1. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
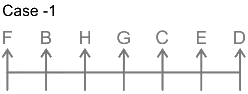
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in a row facing north not necessarily in the same order. G sits three places away from D. Only one person sits between B and G. B sits neither adjacent to D nor at the end. The number of persons to the left of H is the same as the number of persons to the right of C. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
What is the position of F with respect to H?
A. Immediate left
B. Third to the right
C. Second to the left
D. Second to the right
E. Immediate right
Solutions
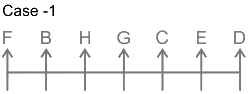
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H
1. G sits three places away from D.
From this we get the possible arrangements.
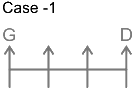
2. Only one person sits between B and G.
3. B sit neither adjacent to D nor at the end.
4. Number of persons to the left of H is the same as the number of persons to the right of C.
5. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
From this case 2 is eliminated, as we cannot place E. In case of 1, C and E sit to the immediate right and second to the right of G.
Thus, F sits at the left end. The final arrangement is as follows.
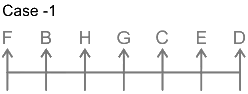
Hence, F sits second to the left to H.
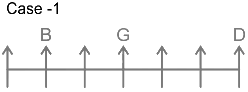
2. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in a row facing north not necessarily in the same order. G sits three places away from D. Only one person sits between B and G. B sits neither adjacent to D nor at the end. The number of persons to the left of H is the same as the number of persons to the right of C. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
Four of the following five are same in some way, find the odd one.
A. FB
B. ED
C. HC
D. DG
E. BE
Solutions
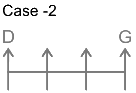
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H
1. G sits three places away from D.
From this, we get the possible arrangements.


2. Only one person sits between B and G.
3. B sits neither adjacent to D nor at the end.


4. Number of persons to the left of H is same as number of persons to the right of C.
5. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
From this case 2 is eliminated, as we cannot place E. In case of 1, C and E sit to the immediate right and second to the right of G.
Thus, F sits at the left end. The final arrangement is as follows.

Except DG, first person sits to the left of the second person.
Therefore, DG is the correct answer.
3. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in a row facing north not necessarily in the same order. G sits three places away from D. Only one person sits between B and G. B sits neither adjacent to D nor at the end. The number of persons to the left of H is the same as the number of persons to the right of C. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
Which of the following is true?
A. C sits to the right of D.
B. Three persons sit between F and E.
C. G sits in the middle of the row.
D. H sits second to the left of D.
E. All are true
Solutions
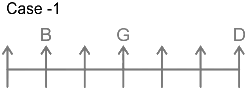
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H
1. G sits three places away from D.
From this, we get the possible arrangements.
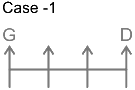
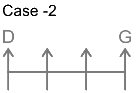
2. Only one person sits between B and G.
3. B sit neither adjacent to D nor at the end.
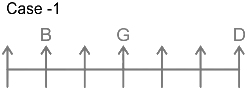
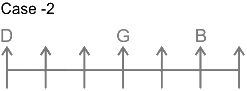
4. Number of persons to the left of H is same as number of persons to the right of C.
5. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
From this case 2 is eliminated, as we cannot place E. In case of 1, C and E sit to the immediate right and second to the right of G.
Thus, F sits at the left end. The final arrangement is as follows.
Hence, ‘G sits in the middle of the row’ is true.
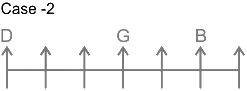
4. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in a row facing north not necessarily in the same order. G sits three places away from D. Only one person sits between B and G. B sits neither adjacent to D nor at the end. The number of persons to the left of H is the same as the number of persons to the right of C. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
Who sits four places away from the person who sit adjacent to D?
A. F
B. B
C. H
D. G
E. No one
Solutions
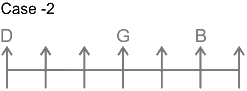
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H
1. G sits three places away from D means there are two person between G and D.
From this we get the possible arrangements.
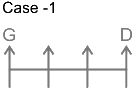
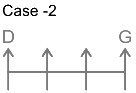
2. Only one person sits between B and G.
3. B sit neither adjacent to D nor at the end.
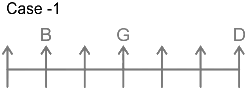
4. Number of persons to the left of H is same as number of persons to the right of C.
5. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
From this case 2 is eliminated, as we cannot place E. In case of 1, C and E sit to the immediate right and second to the right of G.
Thus, F sits at the left end. The final arrangement is as follows.
E sits adjacent to D. B is 4th left from E.
Hence, B sits four places away from the person who sits adjacent to D.
5. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in a row facing north not necessarily in the same order. G sits three places away from D. Only one person sits between B and G. B sits neither adjacent to D nor at the end. The number of persons to the left of H is the same as the number of persons to the right of C. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
How many persons are sitting between H and E?
A. Two
B. One
C. None
D. Three
E. Four
Solutions
7 persons – B, C, D, E, F, G and H
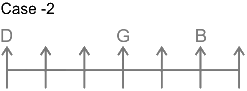
1. G sits three places away from D.
From this we get the possible arrangements.
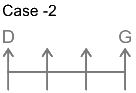
2. Only one person sits between B and G.
3. B sit neither adjacent to D nor at the end.
4. Number of persons to the left of H is same as number of persons to the right of C.
5. C sits to the right of G and to the immediate left of E.
From this case 2 is eliminated, as we cannot place E. In case of 1, C and E sit to the immediate right and second to the right of G.
Thus, F sits at the left end. The final arrangement is as follows.
Hence, two persons are sitting between H and E.
6. What is the difference between the sum of the digits of first four digits of the given number and sum of the last four digits in the number “87345691”?
A. 2
B. 5
C. 1
D. 7
E. 0
Solutions
Given number – 87345691;
Sum of the first four digits – 8+7+3+4 = 22;
Sum of the last four digits – 5+6+9+1 = 21;
The difference between the sum of the digits of the first four digits and the sum of the last four digits i.e., 22 – 21 = 1.
Hence, ‘1’ is the correct answer.
7. Directions: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statement:
I. Only east is north
II. Only a few east is south
III. All south is west
Conclusion:
I. Some north being west is a possibility
II. Some east is north
A. Only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Either conclusion I or II follows
D. Neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. Both conclusion I and II follows
Solutions
The least possible venn diagram for the given statements is
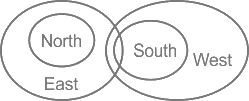
Conclusion:
I. Some north being west is a possibility → False (because the relation of “only” is given for north, so north can make positive relation with east only)
II. Some east is north → True (It is clearly concluded from the venn diagram)
Hence, Only conclusion II follows.
8. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions I, and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statement:
Only a few Cap is Hat
Only a few Hat is Crown
All Crown are Throne
Conclusion:
I. Some Hat is Throne is a possibility
II. No Throne is Hat
A. Only I follows
B. Both I and II follow
C. Only II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Either I or II follows
Solutions
The least possible diagram is given below:
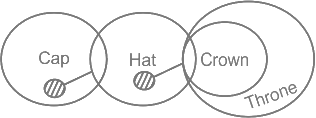
Conclusion:
I. Some Hat is Throne is a possibility → False (Some Hat are Throne is definite so, the case of possibility will be false)
II. No Throne is Hat → False (Some Hat are Throne and this is definite so, the statement is false)
Hence, Neither I nor II follows.
9. Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by two conclusions I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Some roses are pens.
All pens are pencils.
Some pencils are markers.
Conclusions:
I. some markers are pens.
II. No marker is pen.
A. Only conclusion I follow
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Conclusion I and II both follow
D. Neither conclusion I nor conclusion II follows
E. Either conclusion I or conclusion II follows
Solutions
The least possible diagram for the given statements is as follows
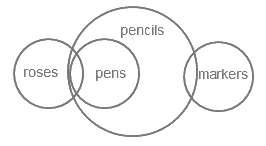
Conclusions:
I. some markers are pens → False (It is possible but not definite)
II. No marker is pen → False (It is possible but not definite)
Conclusion I and II is complementary pair.
Hence, Either conclusion I or conclusion II follows.
10. Directions: These questions are based on the following information.
There are eight people in a family. M, K, A, C, D, E, G, and H consists of 3 generations. Four of them are females. D and A are the daughter and son of K respectively and both are married. E is the sister of H whose father is C. M and G are of 3rd generation and M is the son-in-law of E. K is the brother-in-law of H.
How is K related to A?
A. Son
B. Father
C. son-in law
D. Daughter-in-law
E. Mother
Solutions
From the given information,
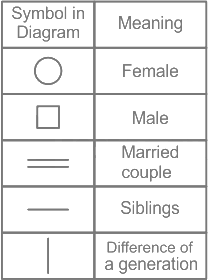
1) D and A are the daughter and son of K respectively and both are married.
2) E is the sister of H whose father is C.
3) M and G are of 3rd generation and M is the son-in-law of E.
4) K is the brother-in-law of H.
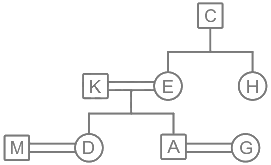
Hence, K is the father of A.
11. Directions: These questions are based on the following information.
There are eight people in a family. M, K, A, C, D, E, G, and H consists of 3 generations. Four of them are females. D and A are the daughter and son of K respectively and both are married. E is the sister of H whose father is C. M and G are of 3rd generation and M is the son-in-law of E. K is the brother-in-law of H.
Who among the following is the son-in-law of C?
A. G
B. A
C. K
D. H
E. Cannot be determined
Solutions
From the given information,
1) D and A are the daughter and son of K respectively and both are married.
2) E is the sister of H whose father is C.
3) M and G are of 3rd generation and M is the son-in-law of E.
4) K is the brother-in-law of H.
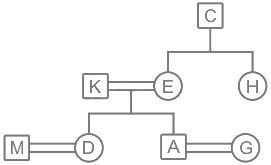
Hence, K is the son-in-law of C.
12. Directions: These questions are based on the following information.
There are eight people in a family. M, K, A, C, D, E, G, and H consists of 3 generations. Four of them are females. D and A are the daughter and son of K respectively and both are married. E is the sister of H whose father is C. M and G are of 3rd generation and M is the son-in-law of E. K is the brother-in-law of H.
Who among the following belongs to the first generation?
A. C
B. H
C. K
D. A
E. E
Solutions
From the given information,
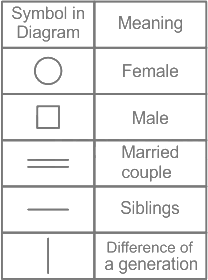
1) D and A are the daughter and son of K respectively and both are married.
2) E is the sister of H whose father is C.
3) M and G are of 3rd generation and M is the son-in-law of E.
4) K is the brother-in-law of H.
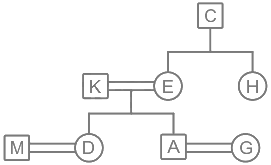
Hence, C belongs to the first generation.
13. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
7 boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U and V – are placed one above the other not necessarily in the same order. Box U is placed third from either of the ends. Box P is placed adjacent to box U. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
How many boxes are placed between boxes R and P?
A. One
B. Three
C. None
D. Two
E. More than three
Solutions
7 boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U and V
1. Box U is placed third from either of the ends.
From this, we get the following possible arrangements.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
2. Box P is placed adjacent to box U.
3. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box P | Box S |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
| Box S | Box P |
4. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot place box V. In the case of 1, the number of boxes above box S is 5, hence the number of boxes below box V is 3.
| Case 1 |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box S |
6. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Case 1 |
| Box Q |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box R |
| Box S |
| Box T |
Hence, two boxes are placed between boxes R and P.
14. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
7 boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U and V – are placed one above the other not necessarily in the same order. Box U is placed third from either of the ends. Box P is placed adjacent to box U. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
Which box is placed three boxes below box U?
A. V
B. Q
C. S
D. T
E. R
Solutions
7 boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U and V
1. Box U is placed third from either of the ends.
From this we get the following possible arrangements.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
2. Box P is placed adjacent to box U.
3. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box P | Box S |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
| Box S | Box P |
4. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot place box V. In case of 1, the number of boxes above box S is 5, hence the number of boxes below box V is 3.
| Case 1 |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box S |
6. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Case 1 |
| Box Q |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box R |
| Box S |
| Box T |
Hence box S is placed three boxes below box U.
15. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
7 boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U and V – are placed one above the other not necessarily in the same order. Box U is placed third from either of the ends. Box P is placed adjacent to box U. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
Number of boxes placed below box Q is same as the number of boxes placed above box ___.
A. P
B. R
C. S
D. T
E. None of the above
Solutions
7 boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U and V
1. Box U is placed third from either of the ends.
From this we get the following possible arrangements.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
2. Box P is placed adjacent to box U.
3. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box P | Box S |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
| Box S | Box P |
4. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot place box V. In case of 1, the number of boxes above box S is 5, hence the number of boxes below box V is 3.
| Case 1 |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box S |
6. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Case 1 |
| Box Q |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box R |
| Box S |
| Box T |
The number of boxes placed below box Q is six which is same as the number of boxes placed above box T.
16. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
7 boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U and V – are placed one above the other not necessarily in the same order. Box U is placed third from either of the ends. Box P is placed adjacent to box U. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
Which of the following is false?
a. Box T is not placed at the bottom.
b. Box V is placed immediately above box R.
c. More than four boxes are placed between boxes Q and S.
A. Only a
B. Only a and b
C. Only c
D. Only a and c
E. Only b and c
Solutions
7 boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U and V
1. Box U is placed third from either of the ends.
From this we get the following possible arrangements.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
2. Box P is placed adjacent to box U.
3. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box P | Box S |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
| Box S | Box P |
4. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot place box V. In case of 1, the number of boxes above box S is 5, hence the number of boxes below box V is 3.
| Case 1 |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box S |
6. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Case 1 |
| Box Q |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box R |
| Box S |
| Box T |
‘Box T is not placed at the bottom’ and ‘More than four boxes are placed between boxes Q and S’ are false.
Hence, only a and c is the correct answer.
17. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
7 boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U and V – are placed one above the other not necessarily in the same order. Box U is placed third from either of the ends. Box P is placed adjacent to box U. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
If all the boxes are arranged to place in the alphabetical order from bottom to top, then how many boxes remain unchanged?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. None
E. More than three
Solutions
1. Box U is placed third from either of the ends.
From this we get the following possible arrangements.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
2. Box P is placed adjacent to box U.
3. Three boxes are placed between boxes P and S.
| Case 1 | Case 2 |
| Box P | Box S |
| Box U | |
| Box U | |
| Box S | Box P |
4. Number of boxes placed above box S is two more than the number of boxes placed below box V.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot place box V. In case of 1, the number of boxes above box S is 5, hence the number of boxes below box V is 3.
| Case 1 |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box S |
6. Box Q is placed above box R, which is not placed below box S.
From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Case 1 |
| Box Q |
| Box P |
| Box U |
| Box V |
| Box R |
| Box S |
| Box T |
ALPHABETICAL ORDER:
| Case 1 | Alphabetical order |
| Box Q | Box V |
| Box P | Box U |
| Box U | Box T |
| Box V | Box S |
| Box R | Box R |
| Box S | Box Q |
| Box T | Box P |
If all the boxes are arranged to place in alphabetical order from bottom to top, then only box R remains unchanged.
Hence, only one box remains unchanged is the correct answer.
18. How many such pairs of letters are there in the word “UNIQUE” which has as many letters between them in the word (in both forward and backward directions), as they have between them in the English alphabetical series?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. None
E. More than three
Solutions
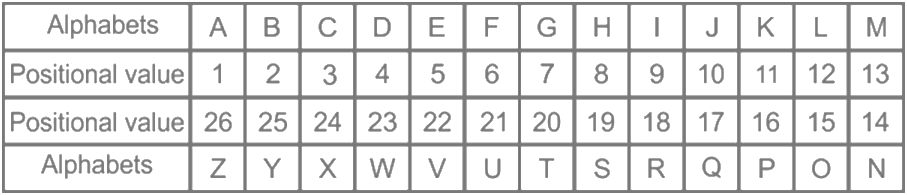
As per the given information,
Given word: UNIQUE
| Alphabets | U | N | I | Q | U | E |
| Position values | 21 | 14 | 9 | 17 | 21 | 5 |
Forward pair – 0
Backward pair – 0
No such pairs have as many letters between in the word as they have between them in the English alphabetical series
Hence, none is the correct answer.
19. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be True, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: W = B; B ≤ F; F < R
Conclusions:
I. W = F
II. W < F
A. Only I is True
B. Only II is True
C. Either I or II is True
D. Neither I or II is True
E. Both I and II are True
Solutions
Given statements: W = B , B ≤ F ;F < R
On Combining: W = B ≤ F < R > F
Conclusions
I. W = F → False (as W = B ≤ F → W ≤ F )
II. W < F → False (as W = B ≤ F → W ≤ F )
But I and II are complementary pairs.
Therefore, Either I or II follow.
Key Points
There are three conditions that should satisfy to qualify for Non-Relational Either Or case. The three conditions are as follows
1) The subject and predicate should be same i.e. the either or will only qualify if the conclusion is between two same subjects and predicates on
2) Both the individual conclusion must be false.
3)
If we have Greater than or equal to ≥ and Lesser than or equal to ≤ relationship between the entities, Two possibilities > and = or < and = must be discussed in the conclusion.
20. Directions: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which conclusion among the given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: F < A > B = E; D < C = G > E
Conclusions:
I. A > E
II. E > D
A. Only I is true
B. Only II is true
C. Either I or II is true
D. Both I or II is true
E. Neither I or II is true
Solutions
Given statements: F < A > B = E; D < C = G > E
On combining: F < A > B = E < G = C > D
Conclusions:
I. A > E → True ( as F > A > E; B = E)
II. E > D → False ( as E < G = C > D thus clear relation cannot be determined between E and D)
Important Points
Whenever there are different signs given between different identities, their relation cannot be determined.
Therefore, only conclusion I follow
21. Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: J > D > A ≥ S; C > X ≤ F ≤ S
Conclusions:
I. D ≥ X
II. C > A
A. Only II is True
B. Neither I nor II is True
C. Both I and II are True
D. Either I or II is True
E. Only I is True
Solutions
Given statements: J > D > A ≥ S; C > X ≤ F ≤ S
On combining: J > D > A ≥ S ≥ F ≥ X < C
Conclusions:
I. D ≥ X → False(as D > A ≥ S ≥ F ≥ X → D > X)
II. C > A → False(as A ≥ S ≥ F ≥ X < C, no clear relationship can be determined between C and A because there are opposite signs between C and A. So, it is false)
Hence, Neither I nor II is true.
22. Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:Kashish went 15 kilometers to the West from my house, then turned right and walked 20 kilometers. He then turned East and walked 25 kilometers and finally turning right covered 20 kilometers. How far was he from his house?
A. 5 kilometers
B. 10 kilometers
C. 40 kilometers
D. 80 kilometers
E. 20 kilometers
Solutions
The movements of Kashish are as shown in figure:
(A to B, B to C, C to D and D to E)
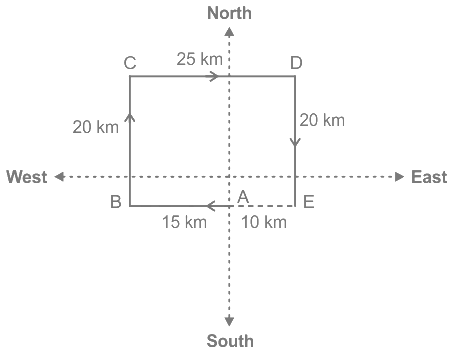
Kashish distance from his house at A.
AE = BE – AB
= CD – AB (BE = CD)
= (25 -15) Km = 10 km
Hence, Kashish is 10 km far from his house.
23. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight persons – A, B, C, D, W, X, Y and Z –are living in a four-storey building such that ground floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above floor 1 is numbered as 2 and so on. Each of the floors has two flats in it as flat P and flat Q. Flat Q is to the east of flat P. Flat P of floor 2 is immediately above the flat P of floor 1 and immediately below the flat P of floor 3 and so on. In the same way, flat Q of floor 2 is immediately above the flat Q of floor 1 and immediately below the flat Q of floor 3 and so on.D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q. There are two floors between the floor on which A and Z live. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives. C lives below the floor on which X lives. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
In which flat and on which floor does W lives?
A. Flat Q, Floor 3
B. Flat P, Floor 4
C. Flat P, Floor 3
D. Flat Q, Floor 1
E. Flat P, Floor 2
Solutions
1. D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q.
2. There is two floors between the floor on which A and Z live.
From this we get the following possibilities.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | D | ||
| 1st | A | A | ||
3. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live.
This implies B lives in flat Q on floor 2 in both the cases.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | A | ||
4. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives.
5. C lives below the floor on which X lives.
From this we can say that Y lives in flat Q and flat P in case 1 and in case 2, respectively. Thus, C lives in flat Q on floor 1 in both the cases. X lives in either flat P or flat Q but lives on floor 3.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y | Y | Z |
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | C | A | C |
6. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot determine the flat in which X lives. Hence, in case 1 X lives in flat Q on floor 3. W lives in flat P on floor 3. From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Cases | Case 1 | |
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y |
| 3rd | W | X |
| 2nd | D | B |
| 1st | A | C |
Hence, W lives in flat P on floor 3.
24. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight persons – A, B, C, D, W, X, Y and Z –are living in a four-storey building such that ground floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above floor 1 is numbered as 2 and so on. Each of the floors has two flats in it as flat P and flat Q. Flat Q is to the east of flat P. Flat P of floor 2 is immediately above the flat P of floor 1 and immediately below the flat P of floor 3 and so on. In the same way, flat Q of floor 2 is immediately above the flat Q of floor 1 and immediately below the flat Q of floor 3 and so on.D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q. There are two floors between the floor on which A and Z live. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives. C lives below the floor on which X lives. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
Who lives on the same floor with Z?
A. Y
B. X
C. B
D. C
E. A
Solutions
1. D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q.
2. There is two floors between the floor on which A and Z live.
From this we get the following possibilities.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | D | ||
| 1st | A | A | ||
3. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live.
This implies B lives in flat Q on floor 2 in both the cases.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | A | ||
4. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives.
5. C lives below the floor on which X lives.
From this we can say that Y lives in flat Q and flat P in case 1 and in case 2, respectively. Thus, C lives in flat Q on floor 1 in both the cases. X lives in either flat P or flat Q but lives on floor 3.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y | Y | Z |
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | C | A | C |
6. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot determine the flat in which X lives. Hence, in case 1 X lives in flat Q on floor 3. W lives in flat P on floor 3. From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Cases | Case 1 | |
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y |
| 3rd | W | X |
| 2nd | D | B |
| 1st | A | C |
Hence, Y lives on the same floor with Z.
25. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight persons – A, B, C, D, W, X, Y and Z –are living in a four-storey building such that ground floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above floor 1 is numbered as 2 and so on. Each of the floors has two flats in it as flat P and flat Q. Flat Q is to the east of flat P. Flat P of floor 2 is immediately above the flat P of floor 1 and immediately below the flat P of floor 3 and so on. In the same way, flat Q of floor 2 is immediately above the flat Q of floor 1 and immediately below the flat Q of floor 3 and so on.D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q. There are two floors between the floor on which A and Z live. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives. C lives below the floor on which X lives. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
Four of the following five are same in some way, find the odd one.
A. W
B. A
C. D
D. C
E. X
Solutions
1. D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q.
2. There is two floors between the floor on which A and Z live.
From this we get the following possibilities.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | D | ||
| 1st | A | A | ||
3. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live.
This implies B lives in flat Q on floor 2 in both the cases.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | A | ||
4. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives.
5. C lives below the floor on which X lives.
From this we can say that Y lives in flat Q and flat P in case 1 and in case 2, respectively. Thus, C lives in flat Q on floor 1 in both the cases. X lives in either flat P or flat Q but lives on floor 3.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y | Y | Z |
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | C | A | C |
6. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot determine the flat in which X lives. Hence, in case 1 X lives in flat Q on floor 3. W lives in flat P on floor 3. From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Cases | Case 1 | |
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y |
| 3rd | W | X |
| 2nd | D | B |
| 1st | A | C |
Except D, all the persons live on an odd numbered floor.
Therefore, D is the odd one out.
26. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight persons – A, B, C, D, W, X, Y and Z –are living in a four-storey building such that ground floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above floor 1 is numbered as 2 and so on. Each of the floors has two flats in it as flat P and flat Q. Flat Q is to the east of flat P. Flat P of floor 2 is immediately above the flat P of floor 1 and immediately below the flat P of floor 3 and so on. In the same way, flat Q of floor 2 is immediately above the flat Q of floor 1 and immediately below the flat Q of floor 3 and so on.D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q. There are two floors between the floor on which A and Z live. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives. C lives below the floor on which X lives. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
If W and B interchange their position, then who among the following lives immediately below B?
A. C
B. A
C. D
D. X
E. Y
Solutions
1. D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q.
2. There is two floors between the floor on which A and Z live.
From this we get the following possibilities.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | D | ||
| 1st | A | A | ||
3. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live.
This implies B lives in flat Q on floor 2 in both the cases.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | A | ||
4. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives.
5. C lives below the floor on which X lives.
From this we can say that Y lives in flat Q and flat P in case 1 and in case 2, respectively. Thus, C lives in flat Q on floor 1 in both the cases. X lives in either flat P or flat Q but lives on floor 3.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y | Y | Z |
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | C | A | C |
6. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot determine the flat in which X lives. Hence, in case 1 X lives in flat Q on floor 3. W lives in flat P on floor 3. From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Cases | Case 1 | |
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y |
| 3rd | W | X |
| 2nd | D | B |
| 1st | A | C |
AFTER INTERCHANGING:
| Cases | Case 1 | |
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y |
| 3rd | B | X |
| 2nd | D | W |
| 1st | A | C |
If W and B interchange their position, then D lives immediately below B.
Hence, D is the correct option.
27. Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight persons – A, B, C, D, W, X, Y and Z –are living in a four-storey building such that ground floor is numbered as 1, the floor immediately above floor 1 is numbered as 2 and so on. Each of the floors has two flats in it as flat P and flat Q. Flat Q is to the east of flat P. Flat P of floor 2 is immediately above the flat P of floor 1 and immediately below the flat P of floor 3 and so on. In the same way, flat Q of floor 2 is immediately above the flat Q of floor 1 and immediately below the flat Q of floor 3 and so on.D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q. There are two floors between the floor on which A and Z live. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives. C lives below the floor on which X lives. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
Which of the following is true?
A. Z lives in flat Q.
B. B and X live in different flats.
C. Y lives on floor 2.
D. D lives below the floor on which W lives.
E. All are true
Solutions
1. D lives immediately above the flat in which A lives in the same flat but not in flat Q.
2. There is two floors between the floor on which A and Z live.
From this we get the following possibilities.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | D | ||
| 1st | A | A | ||
3. There is only one floor between the floors on which Z and B live.
This implies B lives in flat Q on floor 2 in both the cases.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Z | ||
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | A | ||
4. Y who lives on an even numbered floor lives above the floor on which C lives.
5. C lives below the floor on which X lives.
From this we can say that Y lives in flat Q and flat P in case 1 and in case 2, respectively. Thus, C lives in flat Q on floor 1 in both the cases. X lives in either flat P or flat Q but lives on floor 3.
| Cases | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y | Y | Z |
| 3rd | ||||
| 2nd | D | B | D | B |
| 1st | A | C | A | C |
6. C and X live in the same flat but not with Z.
From this case 2 is eliminated as we cannot determine the flat in which X lives. Hence, in case 1 X lives in flat Q on floor 3. W lives in flat P on floor 3. From this we get the final arrangement as follows.
| Cases | Case 1 | |
| Floor/Flat | Flat P | Flat Q |
| 4th | Z | Y |
| 3rd | W | X |
| 2nd | D | B |
| 1st | A | C |
Hence, D lives below the floor on which W lives is true.
28. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D & L O @ P T ! F
How many such symbols are there in the above series which is immediately followed by a consonant and immediately preceded by vowel?
A. Two
B. Three
C. One
D. Four
E. None of these
Solutions
Left side N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D & L O @ P T ! F Right side
So, in the above series only one symbol is immediately followed by a consonant and preceded by vowel i.e. O@P
Hence, one is the correct answer
29. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D & L O @ P T ! F
If we remove all the symbols from the above series then which among the following alphabet is the 9th from the right end?
A. R
B. Q
C. D
D. A
E. None of these
Solutions
Left side N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D & L O @ P T ! F Right side
If all symbols are removed from the given series, we get
Left side N T I A J B B U A R Q D L O P T F Right side
Hence, 9th from the right end is A Hence, A is the correct answer.
30. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D & L O @ P T ! F
Which among the following elements is 5th to the left of 7th from the right end of the series?
A. T
B. A
C. &
D. @
E. None of these
Solutions
Left side N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D & L O @ P T ! F Right side
5th to left + 7th from the right = 12th from the right i.e. A
Hence, A is the correct answer.
31. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D & L O @ P T ! F
How many such vowels are in the series given each of which is immediately followed by symbol and immediately preceded by a letter?
A. Two
B. One
C. Three
D. Four
E. Five
Solutions
Left side N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D &L O @ P T ! F Right side
There are two vowels which are immediately followed and immediately preceded by a letter i.e. I A ^ and L O @
Hence, two is the correct answer.
32. Direction: Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below:
N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D & L O @ P T ! F
If all the symbols are replaced with a digit 5 then how many such 5’s are there in the new series each of which is followed by a consonant?
A. Five
B. Six
C. Four
D. Eight
E. Two
Solutions
Left side N T * I A ^ $ J # B * B U A R Q D & L O @ P T ! F Right side
If all symbols are replaced with a digit 5 then-new series is
N T 5 I A 5 5 J 5 B 5 B U A R Q D 5 L O 5 P T 5 F
Hence, there are six 5’s in the new series each of which is followed by a consonant.
Confusion Points There are eight symbol which changed to 5. After that condition is given that we have to make the pair of 5 – Consonant. so such type of Six pair are there.
33. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions that follow:
There are six members in the group – A, B, C, D, E and F who score different marks in an exam. All are sitting in a row according to their marks. B scores the second highest mark. Marks of F is less than D. A scores fewer marks than C and E. F is the third highest score in the group and has scored 56 marks. D is the highest scorer in the group.
Who score second highest in the group?
A. A
B. B
C. E
D. F
E. C
Solutions
1) F is the third highest score in the group and has scored 56 marks.
2) D is the highest scorer in the group.
D > _____ > F (56) > _____ > _____ > _____
3) B scores the second highest mark.
4) Marks of F is less than D.
5) A scores fewer marks than C and E.
D > B > F (56) > C/E > C/E > A
Hence, B scores second highest in the group.
34. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions that follow:
There are six members in the group – A, B, C, D, E and F who score different marks in an exam. All are sitting in a row according to their marks. B scores the second highest mark. Marks of F is less than D. A scores fewer marks than C and E. F is the third highest score in the group and has scored 56 marks. D is the highest scorer in the group.
Who score second lowest marks in the group?
A. E
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. Either option 1 or option 3
Solutions
1) F is the third highest score in the group and has scored 56 marks.
2) D is the highest scorer in the group.
D > _____ > F (56) > _____ > _____ > _____
3) B scores the second highest mark.
4) Marks of F is less than D.
5) A scores fewer marks than C and E.
D > B > F (56) > C/E > C/E > A
Here either C or E is the second lowest scorer.
Hence, either option 1 or option 2 is the correct answer.
35. Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions that follow:
There are six members in the group – A, B, C, D, E and F who score different marks in an exam. All are sitting in a row according to their marks. B scores the second highest mark. Marks of F is less than D. A scores fewer marks than C and E. F is the third highest score in the group and has scored 56 marks. D is the highest scorer in the group.
If sum of F and B mark is 116. then what is possible marks of D?
A. 62
B. 60
C. 58
D. 57
E. 56
Solutions
1) F is the third highest score in the group and has scored 56 marks.
2) D is the highest scorer in the group.
D > _____ > F (56) > _____ > _____ > _____
3) B scores the second highest mark.
4) Marks of F is less than D.
5) A scores fewer marks than C and E.
D > B > F (56) > C/E > C/E > A
Here either C or E is the second-lowest scorer.
If sum of F and B marks is 116 then marks of B = 116 – 56 = 60.
So the possible mark of D is 62
Hence, the Possible mark of D is 62.
36. If the numerator of a certain fraction is increased by 80%, while the denominator is increased by 200%, then the ratio of the numerator and denominator becomes 21:50, what will be the actual fraction?
A. 5/7
B. 7/8
C. 7/10
D. 8/11
E. 5/8
Solutions
Let numerator of the fraction is x and denominator is y, then fraction will be x/y
Numerator increased 80%, so new numerator would be ,
⇒ [x + (80 × x)/100] = 9x/5 ………(i)
New denominator will be,
⇒ [y + (200 × y)/100] = 3y ………(ii)
Now, according to question, we have,
⇒ (9/5x)/3y = 21/50
⇒ 9x/(3y × 5) = 21/50
⇒ 3x/5y = 21/50
⇒ x/y = 7/10
So, original fraction is 7/10.
37. A certain work was completed by A in 9 days, B in 12 days, C in 15 days, If A and C did work for 4 days and then leftt, then B will finishes rest work in how many days?
A. 4(2/3) days
B. 3(7/15) days
C. 3(1/15) days
D. 4(1/5) days
E. 3(1/2) days
Solutions
A certain work was completed by A in 9 days, B in 12 days, C in 15 days,
So, assume that total work is = 180 units
So, one day work of A = (180/9) = 20 units
One day work of B = (180/12) = 15 units
One day work of C = (180/15) = 12 units
Work done by A and C in 4 days = 4(20+12)=128 units
Remaining work = 180 – 128 = 52 units
Number of days taken by B to finish the remaining = (52/15) = 3(7/15) days
38. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 5x2 + 26x + 33 = 0
II. y2 + 18y + 65 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
Solutions
Given:
I. 5×2 + 26x + 33 = 0
II. y2 + 18y + 65 = 0
Calculation:
From I,
5×2 + 26x + 33 = 0
⇒ 5×2 + 15x + 11x + 33 = 0
⇒ 5x(x + 3) + 11(x + 3) = 0
⇒ (x + 3)(5x + 11) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (x + 3) = 0 or (5x + 11) = 0
⇒ x = -3 or (-11/5)
From II,
y2 + 18y + 65 = 0
⇒ y2 + 13y + 5y + 65 = 0
⇒ y(y + 13) + 5(y + 13) = 0
⇒ (y + 13)(y + 5) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (y + 13) = 0 or (y + 5) = 0
⇒ y = -13 or -5
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| -3 | -13 | x > y |
| -3 | -5 | x > y |
| -11/5 | -13 | x > y |
| -11/5 | -5 | x > y |
∴ x > y.
39. In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. 6x2 – 23x + 20 = 0
II. y2 – 5y + 4 = 0
A. x > y
B. x < y
C. x ≥ y
D. x ≤ y
E. x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
Solutions
Given:
I. 6×2 – 23x + 20 = 0
II. y2 – 5y + 4 = 0
Calculation:
From I,
6×2 – 23x + 20 = 0
⇒ 6×2 – 15x – 8x + 20 = 0
⇒ 3x(2x – 5) – 4(2x – 5) = 0
⇒ (2x – 5)(3x – 4) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (2x – 5) = 0 or (3x – 4) = 0
⇒ x = (5/2) or (4/3)
From II,
y2 – 5y + 4 = 0
⇒ y2 – 4y – y + 4 = 0
⇒ y(y – 4) – 1(y – 4) = 0
⇒ (y – 4)(y – 1) = 0
Taking,
⇒ (y – 4) = 0 or (y – 1) = 0
⇒ y = 4 or 1
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| Value of x | Value of y | Relation |
| 5/2 | 4 | x < y |
| 5/2 | 1 | x > y |
| 4/3 | 4 | x < y |
| 4/3 | 1 | x > y |
∴ x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
40. In the given questions, two equations numbered l and II are given. You have to solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 30x + 81 = 0
II. y2 + 26y + 48 = 0
A. x < y
B. No relation in x and y or x = y
C. x > y
D. x ≤ y
E. x ≥ y
Solutions
Calculations:
From I,
x2 + 30x + 81 = 0
⇒ x2 + 27x + 3x + 81 = 0
⇒ x(x + 27) + 3(x + 27) = 0
⇒ (x + 3)(x + 27) = 0
Taking,
⇒ x + 3 = 0 or x + 27 = 0
⇒ x = – 3 or x = – 27
From II,
y2 + 26y + 48 = 0
⇒ y2 + 24y + 2y + 48 = 0
⇒ y(y + 24) + 2(y + 24) = 0
⇒ (y + 2)(y + 24) = 0
Taking,
⇒ y + 2 = 0 or y + 24 = 0
⇒ y = – 2 or y = – 24
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| x | Y | Relation |
| – 3 | – 2 | x < y |
| – 3 | – 24 | x > y |
| – 27 | – 2 | x < y |
| – 27 | – 24 | x < y |
∴ After comparing x and y both, No relation in x and y or x = y.
41. In the given questions, two equations numbered l and II are given. You have to solve both the equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 14x + 45 = 0
II. y2 – 11y + 30 = 0
A. x ≤ y
B. x > y
C. x ≥ y
D. x < y
E. No relation in x and y or x = y
Solutions
Calculations:
From I,
x2 – 14x + 45 = 0
⇒ x2 – 9x – 5x + 45 = 0
⇒ x(x – 9) – 5(x – 9) = 0
⇒ (x – 5)(x – 9) = 0
⇒ x = 5, 9
From II,
y2 – 11y + 30 = 0
⇒ y2 – 6y – 5y + 30 = 0
⇒ y(y – 6) – 5(y – 6) = 0
⇒ (y – 5)(y – 6) = 0
⇒ y = 5, 6
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):
| x | Y | Relation |
| 5 | 5 | x = y |
| 5 | 6 | x < y |
| 9 | 5 | x > y |
| 9 | 6 | x > y |
∴ After comparing x and y both, No relation in x and y or x = y.
42. Two equations I and II are given below in question. You have to solve these equations and give the answer.
I. x2 + 13x + 42 = 0
II. y2 + 21y + 104 = 0
A. x < y
B. x > y
C. x ≤ y
D. x ≥ y
E. x = y or the relation between x and y can’t be established.
Solutions
Given:
I. x2 + 13x + 42 = 0
II. y2 + 21y + 104 = 0
Calculation:
I. x2 + 13x + 42 = 0
⇒ x2 + 6x + 7x + 42 = 0
⇒ x(x + 6) + 7(x + 6)= 0
⇒ (x + 6)(x + 7) = 0
⇒ x = (-6), (-7)
II. y2 + 21y + 104 = 0
⇒ y2 + 13y + 8y + 104 = 0
⇒ y(y + 13) + 8(y + 13) =0
⇒ (y + 13)(y + 8) = 0
⇒ y = (-13), (-8)
| Value of ‘x’ | Relation | Value of ‘y’ |
| -6 | > | -13 |
| -6 | > | -8 |
| -7 | > | -13 |
| -7 | > | -8 |
When we compared the values of ‘x’ and ‘y’ in the table above, we found that there is only ONE relation between x and y i.e. >. So, a relation between x and y is “x > y”.
