P goes immediately after D. L goes in a month that has 30 days. J goes in a month that has 30 days. M goes after J. Two people go between M and A. Two people go between L and G. M does not go in October. A and P do not go in March and December respectively.
Question:
Which one is odd?
A. D
B. J
C. G
D. P
E. A
Solution
1. L goes in a month that has 30 days.
Here, we have two cases, i.e., Case 1 and Case 2.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | ||
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | ||
| December (31) | ||
2. Two people go between L and G.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
3. J goes in a month that has 30 days.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
4. M goes after J.
5. M does not go in October.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | M/ | |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | M/ |
6. Two people go between M and A.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | A | M/A |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | A/M |
7. P goes immediately after D.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2.
This is our final arrangement,
| Months | Persons |
| Case 1 | |
| March (31) | D |
| May (31) | P |
| June (30) | L |
| July (31) | A |
| September (30) | J |
| October (31) | G |
| December (31) | M |
Except for J, all others go to abroad in the month of 31 days.
Hence, the correct answer is J.
89. Directions: Read the information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, A, D, G, J, L, M, and P, are scheduled to go abroad in seven different months: March, May, June, July, September, October, and December, but not necessarily in the same order. Each person goes in a different month.
P goes immediately after D. L goes in a month that has 30 days. J goes in a month that has 30 days. M goes after J. Two people go between M and A. Two people go between L and G. M does not go in October. A and P do not go in March and December respectively.
Question:
In which month does M go abroad?
A. September
B. June
C. October
D. December
E. March
Solution
1. L goes in a month that has 30 days.
Here, we have two cases, i.e., Case 1 and Case 2.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | ||
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | ||
| December (31) | ||
2. Two people go between L and G.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
3. J goes in a month that has 30 days.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
4. M goes after J.
5. M does not go in October.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | M/ | |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | M/ |
6. Two people go between M and A.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | A | M/A |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | A/M |
7. P goes immediately after D.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2.
This is our final arrangement,
| Months | Persons |
| Case 1 | |
| March (31) | D |
| May (31) | P |
| June (30) | L |
| July (31) | A |
| September (30) | J |
| October (31) | G |
| December (31) | M |
Hence, the correct answer is December.
90. Directions: Read the information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, A, D, G, J, L, M, and P, are scheduled to go abroad in seven different months: March, May, June, July, September, October, and December, but not necessarily in the same order. Each person goes in a different month.
P goes immediately after D. L goes in a month that has 30 days. J goes in a month that has 30 days. M goes after J. Two people go between M and A. Two people go between L and G. M does not go in October. A and P do not go in March and December respectively.
Question:
Who goes immediately after A?
A. M
B. J
C. L
D. P
E. G
Solution
1. L goes in a month that has 30 days.
Here, we have two cases, i.e., Case 1 and Case 2.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | ||
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | ||
| December (31) | ||
2. Two people go between L and G.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
3. J goes in a month that has 30 days.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
4. M goes after J.
5. M does not go in October.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | M/ | |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | M/ |
6. Two people go between M and A.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | A | M/A |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | A/M |
7. P goes immediately after D.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2.
This is our final arrangement,
| Months | Persons |
| Case 1 | |
| March (31) | D |
| May (31) | P |
| June (30) | L |
| July (31) | A |
| September (30) | J |
| October (31) | G |
| December (31) | M |
Hence, the correct answer is J.
91. Directions: Read the information and answer the given questions.
Seven people, namely, A, D, G, J, L, M, and P, are scheduled to go abroad in seven different months: March, May, June, July, September, October, and December, but not necessarily in the same order. Each person goes in a different month.
P goes immediately after D. L goes in a month that has 30 days. J goes in a month that has 30 days. M goes after J. Two people go between M and A. Two people go between L and G. M does not go in October. A and P do not go in March and December respectively.
Question:
How many people go between M and P?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
E. None
Solution
1. L goes in a month that has 30 days.
Here, we have two cases, i.e., Case 1 and Case 2.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | ||
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | ||
| December (31) | ||
2. Two people go between L and G.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | L | |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
3. J goes in a month that has 30 days.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | ||
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | ||
4. M goes after J.
5. M does not go in October.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | M/ | |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | M/ |
6. Two people go between M and A.
| Months | Persons | |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| March (31) | ||
| May (31) | G | |
| June (30) | L | J |
| July (31) | A | M/A |
| September (30) | J | L |
| October (31) | G | |
| December (31) | M | A/M |
7. P goes immediately after D.
Now, we can eliminate Case 2.
This is our final arrangement,
| Months | Persons |
| Case 1 | |
| March (31) | D |
| May (31) | P |
| June (30) | L |
| July (31) | A |
| September (30) | J |
| October (31) | G |
| December (31) | M |
Hence, the correct answer is Four.
92. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
No boys is a girls.
All female are girls.
Some female are woman.
Conclusions:
I. Some woman are not boys.
II. No female is a boys.
A. None follows
B. Either I or II follows
C. Only I follows
D. Only II follows
E. Both I and II follow
Solution
The least possible venn diagram for the given statements is as follows:

Conclusions:
I. Some woman are not boys → True (It is definite because some female are woman.)
II. No female is boys → True (It is definite because all female are girls.)
Hence, both I and II follow.
93. Directions: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Some Iron is Copper.
All Copper is Tin.
Some Tin is Brass.
Conclusions:
I. Some Brass is Iron.
II. Some Iron is Tin.
A. Only I follows
B. Either I or II follows
C. Only II follows
D. Both I and II follow
E. None follow
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as follows,
Conclusions:
I. Some Brass is Iron → False (it is possible but not definite because Brass has no relation with Iron)
II. Some Iron is Tin → True (it is definite because some Iron is Copper and all Copper is Tin)Hence, only conclusion II follows.
94. Directions: In the following questions three statements are given below followed by two conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read both the conclusions and decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements.
Statements:
Only a few apple is orange.
All orange is grapes.
Few grapes is banana.
Conclusions:
I. All apple being orange is a possibility.
II. Some grapes is apple.
A. Only conclusion 1 follow
B. Only conclusion 2 follow
C. Both conclusion 1 and conclusion 2 follows
D. Either conclusion 1 or conclusion 2 follows
E. Neither conclusion 1 nor conclusion 2 follows
Solution
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as follows,

Conclusions:
I. All apple being orange is a possibility → False (Only few apple is orange)
II. Some grapes is apple → True (Only few apple is orange and All orange is grapes.
Hence, Only conclusion 2 is true.
Note: only a few ⇒⇒ in the above question only apple is orange that means some part of the apple is orange but some part is definitely not apple.
so in this case apple and orange have only one definite relation and no possibilities are there.
95. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the question given below-
In a family of three generations, there are seven members. They are Ramesh, Nitin, Vishal, Rahul, Harish, Revati, and Ritesh. Ramesh is the son of Revati who is the mother of Vishal. Vishal is unmarried. Revati is the grandmother of Rahul. Harish is the father of Nitin and grandfather of Ritesh. Ritesh is the only son of Rahul’s father’s sister. Nitin is a female member. Revati is the wife of Harish.
Question:
If Ramesh is married to Birita, then how is Vishal related to Birita?
A. Brother-in-law
B. Brother
C. Sister-in-law
D. Sister
E. Cannot be determined
Solution
Now draw the Family tree diagram using the following notations:
From the given information:
1) Ramesh is the son of Revati who is the mother of Vishal. Revati is the wife of Harish.
From this statement, it can be said that Ramesh and Vishal are siblings and their parents are Harish and Revati. Revati is the mother and Harish is the father of Ramesh and Vishal. Ramesh is the brother of Vishal. Vishal’s gender cannot be determined.
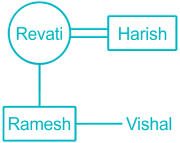
2) Harish is the father of Nitin. Nitin is a female member.
From this statement, it is clear that Nitin is the sister of Ramesh and Vishal.
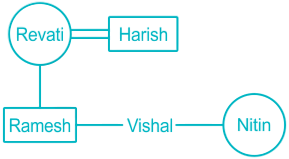
3) Ritesh is the only son of Rahul’s father’s sister.
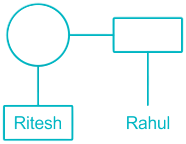
4) Harish is the grandfather of Ritesh. Revati is the grandmother of Rahul. Vishal is unmarried.
From these statements, it can be said that Ritesh is the son of Nitin, and Rahul is the son or daughter of Ramesh since Vishal is unmarried and Ramesh has a sister i.e. Nitin. So the final family tree diagram is like this:
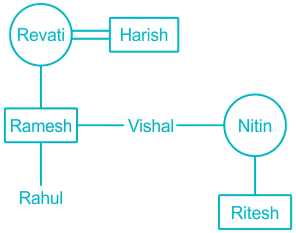
If Ramesh is married to Birita then the family tree diagram will be like this:

Since the gender of Vishal cannot be determined, we can not exactly say how Vishal is related to Birita. Vishal can be the brother-in-law or the sister-in-law of Birita.
Hence, how Vishal is related to Birita cannot be determined.
96. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the question given below-
In a family of three generations, there are seven members. They are Ramesh, Nitin, Vishal, Rahul, Harish, Revati, and Ritesh. Ramesh is the son of Revati who is the mother of Vishal. Vishal is unmarried. Revati is the grandmother of Rahul. Harish is the father of Nitin and grandfather of Ritesh. Ritesh is the only son of Rahul’s father’s sister. Nitin is a female member. Revati is the wife of Harish.
Question:
If Ritesh has a sibling, then how that person will be related to Ramesh?
A. Cannot be determined
B. Niece or nephew
C. Nephew
D. Niece
E. None of the above
Solution
Now draw the Family tree diagram using the following notations:

From the given information:
1) Ramesh is the son of Revati who is the mother of Vishal. Revati is the wife of Harish.
From this statement, it can be said that Ramesh and Vishal are siblings and their parents are Harish and Revati. Revati is the mother and Harish is the father of Ramesh and Vishal. Ramesh is the brother of Vishal. Vishal’s gender cannot be determined.