∴ After comparison, all the values of x and y the relation is “x > y”.
43. What approximate value should come in the place of question mark (?) in the following question?
[(15.98 + 9.99) ÷ 1.99] × 4.98 = ?3 + 1.09
A. 11
B. 8
C. 2
D. 4
E. 5
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
[(15.98 + 9.99) ÷ 1.99] × 4.98 = ?3 + 1.09
⇒ [(16 + 10) ÷ 2] × 5 = ?3 + 1
⇒ (26 ÷ 2) × 5 = ?3 + 1
⇒ 13 × 5 = ?3 + 1
⇒ ?3 = 65 – 1
⇒ ? ≈ 4
44. What approximate value should come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
(222.22 + 71.98) ÷ 2.99 = 8.99% of 299.99 + 29.99 + ?
A. 31
B. 41
C. 21
D. 11
E. 51
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
(222.22 + 71.98) ÷ 2.99 = 8.99% of 299.99 + 29.99 + ?
⇒ (222 + 72) ÷ 3 = 9% of 300 + 30 + ?
⇒ (294 ÷ 3) = (9/100) × 300 + 30 + ?
⇒ 98 = (9 × 3) + 30 + ?
⇒ 98 = 27 + 30 + ?
⇒ ? = 98 – 57
⇒ ? = 41
45. What approximate value should come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?
220.89 + 2.123 + 205.96 = 1.99 × ? + 214.98
A. 90
B. 100
C. 120
D. 80
E. 110
Solutions
Follow BODMAS rule to solve this question, as per the order given below.
Step – 1: Parts of an equation enclosed in ‘Brackets’ must be solved first, and following BODMAS rule in the bracket –
Step – 2: Any mathematical ‘Of’ or ‘Exponent’ must be solved next.
Step – 3: Next, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Division’ and ‘Multiplication’ are calculated.
Step – 4: Last but not the least, the parts of the equation that contain ‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ should be calculated.
Since, we need to find out the approximate value, we can write these values to their nearest integers.
Given expression is
220.89 + 2.123 + 205.96 = 1.99 × ? + 214.98
⇒ 221 + 23 + 206 = 2 × ? + 215
⇒ 221 + 8 + 206 = 2 × ? + 215
⇒ 435 = 2 × ? + 215
⇒ 220 = 2 × ?
⇒ ? = 110
46. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
52% of 150 + 15 × 35 – √841 × 8 = ?
A. 372
B. 373
C. 371
D. 370
E. None of these.
Solutions
Given:
52% of 150 + 15 × 35 – √841 × 8 = ?
Concept used:
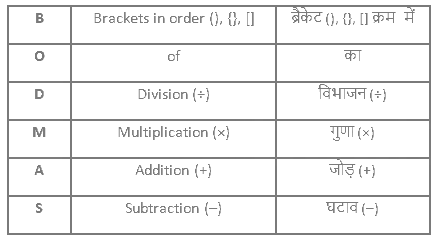
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:
Calculation:
52% of 150 + 15 × 35 – √841 × 8 = ?
⇒ 78 + 525 – 29 × 8 = ?
⇒ 78 + 525 – 232 = ?
⇒ ? = 371
∴ The value of ? is 371.
47. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
80% of 140 = 25 × 8 – ? + 12 × 4
A. 147
B. 137
C. 146
D. 136
E. None of these
Solutions
Given:
80% of 140 = 25 × 8 – ? + 12 × 4
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
80% of 140 = 25 × 8 – ? + 12 × 4
⇒ 112 = 200 – ? + 48
⇒ 200 + 48 – 112 = ?
⇒ ? = 136
∴ The value of ? is 136.
48. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
131 × 6 + 189 = 210 ÷ 7 + ?% of 63
A. 1400
B. 1500
C. 1550
D. 1450
E. None of these.
Solutions
Given:
131 × 6 + 189 = 210 ÷ 7 + ?% of 63
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
131 × 6 + 189 = 210 ÷ 7 + ?% of 63
⇒ 786 + 189 = 30 + ?% of 63
⇒ 975 – 30 = ?% of 63
⇒ 945 = ?% of 63
⇒ ? = 1500
∴ The value of ? is 1500.
49. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
17 × √9 + 30% of 200 = 25% of 80 + ? × 13
A. 7
B. 1
C. 9
D. 5
E. None of these.
Solutions
Given:
17 × √9 + 30% of 200 = 25% of 80 + ? × 13
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
17 × √9 + 30% of 200 = 25% of 80 + ? × 13
⇒ 17 × 3 + (30/100) × 200 = (25/100) × 80 + ? × 13
⇒ 51 + 60 = 20 + ? × 13
⇒ 111 – 20 = ? × 13
⇒ 91 = ? × 13
⇒ ? = 7
∴ The value of ? is 7
50. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
44 × 46 – 80% of 1900 = √441 × ?
A. 23
B. 24
C. 28
D. 14
E. None of these
Solutions
Given:
44 × 46 – 80% of 1900 = √441 × ?
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
44 × 46 – 80% of 1900 = √441 × ?
⇒ 2024 – 1520 = 21 × ?
⇒ 504/21 = ?
⇒ ? = 24
∴ The value of ? is 24.
51. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
?% of 400 × (3/4) + 300 = 66.66% of 900
A. 100
B. 260
C. 70
D. 180
E. 50
Solutions
Given:
?% of 400 × (3/4) + 300 = 66.66% of 900
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
?% of 400 × (3/4) + 300 = 66.66% of 900
⇒ ? × 4 × (3/4) +300 = (2/3) × 900
⇒ ? × 3 + 300 = 600
⇒ ? = 300/3 = 100
∴ The value of ? is 100.
52. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
25% of 212 + 5% of 140 = 2 × 11% of 500 + ?
A. -46
B. -32
C. -50
D. -60
E. -25
Solutions
Given:
25% of 212 + 5% of 140 = 2 × 11% of 500 + ?
Concept Used:

Calculation:
25% of 212 + 5% of 140 = 2 × 11% of 500 + ?
⇒ (1/4) × 212 + (1/20) × 140 = 2 × (11/100) × 500 + ?
⇒ 53 + 7 = 110 + ?
⇒ ? = -110 + 60 = -50
∴ The value of (?) is -50
53. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
√81 + 162 ÷ 18 = 297 ÷ 33 + (?)2
A. 8
B. 6
C. 13
D. 3
E. None of these.
Solutions
Given:
√81 + 162 ÷ 18 = 297 ÷ 33 + (?)2
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
√81 + 162 ÷ 18 = 297 ÷ 33 + (?)2
⇒ 9 + 9 = 9 + (?)2
⇒ 18 – 9 = (?)2
⇒ 9 = (?)2
⇒ ? = 3
∴ The value of ? is 3.
54. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
33 × √25 – 30% of 200 = 25% of √1296 + ? × 12
A. 7
B. 8
C. 9
D. 5
E. None of these.
Solutions
Given:
33 × √25 – 30% of 200 = 25% of √1296 + ? × 12
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
33 × √25 – 30% of 200 = 25% of √1296 + ? × 12
⇒ 33 × 5 – (30/100) × 200 = (25/100) × 36 + ? × 12
⇒ 165 – 60 = 9 + ? × 12
⇒ 105 – 9 = ? × 12
⇒ 96 = ? × 12
⇒ ? = 8
∴ The value of ? is 8.
55. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
?% of 550 × (3/5) + √625 = 28.57% of 630 + 10
A. 100
B. 260
C. 70
D. 180
E. 50
Solutions
Given:
?% of 550 × (3/5) + √625 = 28.57% of 630 + 10
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
?% of 550 × (3/5) + √625 = 28.57% of 630 + 10
⇒ ?/100 × 550 × (3/5) + 25 = (2/7) × 630 + 10
⇒ ? × 33/10 + 25 = 180 + 10
⇒ ? × 33/10 = 190 – 25
⇒ ? × 33/10 = 165
⇒ ? = 165 × 10/33
⇒ ? = 50
∴ The value of ? is 50.
56. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
112 + 120 ÷ 12 × 2 = ? – 30
A. 270
B. 137
C. 190
D. 171
E. None of these.
Solutions
Given:
112 + 120 ÷ 12 × 2 = ? – 30
Concept used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
112 + 120 ÷ 12 × 2 = ? – 30
⇒ 121 + 10 × 2 = ? – 30
⇒ 121 + 20 = ? – 30
⇒ ? = 141 + 30 = 171
⇒ ? = 171
∴ The value of ? is 171.
57. What will come in the place of the question mark ‘?’ in the following question?
25% of 28 – 20% of 30 + 22 = 5 × ?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 0
E. 4
Solutions
Given:
25% of 28 – 20% of 30 + 22 = 5 × ?
Concept Used:
Follow the BODMAS rule according to the table given below:

Calculation:
25% of 28 – 20% of 30 + 22 = 5 × ?
⇒ 28 × (25/100) – 30 × (20/100) + 4 = 5 × ?
⇒ 28 × (1/4) – 30 × (1/5) + 4 = 5 × ?
⇒ 7 – 6 + 4 = 5 × ?
⇒ 5 = 5 × ?
⇒ ? = 1
∴ 1 will come in place of the question mark (‘?’).
58. In the below given table, the total number of headphones, Adaptors and Chargers sold by five different companies in 2019 is given. On the basis of the given data determine the answered of the questions asked.
| Companies | Headphone | Adaptor | Charger |
| I | 500 | 150 | 150 |
| J | 650 | 100 | 200 |
| K | 750 | 100 | 300 |
| L | 800 | 200 | 400 |
| M | 500 | 250 | 500 |
In 2020, a new company T&T joins, and it was found that the sale of headphone for the company is 50% more than the sale of headphone by L in 2019, while the sale of Charger by the company is 30% less than the sale of charger by K in 2019. Find the total number of the headphones and chargers sold by T&T company in 2020?
A. 1400
B. 1390
C. 1410
D. 1430
E. 1470
Solutions
Sale of headphones by T&T in 2020 = (150/100)× 800 = 1200
Sale of charger by T&T in 2020 = (70/100)× 300=210
Hence, total sale = 1200+210 = 1410
59. In the below given table, the total number of headphones, Adaptors and Chargers sold by five different companies in 2019 is given. On the basis of the given data determine the answered of the questions asked.
| Companies | Headphone | Adaptor | Charger |
| I | 500 | 150 | 150 |
| J | 650 | 100 | 200 |
| K | 750 | 100 | 300 |
| L | 800 | 200 | 400 |
| M | 500 | 250 | 500 |
If each company has targeted to increase their sale of chargers by at least 25% in 2020, but it was found that I, J and K have scale up their target only by 20%, while M have scale up by 35%. The sale of charger by M in 2020 is approximately what percent to the sale of I,J and K in 2020?
A. 84%
B. 85%
C. 87%
D. 77%
E. 80%
Solutions
Number of Charger sold by M in 2020 = (135/100)× 500 = 675
Number of Charger sold by I in 2020 = (120/100)× 150 = 180
Number of Charger sold by J in 2020 = (120/100)× 200 = 240
Number of Charger sold by K in+ 2020 = (120/100)× 300 = 360
Hence, required percentage will be = [675 / (180+240+360)]× 100=86.53 = 87% (approx.)
60. In the below given table, the total number of headphones, Adaptors and Chargers sold by five different companies in 2019 is given. On the basis of the given data determine the answered of the questions asked.
| Companies | Headphone | Adaptor | Charger |
| I | 500 | 150 | 150 |
| J | 650 | 100 | 200 |
| K | 750 | 100 | 300 |
| L | 800 | 200 | 400 |
| M | 500 | 250 | 500 |
If the sale for headphones is increased by 50% in 2020, and sale for Adaptor is increased by 40% in 2020 for shop M, then what will be the new ratio of sale of headphones and adaptors in 2020?
A. 17:5
B. 14:5
C. 11:7
D. 15:7
E. 13:8
Solutions
Number of adaptors sold in 2020 by M = (140/100)× 250 = 350
Number of headphones sold in 2020 by M = (150/100)× 500 = 750
So, new ratio will be = 750 : 350 = 15:7
61. In the below given table, the total number of headphones, Adaptors and Chargers sold by five different companies in 2019 is given. On the basis of the given data determine the answered of the questions asked.
| Companies | Headphone | Adaptor | Charger |
| I | 500 | 150 | 150 |
| J | 650 | 100 | 200 |
| K | 750 | 100 | 300 |
| L | 800 | 200 | 400 |
| M | 500 | 250 | 500 |
In 2020 the total sales of Headphones for all the shops together increased by 120%. What will be the total number of Headphones sold by shop M in 2019 and 2020, if it was considered that the sales of other shops are same as 2019 except M and L. M and L sell an equal number of headphones in 2020?
A. 2090
B. 2190
C. 3070
D. 2420
E. 1990
Solutions
Total number of headphones sold in 2019 = 500 + 650 + 750 + 800 + 500 = 3200
Total number of headphones sold in 2020 = (220/100) × 3200 = 7040
As the sales of other shops are same except M and L.
So, number of headphones sold in 2020 from I, J, and K = 500 + 650 + 750 = 1900
So, number of headphones sold in 2020 from M and L = 7040 – 1900 = 5140
Number of headphones sold in 2020 by M = 5140/2 = 2570
Hence, the total number of headphones sold by M in 2019 and 2020 = 500 + 2570 = 3070
62. In the below given table, the total number of headphones, Adaptors and Chargers sold by five different companies in 2019 is given. On the basis of the given data determine the answered of the questions asked.
| Companies | Headphone | Adaptor | Charger |
| I | 500 | 150 | 150 |
| J | 650 | 100 | 200 |
| K | 750 | 100 | 300 |
| L | 800 | 200 | 400 |
| M | 500 | 250 | 500 |
What will be the total ratio of the Headphones and the Chargers sold by all of the company in 2019?
A. 55:31
B. 54:31
C. 57:31
D. 64:31
E. 59:31
Solutions
As per data.
Total number of headphones sold in 2019 = 500+650+750+800+500=3200
Total number of the Chargers sold in 2019 = 150+200+300+400+500=1550
Hence, required ratio = 3200:1550 = 320:155 = 64:31
63. A boat having a speed of 12 Kmph covering a distance of 36 Km in upstream, and a distance of 30 Km in downstream. if the time taken by the boat to cover the distance in up and down is in ratio of 2:1. Find the speed of the stream.
A. 3 Kmph
B. 4 Kmph
C. 5 Kmph
D. 6 Kmph
E. 8 Kmph
Solutions
Speed of boat = x = 12 Kmph
Speed of stream = y = y Kmph
Upstream speed = (x-y) = (12-y) Kmph
Downstream speed = (x+y) = (12+y) Kmph
As, Time = (Distance / Speed)
Time taken in Upstream = (36/12-x)
Time taken in Downstream = (30/12+x)
So, As per question,
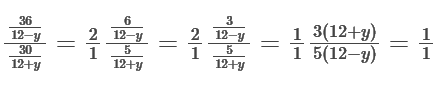
36+3y=60-5y
8y=24
y=(24/8)=3 Kmph
64. If the height of the triangle is 24 cm, and the area of the triangle is 168 sq. cm. The perimeter of the rectangle is 84 cm. If it were given that the base of a triangle is equal to the breadth of a rectangle. Find length of rectangle.
A. 30 cm
B. 32 cm
C. 28 cm
D. 40 cm
E. 25 cm
Solutions
if the height of the right angle triangle is 24 cm, and the area of the triangle is 168 sq. cm.
Area of right angle triangle
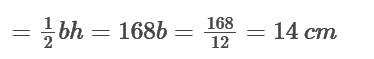
The perimeter of the rectangle is 84 cm.
The base of a triangle is equal to the breadth of a rectangle.
So, 2(l+b) = 84
2l + 2×14 = 84
L = (56/2) = 28cm
65. If the ratio of Income of 2 companies is 7 : 5, while it was found that the ratio of expenditure is 5:3, If both the companies saves Rs.10,000 in each month. Find sum of monthly income of both the companies?
A. Rs. 50000
B. Rs. 55000
C. Rs. 60000
D. Rs. 65000
E. Rs. 70000
Solutions
The incomes of A and B are in the ratio 7: 5.
The expenditure of A and B are in the ratio 5: 3.
The saving of each is Rs. 10000
Income = Expenditure + Saving
Let the income of A and B be 7x and 5x
The expenditure of A=7x-10000
The expenditure of B=5x-10000
According to the question;
⇒ (7x-10000) /(5x-10000)=(5/3)
⇒ 21x-30000=25x-50000
⇒ 4x=20000 ⇒ x = 5000
The income of A=7×5000= Rs. 35000
The income of B=5×5000= Rs. 25000
sum of income = 35000+25000 = Rs. 60000
66. The average weight of 80 students in a class is 30kg. The number of girls in a class are 40% less than the number of boys in a class. The average weight of girls in a class is 24kg. Find the difference between the average weight of boys and average weight of girls in a class.
A. 12.6 kg
B. 7.5 kg
C. 11.9 kg
D. 9.6 kg
E. 12.8 kg
Solutions
Shortcut Trick
Number of students = 80 (G : B = 6 : 10 )
G = 30 & B = 50
Average Weight of students= 30 kg
Average Weight of girls = 24 kg
Acc to allegation rule,
Girls Boys
24 x Avg weight
30
30 50 No of student
—————————
-6 × 30 = +(y) × 50
y = -18/5 = -3.6
Avg wt. of boys = 30 + y = 30 – 3.6 = 33.6
The difference between the average weight of boys and average weight of girls in a class. = 6 + 3.6 = 9.6
Alternate Method
Given:
Let number of girls in a class be N.
Total number of boys in a class = N × 100/60 = 5N/3
Total number of students in a class = N + 5N/3 = 8N/3
⇒ 80 = 8N/3
⇒ N = 30
Total number of girls in a class = 30
Total number of boys in a class = 50
Total weight of 80 students = 80 × 30 = 2400 kg
Total weight of girls = 30 × 24 = 720 kg
Total weight of boys = 2400 – 720 = 1680
Average weight of boys = 1680/50 = 33.6 kg
∴ Required difference = 33.6 – 24 = 9.6 kg
67. There are 3 friends named Sahil, Tanya, and Deepak. It was found that the average age of Sahil and Tanya is 22 years. While the ratio of Sahil and Deepak’s ages is 5:7, and the sum of all the friends together is 72 years. what will be the present age of Tanya?
A. 14 years
B. 20 years
C. 12 years
D. 18 years
E. 24 years
Solutions
Let the age of Sahil be 5x
Age of Deepak = 7x
Age of Tanya = y
The average age of Sahil and Tanya is 22 years.
So, 5x+y = (22 × 2) = 44 —-(i)
And, 5x+7x+y = 72 ⇒ 12x+y = 72 —–(ii)
From (i) and (ii)
We will get, x = 4
So, age of Sahil will be = 5x = 20 years.
Age of Tanya will be: y + 20 = 44 ⇒ y = 24 years.
68. A sum of money gives an interest of 1/5 of itself in T years, when it is given in the rate of 10%, Find amount after (T+3) years.
A. 1.2 P
B. 1.25 P
C. 1.35 P
D. 1.5 P
E. 1.6 P
Solutions
A sum of money gives an interest of 1/5 of itself in T years, when it is given in the rate of 10%,
So, after T year,
SI = (PRT)/100
Let us assume that the principal be Rs. P.
So,
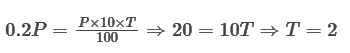
So, amount obtained after (2+3) = 5 years will be = [P+(P×10×5)/100]=P+0.5P=1.5P
69. Monthly income of a person was Rs. 36,000. if he spent 25% on food, 12 % on his children’s education and saves x% in bank account. After the calculation, he found that he was left with Rs. 2160. Find the sum of amount which he saves in his bank.
A. Rs. 18840
B. Rs. 16420
C. Rs. 20520
D. Rs. 22140
E. Rs. 24720
Solutions
Monthly income of a person was Rs. 36,000.
25% on food = (25/100)×36000 = 9000 Rs.
12 % on his children’s education = (12/100)× 36000 = Rs. 4320
x% in bank account = (x/100) × 36000 = 360x
Remaining amount =Rs. 2160.
So, we can write the above as:
9000+4320+360x+2160=36000
360x = 36000-15480=20520
⇒ x = (20520/360)=57%
The sum of amount which he saves in his bank =(57/100)× 36000=Rs. 20520
70. A train having a certain length of x m covers the two different platforms having lengths of 140 m and 180 m in 18 sec and 20 sec, respectively. Find speed of train (in kmph).
A. 70 Kmph
B. 72 Kmph
C. 75 Kmph
D. 78 Kmph
E. 80 Kmph
Solutions
As it covers the platform having lengths of 140 m in 18 sec.
So,
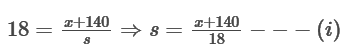
As it covers a platofrm of length180 m in 20 sec.
So,
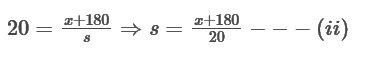
From (i) and (ii)

71. Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions. Some words are highlighted to help you answer some of the questions.
With the Humane Agrarian Centre, a one-of-a-kind rural museum, Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability. Despite all the odds stacked against him, Prem Singh made out against these tribulations as a farmer who went debt-free without loans from the banks only by using taking the less travelled road. Singh’s lush green farmland paints a vivid picture of sustainable farming: organic produce and homegrown compost, fruit-bearing trees, livestock shelter with water- bodies, well-nourished soil, natural fertilisers and, most importantly, a continuous source of income.
Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt. Further, the increased use of fertilisers and chemicals proved to be harmful to the soil’s ecological balance.
That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.
Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming, which he says is the way forward for farmers in the country. Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence. Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling. Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.
He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.
Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk. He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market. Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.
Mr. Singh’s multi-pronged technique, pioneered and implemented by him for over a decade, is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers.
What are the processed foods Prem produces and sells?
A. Pickle from turmeric
B. Candy and powder from amla
C. Gram flour from chickpeas
D. Paneer from milk
E. All of the above
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘All of the above.’
Key Points
- The given passage is a news feature story about a farmer who changed his farming methods to achieve success and fortune.
- Let us take a look at the reference sentences in the passage:
- ‘Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickles out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour out of chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk.‘
- We can see that all of the first four given options name the processed products Mr Singh produces from his farmland harvests.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 5.
72. Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions. Some words are highlighted to help you answer some of the questions.
With the Humane Agrarian Centre, a one-of-a-kind rural museum, Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability. Despite all the odds stacked against him, Prem Singh made out against these tribulations as a farmer who went debt-free without loans from the banks only by using taking the less travelled road. Singh’s lush green farmland paints a vivid picture of sustainable farming: organic produce and homegrown compost, fruit-bearing trees, livestock shelter with water- bodies, well-nourished soil, natural fertilisers and, most importantly, a continuous source of income.
Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt. Further, the increased use of fertilisers and chemicals proved to be harmful to the soil’s ecological balance.
That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.
Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming, which he says is the way forward for farmers in the country. Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence. Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling. Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.
He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.
Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk. He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market. Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.
Mr. Singh’s multi-pronged technique, pioneered and implemented by him for over a decade, is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers.
Which of the following is/are correct according to the given passage?
A. Prem did Master’s in Philosophy from Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development from Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya.
B. Prem’s family was not associated with farming before his entry into the occupation.
C. Prem’s meeting with Nagaraj influenced him to change his way of farming into Avartansheel Kheti.
A. Only A
B. Both A & B
C. Both A & C
D. Both B & C
E. Only C
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Both A & C.’
Key Points
- The given passage is a news feature story about a farmer who changed his farming methods to achieve success and fortune.
- Let’s take a look at the following sentences:
- ‘Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987.‘
- From the above sentence, we can say that Statement A is correct but Statement B is incorrect according to the given passage.
- ‘That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.’
- From the above sentence, we can say that Statement C is correct according to the given passage.
- ‘Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987.‘
- So, it is clear that only A & C are correct.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 3.
73. Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions. Some words are highlighted to help you answer some of the questions.
With the Humane Agrarian Centre, a one-of-a-kind rural museum, Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability. Despite all the odds stacked against him, Prem Singh made out against these tribulations as a farmer who went debt-free without loans from the banks only by using taking the less travelled road. Singh’s lush green farmland paints a vivid picture of sustainable farming: organic produce and homegrown compost, fruit-bearing trees, livestock shelter with water- bodies, well-nourished soil, natural fertilisers and, most importantly, a continuous source of income.
Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt. Further, the increased use of fertilisers and chemicals proved to be harmful to the soil’s ecological balance.
That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.
Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming, which he says is the way forward for farmers in the country. Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence. Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling. Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.
He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.
Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk. He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market. Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.
Mr. Singh’s multi-pronged technique, pioneered and implemented by him for over a decade, is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers.
Which of the following is correct according to the given passage?
A. Prem’s family was incurring loss when they were following the traditional methods.
B. Prem always wanted to move away from the farming occupation.
C. Mr Singh believes that despite other problems with the middlemen, they can really help the farmers.
D. Periodic proportionate farming requires dividing the land in four equal parts.
E. Mr Singh thinks that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by delegating the step of processing the produce to the middlemen.
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Prem’s family was incurring loss when they were following the traditional methods.’
Key Points
- The given passage is a news feature story about a farmer who changed his farming methods to achieve success and fortune.
- Let’s take a look at the following sentences:
- ‘Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt.’
- From the above sentence, we can say that the marked statement is correct according to the given passage.
- Also from the same text, we can see that Prem’s ancestors have been into farming and he followed suit after completing his Master’s. There is no indication in the text anywhere that he wanted to move away from the job. Moreover, he has changed his way of farming and become successful in the same. So, we can say that it is not correct to say that ‘Prem always wanted to move away from the farming occupation.‘
- ‘Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.’
- From the above sentence, we can say that the following statement is not correct according to the given passage: ‘Mr Singh believes that despite other problems with the middlemen, they can really help the farmers.’
- From the same text, we can say that the following statement is not correct according to the given passage: ‘Mr Singh thinks that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by delegating the step of processing the produce to the middlemen.’
- ‘He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry.’
- From the above sentence, we can say that the following statement is not correct according to the given passage: ‘Periodic proportionate farming requires dividing the land in four equal parts.’
- ‘Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt.’
Hence, the correct answer is Option 1.
74. Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions. Some words are highlighted to help you answer some of the questions.