2) Harish is the father of Nitin. Nitin is a female member.
From this statement, it is clear that Nitin is the sister of Ramesh and Vishal.

3) Ritesh is the only son of Rahul’s father’s sister.

4) Harish is the grandfather of Ritesh. Revati is the grandmother of Rahul. Vishal is unmarried.
From these statements, it can be said that Ritesh is the son of Nitin, and Rahul is the son or daughter of Ramesh since Vishal is unmarried and Ramesh has a sister i.e. Nitin. So the final family tree diagram is like this:

Ritesh is the only son of Rahul’s father’s sister. From this statement, it is clear that if Ritesh has a sibling then it will be his sister. Let X be the sister of Ritesh. Now the family tree diagram will be as follows:

Hence, the sibling of Ritesh will be the niece of Ramesh.
MISTAKE POINT;
A point in question has been given Ritesh is the only son of Rahul’s father’s sister. which proves that the sibling would be a girl for sure.
97.Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the question given below-
In a family of three generations, there are seven members. They are Ramesh, Nitin, Vishal, Rahul, Harish, Revati, and Ritesh. Ramesh is the son of Revati who is the mother of Vishal. Vishal is unmarried. Revati is the grandmother of Rahul. Harish is the father of Nitin and grandfather of Ritesh. Ritesh is the only son of Rahul’s father’s sister. Nitin is a female member. Revati is the wife of Harish.
Question:
How is Vishal related to Rahul?
A. Father
B. Paternal aunt
C. Mother
D. Paternal uncle
E. Either option 2 or 4
Solution
Now draw the Family tree diagram using the following notations:

From the given information:
1) Ramesh is the son of Revati who is the mother of Vishal. Revati is the wife of Harish.
From this statement, it can be said that Ramesh and Vishal are siblings and their parents are Harish and Revati. Revati is the mother and Harish is the father of Ramesh and Vishal. Ramesh is the brother of Vishal. Vishal’s gender cannot be determined.

2) Harish is the father of Nitin. Nitin is a female member.
From this statement, it is clear that Nitin is the sister of Ramesh and Vishal.

3) Ritesh is the only son of Rahul’s father’s sister.

4) Harish is the grandfather of Ritesh. Revati is the grandmother of Rahul. Vishal is unmarried.
From these statements, it can be said that Ritesh is the son of Nitin, and Rahul is the son or daughter of Ramesh since Vishal is unmarried and Ramesh has a sister i.e. Nitin. So the final family tree diagram is like this:

Hence, Vishal is the paternal uncle or aunt of Rahul.
98. Directions: These questions are based on the following letter/number/symbol arrangement. Study it carefully and answer the questions.
3 D 6 $ C 4 E 8 # N 5 F I A P * 9 M @ K 2 B % 7 H U
Question:
Four of the following are alike in a certain way based on their position in the above arrangement and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
A. A*F
B. MK9
C. 2%@
D. $4D
E. #5E
Solution
Answer: 2
Given Series:
Left Side 3 D 6 $ C 4 E 8 # N 5 F I A P * 9 M @ K 2 B % 7 H U Right Side
In terms A*F, 2%@, $4D and #5E. Here we see the first element of each term(A, 2, $ and #) are followed by the second next element in both forward and backward direction but in the case of MK9, we see that the first term (M) is followed by second next (k) in forward and immediate next (9) in the backward direction.
Here the group is formed in which the second element is second to next for both the other element.
Hence, MK9 does belong to that group.
99. Directions: These questions are based on the following letter/number/symbol arrangement. Study it carefully and answer the questions.
3 D 6 $ C 4 E 8 # N 5 F I A P * 9 M @ K 2 B % 7 H U
Question:
Which of the following is exactly in the middle of the 17th from the right and 18th from the left of the arrangement?
A. A
B. I
C. F
D. %
E. None of these
Solution
Answer: 1
Given Series:
Left Side 3 D 6 $ C 4 E 8 # N 5 F I A P * 9 M @ K 2 B % 7 H U Right Side
17th from the right side of an arrangement is N and 18th from the left side of an arrangement is M and hence, the following series we get is N 5 F I A P * 9 M. These are the 9 observation and the middle one is A as it lies in 5th position from both the sides.
Hence, A is exactly in the middle of the 17th from the right and 18th from the left of the arrangement.
100. Directions: These questions are based on the following letter/number/symbol arrangement. Study it carefully and answer the questions.
3 D 6 $ C 4 E 8 # N 5 F I A P * 9 M @ K 2 B % 7 H U
Question:
How many such symbols are there in the above arrangement each of which is immediately preceded by a consonant and also immediately followed by a number?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D.None
E. None of these
Solution
Answer: 2
Given Series:
Left Side 3 D 6 $ C 4 E 8 # N 5 F I A P * 9 M @ K 2 B % 7 H U Right Side
Symbols which are immediately preceded by a consonant and immediately followed by a number:
3 D 6 $ C 4 E 8 # N 5 F I A P * 9 M @ K 2 B % 7 H U
Hence, there are two symbols that are immediately preceded by a consonant and immediately followed by a number: P * 9 and B % 7.