With the Humane Agrarian Centre, a one-of-a-kind rural museum, Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability. Despite all the odds stacked against him, Prem Singh made out against these tribulations as a farmer who went debt-free without loans from the banks only by using taking the less travelled road. Singh’s lush green farmland paints a vivid picture of sustainable farming: organic produce and homegrown compost, fruit-bearing trees, livestock shelter with water- bodies, well-nourished soil, natural fertilisers and, most importantly, a continuous source of income.
Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt. Further, the increased use of fertilisers and chemicals proved to be harmful to the soil’s ecological balance.
That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.
Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming, which he says is the way forward for farmers in the country. Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence. Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling. Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.
He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.
Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk. He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market. Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.
Mr. Singh’s multi-pronged technique, pioneered and implemented by him for over a decade, is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers.
Which of the following is incorrect, according to the given passage?
A. Periodic proportionate farming is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj.
B. In Avartansheel Kheti, the outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from various kinds of weather ex. remities.
C. Mr Singh suggests that the farmers should only sell the remaining produce in the market after keeping food for themselves
D. Mr Singh sells the mangoes harvested from his farm directly through contract farming to the dealers in rural mandis.
E. Mr Singh opines that farmers should also process everything before selling
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Mr Singh sells the mangoes harvested from his farm directly to the rural mandis‘ i.e., this statement is incorrect, according to the given passage.
Key Points
- The given passage is a news feature story about a farmer who changed his farming methods to achieve success and fortune.
- Let’s take a look at the following sentences:
- ‘Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming… Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence.’
- From the above sentence, we can say that the following statement is correct according to the given passage: ‘Periodic proportionate farming is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj.’
- ‘…the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.’
- From the above sentence, we can say that the following statement is correct according to the given passage: ‘In Avartansheel Kheti, the outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from various kinds of weather extremities.’
- ‘Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.’
- From the above sentence, we can say that the following statement is correct according to the given passage: ‘Mr Singh suggests that the farmers should only sell the remaining produce in the market produce after keeping food for themselves.’
- ‘He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market.’
- From the above sentence, we can say that the following statement is not correct according to the given passage: ‘Mr Singh sells the mangoes harvested from his farm directly through contract farming to the dealers in rural mandis.’
- ‘Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling.’
- From the above sentence, we can say that the following statement is correct according to the given passage: ‘Mr Singh opines that farmers should also process everything before selling.‘
- ‘Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming… Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence.’
Hence, the correct answer is Option 1.
75. Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions. Some words are highlighted to help you answer some of the questions.
With the Humane Agrarian Centre, a one-of-a-kind rural museum, Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability. Despite all the odds stacked against him, Prem Singh made out against these tribulations as a farmer who went debt-free without loans from the banks only by using taking the less travelled road. Singh’s lush green farmland paints a vivid picture of sustainable farming: organic produce and homegrown compost, fruit-bearing trees, livestock shelter with water- bodies, well-nourished soil, natural fertilisers and, most importantly, a continuous source of income.
Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt. Further, the increased use of fertilisers and chemicals proved to be harmful to the soil’s ecological balance.
That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.
Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming, which he says is the way forward for farmers in the country. Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence. Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling. Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.
He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.
Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk. He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market. Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.
Mr. Singh’s multi-pronged technique, pioneered and implemented by him for over a decade, is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers.
Out of the given alternatives, choose the one which is most similar to the meaning of the given word.
Start
A. Surcease
B. Halt
C. Pause
D. Conclude
E. Begin
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Begin‘.
Key Points
- The word ‘Start’ can act as a noun or verb; in the passage, it functions as a verb. It means to begin.
- For example, When do you start your new job?
- The marked option ‘Begin’ means to proceed to perform something.
- For example, The film they want to watch begins at seven.
- We can see that the word ‘Begin‘ can express the meaning of the word ‘Start.’
Hence, the correct answer is Option 5.
Additional Information
- Surcease ⇒ stop, cease.
- Halt ⇒ bring or come to an abrupt stop, usually temporarily.
- Pause ⇒ interrupt action briefly and temporarily.
- Conclude ⇒ bring or come to an end.
76. Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions. Some words are highlighted to help you answer some of the questions.
With the Humane Agrarian Centre, a one-of-a-kind rural museum, Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability. Despite all the odds stacked against him, Prem Singh made out against these tribulations as a farmer who went debt-free without loans from the banks only by using taking the less travelled road. Singh’s lush green farmland paints a vivid picture of sustainable farming: organic produce and homegrown compost, fruit-bearing trees, livestock shelter with water- bodies, well-nourished soil, natural fertilisers and, most importantly, a continuous source of income.
Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt. Further, the increased use of fertilisers and chemicals proved to be harmful to the soil’s ecological balance.
That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.
Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming, which he says is the way forward for farmers in the country. Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence. Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling. Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.
He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.
Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk. He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market. Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.
Mr. Singh’s multi-pronged technique, pioneered and implemented by him for over a decade, is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers.
Out of the given alternatives, choose the one which is most opposite to the meaning of the given word.
Shield
A. Protect
B. Obfuscate
C. Defend
D. Screen
E. Imperil
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Imperil‘.
Key Points
- The word ‘Shield’ as a verb means to protect from danger, risk, or unpleasant experience.
- For example, She held her hand above her eyes to shield them from the sun.
- The marked option ‘Imperil’ is a verb that means to put something or someone at risk or in danger of being harmed or destroyed.
- For example, Withdrawing the medical team would imperil the effort to control the spread of Dengue in rural areas.
- So, we can say that ‘Imperil‘ can function as the opposite word of ‘Shield.’
Hence, the correct answer is Option 5.
Additional Information
- Protect ⇒ keep safe from harm or injury.
- Obfuscate ⇒ make obscure, unclear, or unintelligible.
- Defend ⇒ resist an attack made on someone or something and protect from harm or danger.
- Screen ⇒ conceal, protect, or shelter someone or something.
77. Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions. Some words are highlighted to help you answer some of the questions.
With the Humane Agrarian Centre, a one-of-a-kind rural museum, Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability. Despite all the odds stacked against him, Prem Singh made out against these tribulations as a farmer who went debt-free without loans from the banks only by using taking the less travelled road. Singh’s lush green farmland paints a vivid picture of sustainable farming: organic produce and homegrown compost, fruit-bearing trees, livestock shelter with water- bodies, well-nourished soil, natural fertilisers and, most importantly, a continuous source of income.
Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt. Further, the increased use of fertilisers and chemicals proved to be harmful to the soil’s ecological balance.
That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.
Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming, which he says is the way forward for farmers in the country. Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence. Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling. Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.
He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.
Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk. He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market. Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.
Mr. Singh’s multi-pronged technique, pioneered and implemented by him for over a decade, is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers.
What will fit in the blank taken from the passage:
“He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk.”
A. in with
B. make from
C. out of
D. out with
E. along with
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘out of‘.
Key Points
- By reading the sentence, we can see that the blank needs a preposition or adverb particle that can be used to show what something is made from.
- Among the options, the best choice is ‘out of.’
- Also, by reading the usage of similar prepositions/particles in the same sentence for other entities at the same position (pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla) and conforming to parallelism, we can find this out.
- Correct sentence: “He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour out of chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk.”
Hence, the correct answer is Option 3.
78. Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions. Some words are highlighted to help you answer some of the questions.
With the Humane Agrarian Centre, a one-of-a-kind rural museum, Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability. Despite all the odds stacked against him, Prem Singh made out against these tribulations as a farmer who went debt-free without loans from the banks only by using taking the less travelled road. Singh’s lush green farmland paints a vivid picture of sustainable farming: organic produce and homegrown compost, fruit-bearing trees, livestock shelter with water- bodies, well-nourished soil, natural fertilisers and, most importantly, a continuous source of income.
Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt. Further, the increased use of fertilisers and chemicals proved to be harmful to the soil’s ecological balance.
That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.
Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming, which he says is the way forward for farmers in the country. Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence. Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling. Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.
He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.
Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk. He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market. Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.
Mr. Singh’s multi-pronged technique, pioneered and implemented by him for over a decade, is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers.
According to the passage, which of the following is NOT a problem plaguing the agrarian scenario of Bundelkhand?
A. Below average rainfall and droughts
B. Farmer Suicide
C. Low water availability
D. Lack of goods transport facilities
E. None of these
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Lack of goods transport facilities.’
Key Points
- The given passage is a news feature story about a farmer who changed his farming methods to achieve success and fortune.
- Let us take a look at the reference sentences in the passage:
- ‘Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability.‘
- We can see that all of the given options except the marked one have been mentioned in the article as problems that Bundelkhand has been facing from an agrarian aspect.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 4.
79. Directions: Read the following passage and answer the following questions. Some words are highlighted to help you answer some of the questions.
With the Humane Agrarian Centre, a one-of-a-kind rural museum, Prem Singh’s farm stands as an exception in the hilly region of Bundelkhand, divided between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The land is otherwise synonymous with droughts, farmer suicides, unemployment as a result of crop failure, extreme weather conditions with below-average rainfall, and low water availability. Despite all the odds stacked against him, Prem Singh made out against these tribulations as a farmer who went debt-free without loans from the banks only by using taking the less travelled road. Singh’s lush green farmland paints a vivid picture of sustainable farming: organic produce and homegrown compost, fruit-bearing trees, livestock shelter with water- bodies, well-nourished soil, natural fertilisers and, most importantly, a continuous source of income.
Born into a family of farmers, Prem (54) grew up on the fields amidst the once lush green farms, fresh harvest and livestock. After studying MA Philosophy at Allahabad University and Management in Rural Development under Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, he joined his ancestors’ occupation and began farming in 1987. Despite toiling daily, Prem’s family continued to be in loss; bank loans and interest rates increased with each passing loan repayment date. Two years into the profession, he realised that something was wrong: conventional agriculture was proving to be very expensive and his family began slipping into debt. Further, the increased use of fertilisers and chemicals proved to be harmful to the soil’s ecological balance.
That is when he started to look for alternative ways of farming and his meeting with Nagraj helped. In 1989, he sought his father’s permission to start experimenting with sustainable and traditional farming in a small part of his land.
Prem Singh of Banda district in Uttar Pradesh now practices Avartansheel Kheti, also known as Periodic proportionate farming, which he says is the way forward for farmers in the country. Avartansheel Kheti is based on the philosophy of A Nagraj, who was a proponent of harmonious co-existence. Singh believes that nature value adds to everything, like trees add value to the soil nutrients by producing fruits. Similarly, farmers should also process everything before selling. Mr Singh, in accordance with the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti, insists that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This way, the farmer will never put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves.
He explains the method of his technique: the farmer would have to utilise his farm by dividing it into three parts: core one-third would be used for rearing fruits and crops, the outer one-third for growing timber and the remaining portion for animal husbandry. The outer circle of trees shields the inner crops from wind and reduces the intensity of the weather extremities.
Mr Singh now processes all the produce from his farm, He makes pickle out of turmeric; candy and powder out of amla (gooseberry), sattu or gram flour __________ chickpeas, and produces paneer from milk. He also gets about 15-20 tonnes of mango every year, which he sells in the open market. Middlemen, he thinks, are one of the biggest problems for farmers and he says that the only way to reach the consumer directly is by processing the produce at the farm level.
Mr. Singh’s multi-pronged technique, pioneered and implemented by him for over a decade, is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers.
Which of the following cannot be inferred from the passage?
A. It is possible to earn more through Periodic proportionate farming than following the traditional m. thod.
B. Making farmers produce food for themselves first before selling the produce in the market will reduce the possibility of their putting harmful pesticides and fertilisers.
C. Periodic proportionate farming can solve the problem of water availability in India completely.
D. Mr Singh’s approach towards farming is similar to that of the Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
E. None of these
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘Periodic proportionate farming can solve the problem of water availability in India completely‘ i.e., it cannot be inferred from the given passage.
Key Points
- The given passage is a news feature story about a farmer who changed his farming methods to achieve success and fortune.
- Let’s consider the following points:
- By reading the passage, we can see that Mr Prem Singh is a farmer who has taken a different path than the conventional methods of farming and has become successful, albeit more than the usual ones. So it is clear that It is possible to earn more through Periodic proportionate farming than following the traditional method.
- It is one of the corollaries of the philosophy of Avartansheel Kheti that farmers should produce food for themselves first and what remains after consumption should be sold in the market. This generally ensures that the farmer will not put harmful pesticides and fertilisers if they are growing for themselves. So it is clear that Making farmers produce food for themselves first before selling the produce in the market will reduce the possibility of their putting harmful pesticides and fertilisers.
- By reading the seventh paragraph, we can learn that the approach Mr Singh has taken, pioneered and implemented for the last decade is similar to the idea of farming Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been propagating in his addresses to farmers. So it is clear that Mr Singh’s approach towards farming is similar to that of Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- But by reading the passage, we never encounter any finding that Periodic proportionate farming or Avartansheel Kheti can solve the problem of water availability in India completely.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 3.
80. Directions: The following sentence has been split into five segments. Identify the segment that contains a grammatical error.
The law further provide (A)/ for the re-engagement (B)/ of men of all ranks, (C)/ under conditions varying (D)/ according to their ranks (E)/.
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘A‘ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the first part of the given sentence, the plural form of the verb ‘provide’ is incorrect.
- The subject ‘The law’ in the given sentence is a singular subject.
- We know that a singular subject always takes a singular verb.
- The singular form of the verb ‘provides‘ should be used with the singular subject ‘The law‘.
- Therefore, the singular form of the verb ‘provides’ should be used in place of the plural form of the verb ‘provide‘.
Hence, the correct answer is option 1.
Correct sentence: The law further provides for the re-engagement of men of all ranks, under conditions varying according to their rank.
Additional Information
Thus, if a subject is singular, its verb must also be singular; if the subject is plural, its verb must also be plural.
Subjects and verbs must agree with one another in number (singular or plural).
81. Direction: Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If a sentence is free from error, select ‘No Error’.
To maximize the scholarship (A)/ opportunities, we should focus (B)/ on our educations and keep (C)/ our priorities in the right place.(D)/ no error
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. NO ERROR
Solutions
The correct Answer is Option 3.
Key Points
- The error is in part c of the sentence, due to the wrong usage of uncountable noun and ABSTRACT NOUN.
- Education is an uncountable noun and an abstract noun and is not used in -s form.
- Uncountable nouns are always considered to be singular.
- The plural of education is education.
Correct sentence: “To maximize the scholarship opportunities, we should focus on our education and keep our priorities in the right place.”
Important Points
- An abstract noun is a noun that cannot be perceived using one of the five senses.
Additional Information
- Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity that is impossible to count.
- Uncountable nouns are always considered to be singular.
- Hence, require singular verbs.
82. Read the sentence below to find out if there is any error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error the answer is (5). (Ignore errors in punctuation if any).
Three men were arrested for alleged (A)/ impersonating civic body officials (B)/ and extorting money from shopkeepers (C) /in east Delhi’s Mansarovar Park, the police said on Sunday. (D)/. No Error. (E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The Correct answer is option A
Key Points
- Error is in part A of the sentence.
- The word ‘alleged’ is giving additional information regarding ‘impersonating civic body officials’
- Here we need to use the adverb of ‘Alleged‘ i.e ‘Allegedly’
Correct answer – Three men were arrested for allegedly impersonating civic body officials and extorting money from shopkeepers in east Delhi’s Mansarovar Park, the police said on Sunday.
83. Directions: In this question, a sentence has been divided into five parts (A), (B), (C), (D), and (E). Read the sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical error in it. The error if any, will be in one part of the sentence. If there is no error, the answer is ‘No error’. Ignore the error of punctuation if any.
A pair of supportive (A)/ shoes are important (B)/ if you are (C)/ experiencing lower back pain. (D)/ No error (E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘B’ i.e. this part of the sentence has an error.
Key Points
- In the second part of the given sentence, the plural form of the verb ‘are’ is incorrect.
- Some nouns are always plural and require plural verbs, these include shoes, glasses, trousers, scissors, remains, etc.
- However, if they are preceded by the phrase ”a pair of”, the verb is singular because the noun ‘pair’ becomes the subject.
- The plural verb ‘are’ in the given sentence agrees with a plural subject, but the subject of this sentence is singular ‘pair.‘
- Therefore, the singular verb ‘is’ should be used in place of the plural verb ‘are‘.
Hence, the correct answer is option 2.
Correct sentence: A pair of supportive shoes is important if you are experiencing lower back pain.
Additional Information
Thus, if a subject is singular, its verb must also be singular; if the subject is plural, its verb must also be plural.
Subjects and verbs must agree with one another in number (singular or plural).
84. Read the sentence below to find out if there is any error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error the answer is (5). (Ignore errors in punctuation if any).
The result was a material(A)/ which was tough(B)/ or tensile, possessing (C)the dexterity of fabric.(D)/ No error(E)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
Solutions
The correct answer is option 3.
Key Points
- The error is in Part C of the sentence, the error is in use of or.
- Coordinate adjectives should be separated by a comma or the word and.
- Adjectives are said to be coordinated if they modify the same noun in a sentence.
- Hence in the given sentence ‘or’ should be replaced with ‘and’
- Correct sentence – The result was a material which was tough and tensile, possessing the dexterity of fabric.
Additional Information
Adjective is the word which gives additional information regarding the noun.
85. Directions: In the following passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each five words are suggested one of which fits the blank appropriately. Find out the appropriate word in each case.
Good nutrition has the potential to __(A)__ the present and future generations. India’s greatest national __(B)__ is its people — especially women and children – but even after 75 years of independence, a __(C)__ of them do not get the required diet to meet their nutritional needs. A child’s nutritional status is directly linked to their mother. Poor nutrition among pregnant women affects the nutritional status of the child and has a greater chance to __(D)__ future generations. Undernourished children are at risk of underperforming in studies and have limited job prospects. This __(E)__ cycle restrains the development of the country, whose workforce, affected mentally and physically, has reduced work capacity. While there has been some progress in tackling malnutrition among children and women over the past decade, the improvement has been modest at best. This is despite declining rates of poverty, increased self-sufficiency in food production, and the implementation of a range of government programmes.
Which of the following words most appropriately fits the blank labelled (A)?
A. empower
B. enervate
C. exhaust
D. undermine
E. beholden
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘empower‘.
Key Points
- By reading the relevant sentence in the passage, we can see that the blank in question needs a verb that means to make stronger.
- Among the given options, we can see that the only word with the required denotation is ’empower.’ It means to enable people by giving them the means to achieve something.
- For example, This law empowers the president to declare an emergency for a wide range of reasons.
- Correct sentence: Good nutrition has the potential to empower the present and future generations.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 1.
Additional Information
enervate ⇒ make (someone) feel drained of energy or vitality.
exhaust ⇒ make someone feel very tired.
undermine ⇒ lessen the effectiveness, power, or ability of, especially gradually or insidiously.
beholden ⇒ indebted; obligated.
86. Directions: In the following passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each five words are suggested one of which fits the blank appropriately. Find out the appropriate word in each case.
Good nutrition has the potential to __(A)__ the present and future generations. India’s greatest national __(B)__ is its people — especially women and children – but even after 75 years of independence, a __(C)__ of them do not get the required diet to meet their nutritional needs. A child’s nutritional status is directly linked to their mother. Poor nutrition among pregnant women affects the nutritional status of the child and has a greater chance to __(D)__ future generations. Undernourished children are at risk of underperforming in studies and have limited job prospects. This __(E)__ cycle restrains the development of the country, whose workforce, affected mentally and physically, has reduced work capacity. While there has been some progress in tackling malnutrition among children and women over the past decade, the improvement has been modest at best. This is despite declining rates of poverty, increased self-sufficiency in food production, and the implementation of a range of government programmes.
Which of the following words most appropriately fits the blank labelled (B)?
A. burden
B. coterie
C. treasure
D. totem
E. rancour
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘treasure‘.
Key Points
- By reading the relevant sentence in the passage, we can see that the blank in question needs a noun that means something/someone of high value.
- Among the given options, we can see that the only word with the required denotation is ‘treasure.’ It refers to a very valuable object.
- For example, I don’t know what I’d have done without my girlfriend Rashi when I was ill – she is an absolute treasure.
- Correct sentence: India’s greatest national treasure is its people — especially women and children…
Hence, the correct answer is Option 3.
Additional Information
- burden ⇒ a kind of load; liability.
- coterie ⇒ a secret and exclusive group.
- totem ⇒ a spirit being, sacred object, or symbol that serves as an emblem of a group of people.
- rancour ⇒ bitterness; resentfulness.
87. Directions: In the following passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each five words are suggested one of which fits the blank appropriately. Find out the appropriate word in each case.
Good nutrition has the potential to __(A)__ the present and future generations. India’s greatest national __(B)__ is its people — especially women and children – but even after 75 years of independence, a __(C)__ of them do not get the required diet to meet their nutritional needs. A child’s nutritional status is directly linked to their mother. Poor nutrition among pregnant women affects the nutritional status of the child and has a greater chance to __(D)__ future generations. Undernourished children are at risk of underperforming in studies and have limited job prospects. This __(E)__ cycle restrains the development of the country, whose workforce, affected mentally and physically, has reduced work capacity. While there has been some progress in tackling malnutrition among children and women over the past decade, the improvement has been modest at best. This is despite declining rates of poverty, increased self-sufficiency in food production, and the implementation of a range of government programmes.
Which of the following words most appropriately fits the blank labelled (C)?
A. many
B. much
C. most
D. little
E. majority
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘majority‘.
Key Points
- By reading the relevant sentence in the passage, we can see that the blank in question needs a noun that means the greater number. It also needs to be compatible with countable nouns.
- Among the given options, we can see that the only word with the required denotation is ‘majority.’ It means more than half of a total number or amount.
- For example, The majority of our employees have university degrees.
- Correct sentence: …but even after 75 years of independence, a majority of them do not get the required diet to meet their nutritional needs.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 5.
Additional Information
- We don’t use quantifiers like much, most, many after an article (‘a’ preceding the blank).
- ‘A little’ is normally used before non-count nouns. That is why it cannot go to the blank here.
- For example, There is a little oil inside the bottle.
88. Directions: In the following passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each five words are suggested one of which fits the blank appropriately. Find out the appropriate word in each case.
Good nutrition has the potential to __(A)__ the present and future generations. India’s greatest national __(B)__ is its people — especially women and children – but even after 75 years of independence, a __(C)__ of them do not get the required diet to meet their nutritional needs. A child’s nutritional status is directly linked to their mother. Poor nutrition among pregnant women affects the nutritional status of the child and has a greater chance to __(D)__ future generations. Undernourished children are at risk of underperforming in studies and have limited job prospects. This __(E)__ cycle restrains the development of the country, whose workforce, affected mentally and physically, has reduced work capacity. While there has been some progress in tackling malnutrition among children and women over the past decade, the improvement has been modest at best. This is despite declining rates of poverty, increased self-sufficiency in food production, and the implementation of a range of government programmes.
Which of the following words most appropriately fits the blank labelled (D)?
A. empower
B. affect
C. improve
D. embolden
E. enable
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘affect‘.
Key Points
- By reading the relevant sentence in the passage, we can see that the blank in question needs a verb that means to produce an effect or change in something, in a way that is not good.
- Among the given options, we can see that the only word with the required denotation is ‘affect.’ It means to produce an effect upon, usually with a negative connotation.
- For example, The storm affected citizens within forty kilometres of the coast lines of Sunderbans.
- Correct sentence: Poor nutrition among pregnant women affects the nutritional status of the child and has a greater chance to affect future generations.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 2.
Additional Information
- empower ⇒ provide someone with the means to give them the means to achieve something.
- improve ⇒ make something better.
- embolden ⇒ give someone the courage or confidence to do something.
- enable ⇒ make it possible for.
89. Directions: In the following passage, there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. Against each five words are suggested one of which fits the blank appropriately. Find out the appropriate word in each case.
Good nutrition has the potential to __(A)__ the present and future generations. India’s greatest national __(B)__ is its people — especially women and children – but even after 75 years of independence, a __(C)__ of them do not get the required diet to meet their nutritional needs. A child’s nutritional status is directly linked to their mother. Poor nutrition among pregnant women affects the nutritional status of the child and has a greater chance to __(D)__ future generations. Undernourished children are at risk of underperforming in studies and have limited job prospects. This __(E)__ cycle restrains the development of the country, whose workforce, affected mentally and physically, has reduced work capacity. While there has been some progress in tackling malnutrition among children and women over the past decade, the improvement has been modest at best. This is despite declining rates of poverty, increased self-sufficiency in food production, and the implementation of a range of government programmes.
Which of the following words most appropriately fits the blank labelled (E)?
A. seasonal
B. lunar
C. natural
D. vicious
E. complete
Solutions
The correct answer is ‘vicious‘.
Key Points
- By reading the relevant sentence in the passage, we can see that the blank in question needs an adjective that can collocate with the word cycle and together can mean a sequence of reciprocal cause and effect in which two or more elements intensify and aggravate each other, leading inexorably to a worsening of the situation.
- Among the given options, we can see that the word that can perform that function is ‘vicious.’
- For example, The debtors were caught in a vicious circle: they could not be freed until they had paid their debt, and were not able to pay their debt as long as they were in prison.
- Correct sentence: This vicious cycle restrains the development of the country…
Hence, the correct answer is Option 4.
Additional Information
- seasonal ⇒ available in or fluctuating or restricted according to the season or time of year.
- lunar ⇒ of, determined by, or resembling the moon.
- natural ⇒ born in or with one, innate; existing in or derived from nature.
- complete ⇒ whole.
90. Which of the phrases given in the options should replace the word phrase that is underlined in the sentence to make it grammatically correct? If the sentence is correct as it is and no correction is required, select ‘No correction required’ as the answer.
The car I brought is ten times cheaper than his luxury car.
A. cheaper then
B. as cheap as
C. cheap than
D. as cheap than
E. No correction required
Solutions
The correct answer is, ‘as cheap as‘
Key Points
- Because comparison is being made between the prices of two different cars, a comparative degree of the adjective ‘cheap’ should be used, so we can eliminate options 3 and 4.
- As a rule, no comparison is implied in the sentences when there is ‘time‘ used for comparison, like ‘ten times‘ is used here, so ‘cheaper than‘ makes the sentence incorrect.
- Therefore, the use of positive degree ‘as cheap as’ is correct.
Hence, the correct option is option 2.
The correct sentence is: The car I brought is 10 times as cheap as his luxury car.
Additional Information
- We use comparative degree when the sentence is without ‘times’.
- example: The car I brought is a lakh rupees cheaper than his car.
91. Which of the phrases given in the options should replace the word phrase that is underlined in the sentence to make it grammatically correct? If the sentence is correct as it is and no correction is required, select ‘No correction required’ as the answer.
As a law-abiding citizen, it was difficult to put on with the anti-government group of neighbours with questionable activities.
A. put off with
B. put out with
C. put up with
D. put down with
E. No correction required
Solutions
The correct answer is, ‘put up with’
Key Points
- The verbs used with prepositions, adverbs or both are defined as phrasal verbs that denote idiomatic meaning only when taken as a whole.
- Let’s look at the meaning of phrasal verbs given in the options:
- put off: postpone, avoid, discourage
- example: The event was put off because the celebrity guest did not come.
- put out: extinguish
- example: The locals helped to put out the fire before the fire department arrived.
- put up with: tolerate patiently
- example: He was willing to put up with her shenanigans.
- put down: crush, keep down
- example: The protests were put down by the local police.
- put off: postpone, avoid, discourage
- In the given sentence, the subject ‘law-abiding citizen’, is having difficulty tolerating the anti-government neighbours, therefore the correct phrasal verb used here will be ‘put up with’.
Hence, the correct option is option 3.
The correct sentence is: As a law-abiding citizen, it was difficult to put up with the anti-government group of neighbours with questionable activities.
Additional Information
- Types of phrasal verbs:
- Intransitive, inseparable and without an object.
- example: Come back.
- Transitive, separable and with an object.
- example: give it back.
- Transitive, inseparable and with an object.
- example: Pick up the pen.
- Transitive with two inseparable particles
- example: look it up.
- Intransitive, inseparable and without an object.
92. Which of the phrases given in the options should replace the word/phrase that is underlined in the sentence to make it grammatically correct? if the sentence is correct as it is given and no correction is required, select ‘No correction required’ as the answer.
The committee was split on whether the new regulations for the National Health Protection Scheme should be implemented.
A. were split on whether
B. is split on whether
C. has been split on whether
D. was split over whether
E. No correction required
Solutions
The correct answer is were split on whether
Key Points
- If the committee members are unanimous regarding a decision, in that case, the committee is considered as a singular collective noun and a singular verb is used in the context. On the other hand, if a committee has members differing in their views regarding something, the plural form of the verb is used in that case.
- In the given context, the committee members are differing in their opinions and therefore a plural form of the verb should be used. As the tense is correct in the sentence, the correct verb should have been ‘were’.
- This makes option 1 the correct choice among the given options.
The correct sentence is: The committee were split on whether the new regulations for the National Health Protection Scheme should be implemented.
93. A sentence/ a part of sentence underlined.5 alternatives are given to embolden parts that will improve the meaning of the sentence. Choose the correct alternative. In case, no improvement is needed, click the option corresponding to ‘no improvement’
Moral ethics are to be taught to students at an early age by their parents, teachers, and society for their overall development.
A. is to be
B. are be
C. were to be
D. was to be
E. No Improvement
Solutions
The correct answer is Option 1.
Key Points
- In the given sentence use of are to be is incorrect.
- Some nouns appear to be multiple because they end in a “s,” yet they are actually singulars.
- Examples are Summons, News, Politics, Physics, Economics, Ethics, etc.
- Hence in the given sentence are to be should be replaced with is to be
Correct sentence – Moral ethics is to be taught to the students at an early age by their parents, teachers, and society for their overall development.
Additional Information
- A noun is a word that refers to a thing (book), a person (Betty Crocker), an animal (cat), a place (Omaha), a quality (softness), an idea (justice), or an action (yodeling). It’s usually a single word, but not always: cake, shoes, school bus, and time and a half are all nouns.
- When you have a collection of things in a particular noun, you use a term to address that group. This term is called a collective noun. In this category, we are dealing with those collective nouns which look singular but are actually used as a plural
- Example: The gentry are well educated.
- There are some words that look plural as they end with a “s” but are actually used as singulars
- Example: Gymnastics is his favorite sport.
94. In the following sentence, a part of the sentence is underlined. Below are given alternatives to the underlined part, which may improve the sentence. Choose the correct alternative. In case no improvement is needed, choose the alternative that indicates ‘No improvement’.Due to its complex tribal equations and rugged mountainous terrain, Rajasthan has historically be an difficult place for external invaders.
A. historic has a difficult place
B. historically been a difficult place
C. historically being a difficult place
D. historically been a difficult places
E. No improvement
Solutions
The correct answer is Option 2 i.e. historically been a difficult place
Key Points
- We need the adverb form of ‘history’. Thus, ‘historically’ is correct while ‘historic’ is incorrect. This eliminates option A.
- Being is incorrect as it is used to refer to an individual/person. Been is correct here. This eliminates option C.
- Due to article ‘a’, the correct form is singular ‘place’
- Hence, option B is correct.
Correct sentence: Due to its complex tribal equations and rugged mountainous terrain, Rajasthan has historically been a difficult place for external invaders.
Additional Information
Been and Being
- Been: The word “been” is the past participle of the verb “to be.” As such, it can be used with “have” (in all its guises) to form tenses in the perfect (or complete) aspect.
- Ex: The dog has been naughty.
- Being: The word “being” is the present participle of the verb “to be.” As such, it can be used with “be” (in all its guises) to form tenses in the progressive (or continuous) aspect.
- Ex: The dog is being naughty.
95. Given below is a sentence that may or may not be grammatically viable, choose the most suitable alternative that reflects the grammatically correct sentence.
He would often say the exact opposite of what he had said on a previous occasion, so both points would be right after the debate had ended.
A. and both points
B. so both points
C. yet both points
D. nor both points
E. or both points
Solutions
The correct answer is Option 3)i.e. yet both points.
Key Points
- Here we are speaking about a contrasting view presented by the subject ‘he‘ and the action being ‘says the exact opposite of what he had said’, a sort of contrast is being expressed in the full sentence.
- Let us explore the given option.
- The conjunction ‘and’ is used toconnect words of the same part of speech, clauses or sentences that are to be taken jointly.
- Example: James and Sam went to town.
- Both individuals have gone to town and are joined by ‘and‘.
- Here we are talking about two contrasting ideas. So option 1 is incorrect.
- The conjunction ‘so’ means and for this reason; therefore.
- Example: He slept late so that he could finish the movie.
- Here the explanation or reason for sleeping late has been explained by using ‘so.’
- There is no justification regarding an action being given in the further parts of the given sentence.
- So option 2 is incorrect.
- The conjunction ‘yet’ means but at the same time, but nevertheless.
- Example: He was smart yet he panicked and lost the fight.
- ‘yet‘ expresses the fact that even though he was ‘smart‘ he still lost the fight as he ‘panicked.’
- Here in the latter parts, we are trying to show contrast that even though the ruling was different yet both sides still agree with each other
- So option 3 is correct.
- The conjunction ‘nor’ is used before the second or further of two or more alternatives to indicate that they are each untrue or each does not happen.
- So option 4 is incorrect.
- The conjunction ‘or’ is used tolink alternatives.
- Example: Orange or mango pick one.
- We have to choose between an orange or mango.
- In the given sentence we do not have to choose between two options, So option 5 is incorrect.
Correct sentence: He would often say the exact opposite of what he had said on a previous occasion, yet both points would be right after the debate had ended.
96. In the following question, a sentence is given with three words marked as (A), (B) and (C). These words may or may not be placed in their correct order. Four options with different arrangements of these words have been provided. Mark the option with the correct arrangement as the answer. If no rearrangement is required, mark option (5) as your answer.
In the rainfall (A) when water droplets (B) fuse together and become heavy, they come down as clouds. (C)
A. ABC
B. CBA
C. BCA
D. CAB
E. No Rearrangement
Solutions
The correct answer is option 2 i.e. CBA
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
In the _______ (A) when water _______ (B) fuse together and become heavy, they come down as _______ (C).
Rainfall: Refers to a shower of water from clouds to the earth. Rainfall is the final outcome of the process, the droplets have to fuse before they become rainfall.
Droplets: Small drops of a liquid.
Clouds: Visible masses of condensed water vapour floating in the atmosphere, typically high above the general level of the ground. Clouds cannot fall to the ground, only the rain can.
Hence, C and A need to be interchanged.
Correct sentence: In the clouds (C) when water droplets (B) fuse together and become heavy, they come down as rainfall. (A)
97. In the following question, a sentence is given with three words marked as (A), (B) and (C). These words may or may not be placed in their correct order. Four options with different arrangements of these words have been provided. Mark the option with the correct arrangement as the answer. If no rearrangement is required, mark option (5) as your answer.
The lungs (A) of the RBC transports haemoglobin (B) from the oxygen (C) to all the cells of the body.
A. BCA
B. ABC
C. CAB
D. BAC
E. No Rearrangement
Solutions
The correct answer is option 1 i.e. BCA
Explanation:
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
The _______ (A) of the RBC transports _______ (B) from the _______ (C) to all the cells of the body.
Lungs: A pair of air-filled organs located on either side of the chest. The RBC is a type of cell and cannot have its own set of lungs.
Haemoglobin: A protein that is found in red blood cells (RBC) that carry oxygen in a human body. Haemoglobin does not transport anything, it is a carrier of oxygen.
Oxygen: A colourless, odourless gas that is a chemical element that supports life. Haemoglobin is not transported from oxygen, oxygen is transported through haemoglobin.
Hence A and B have to be interchanged, then C and A have to be interchanged to make the sentence contextually correct.
Correct sentence: The haemoglobin (B) of the RBC transports oxygen (C) from the lungs (A) to the cells of the body.
98. In the following question, a sentence is given with three words marked as (A), (B) and (C). These words may or may not be placed in their correct order. Four options with different arrangements of these words have been provided. Mark the option with the correct arrangement as the answer. If no rearrangement is required, mark option (5) as your answer.
The use of atmosphere (A) is responsible for causing an increase in fossil fuels (B) concentration in the carbon dioxide(C).
A. BAC
B. ABC
C. CAB
D. BCA
E. No Rearrangement
Solutions
The correct answer is option 4 i.e. BCA.
We can look at the sentence like this:
The use of _______ (A) is responsible for causing an increase in _______ (B) concentration in _______(C).
Atmosphere: It is a layer or a set of layers of gases that surround the planet and other bodies. It is not an entity that can be used.
Fossil fuels: Fuels formed on Earth through natural processes. No kind of changes in the atmospheres can cause an increase in fossil fuels, they occur naturally, man-made processes can only increase their depletion.
Carbon dioxide: A chemical compound that is composed of carbon and oxygen. It doesn’t fit here contextually or grammatically.
Hence, A should be replaced by B, B should be replaced by C and A should replace C, in order to make a contextually correct sentence.
Correct sentence: The use of fossil fuels (A) is responsible for causing an increase in carbon dioxide (B) concentration in the atmosphere (C).
99. In the following question, a sentence is given with three words marked as (A), (B) and (C). These words may or may not be placed in their correct order. Four options with different arrangements of these words have been provided. Mark the option with the correct arrangement as the answer. If no rearrangement is required, mark option (5) as your answer.
Virus (A) countries have faced a large developing (B) due to the recent onset of the Corona setback (C) worldwide.
A. ABC
B. CAB
C. CBA
D. BCA
E. No Rearrangement
Solutions
The correct answer is option 4 i.e. BCA.
We can look at the sentence in the following way:
_______ (A) countries have faced a large _______ (B) due to the recent onset of the Corona _______ (C) worldwide.
Virus: Refers to a microscopic agent that settles in a living being and infects. It can affect a country, but no country can be referred to as “virus country”.
Developing: Refers to something that is growing or becoming more stable. Developing is an adjective that needs to be followed by a noun.
Setback: A reversal in progress. ‘Corona’ is a name for something and so the following blank should tell us what ‘Corona’ is.
Hence, A should be replaced by B, B should be replaced by C, and A should take C’s place.
Correct sentence: Developing (A) countries have faced a large setback (B) due to the onset of the Corona virus (C) worldwide.
100. In the following question, a sentence is given with three words marked as (A), (B) and (C). These words may or may not be placed in their correct order. Four options with different arrangements of these words have been provided. Mark the option with the correct arrangement as the answer. If no rearrangement is required, mark option (5) as your answer.
The puppy was finally found faint (A) in the nearby park, it was dehydrated (B) and about to roaming. (C)
A. CBA
B. CAB
C. ABC
D. BAC
E. No Rearrangement
Solutions
The correct answer is option 1 i.e. A-C ie. CBA
We can look at the sentence the following way:
The puppy was finally found _______ (A) in the nearby park, it was _______ (B) and about to _______ (C).
Faint: Lose consciousness for a short time because of a temporarily insufficient supply of oxygen to the brain. This part of the sentence is in the past continuous tense(was/were + -ing form of verb) and so the blank cannot have ‘faint’ as it is in the present tense.
Dehydrated: Refers to someone who has lost a large amount of water from their body
Roaming: Going from place to place without any purpose. This is in the continuous tense and the blank requires a verb in the base form because ‘to’ is used in front of it(‘to + base form of verb’ is the to-infinitive).
Hence, A and C need to be interchanged to make the sentence contextually correct.
Correct sentence: The puppy was finally found roaming (A) in the nearby park, it was dehydrated (B) and about to faint (C).
